Periodicity (copy)
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
First ionisation energy definition
energy required to remove one mole of electrons from one mole of atoms of an element in the gaseous state to form one mole of gaseous ions
First ionisation energy equation
E (g) —> E+ (g) + e-
First ionisation energy _____ across a period
increases
First ionisation energy ______ down a group
deacreases
What 3 factors influence ionisation energy?
1- Atomic radii
2- Nuclear charge
3- Electron shielding
How does atomic radii affect first ionisation energy?
Electrons in shells further from nucleus are less attracted to nucleus.
∴ the further the outer electron shell is from nucleus, the lower the ionisation energy
How does nuclear charge affect first ionisation energy?
Nuclear charge increases w. increasing atomic n. means there are greater attractive forces between the nucleus and outer electrons
∴ more energy is required to overcome the attractive forces when removing an electron
How does electron shielding effect first ionisation energy?
shielding effect- when electrons in full inner shells repel electrons in outer shells preventing them to feel the full nuclear charge
∴ greater shielding of outer electrons by inner electron shells = lower ionisation E
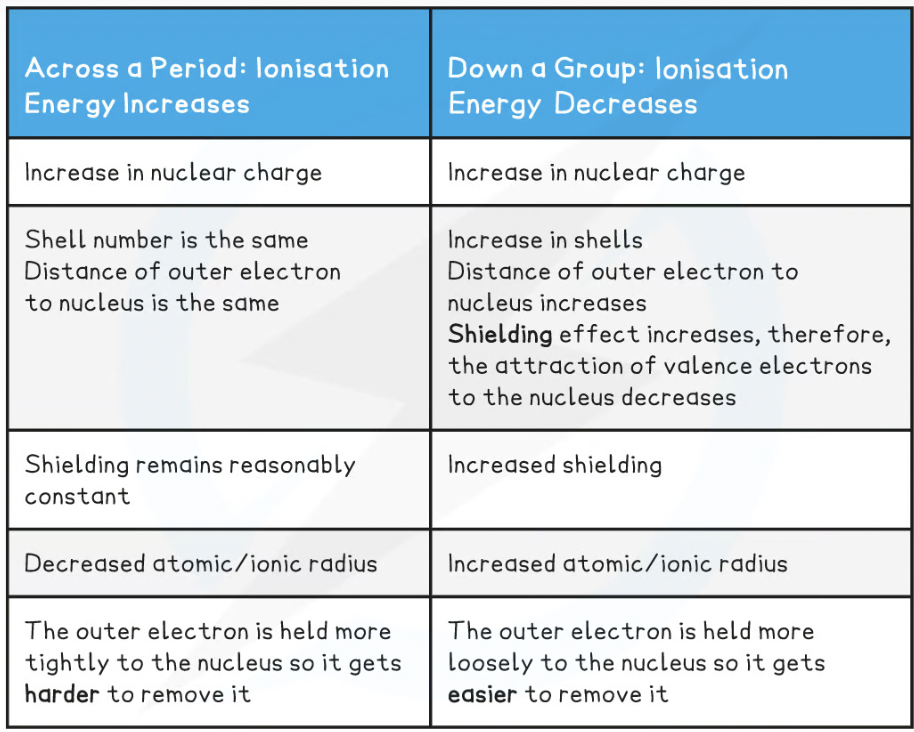
Why does ionisation energy decrease down a group despite increase nuclear charge?
Atomic radius increases
Shielding (by inner shell electrons) increases
∴ attraction between nucleus + outer electrons decreases
Why does ionisation energy across a period increase?
Across nuclear charge increases
Distance between nucleus and outer electrons remains reasonably constant no significant change in atomic radii
Shielding by inner shell electrons remains the same
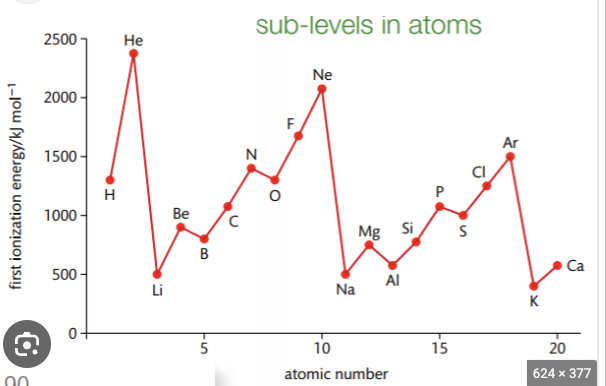
Why is there a rapid decrease in ionisation E between last element in one period and 1st element in next period
Increased distance between nucleus and outer electrons
Increased shielding by inner electrons
Which outweigh increased nuclear charge
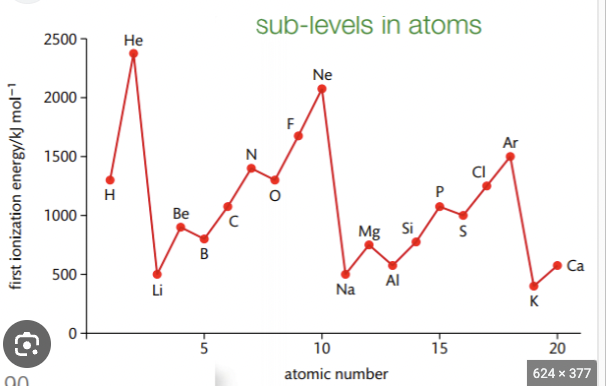
Why is there a slight decrease in first ionisation energy between Beryllium and boron?
