CFB 16: Fatty Acids (Biochemistry)
1/115
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
116 Terms
Are lipids hydrophobic or hydrophilic?
Hydrophobic
Lipids associate with ____ _____, excluding water.
Each other
What are the roles of fats?
Provide energy
TAG fat stores energy
Membrane lipids
Protein modification
Signaling lipids
2 major classes of lipids
1. Isoprenoids
2. Fatty acids
Isoprenoids are synthesized out of _________ units.
Isoprene
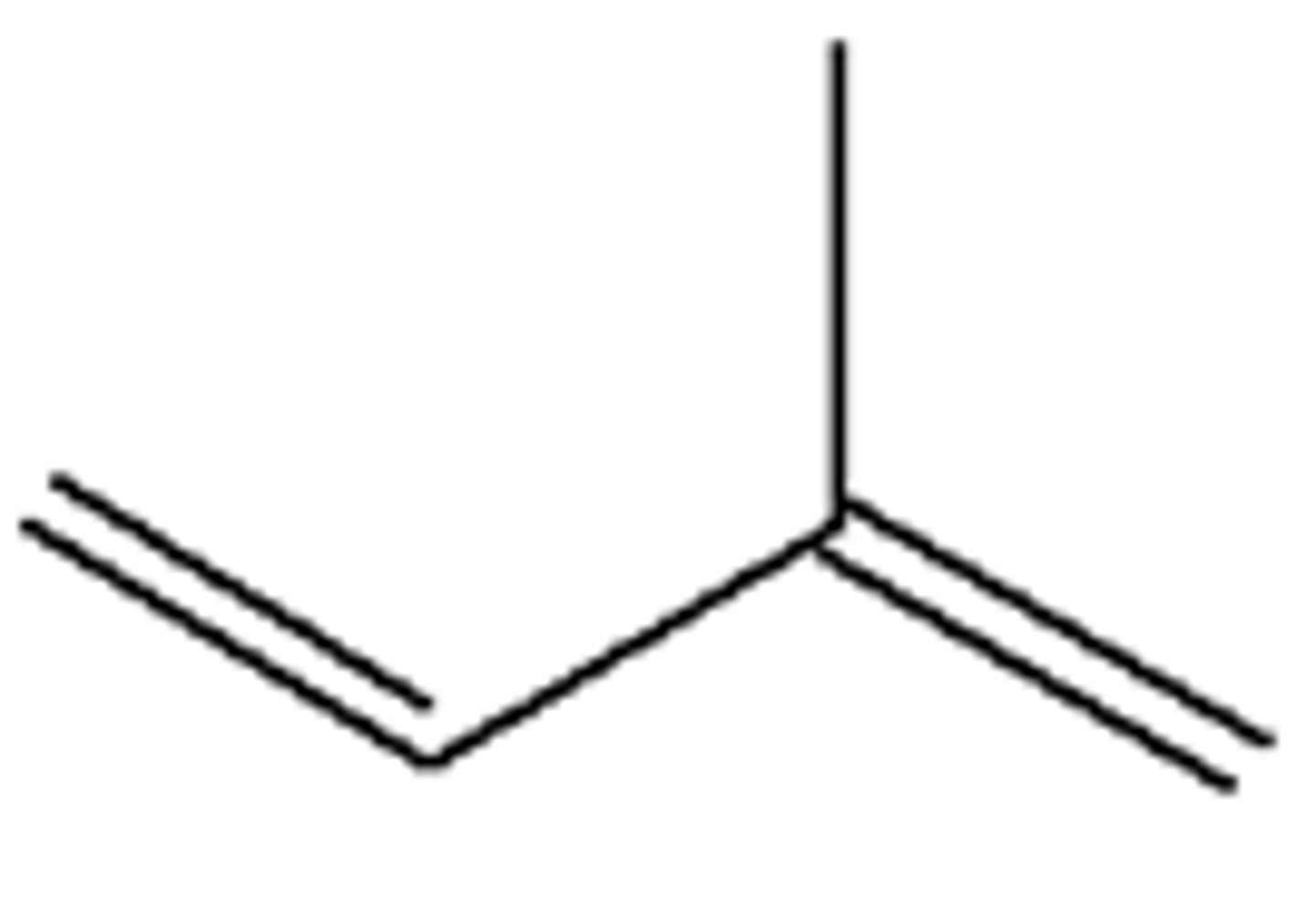
What is the typical example of an isoprenoid?
Cholesterol
Examples of isoprenoids
Bile acids/salts
Membranes
Hormones
Cofactors
Fat soluble vitamins
Isoprenoid names
Testosterone
Estradiol
Cortisol
Aldosterone
Prednisolone
Prednisone
Are fatty acids charged?
Yes
T/F: Fatty acids are amphipathic.
True
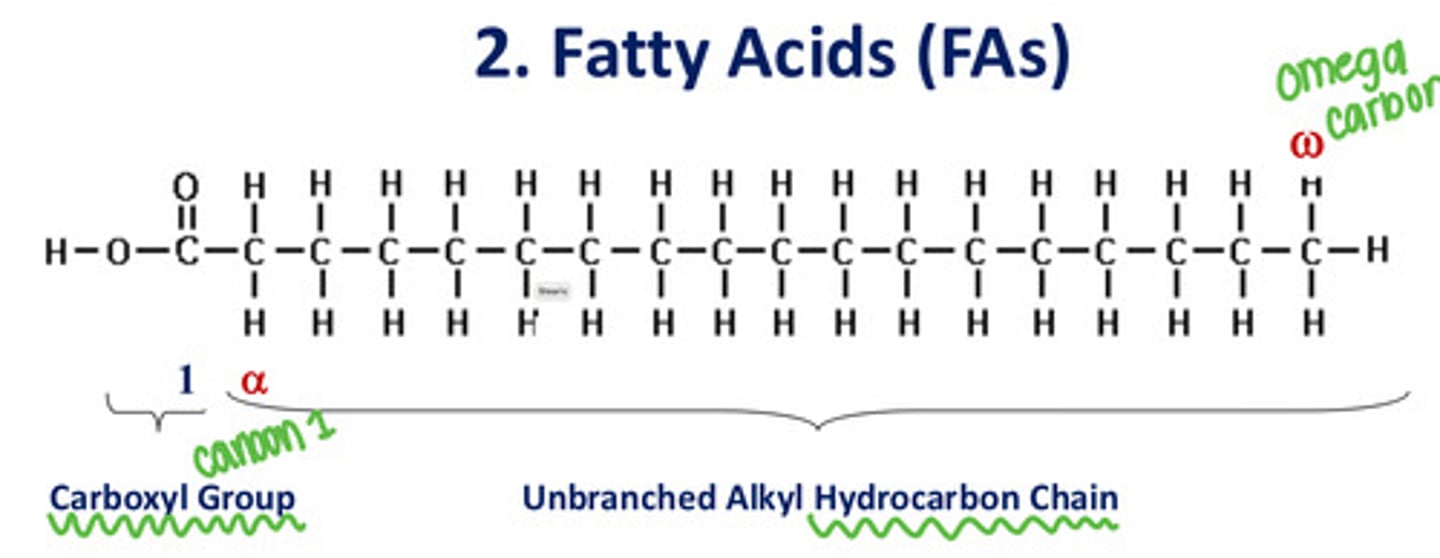
What makes up fatty acids?
Carboxyl group + unbranched alkyl hydrocarbon chain
Where is the alpha carbon?
