biopsychology
1/101
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
102 Terms
neuron
a nerve cell that sends messages throughout the body, the basic cell of the nervous system
dendrites
receptor sites that receive incoming info from the chemical neurotransmitters
receptor site
where neurotransmitters bond, works like a lock and key (only certain neurotransmitters can fit in certain receptor sites)
dendritic trees
more than one set of dendrites
soma (cell body)
the core section of the neuron that contains genetic information, maintains the neuron’s structure and provides energy to drive activities
nucleus
the control center of the cell in the soma which controls the cell’s activities and contains its genetic material
myelin sheaths
fatty substance that acts as an insulating layer around the axon. allows electrical impulses to transmit quickly and effectively throughout the nerve cell. exists to keep the message intact and travel quickly, so, if damaged impulses slow down
myelinated neurons are mostly in the NS
axon
a long tail-like structure that carries nerve impulses away from the cell body to the axon terminals
length can vary depending on where it is (some go from spinal cord to toe)
axon terminals
end of the neuron where it reaches out to make connections and transmit messages to other neurons at the synapse
convert electrical signals (in neuron) to chemical signals (neurotransmitters)
terminal buttons or terminal sacs
small knobs at the end of axon terminals that hold and release neurotransmitters
synapse (synaptic cleft)
the space between each neuron where they connect and communicate w each other
how a neuron fires (just list 1-6)
resting potential
threshold
action potential/neural impulse/ impulse
release
refractory period
reuptake (sometimes)
hnf - resting potential
it is ready to receive the signal, but is at rest
it is polarised w a neg charge compared to the pos charge outside the cell
membrane is semi-permeable
hnf - threshold
reaches this point when enough neurotransmitters bond to dendrites
in this stage, the neuron will fire (all or nothing)
membrane is now permeable (interactions between + and - ions)
all or none law - hnf
once the stimulus threshold is met, the neuron fires
hnf - action potential/neural impulse/ impulse
an ELECTRICAL signal is sent down the axon where there is a collision of pos & neg ions, and its loses its neg charge (depolarisation)
neurons always fire at full strength so the signal doesn’t weaken as it travels
hnf - release
terminal buttons release neurotransmitters in the synapse. CHEMICAL LANGUAGE.
these release neurotransmitters bind to the receptor sites of the next cell
hnf - refractory period
very brief period (fraction of a millisecond) where the neuron can’t fire
it repolarises and returns to resting potential gradually
hnf - reuptake (sometimes)
when the 1st neuron reabsorbs unused neurotransmitters
they’re recycles and reused in the next cycle
neurotransmitters
chemical messengers; they carry messages from one neuron to another cell (nerve. muscle, gland cell)
makes sure the body functions normally
acetylcholine (ACh)
an excitatory neurotransmitter that enables voluntary muscle movement, aids in memory production (hippocampus) and learning
ACh - associated conditions
alzheimer’s disease - linked w low levels of ACh
memory erodes, muscles weaken, decline in thinking, learning and organising
usually affects people 65 or older
dopamine
involved in muscle movement, pleasurable reward and motivation, behaviour, cognition, attention, sleep, arousal, mood, learning and impulse control
“feel good hormone” - gives you a sense of pleasure and motivation, humans actively seek doing things that release dopamine (reward system)
dopamine - associated conditions
parkinson’s disease - linked to low dopamine; an age-related degenerative brain condition that causes parts of the brain to deteriorate. causes slowed movements, tremors, depression, decreased mobility, gut problems, mild cognitive problems, etc.
schizophrenia - linked to excess dopamine; characterised by erratic behaviours, hallucinations, delusions, disconnection from reality, etc.
serotonin
influences mood by acting as the body’s natural “feel-good chemical”; digestion (90% of serotonin found in gastrointestinal tract), hunger, sleep (quality) & arousal
can raise levels by exercising or eating foods that contain it
serotonin - associated conditions
depression and other mood and anxiety disorders are linked to low serotonin levels
endorphins
acts as a natural pain-reliever that’s made in the pituitary gland and hypothalamus
released when the body feels pain or stress to temporarily turn off the body’s feeling of pain
also released during pleasurable activities (ex: runner’s high)
endorphins - associated conditions
low release can cause depression, body aches, addiction, sleep issues
norepinephrine
excitatory neurotransmitter that acts as the brain’s version of adrenaline to increase alertness, arousal and attention
is released during fight-or-flight and causes adrenaline to release
norepinephrine - associated conditions
low levels can be related to depressed mood, anxiety disorders, etc.
