Ocular and Otic Infections- McQuaid - EXAM 4
1/42
Earn XP
Description and Tags
said to know brand/generic!
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
What do the following abbreviations mean:
O
OS
OD
OU
O- oculus aka EYE
OS- left eye
OD- right eye
OU- both eyes
What do the following abbreviations mean:
A
AS
AD
AU
A- auris aka EAR
AS- left ear
AD- right ear
AU- both ears
1 ml= ___ cc = ___ drops
1 ml= 1cc = 20 drops
What does a ribbon or line mean on an rx?
expressed in cm or in
some eye meds are expressed this way (see pic)
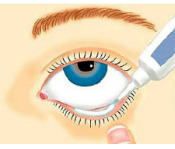
PRACTICE:
Interpret this rx: 1 gtt OU QD x 14 days
1 drop both eyes every day for 14 days
What is inflammation of the thin, clear membrane covering the white of the eye and eyelid?
conjunctivitis aka pink eye
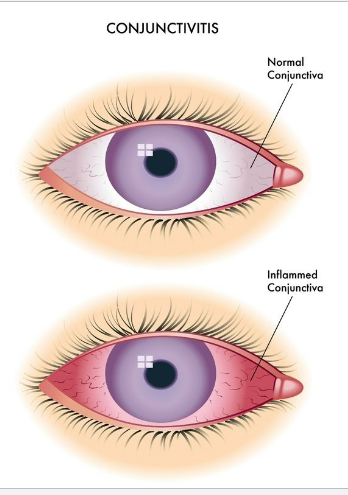
What are the 3 main types of conjunctivitis?
bacterial
viral
allergic
Compare the presentations of bacterial, viral, and allergic conjunctivitis:
Type of Conjunctivitis | Presentation |
Bacterial | |
Viral | |
Allergic |
Type of Conjunctivitis | Presentation |
Bacterial |
|
Viral |
|
Allergic |
|
pay attention to bolded
Which types of conjunctivitis are contagious?
SATA:
a. bacterial
b. viral
c. allergic
a, b—> HIGHLY CONTAGIOUS!!!!!!!!!!!
What’s the common pathogen or allergen for each type of conjunctivitis?
Type of Conjunctivitis | Common Pathogen or Allergen |
Bacterial | |
Viral | |
Allergic |
Type of Conjunctivitis | Common Pathogen or Allergen |
Bacterial |
|
Viral | **********Adenovirus********* |
Allergic |
|
What are some exclusions to self-tx for bacterial conjunctivitis?
(use common sense)
vision changes
photophobia
foreign body sensation
severe HA/n
corneal opacity (cloudy looking eye)
hyperacute bacterial conjunctivitis
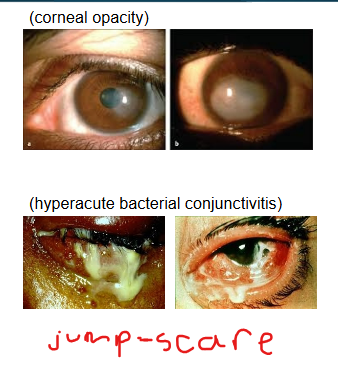
A concern with bacterial conjunctivitis is progression to _____________________ which is often caused by gonorrhea or meningitis and can result in vision loss.
hyperacute bacterial conjunctivitis
Pharm tx for bacterial conjunctivitis is split into pts. who don’t wear contact lenses and those that do.
What the preferred agents for each? (brand/generic)
no contact lens
erythromycin 0.5% ointment
trimethoprim-polymyxin B (Polytrim) drops
contact lens
ofloxacin (Ocuflox) 0.5% drops
ciprofloxacin (Ciloxan) 0.3% drops OR ointment
What’s the pharm tx for bacterial conjunctivitis caused by GONORRHEA?
Ceftriaxone (Rocephin) 1g IM once
What’s the pharm tx for bacterial conjunctivitis caused by CHLAMYDIA?
Azithromycin (Zithromax) 20mg/kg PO once
Do all pts. that have bacterial conjunctivitis have to go to the ophthalmologist if symptoms continue/worsen after 2-3 days of abx? exceptions?
ALL PTS. GO
PRACTICE:
Which of the following are exclusions to self-tx? SATA
a. profuse purulent discharge
b. redness/itching
c. eyes are crusty
d. photophobia
e. foreign body sensation
a, d, e
What is the topical tx for VIRAL conjunctivitis?
trick question—> NONE!!!!!
infection is self-limiting
What are some non-pharm self tx for each type of conjunctivitis:
(just recognize)
Type of Conjunctivitis | Non-pharm/self-tx recommendations |
Bacterial | |
Viral | |
Allergic |
Type of Conjunctivitis | Non-pharm/self-tx recommendations |
Bacterial |
|
Viral |
|
Allergic |
|
What classes of drugs can be used to tx allergic conjunctivitis?
topical mast cell stabilizers
topical antihistamines
combo of mast cell + antihistamine
oral antihistamines—> non preferred
if necessary use 2nd gen H1-antagonists
What ophthalmic mast cell stabilizers can be used for allergic conjunctivitis?
(brand/generic, %)
cromolyn 4% solution
Lodoxamide 0.1% solution
Nedocromil (Alocril) 2% solution
What ophthalmic antihistamines can be used for allergic conjunctivitis?