The carbon that is adjacent to the carbon of the carbonyl group
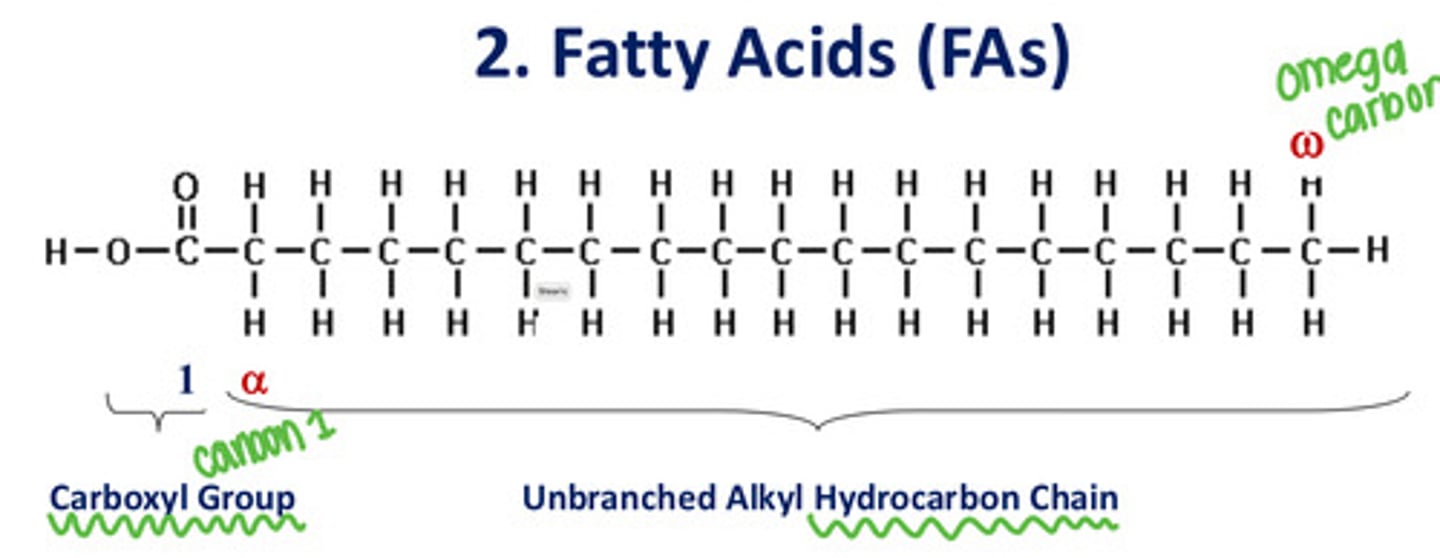
Where is the omega carbon?
At the very end of the carbon chain, furthest from the carboxyl group
What are fatty acids used for?
Energy storage (and fat deposits cushion organs and insulate against heat loss)
Membranes (and electrical insulation of nerves) including phospholipids and sphingolipids
Signals
How long are long chain fatty acids?
>12 carbons
How long are medium chain fatty acids?
6-12 carbons
How long are short chain fatty acids?
<6 carbons
Where are long chain fatty acids absorbed?
Small intestine
Where are medium chain fatty acids produced?
Mammary gland
Medium chain fatty acids are used in treatment of...
Waldmann disease
Epilepsy
Chronic pancreatitis
Where are short chain fatty acids produced?
Colon by microbiome
Which fatty acids can cross the blood brain barrier?
Short chain
Which fatty acids account for 6-10% of total energy, 80% in coloncytes?
Short chain
What is the symbol of stearic acid?
18:0
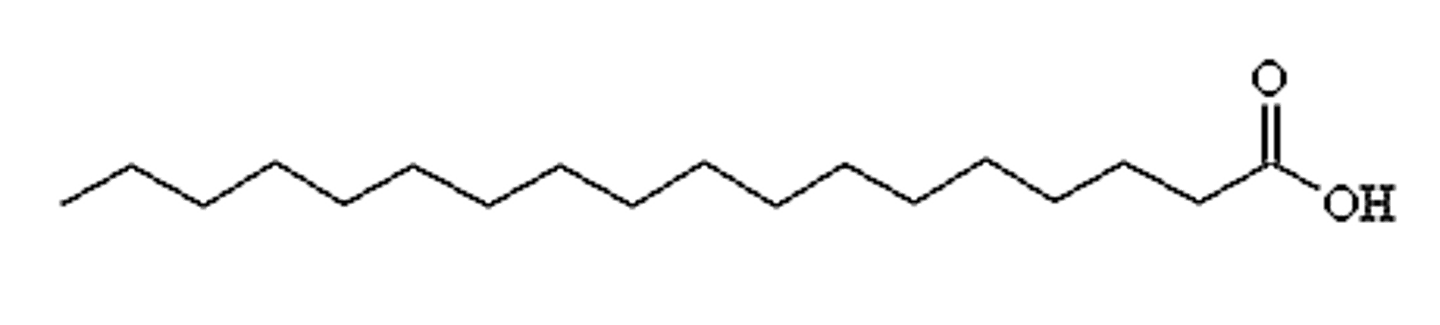
What is the systematic name of stearic acid?
Octadecanoic acid
How do you name a fatty acid?
Numbering: carboxyl carbon = 1
- Omega carbon at the end C and alpha at C2
How do you make the FA symbol?
# before colon = total length of chain
# after colon = # double bonds
Superscript = list of double bond positions
What is the symbol of palmitic acid?
16:0
At neutral pH, FAs are _______ and act as ______.
Charged; soaps
Is stearic acid saturated or unsaturated?
Saturated, 18:0
Oleic acid nomenclature
18:1Δ^9
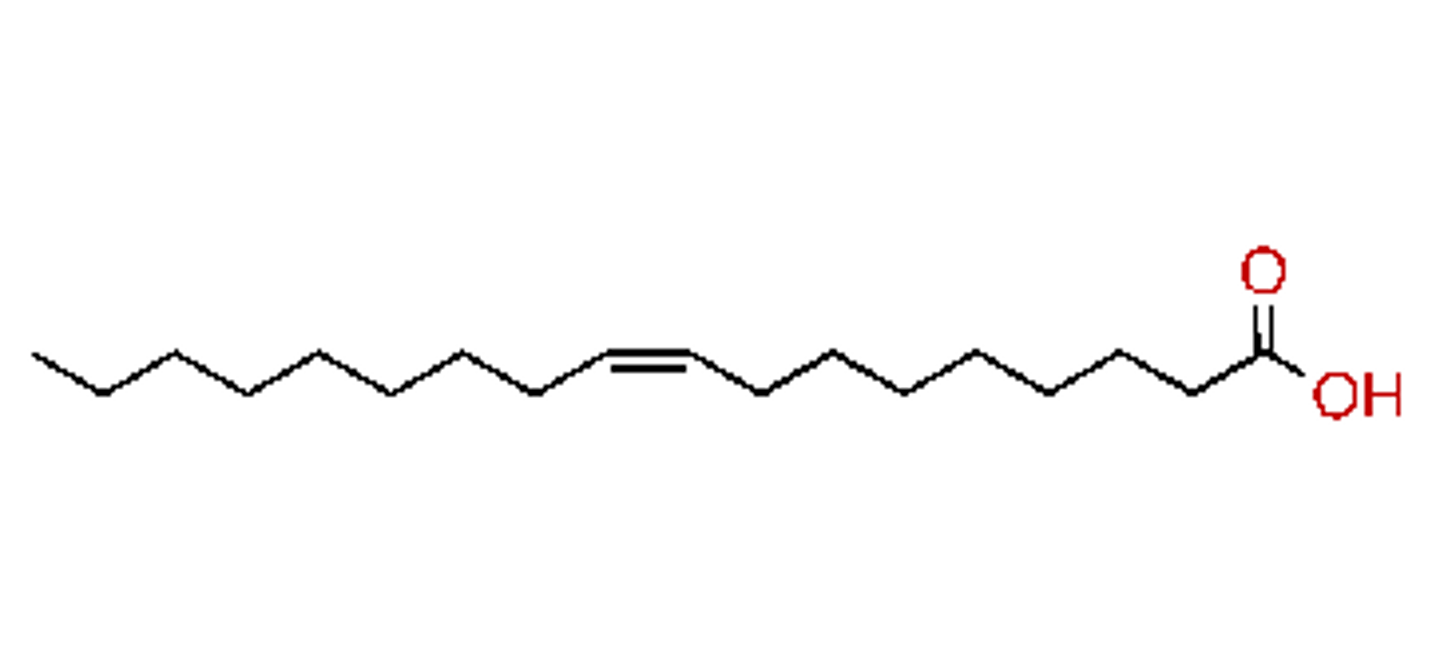
Is oleic acid saturated or unsaturated?