high levels are associated w bipolar disorders
GABA
main inhibitory neurotransmitter that lessens a nerve cell’s ability to receive or send messages
slows down brain function & has a calming effect to control nerve cell hyperactivity
reduces stress & anxiety
improves sleep
GABA - associated condition
undersupply is linked to seizures, tremors, insomnia, anxiety and mood disorders
glutamate
the most abundant excitatory neurotransmitter (makes more likely a message will travel)
affects learning and memory bc it spreads info quickly
activity is high when awake and in REM sleep
also called MSG (monosodium glutamate) in food
glutamate - associated conditions
oversupply can overstimulate the brain, producing migraines or seizures
can damage the brain if optimal conditions deviate too much
endocrine system
the body’s glands and organs that release hormones into the bloodstream
pituitary gland
“master gland” of the endocrine system that releases many hormones into the bloodstream
is a pea-sized gland at base of brain below hypothalamus
regulates growth and controls other endocrine glands
controlled by the hypothalamus
releases growth hormones
also apart of the forebrain
adrenal glands
small triangle-shaped glands on top of each of 2 kidneys
released hormones to manage bodily processes like metabolism, blood pressure, stress response, etc.
releases adrenaline
hormones
chemical messengers produced by the endocrine system that travel through the bloodstream to affect bodily functions
adrenaline (epinephrine)
released by adrenal glands in response to stress - causes fight-or-flight response as part of the sympathetic NS
allows the body to metabolise energy sources faster
causes “cold sweat” - where you’re sweating when you’re not hot or physically active bc you perceive smth as stressful
oxytocin
connected to love and social bonding
released during childbirth to stimulate contractions, lactation and promote pair bondings betw. mom & baby
promotes group cohesion and social trust
made by hypothalamus but posterior pituitary gland stores and releases it
females have higher levels than males
more than 20s of skin-to-skin contact can increase levels
positive feedback loop (releasing causes more to be released and produced)
causes “tend and befriend response” - helping others first in stressful situations
melatonin
plays a role in managing sleeping and waking cycles (Circadian rhythm - 24hr cycle); body temp; overall mood
more of this makes u drowsy & helps u fall asleep
hypothalamus tracks daylight & regulates the release of melatonin
can be related to sleep disorders
the nervous system
body’s control center made of the CNS & peripheral NS f
Central Nervous System (CNS)
brain + spinal cord
takes in info from sensory nerves to process & respond to the,
3 main functions of the CNS
receive sensory info
process info it receives (integration)
respond w/ motor output
CNS - brain
regulates thoughts, feelings & mvmts
brain sends messages to spinal cord that sends messages to nerves (peripheral NS) to complete an action
signals are constantly travelling to keep the body functioning
interneurons
neurons found exclusively in the CNS that act as the “middle man” between sensory neurons and motor neurons; sends messages within CNS
CNS - spinal cord
column of nerves (bundle of axons) that come together encased in bone found in the vertebral column
CNS - spinal cord function
send motor commands from the brain to the peripheral body & relay info from the sensory organs to the brain
CNS - spinal cord - reflex
ability to direct behaviours in a limited but very specific way called a reflex
a basic involuntary response-innate-that is designed to protect the individual that doesn’t require the brain to interpret it
peripheral nervous system (peripheral NS)
rest of the NS outside of the CNS
key role in sending info from diff areas of the body back to the brain
carries out commands from the brain to various parts of the body
peripheral NS - 3 main functions
sense the environment/ body (somatic)
movement (somatic)
unconscious processes (autonomic)
sensory neurons
nerve cells that are responsible for detecting & transmitting sensory info from the env to the body or body to CNS for processing
important to how we respond to outside stimuli & our senses
motor neurons
nerve cells that carry messages FROM CNS to muscles & glands
enables mvmt and other motor functions
somatic nervous system
“skeletal nervous system”
all of the muscles connected to bone
