Psychology Chapter 8 and 9 Exam
1/42
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
43 Terms
prefrontal cortex
necessary for making judgements about behavior and consequences
sympathetic nervous system
prepares the body for stressful or dangerous situations “fight or flight”
parasympathetic nervous system
regulates “rest and digest” functions
James-Lange Theory
Claims that emotional experience results from physiological arousal that precedes it, and different emotions are the result of different patterns of arousal (emotional stimulus → physiological response →affective experience)
Paul Eckman
discovered that some facial expressions of emotion are universal by observing a culturally isolated man from New Guinea convey emotions via facial expression
adrenal glands
part of the sympathetic nervous system, releases various hormones, particularly cortisol
mirror neurons
fire both when we engage in a specific act and while observing the acts of others
cognitive theory of emotion
Schachter and Singer’s theory that the identity of the emotion is based on the cognitive assessment of the situation, and physiological arousal contributes only to the emotions intensity
Schachter and Singer
(cognitive theory) stated that the identity of the emotion is based on the cognitive assessment of the situation, and physiological arousal contributes only to the emotion’s intensity.
limbic system
network of structures arranged around the upper brain stem consisting of the amygdala, hippocampus, thalamus, hypothalamus, basal ganglia, and cingulate gyrus
stress
internal/external condition in environment/body that makes unusual demands on an organism
hypothalamus-pituitary-adrenal-axis
brain region consisting of the hypothalamus, pituitary glands and adrenal glands- responsible for maintaining physiological homeostasis
sensation