Monounsaturated
α Linolenic acid FA symbol
18:3Δ^9,12,15
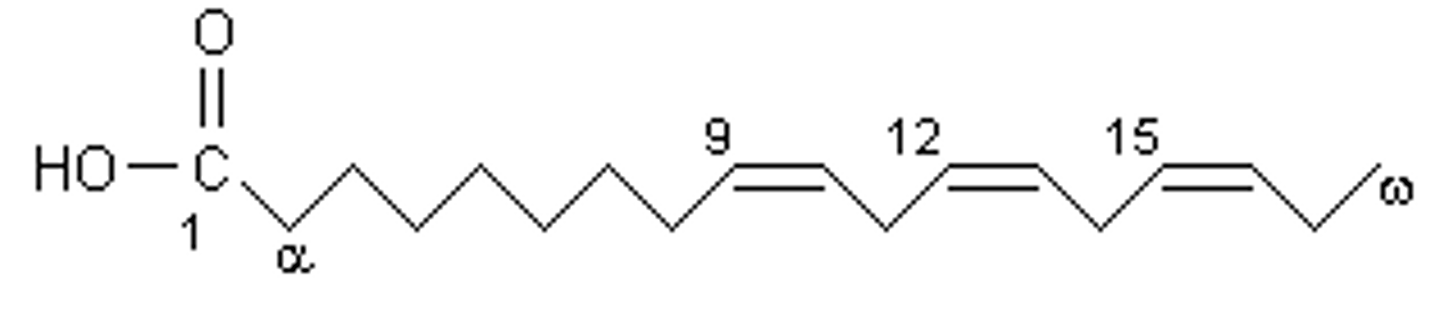
How do you calculate the omega numner?
Number of carbons from the terminal methyl (ω) carbon to the nearest double bond
ω# = (# of carbons) - (carbon # starting last double bond)
How to calculate omega number of α Linolenic acid
18:3Δ^9,12,15
18 - 15 = ω3
How to calculate omega number of Linoleic acid
18:2Δ^9,12
18 - 12 = ω6
Linoleic and linolenic are _________ fatty acids.
Essential
Symptoms of linoleic and linolenic fatty acid deficiency
Scaly dermatitis, alopecia, thrombocytopenia (low platelet count), cognitive development
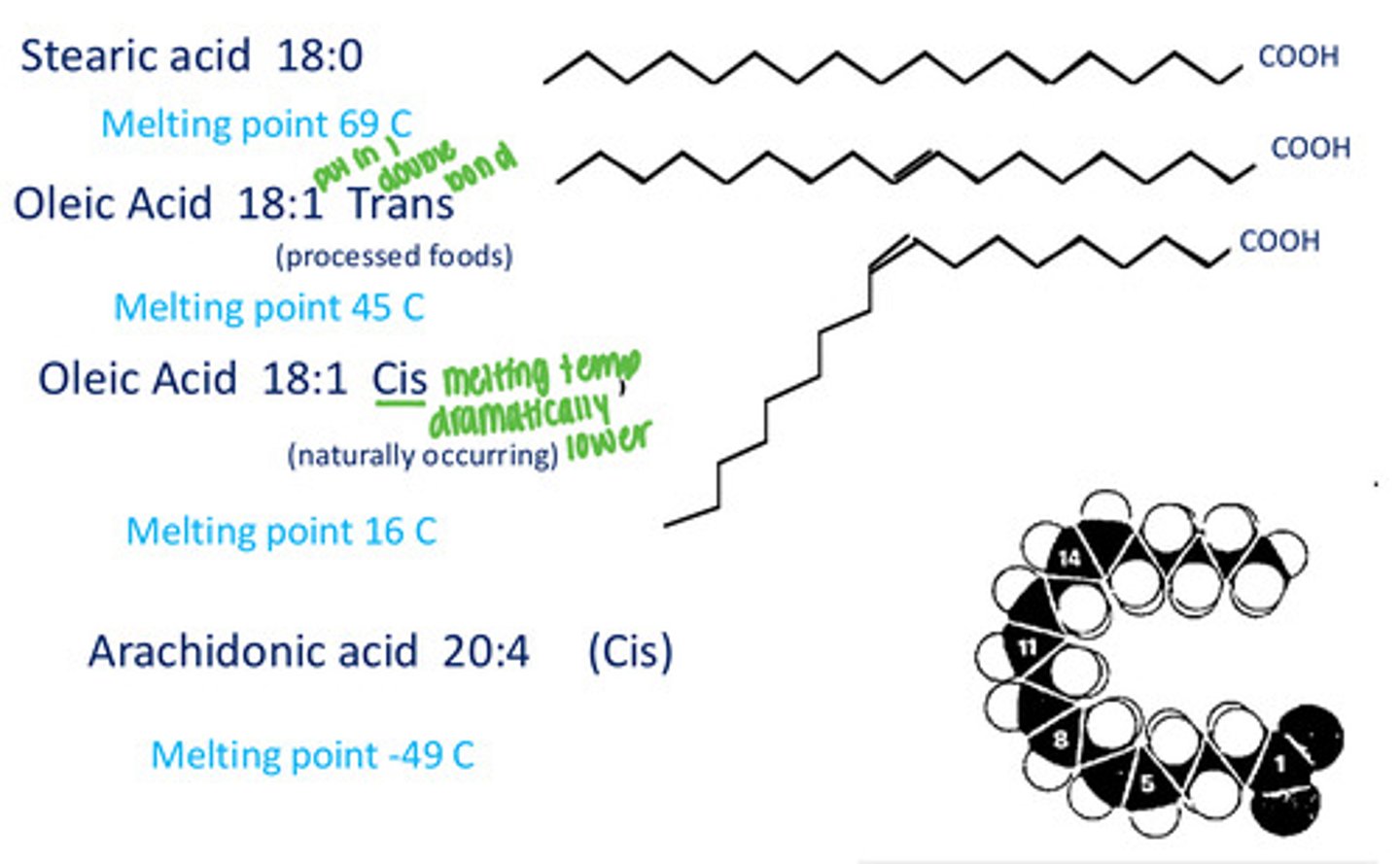
What determines physical properties of FA-containing compounds?
Fatty acid melting point
Melting points of uncharged FAs (R-COOH) increase with what?
Chain length
Why do long chain FAs have higher melting points?
More Van der Waals contacts
Effect of double bonds on FA melting point
Double bonds decrease melting point
Is melting point lower or higher in cis fatty acids?
Cis: lower melting point than trans
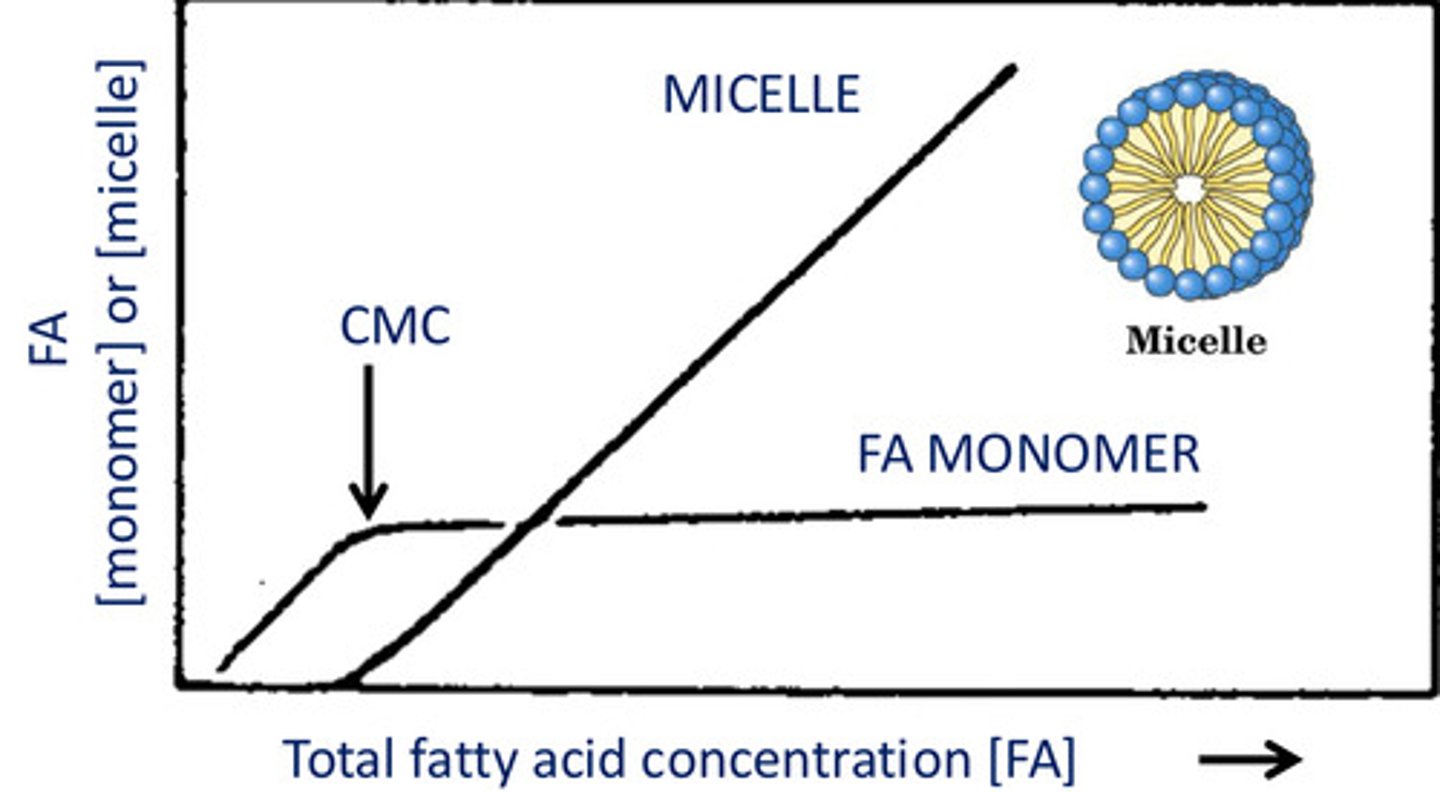
When do lipid micelles form?
