WBC HW Review
1/161
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
162 Terms
adult reference range WBC
4,500-11,000/uL
calculate hemacytometer white cell count
dilution factor x # white cells per WBC counting area
0.1 x WBC counting area
calculate absolute lymph count
% lymph x white count = # x 10³/uL
calculate corrected WBC for NRBCs
WBC x 100
NRBC + 100
usually correct WBC when NRBC is 5 or more
what stimulus causes CFU-GEMM cells to mature into CFU-GM?
IL-3 and GM-CSF
describe primary granules
lysosomal and non-specific
secondary granules appear in which phase?
myelocyte
function of primary granules
supply lytic and neutralizing enzymes for phagocytosis
which granulocyte stage is the last stage capable of mitotic division?
myelocyte
% of peripheral blod granulocytes in the marginal pool?
50%
capsule surrounding primary and secondary granules made up of what?
phospholipids
what form do granulocytes store energy for their journey into tissues?
glycogen
(anaerobic glycolysis)
what do superoxides produce?
hypochlorite and hydrogen peroxide
define respiratory burst
the sharp increase in oxygen uptake that macrophages experience during phagocytosiss
specific granules in basophils contain which stain with the basic dye in Wright’s stain?
heparin sulfate
at which stage of maturation are eosinophilic granules first expressed?
myelocyte
how do eosinophils respond to adrenal corticosteroids?
they decrease in the presence of corticosteroids
which cytokine is unique to eo maturation?
IL-5
Eosinophils kill parasites by what?
lytic enzyme exocytosis
myeloperoxidase in neutrophils is also found where?
monocytes
which Colony stimulating factor is responsible for forming a monoblast from GEMM?
GM-CSF and M-CSF
in peripheral blood, how many times larger is the pool of marginating monocytes comapred to circulating monocytes?
3 times
function of macrophages?
recognize antigen and phagocytize
where do lymph precursors differentiate to T or B cell?
primary lymphoid tissue
memory T cells live how long?
YEARS
when monocyte matures, it becomes
a macrophage
tissue basophil aka
mast cell
how does MPO and SBB separate acute lymphocytic from acute non-lymphocytic?
both positive for AML
both negative for ALL
what describes acute leukemia?
rapid onset with greater than 20% blasts
which chromosome with M3?
t(15;17)
acute myeloblastic leukemia without maturation
which FAB distinction?
M1
pathognomonic inclusion body in hematology lab in AML or AMoL is
auer rods
SBB stains which part of cell
phospholipid capsules
which cytochemical stain detects glycogen in cells?
periodic acid schiff (PAS)
which cytoplasmic enzyme is found in monocytes?
non-specific esterase
“kiddie leukemia” FAB category
L1
dohle bodies and toxic gran mean what?
inflammation conditions
polycythemia vera turns to which leukemia
AML
acute malignant proliferation of erythroblasts (>50%) in marrow with moderate anemia is which FAB classification
DiGuglielmo’s syndrome (M6)
what’s helpful about an LAP score?
it differentiates CML (low LAP) from leukemoid reaction (high LAP)
block positive PAS stain in blast cell shows what?
acute lymphocytic leukemia
which AML shows fluoride sensitive (non-specific) esterase activity?
Monocytic leukemia (M4/M5)
philadelphia chromosme in how much of CML patients?
90%
bundles of Auer rods are in which FAB stage?
M3
what abnormal cell found in peripheral blood of MM patient?
plasma cell
which WBC anomaly has no clinical significance?
Pelger-Huet
which WBC anomaly has dohle-like inclusion bodies?
May-Hegglin
Hurler’s and Hunter’s syndromes have which inclusions?
metachromatic granules (Reilly bodies)
hyperlobulation of neutrophils means
B12-folate deficiency
MEGALOBLASTIC anemia
most common ALL in adults
B cell ALL (L2)
which ALL blasts have vacuoles in the cytoplasm
L3 (burkitt’s)
Most L1 ALLs are what?
TdT and CALLA positive
M3 leukemia defined as what?
promyelocytic
M4Eo means what?
myelomonocytic leukemia with eosinophilia
which AML shows megaloblastoid changes?
M6
WHICH factor increases reticulum fibers in bone marrow found in M7 and myelofibrosis
platelet derived growth factor (PDGF)
which cell line is CML
myeloid
which cell line is PV
erythrocytes
which cell line is myelofibrosis
fibroblasts
which cell line is essential thrombocythemia?
megakaryocyte
common finding in myelodysplastic syndrome
cytopenia, dysplasia, anemia
which CD found on blast cells is on mature WBCs in MDS
CD34
which refractory anemia close to being an acute leukemia?
RAEB
cure for MDS and meyloproliferative disease
marrow transplantation
over 90% of CLL are which type?
B cell type
common finding on peripheral smear in CLL
smudge cells
which lipid storage disease has glucocerebrosides?
Gaucher’s
sea blue histocytes what type of disorder?
lipid metabolism disorder
which cell is pathognomonic in Hodgkin’s disease?