the acquisition of sensory information
perception
the interpretation of sensory information
receptor
cell, often specialized neuron, suited by its structure to respond to a specific form of energy, such as the vibration of sound
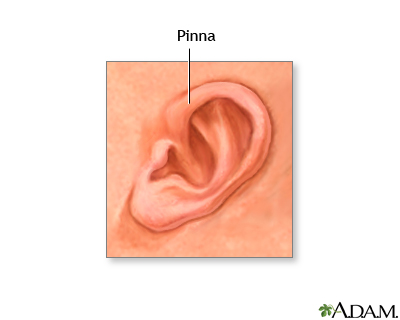
pinna
flap of the ear that graces the side of the head also called the outer ear
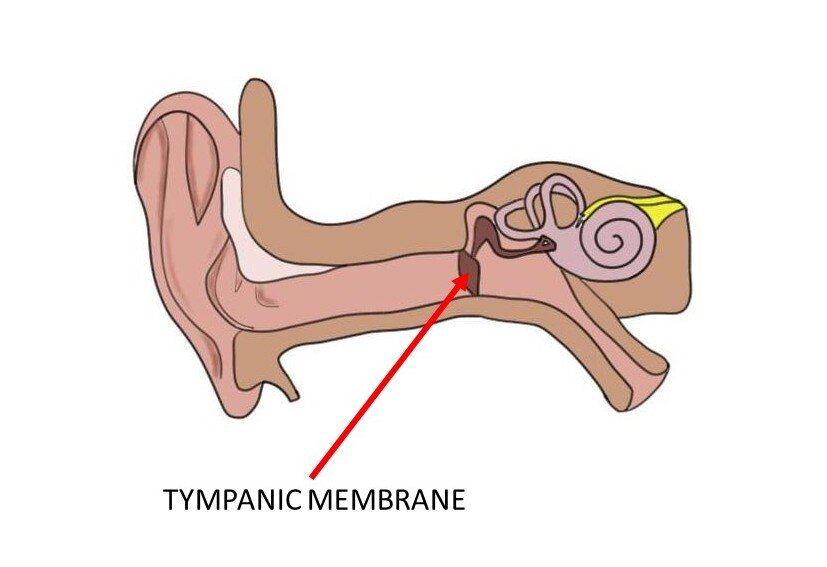
tympanic membrane
very thin membrane stretched across the auditory canal
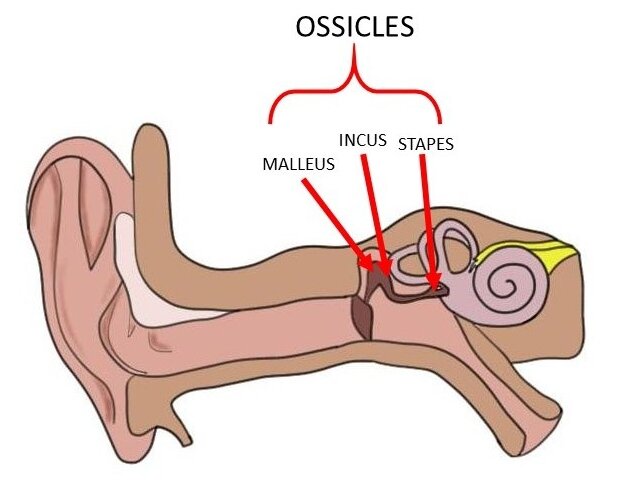
ossicles
tinny bones in the middle ear that operate in lever fashion to transfer vibrations from tympanic membrane to the cochlea (malleus, incus, and stapes)
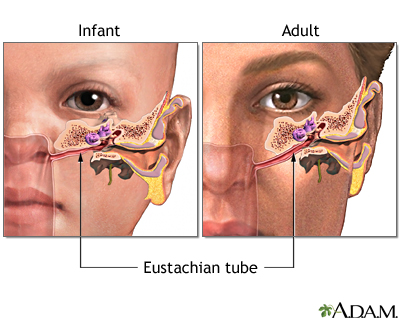
eustachian tube
middle ear structure that connects middle ear to the back of the mouth, equalizing air pressure of middle ear with the outside world
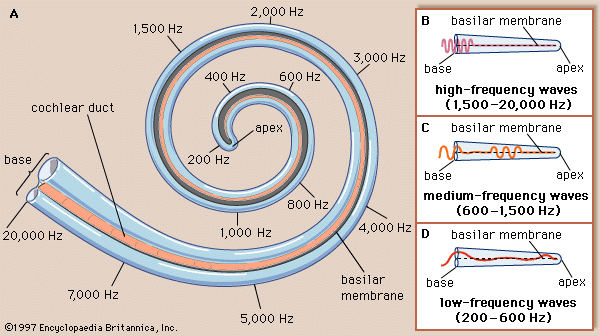
cochlear canal
location of auditory receptors which vibrate due to activity in vestibular and tympanic canals
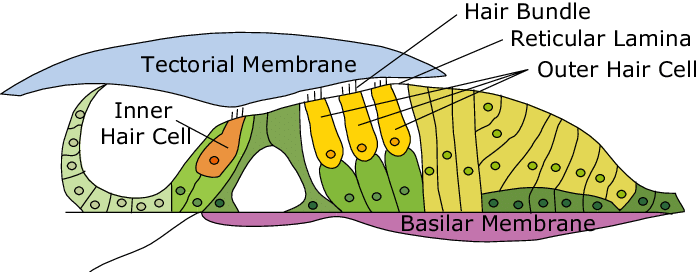
organ of corti
sound analyzing structure that rests on the basilar membrane which consists of four rows of specialized cells called hair cells.
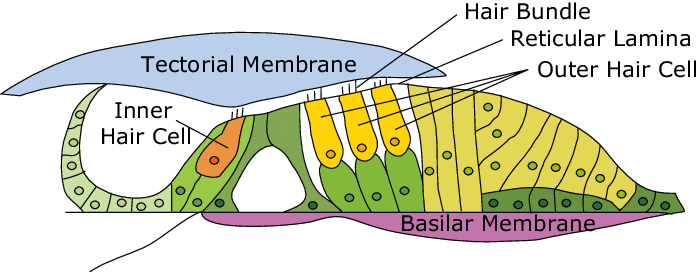
basilar membrane
supports organ of corti
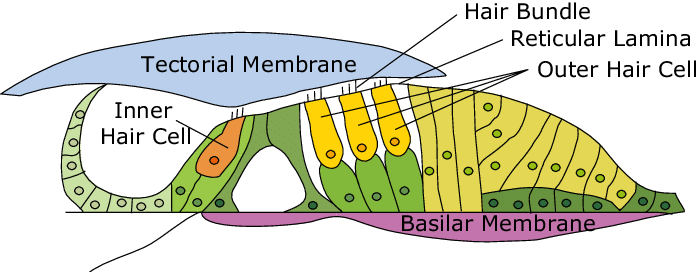
tectorial membrane
membrane above hair cells
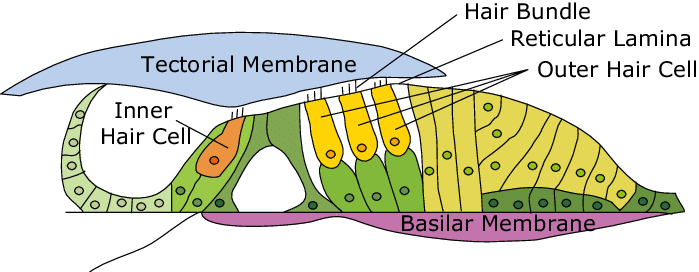
inner hair cells
sensory cells that receive 90-95% of auditory neurons
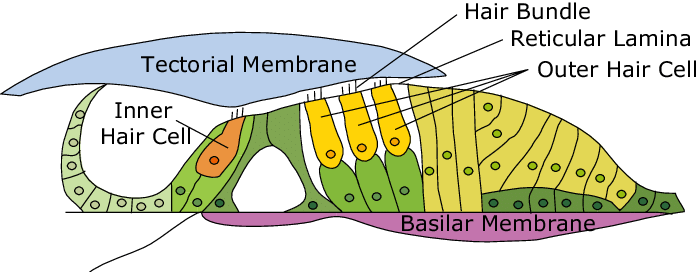
outer hair cells
increase cochlea’s sensitivity both by amplifying its output and sharpening frequency tuning at location of peak vibration
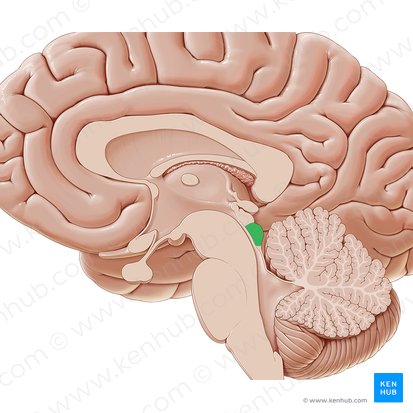
inferior colliculi
involved in sound localization
tonotopically organized
neurons from adjacent receptor locations project to adjacent cells
frequency