At critical micelle concentration (CMC)
From the CMC and on, everything added ends up in a _______.
Micelle
Fatty acids esterified to glycerol
Triglycerides
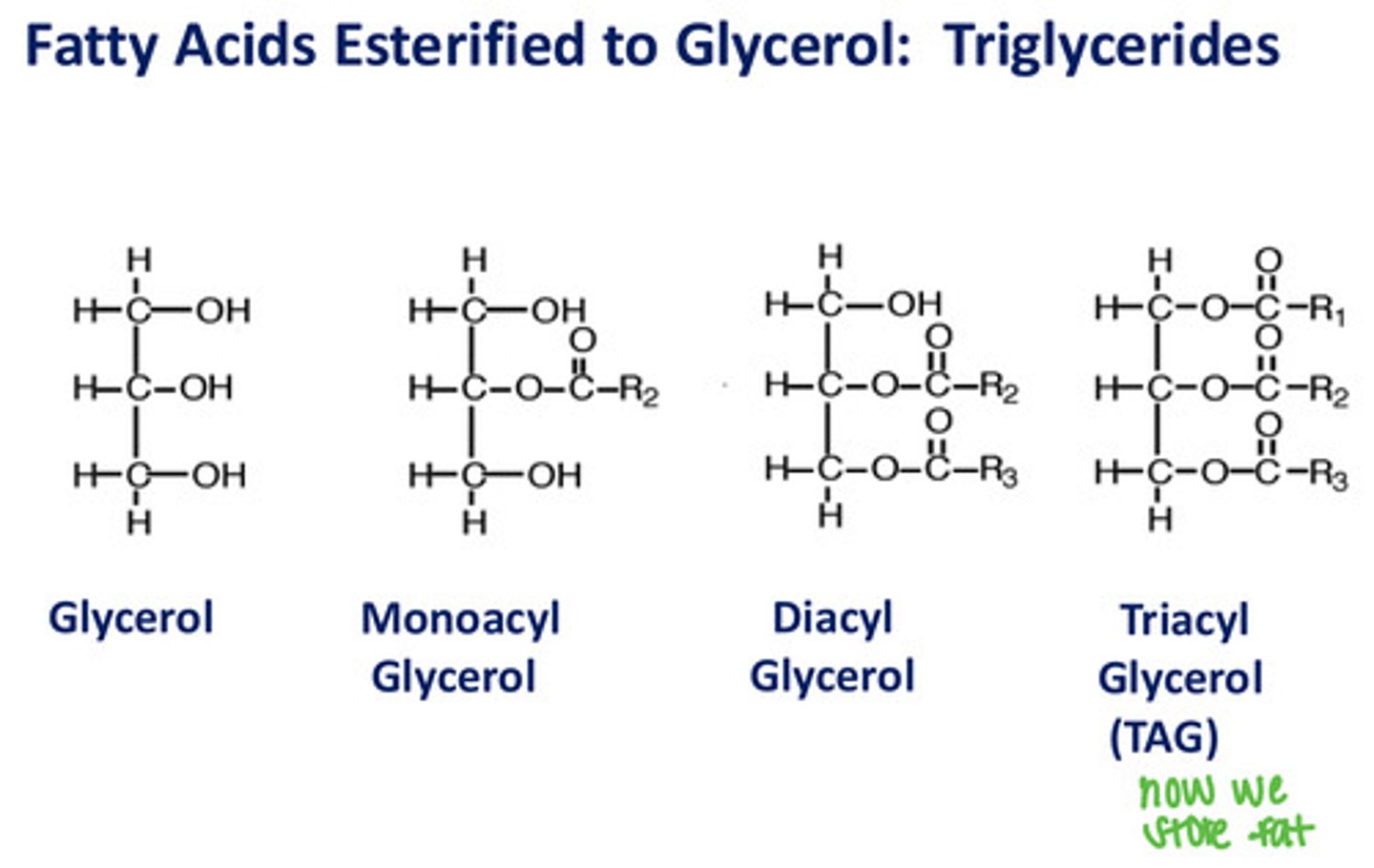
What fatty acids are often esterified?
Glycerol and sphingosine
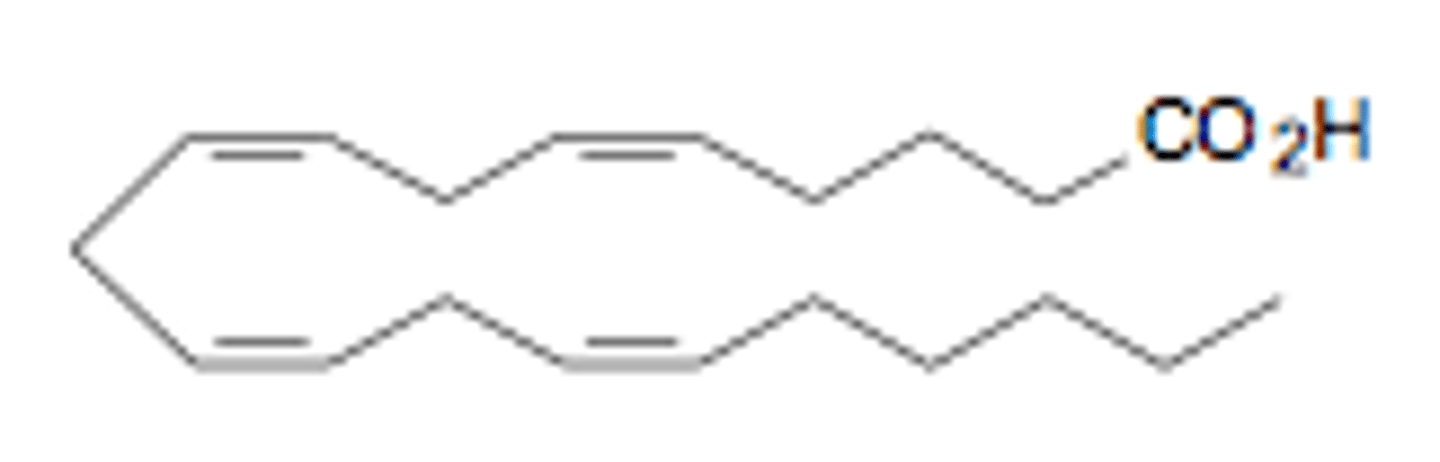
Name the structure of arachidonic acid.
20:4Δ^5,8,11,14
ω6
What percent of US caloric intake is fat (vs. what is recommended)?
35-40%
20-35%
What is the major source of US caloric fat intake?
Triglycerides
What chews up medium chain FAs in the mouth?
Lingual lipase
What does CCK do?
Makes pancreas release pancreatic lipase
What is key to hydrolysis of TAGs?
Pancreatic lipase
Pancreatic lipase has an important protein cofactor called ________.
Colipase
Why is full hydrolysis of pancreatic lipase not necessary?
The two hydroxyl groups on 2-MAG make it sufficiently soluble in water
Does pancreatic lipase recognize olestra?
No!
T/F: Pancreatic lipase can easily access fat droplets.
False
What is required for pancreatic lipase to access fat droplets?
Emulsification by amphipathic lipid
What does gallbladder release?
Bile salts (cholesterol derivatives) and phospholipids
What does pancreatic lipase produce?
Free FA salts (soaps)
2-MAG
Bile acids made from cholesterol in the liver are converted to...?
Bile salts
80-95% of bile salts are recycled via...?
Enterohepatic circulation
What does cholestyramine do?
Prevents recycling
Causes loss of bile salts to feces
What happens when bile salts are not released through bile duct from gallbladder?
Biliary obstruction
What can lead to gallstones?
