2.6 macroeconomic objectives and policies - 25 markers
1/28
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
29 Terms
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - intro
inflation = sustained increase in PL
target = 2±1% - use as a measure to judge current inflation level
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - KAA1 point
contractionary fiscal policy - lower G and increase T to lower AD and therefore lower demand-pull inflation
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - KAA1 - first increased T analysis
increase in income tax - decrease disposable income - decrease C and therefore AD - quite a large shift as C makes up 60% of AD - fall in PL
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - KAA1 - first increased T diagram
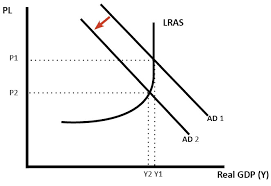
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - KAA1 - second increased T analysis
increase corporation tax e.g. increase from 19 to 25% in 2021 - reduce retained profits for firms - reduce investment - AD shifts in
second increased T diagram
fall from Y1 to Y2
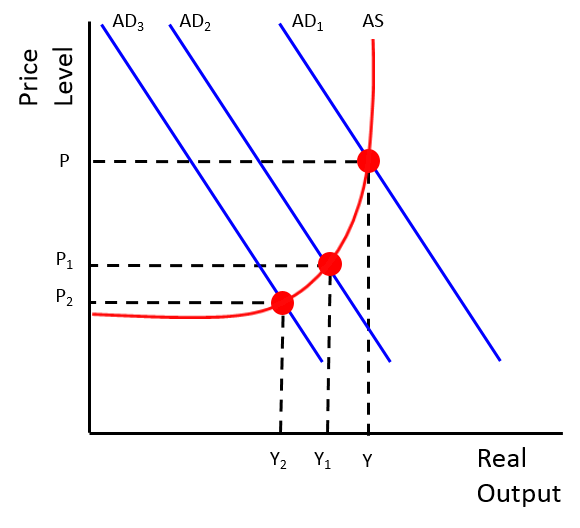
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - KAA1 - decreased G
e.g. lower spending on NHS - current budget is equal to 10% of UK GDP
fewer injections into circular flow - AD shifts inward - lower inflation
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - EV1 against increased taxation
cfp would lead to higher production costs for firms in SR - shift SRAS inwards - increase in cost-push inflation - harder to control - cannot use interest rates
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - EV1 against decreased G
quality of public services fall - waiting lists in NHS - worsen labour productivity - already very low - increase costs per unit - increasing production costs - worsening cost-push inflation
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - KAA2 point
supply side policies - aim to increase productivity and efficiency e.g. privatisation - transfer of ownership of a public service to the private sector
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - KAA2 analysis
should lead to more efficient outcomes as private firms act on the profit motive - incentive to reduce costs to remain competitive in the market
increase LRAS - would result in a significant reduction in the price level
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - KAA2 another example
reduce minimum wage costs - lower wage costs for firms - lower costs of production - outward shift of SRAS - decrease in cost-push inflation
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - EV2
may not be effective at reducing inflation due to the effects of LR
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - EV2 analysis
assuming geographical immobility of labour, may lead to emigration - labour force would decrease - fall in quantity of factors of production - LRAS shifts inwards
evaluate macroeconomic policies, apart from monetary policy, the UK government could use to reduce inflation - final judgement
most effective policy depends on the cause of inflation
recent inflation has come from supply-side shocks e.g. invasion of Ukraine
suggests measures like increasing taxes would not be effective as they focus on demand-side causes
supply-side policies may be more effective as they would increase the UK’s flexibility to grow without feeling the effects of an acceleration of the price level
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - intro
define recession - period where there is 2 or more consecutive quarters of negative economic growth
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - KAA1 point
increase in G - direct injection into the circular flow of income
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - KAA1 analysis
outward shift in AD - assuming AD was originally on the horizontal section (in recession), will create a large increase in real incomes - increase in employment
lead to multiplier - final value of the increase in spending will be higher than the initial injection - further outward shift of AD
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - KAA1 further analysis
if G was focused on infrastructure would also lead to an outwards shift in LRAS due to the economy becoming more productive - leads to growth as well as reduced inflation
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - EV1 point
if not targeted, ir may not lead to increases in productivity - increase in growth will be limited
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - EV1 analysis
e.g. increased G on the NHS would be effective as there record waiting-lists, which are stifling labour productivity
also, the effects of G are usually seen quickly but with increased infrastructure spending, this may not be the case
government spending may not be he most effective way to avoid or reduce the impacts of a recession
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - KAA2 point
decreased taxation - income and corporation
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - KAA2 analysis - decreased income tax
lower levels of disposable income - more willing to spend on goods and services - large outward shift in AD as C makes up 60% of AD
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - KAA2 analysis - decreased income tax, effect on firms
may be increase investment in order to meet increasing demands for goods and services as a result of the decreased income tax - further growth and employment
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - KAA2 analysis - decreased corporation tax
to encourage increased levels of investment may cut corporation tax e.g. reverse the increase from 19% to 25% in 2021
larger incentive to spend retained profits on capital goods - further outward shift in AD
also increase in LRAS - quality and/or quantity of fop are increasing - increase in growth
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - EV2 point
increase in consumption not guaranteed
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - EV2 analysis - consumers
confidence levels may be low e.g. after GFC, despite a cut in interest rates, saving levels increased - may not be willing to purchase more goods and services - severely limit shift in AD
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - EV2 analysis - firms
animal spirits - even if economic conditions suggest there should be an increase in investment (low corporation tax), firms may not be willing to invest
may be because they can see consumers have low confidence - worried they will not see an increase in C that would make their I worthwhile
evaluate the effects of the government using expansionary fiscal policy in the event that the UK economy goes into recession - final judgement
extent to which growth occurs after using expansionary fiscal policy depends on factors such as confidence
may not be viable depending on objectives of government e.g. if they were focused on decreasing national debt as efp would likely lead to increased borrowing