the number of times per second that a sound pressure wave repeats itself
pitch
the quality of a sound governed by the rate of vibrations producing it; the degree of highness or lowness of a tone
amplitude
the relative strength of sound waves (transmitted vibrations), which we perceive as loudness or volume
loudness
the attribute of a sound that determines the magnitude of the auditory sensation
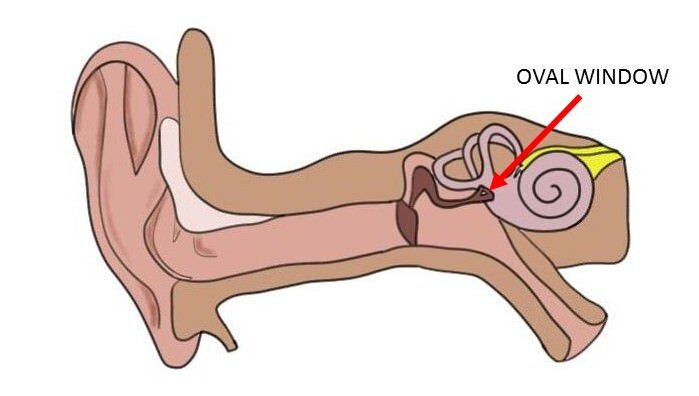
oval window
a kidney-shaped aperture in the medial wall of the mesotympanum of the middle ear, providing communication with the vestibule of the inner ear
hair cells
specialized inner-ear cells responsible for the transduction of sound-evoked mechanical vibrations into electrical signals that are then relayed to the brain
pathway of soundwaves
pinna → ear canal (external auditory meatus) → tympanic membrane
frequency theory
assumes neurons from adjacent receptor locations project to adjacent cells
telephone theory
early form of frequency theory, developed by William Rutherford that claimed individual neurons in auditory nerves fired at same frequency as rate of vibration of sound source
volley theory
groups of neurons follow frequency of sound at a higher frequency when single neuron cannot
responsible for transduction (transformation of sound into electrical impulses)
cochlea
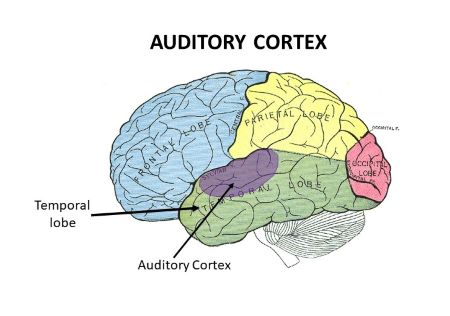
auditory cortex
located on the superior temporal gyrus in the temporal lobe
aphasia
language impairment caused by damage to the brain
Broca’s aphasia
a non-fluent aphasia in which the output of spontaneous speech is markedly diminished and there is a loss of normal grammatical structure
Wernicke’s aphasia
impaired language comprehension
How have we obtained most of our knowledge on brain structures related to language?
Lesion, neuroimaging, brain stimulation, neuropsychological, and animal studies