Imbalance of cholesterol, bile salt, and phospholipid secretion
What causes these symptoms?
Steatorrhea in chronic cases
Deep recurrent moderate to severe abdominal, back, or epigastric pain exacerbated by alcohol
Nausea and vomiting
Elevated serum lipase and serum amylase
Pancreatitis
Lipid digestion disorders lead to...?
Malabsorption/steatorrhea
What happens if bile salts are not released through bile duct from gallbladder?
Biliary obstruction
What happens if there is no release of pancreatic lipase?
Pancreatic disease
Which statement about bile acids and salts is correct?
Using a drug to prevent the reabsorption of bile acids and salts from the intestine causes the liver to increase metabolism of cholesterol
Using a drug to prevent the reabsorption of bile acids and salts from the intestine causes the liver to do what?
Increase metabolism of cholesterol
Micelles diffusing to surface release _______ and ____ that are taken up.
LCFAs and MAG
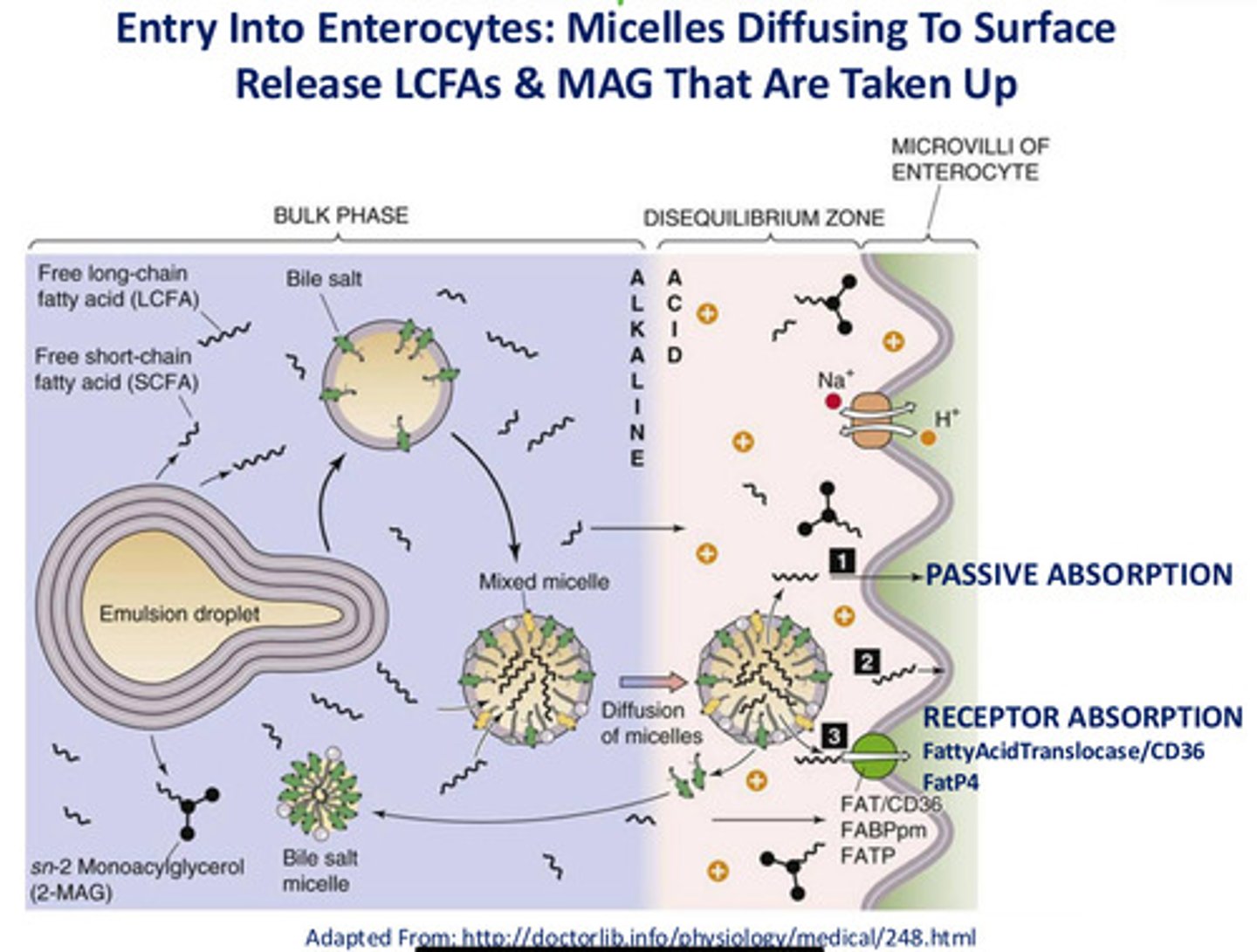
Cholesterol transport is ________ mediated.
REceptor
What does ezetimibe do?
Inhibits cholesterol absorption by inhibiting NPC1L1
What is NPC1L1?
Cholesterol receptor
T/F: Fatty acids diffuse into the circulation.
False
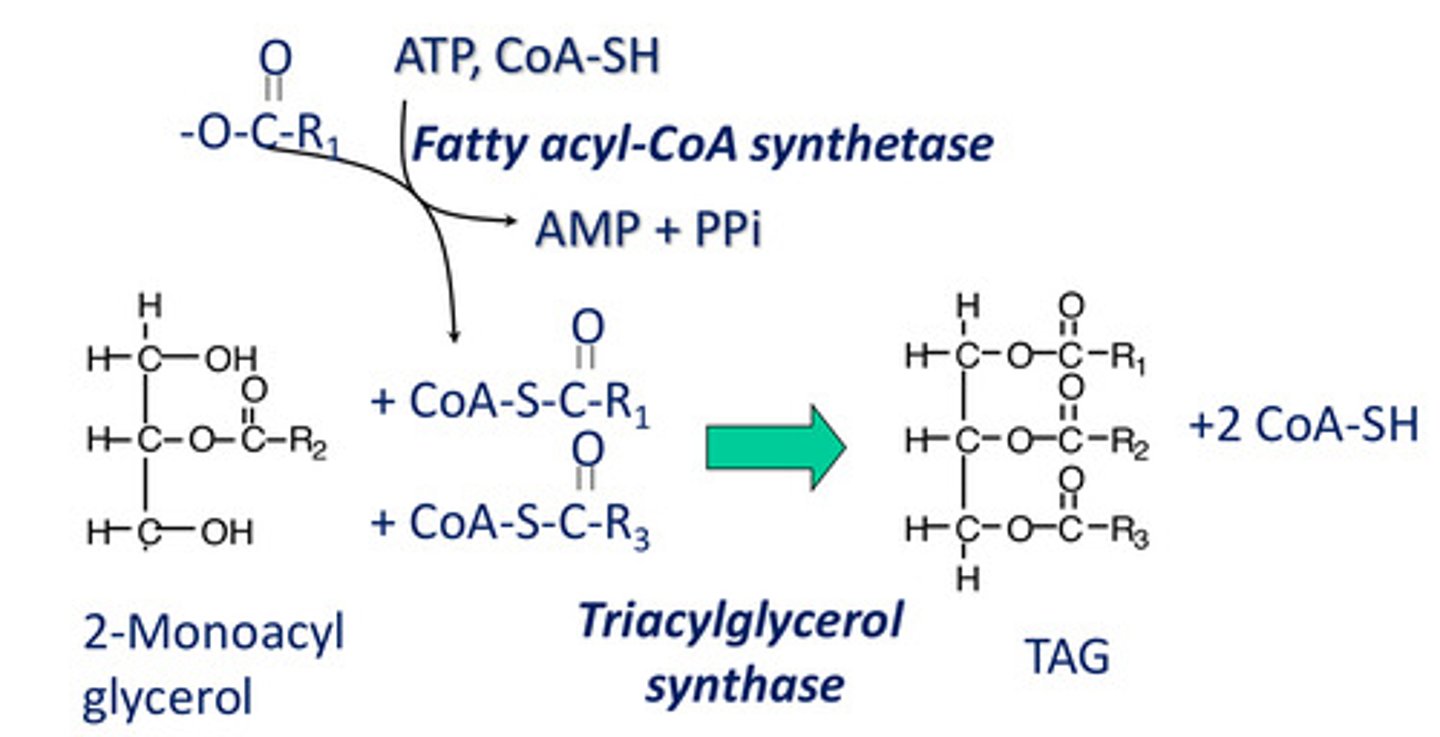
Fatty acid transport to the body begins with what?