in charge of voluntary mvmt
motor neurons travel via the somatic NS to stimulate skeletal muscles leading to contractions & mvmts
uses sensory neurons to relay info (touch, temp, pain) to CNS & involved in reflexes
autonomic nervous system
regulates involuntary physiological processes
ex: heart rate, digestion, breathing
governs the “vegetative state” where internal bodily processes still function normally but somatic processes do not
biofeedback
trying to exert control over smth that is automatic
Sympathetic Nervous System
Involved in the flight-or-fight response
Stress
Uses adrenaline, norepinephrine and endorphins
Flight or fight response
Automatic physiological response that activates in times of stressful or threatening situations to prepare the body for physical actions either fighting off danger or fleeing
Physical response from fight or flight
Dilates pupils
Blood and oxygen are redirected to leg and arm muscles
Heart rate and blood sugar increase
Energy sources are metabolised faster to provide energy surge
Airways open up for more oxygen
Inhibits digestion
Endorphins make you sweat and not feel pain
Possible urination or defecation in extreme cases
Parasympathetic nervous system
Responsible for calming the body down and conserving energy after a stressful situation
Return to homeostasis
Promotes relaxation of bodily functions
Slows heart rate and metabolism
Constricts pupils
Stimulates digestion
Tend or befriend response
Response to stressful situations where u think of other people’s safety before your own
You form a bond & make connections
Opponent response
Parasympathetic NS counteracts the effects of the Sympathetic NS
Both in the autonomic NS in peripheral NS but work in opposition
Brain
Hindbrain structure
Most primitive of the 3 major regions of the brain
Located on the posterior (back) of the brain
Plays a crucial role in regulating basic life functions like heart rate, breathing, balance and coordination
Contains the brain stem (pons and medulla) and cerebellum
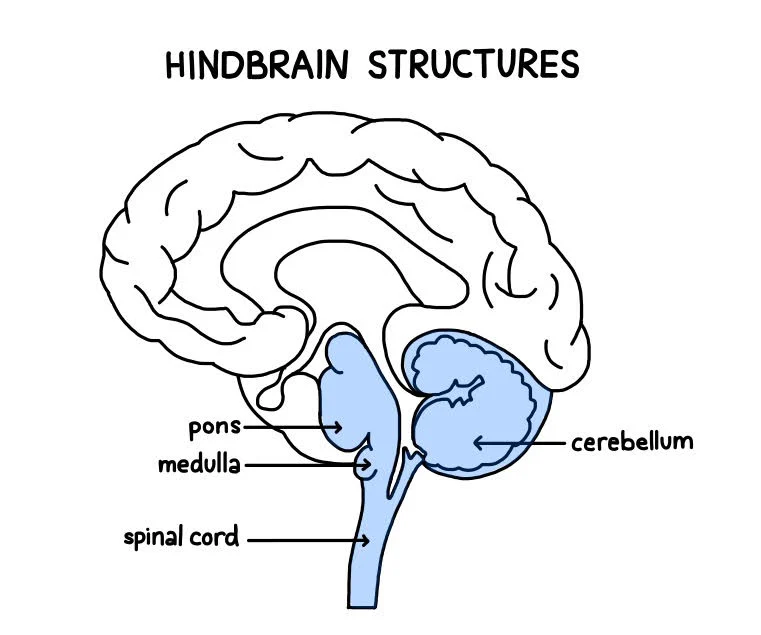
Cerebellum
Located at the back of the brain extending from the rear of the brainstem beneath the cerebral cortex
Crucial for coordinating voluntary movements by fine tuning motor control, balance & posture, motor learning, timing & precision
Stores implicit memories
Called “little brain” bc of its size & appearance
Medulla
Connects the brain and spinal cord (base of brain, top of spinal cord) and surrounds the spinal cord
Involved in regulating essential autonomic functions like heart rate, breathing & reflexes
Pons
Located above the medulla in front of the cerebellum and serves as a bridge between different parts of the brain
Involved in sleep, arousal, relaying info, breathing (secondary)
Midbrain structure
Smallest part of the brainstem
Huge role in alertness
Above hindbrain & below forebrain
Bridge between them
Reticular Activating System/ Reticular Formation (RAS)
A network that spans from the brainstem to the midbrain
Critical for sustaining consciousness, sensory processing and attention
Damage to the RAS can induce coma/vegetative state/ sleep disorders
Forebrain structure (cerebrum)
Most complex & large (takes up 70%)
Allows for complex behaviour and thinking processes
Made of the limbic system, corpus callosum & cerebral cortex
Limbic system
Complex set of structures involved in emotion, memory & motivation
Located in the inner edges of the cerebral cortex
Plays an essential role in regulating emotional responses
Contains the amygdala, hippocampus, hypothalamus and thalamus
Amygdala
Small almond shapes cluster of neurons deep within the temporal lobe above the brainstem
Essential for processing and modulating extreme emotions
“Panic button” of flight or fight response
Hippocampus
Small curved structure in the medial temporal lobe above
Memory formation/storage (converts STM to LTM during sleep) & spatial navigation
Holds declarative/ explicit memories
Left hippocampus
Holds semantic memories (language, learning, logic, linguistics, general knowledge)
Holds episodic memories (events, episodes of your life-personal memories). The analytic part of the brain that deals w facts, events & explicit info (remembers phone #s, stories)
Right hippocampus
More visual side that helps w colour, shapes, creativity spacial memory (locations, physical spaces, ect. w/ mental map) by integrating memory info w/ senses; and performing tasks of visual or spatial nature(dancing, drawing, ect.)