Reed-Sternberg cell
Hodgkin’s patient with organ involvement
IV
type of hodgkin lymphoma composed of cells with multilobulated nculeus with delicate nuclear membranes, fine granular chromatin, small indistinct nucleoli (popcorn or L and H cells)
lymphocyte predominant
what term is used if cell has chromosome count other than 46?
aneuploid
term given for patient with 46 karyotype, XX, +8, -21?
pseudodiploid
karyotype 47, XY, +8 -21 means what
male
trisomy 8
monosomy 21
philadelphia chromosome t(9;22) found in which cells?
myeloid and lymphocyte
mycosis fungoides describes what?
skin lesions progressing to tumor
when mycosis fungoides T-helper cells invade peripheral blood, what’s it called?
Sezary syndrome
in Waldenstrom’s macroglobulenemia, which aberrant cell makes monoclonal IgM?
plasmacytoid lymphocytes
which lymphoma associated virus is incriminated in T cell leukemia/lymphoma?
HTLV-1
which test is helpful in diagnosing CGD?
nitroblue tetrazolium test
protein p210 found when the philadelphia chromosome is present has what kind of increased activity?
tyrosine kinase
idiopathic myelofibrosis vs other types of chronic MPD
marro fibrosis is greatly increased
how to calculate LAP stain
multiply the number and grade, then add ‘em up
WHO blast criteria vs FAB criteria
WHO: >20% blast
FAB: >30% blasts in bone marrow
immunophenotyping for WHO
Lymph progenitor: CD34
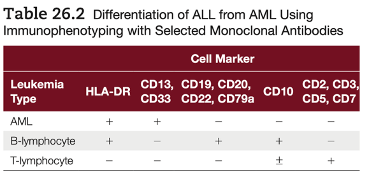
cytochemical stains for WHO
MPO and SBB (+) for AML and (=) for ALL
cytochemical stains for FAB
M1-4: MPO, SBB, CAE (+)
M0: all = stains
M5: ACP, non-specific (+)
M6a: MPO, specific esterase, SBB (+)
M6: Acid phosphatase
M7: PAS (+)
FAB immunophenotyping
is used
how to differentiate WHO ALL?
immunophenotype, cytochemical lymphocytes (T, B, NK cells), and clinical features
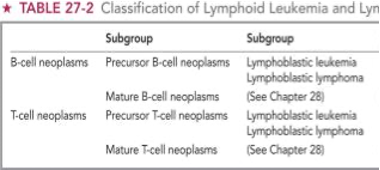
how to differentiate WHO ALL?
Acute: L1 L2
Burket’s Mature: L3
L1: Lymphoblastic Leukemia with homogeneity
L2: Lymphoblastic leukemia with heterogeneity
L3: Burkitt-type lymphoblastic leukemia
how to differentiate WHO AML

how to differentiate FAB AML
Blast count, degree of dyspoiesis, cytochemical cell reactions
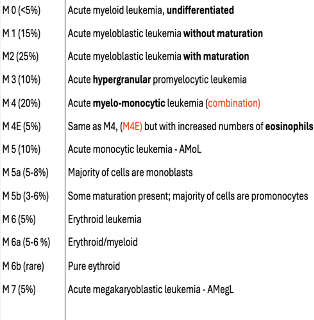
WHO MDS subgroups
MDS Subgroups:
1. MDS with single lineage dysplasia (MDS-SLD)
2. MDS with ring sideroblasts (MDS-RS)
• MDS-RS and single lineage dysplasia (MDS-RS-SLD)
• MDS-RS and multilineage dysplasia (MDS-RS-MLD)
3. MDS with multilineage dysplasia (MDS-MLD)
4. MDS excess blasts (MDS-EB)
• MDS-EB-1
• MDS-EB-2
5. MDS with isolated del(5q)
6. MDS, unclassifiable
7. Childhood MDS
• Refractory cytopenia of childhood (provisional)
what’s the NBT test and reaction?
detect affected neutrophils in chronic granulomatous disease (CGD). If the neutrophil is able to produce the oxygen burst normally, it will reduce the NBT to a blue-black compound that makes the cell appear like a dark crystal. The affected cells cannot produce oxygen so they will not turn dark.
During a respiratory burst, there is a combination of metabolic activities. Phagocytosis increases that oxygen consumption 2-3 times, and glucose oxidation 2-10 times.
what condition is NBT test diagnostic?
Chronic Granulomatous Disease, since the cells are morphologically normal but cannot make the H2O2 metabolites, so the patients suffer from recurrent infections.
what type of lymphoma is Burkitt?
B-cell lymphoma
Burkitt lymphoma describe the different types
Endemic Burkitt: EBV and involves the face and jaw
HIV associated Burkitt: EBV, and causes a “starry sky” biopsy of neoplastic cells. The sky is the neoplastic lymphs and stars are the body macrophages. The macrophages get ingested. The cells affected are the intense cytoplasmic vacuolization of ALL blasts, and the ingested macrophages.
burkitt lymphoma positive stains
CD19, sIg, CD10, CD20, CD22
burkitt lymphoma negative stains
CD5, CD23, Tdt
how to differentiate burkett lymphoma from other lymphomas/leukemias?
C-MYC gene, which impacts the t(8;14), which is not found in DCLBCL
Starry sky, sIg+, t(2,8), t(8,22)