TAG re-synthesis
What enzymes re-synthesize TAG?
1. Fatty acyl-CoA synthetase
2. Triacylglycerol synthase
What does ACAT do?
Re-esterification of cholesterol
(Acyl-Cholesterol Acyl Transferase)
How do FAs/triglycerides get into the system?
Short and medium chain molecules absorbed in portal circulation
What do chylomicrons do?
Transport long chain FAs, cholesterol, and fat-soluble vitamins from intestinal cells to the liver and other tissues
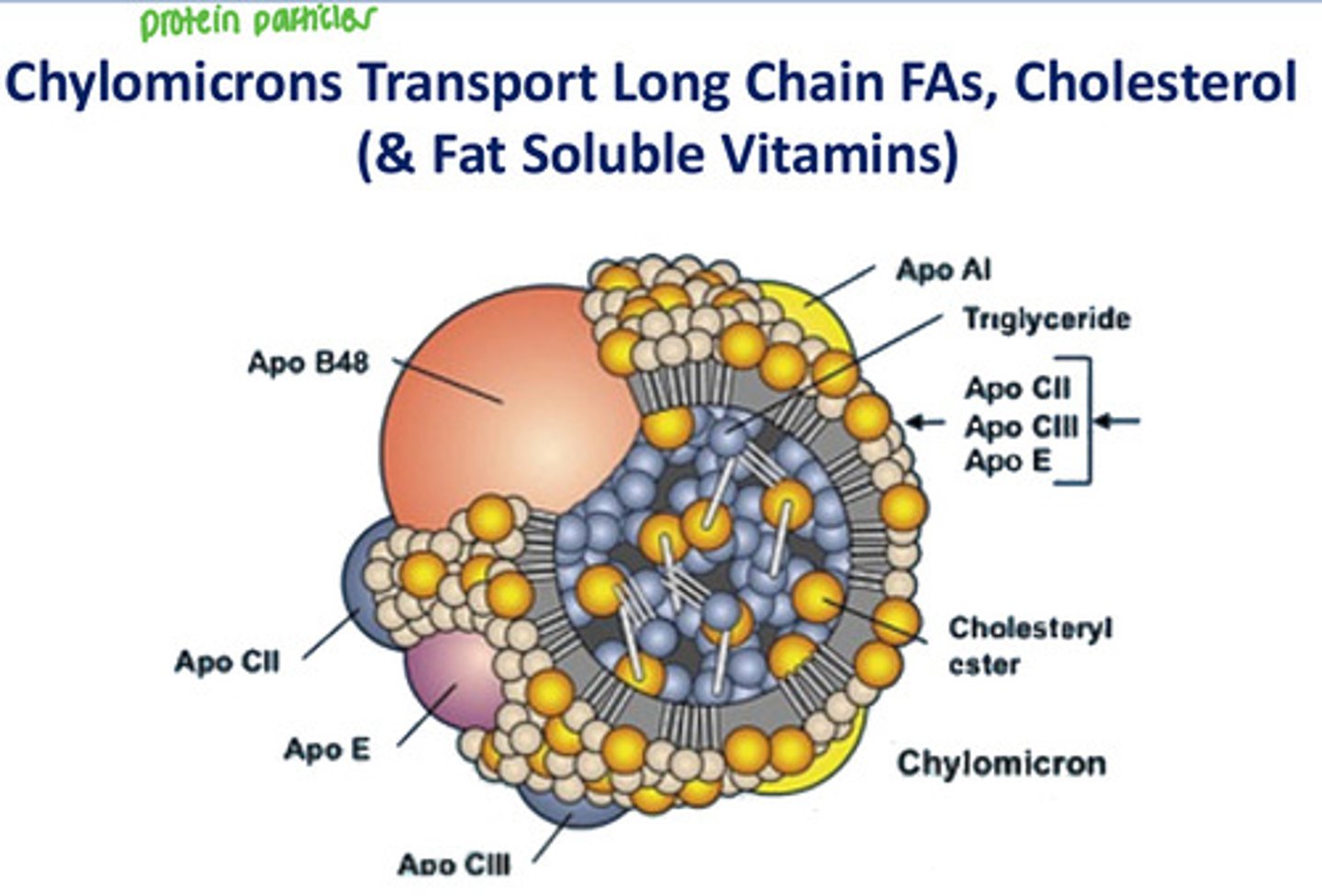
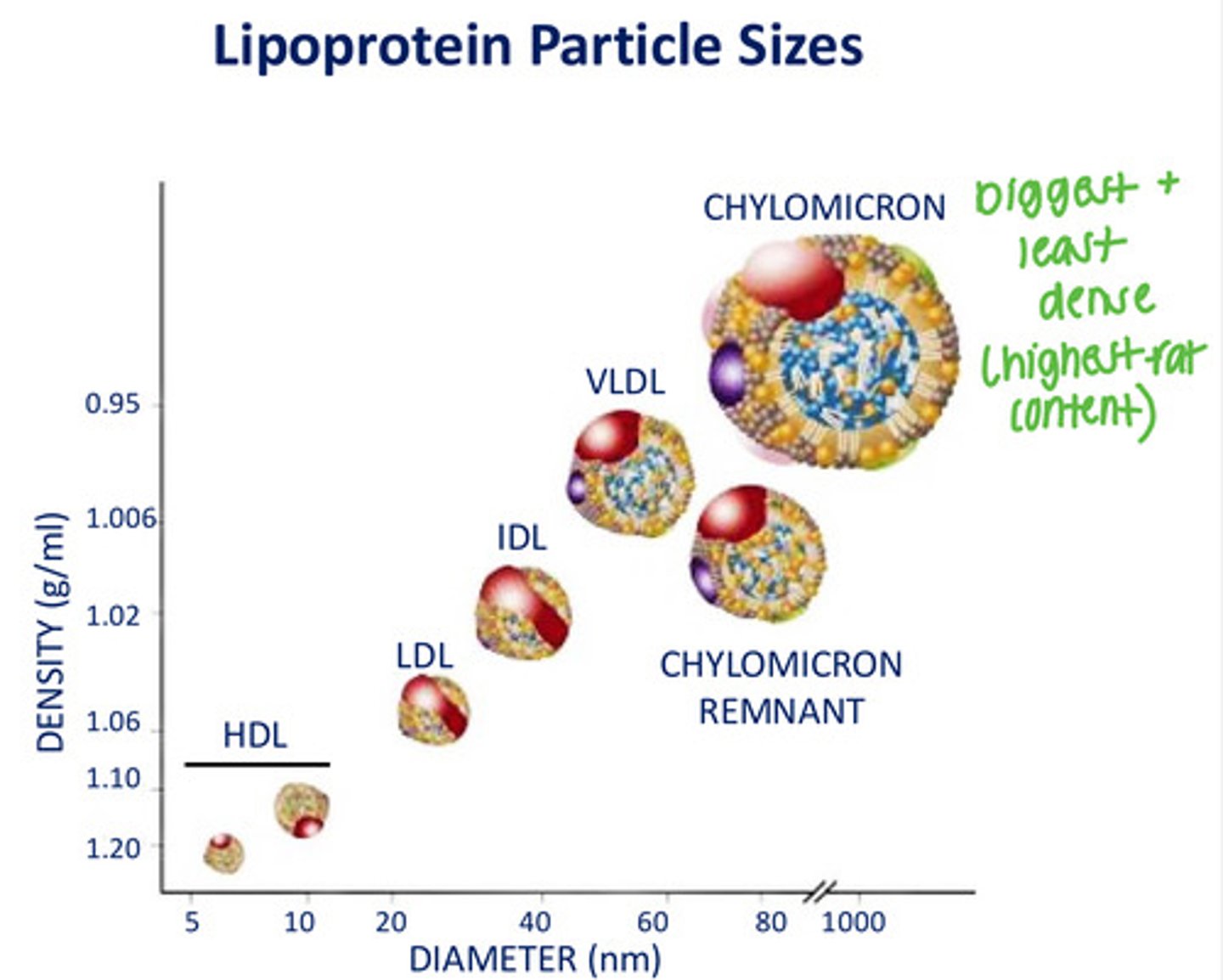
What is the largest lipoprotein particle?