(brand/generic, %)
Azelastine 0.05% solution
Olopatadine (Pataday) OTC 0.1,0.2,0.7% solution
Cetirizine (Zerviate) 0.24% solution
What drug is a combination ophthalmic mast cell stabilizer/antihistamine used for ALLERGIC conjunctivitis?
Ketotifen (Alaway, Zaditor) OTC 0.025% solution
PRACTICE:
Which of the following is the most common pathogen associated with viral conjunctivitis?
a. Herpes Simplex Virus
b. S. aureus
c. adenovirus
d. norovirus
c
What is Blepharitis?
common eye condition characterized by inflammation of the eyelid margin with eye irritation
What are some predisposing conditions/factors that may lead to Blepharitis?
chronic inflammatory skin conditions
colonization of eyelid by S. aureus or other staph
irritant exposure
RETINOIDS
Presentation of Blepharitis? Contagious?
presentation: red, swollen eyelids, crusting/flaking/scaling of skin of the eyelid
NOT contagious
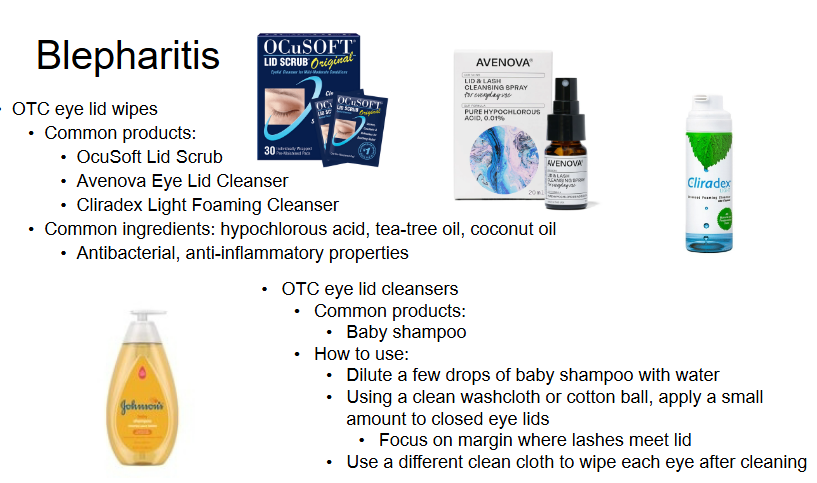
What are the self-treatment recommendations and pharm tx for Blepharitis?
(focus on self-tx)
self-tx
WARM COMPRESS
OTC eye lid wipes/cleansers
pharm
FOR SEVERE
abx ointments, steroid eye drops, artificial tears
PRACTICE:
Which of the following could you recommend to a patient who comes to your pharmacy and asks for an OTC antihistamine eye drop?
a. Cromolyn
b. Azelastine
c. Pataday
d. Zaditor
e. Ketotifen
c—> Pataday brand name of Olopatadine
others:
cromolyn—> mast cell stabilizer
azelastine—> antihistamine, but not OTC
Ketotifen (Zaditor)—> mast cell+ antihistamine
Which of the following do you NOT need to shake before use?
a. solution
b. suspension
c. gel
a
Answer the following about administering eye drops:
When you’re administering EYE DROPS how many drops do you place at a time?
Should you allow the applicator to touch the eye?
If multiple drops are being administered how long do you WAIT IN BETWEEN DROPS for the SAME medications vs. a DIFFERENT medication
1 drop at a time
don’t let applicator touch eye
if multiple drops are administered:
same medication—> wait 5 MINUTES
different medication—> wait 5-10 MINUTES
but then 2 slides later she says this:
solution—> wait 5 minutes
suspension—> wait 10 minutes
idk man
Answer the following about administering eye ointment:
how long to keep eye closed after administering?
how long to reinsert contacts?
close eye for 1-2 minutes
wait 15-30 minutes or overnight to reinsert contacts
PRACTICE:
Select the preferred self-tx for blepharitis:
a. warm compress
b. abx eye drops
c. antihistamine eye drops
d. oral antihistamines
a
Definition of Acute Otitis Externa (AOE)?
(recognize)
“swimmer’s ear”
inflammation of the external auditory canal or auricle
Acute Otitis Externa has 3 severities: mild, moderate, and severe. Describe them.
Severity | Symptoms |
Mild |
|
Moderate |
|
Severe |
|
Common pathogen that causes AOE?
S. aureus
Pseudomonas aeruginosa
What is the tx for AOE? (brand/generic)
mild
moderate-severe
mild
acetic acid and hydrocortisone otic drops (VoSol HC)
moderate-severe
ciprofloxacin and dexamethasone otic drops (Ciprodex)
ciprofloxacin and hydrocortisone (Cipro HC)
neomycin, colistin, hydrocortisone, and thonzonium (Cortisporin-TC)
What is a blockage of the ear canal due to accumulation of wax (cerumen) when it becomes too hard to wash away naturally?
cerumen impaction
Tx of a cerumen impaction?
cerumenolytics
helps soften earwax for easy removal
at home or medical office
manual removal (by a dr.)
removal by irrigation (by a dr.)
Examples of Cerumenolytics?
water
saline solution
mineral oil
hydrogen peroxide
CARBAMIDE PEROXIDE (Debrox) OTC otic solution
instructions for carbamide peroxide (Debrox)?
5-10 drops per ear BID for up to 4 days
When administering ear drops, what’s the difference between adult admin and <3 admin?
adult—> pull earlobe up and back
<3 —> pull earlobe down and back