In boron- 5th electron in 2p subshell (higher energy) - further from nucleus than 2s subshell of beryllium therefore has less attraction to nucleus and requires less energy to remove
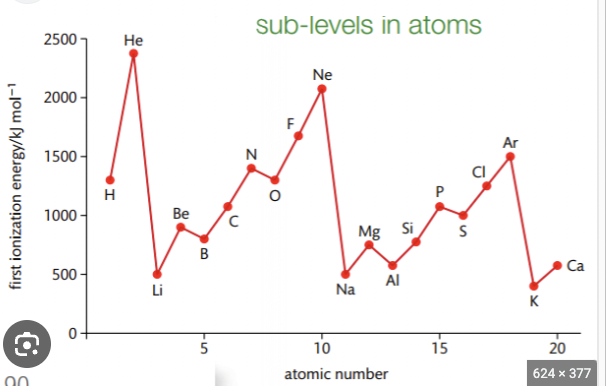
Why is there a slight decrease in first ionisation energy between N and O?
Oxygen- paired electrons in 2p subshell - repel each other - makes it easier to remove an electron in O than N
Across a period and down a group first ionisation factors- table
Successive ionisation energies of an element ______
Increase
Why do successive ionisation energies increase?
Removing an electron from a pos ion is more difficult than from a neutral atom
cuz as electrons are removed- attractive force increase- cuz of decreasing shielding + increase in proton to electron ratio
The big jumps on the graph show the change of ____ and the small jumps are the change of _____
shell
sub-shell
Diamond
Giant cov lattice of carbon atoms
Each carbon is cov bonded to 4 others
Tetrahedral arrangement- bond angle 109.5
Giant lattice structure- strong bonds in all directions
Hardest known structure
Diamond uses
drills and glass-cutting tools
Graphite
Each carbon bonded to three others in layered structure
Layers made of hexagons- bond angle 120
Spare electrons are delocalised ∴ occupy the space between layers
Same layer atoms held by strong cov bonds
Layers held by weak IMF allow layers to slide over each other
Graphene
Infinite lattice of cov bonded atoms in 2D only to form layers
Made of single layer of carbon atoms that are bonded in repeating pattern of hexagons
Silicon(IV) oxide
Also known as silicon dioxide
Same structure as diamond- giant cov lattice/ macromolecular structure made of tetrahedral units all bonded by strong cov bonds
Empirical formula of Silicon(IV) oxide
SiO2
Solubility of metallic substances
Metals do not dissolve
Interaction between polar solvents and charges in the metallic lattice but these lead to reactions, rather than dissolving
M.p. across period 2 and period 3
M.p increase group 1-4:
Group 1-3 have metallic bonding which increases in strength due to increased forces of attraction between more electrons in outer shell that are released to the sea of electrons and smaller pos ion
Group 4 has giant cov structure w. many strong cov bonds requiring a lot of E to overcome
Sharp increase in m.p from group 4 to 5:
Group 5 to 0 have simple molecular structure w. weak London forces between molecules requiring little energy to overcome
periodicity
Pattern in the change in the properties of a row of elements
OR
Trend in the properties of elements across a period
Repeated in the next row
Why does He have largest first ionisation energy?
cuz of small distance ionisation energy increases, higher nuclear charge but no shielding ∴ takes more E to remove outer electron
Electronegativities
Ability of atom to attract the pair of electrons in a cov bond
what is m.p a measure of?
Change of state that occurs between solid and liquid. Idea of strength of bond holding it together
If charge in ionic bond increases what happens?
More attraction therefore stronger bonding
What has the highest m.p of period 3?
Silicon is a metalloid with a giant covalent structure held together by strong covalent bonds which require a lot of energy to break.
Silicon is the only element in period 3 that is a giant covalent structure and so it has the highest melting point at 1.414oC
Why is the melting point of sulfur (S8) is greater than that of phosphorus (P4)
S8 molecules are bigger than P4 molecules
Sulfur and phosphorus both have weak London forces between molecules
The strength of London forces depends on the number of electrons the molecule has
Hence larger molecules will experience stronger London forces
Similarities between graphite and copper
They both have layers / planes / sheets of atoms or ions that can slide over one another
What group has highest m.p
group 4
The difference in melting points between Na and Mg is due to:
Magnesium ions have a greater charge
Magnesium has more delocalised/outer electrons
Magnesium has greater attraction between ions and electrons
OR
Magnesium has stronger metallic bonds