Chylomicron
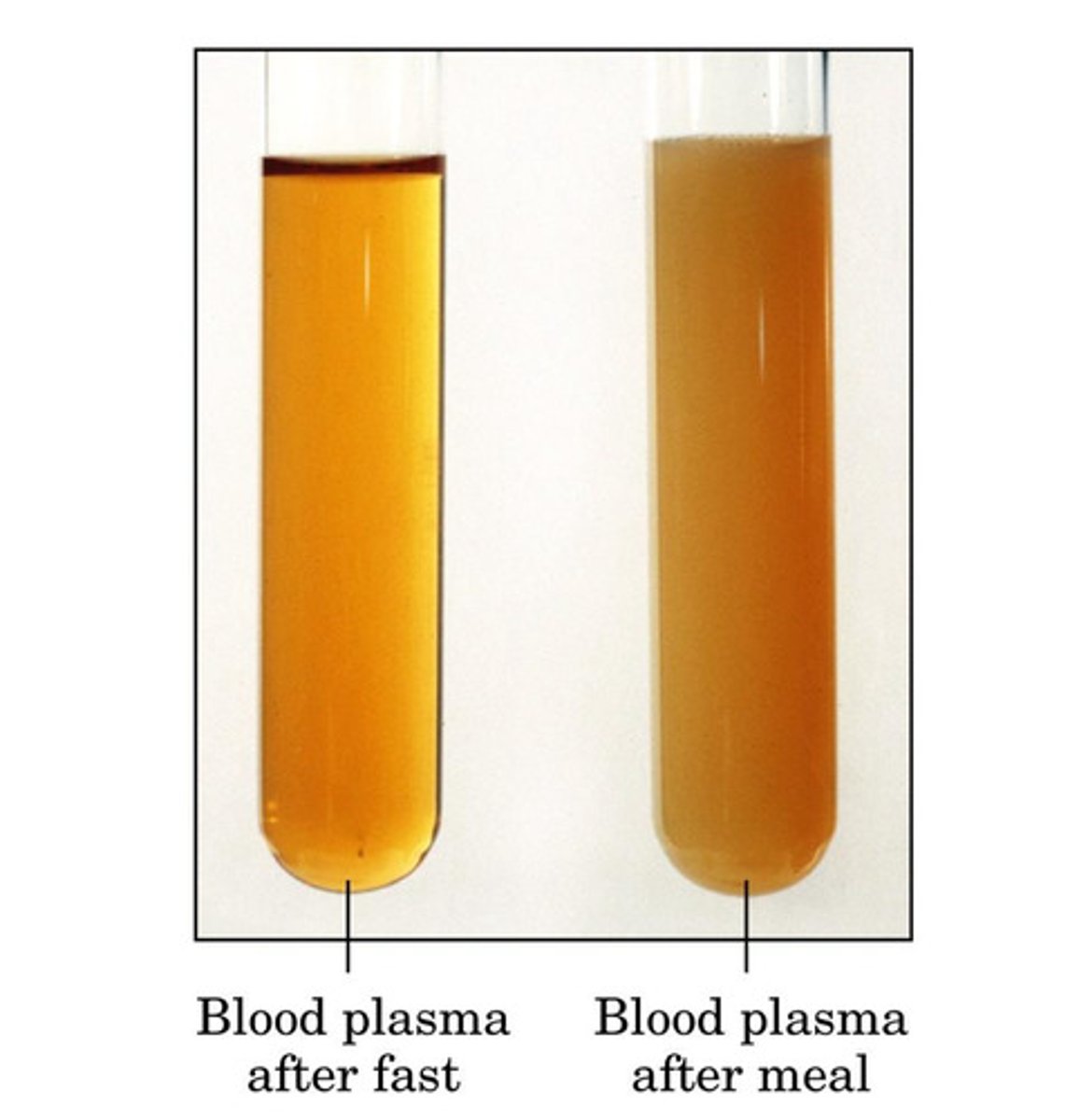
How do chylomicrons alter serum color?
Milky appearance
Where does chylomicron formation begin?
ER
Where are TAGs and CEs synthesized?
Between the phospholipid bilayers of ER membranes
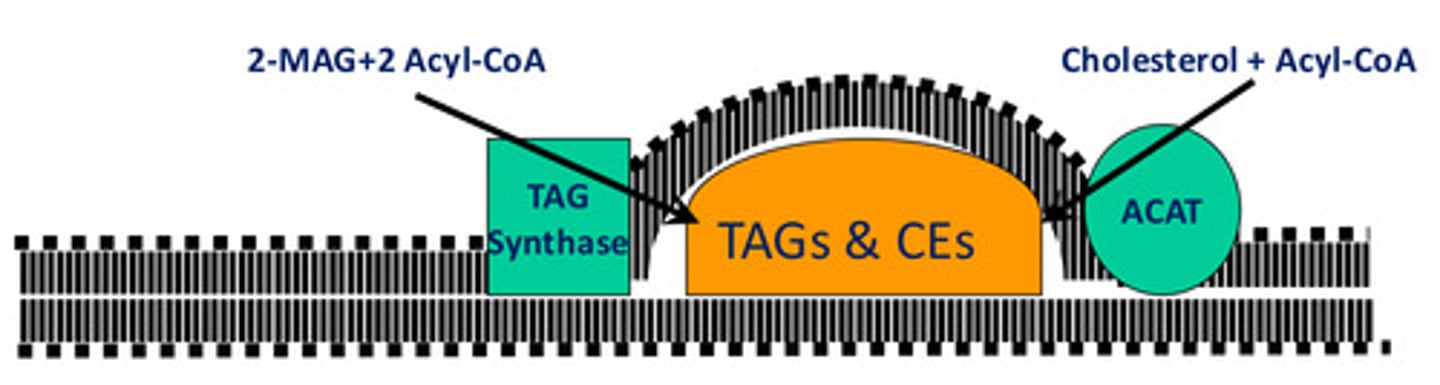
Membrane bound lipid droplets bud into the __ lumen.
ER
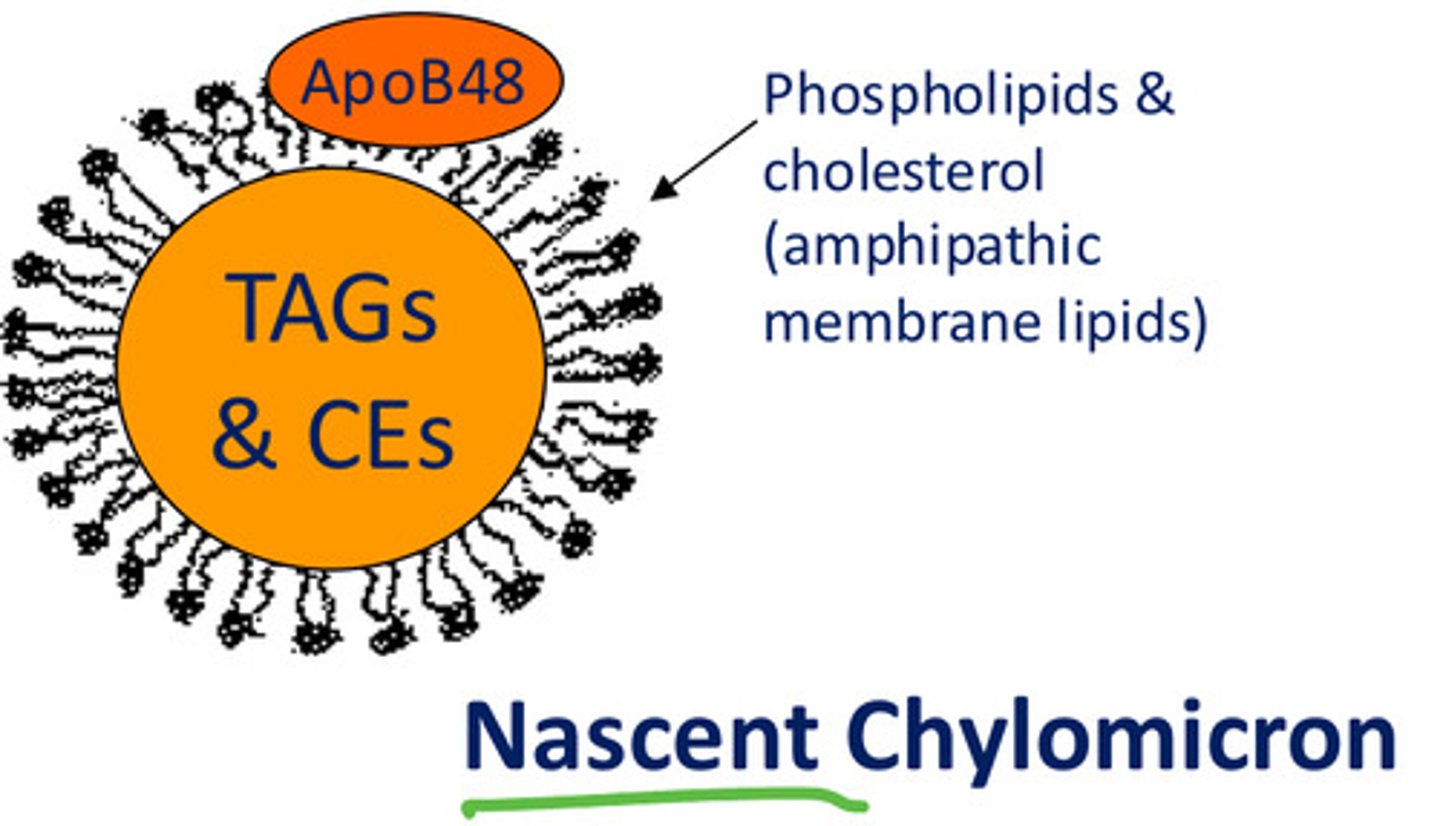
What is added in order to form a nascent chylomicron?
Apolipoprotein ApoB48
What is a nascent chylomicron?
Lipoprotein
What protein loads chylomicrons?
Microsomal Triglyceride Transfer Protein (MTP)
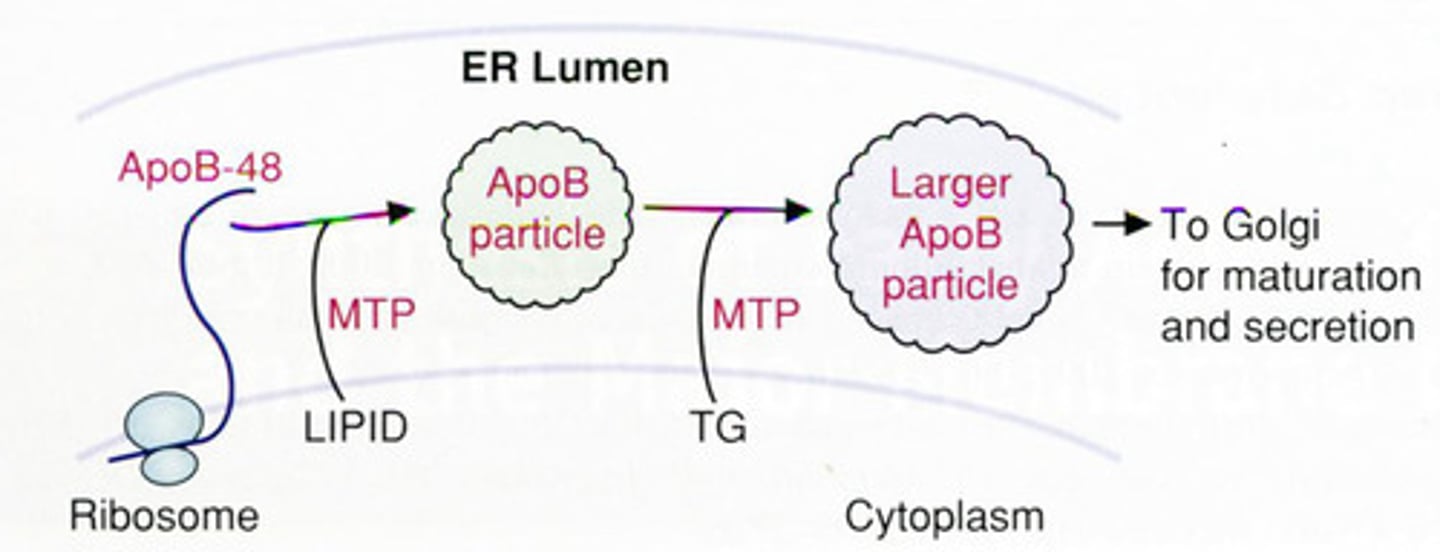
What happens if you cannot load the lipid onto the chylomicron?
The system will back up
What is an MTP deficiency characterized by very low blood triglyceride and total cholesterol levels?
Abetalipoproteinemia (aka Bassen-Kornzweig disease)
Nascent chylomicrons are transported from where to where?
ER → Golgi apparatus
Vesicles from the Golgi fuse with the cell membrane, releasing what into where?
Chylomicrons into lymphatic system
Chylomicrons are released into the lymphatic system through what?
Lacteals
Where do lacteals lead to?
Subclavian vein
Nascent chylomicrons exchange with ___ to mature.
HDL
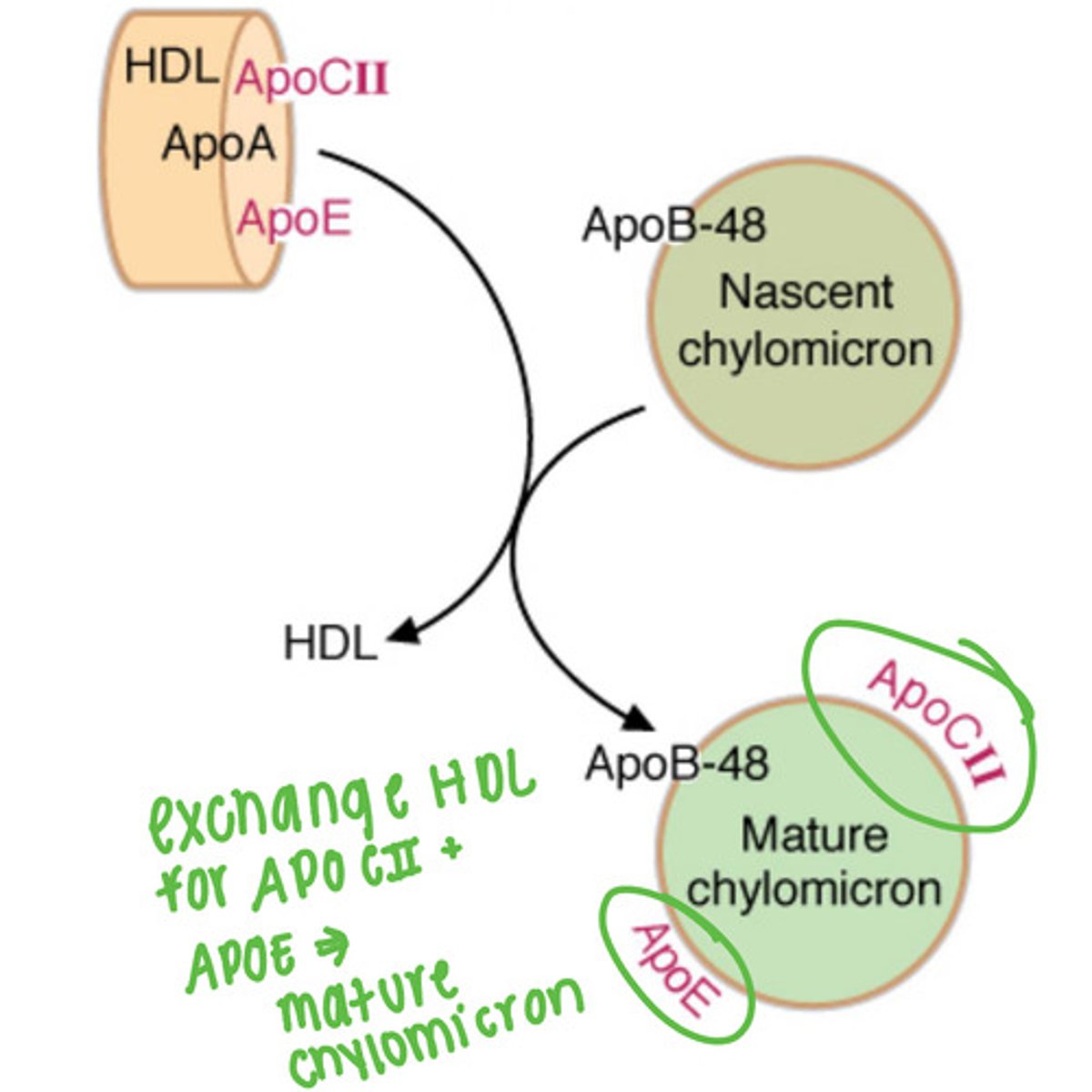
What does ApoC-II activate?
Lipoprotein lipase on blood vessel inner surface (adipose and other tissues)
Where is lipoprotein lipase (LPL) found?
Epithelial surfaces
Where is LPL synthesized?
Parenchymal cells
Where is LPL trafficked to?
Endothelial surface