Hypothalamus
small structure below the thalamus that plays a crucial role in maintaining homeostasis and regulating physiological functions(hunger, thirst; body temp; sex; aggression) acting as the major link between the endocrine system and the Nervous System(controls release of hormones in pituitary gland).
regulates emotional and behavioral responses
Damage can lead to disruptions of homeostasis, sleep disorders, endocrine disorders, obesity or starvation, emotional dysregulation or sexual dysfunction
thalamus
Sits on top of the brainstem above the RAS as the brain’s “relay station” the processes and relays sensory info to the cerebral cortex; essentially acts as the gatekeeper of sensory signals(except olfactory) to be involved w/ perception, movement and cognition. Blocks sensory input during sleep(regulate sleep w/ RAS)
Damage can lead to sensory deficits, emotional disorders, sleep disorders
Corpus Callosum
thick bundle of fibers (myelinated axons) that’s shaped like a C and sits beneath the cerebral cortex
connects the right and left hemispheres to facilitate communication between the 2 sides of the cortex
allows coordination of functions of each side to create unified perception of the world
split brain procedure
procedure where the corpus callosum is surgically severed
usually for people who suffer from grand mal seizures to prevent seizure activity from spreading between the hemispheres
can lead to split brain syndrome
split brain syndrome
when the 2 halves of the brain can no longer communicate directly
cerebral cortex
the outer layer of cells wrapped around the brain
referred to as grey matter (lack of myelinated neurons)
most advanced part of the brain that integrates info from various regions to produce conscious experiences
frontal lobe
largest region located at the front of the brain
plays a central role in many higher executive functions
functions of the frontal lobe
critical for executive functions - mental skills (plan, organise, manage tasks, decision making etc)
primary motor area - responsible for initiating voluntary movement by sending motor commands throughout the body
premotor cortex
located in front of the primary motor cortex to plan and coordinate complex movements and actions
prefrontal cortex
most-front part of the frontal lobe
responsible for higher-cognitive functions like decision making, problem solving, personality, emotional regulation & social behaviour
last part of the brain to fully develop
parietal lobe
located near the top and back of the brain
essential role in processing sensory info from the body’s sensory neurons
primary somatosensory cortex
map of sensory receptors that’s responsible for processing tactile info to understand & navigate the environment
plays a role in mathematical reasoning and processing numerical info
damage can result in sensory processing disorders, spatial awareness, motor coordinations, mathematical task issues
occipital lobe
smallest lobe located in the back of the brain behind parietal & temporal
essential for seeing and interpreting the visual world
helps recall visual experiences
primary visual cortex
first area of the cerebrum to receive visual input from eyes
processes raw visual data (light, colour & basic shapes)
allows you to process visual info w other complex visual stimuli in coherent spatial manner
temporal lobe
2nd largest lobe located on the sides of the brain (temples)
important for processing hearing and language
primary auditory cortex
processes raw sound info to analyse and interpret noises to familiarise & differentiate
damage can result in language disorders, difficulty hearing & understanding others
which part of the brain controls which side of the body?
the brain controls opposite sides of the body (left control right & right control left)
aphasia - broca’s area
left frontal lobe
involved in language production, specifically the muscle movement needed to produce speech
damage to this region can cause motor/broca’s aphasia where speech production is impaired or there are problems moving muscles to make sound
people w this speak slowly w short, grammatically incorrect sentences
rare to be completely destroyed
aphasia - wernicke’s area
left temporal lobe
involved in understanding speech
helps understand spoken & written language
damage to this area causes Wernicke’s aphasia: where a person can speak fluently but has trouble understanding others
EEG
quick & harmless method that uses electrodes placed on the outside of the head that detects brainwave activity
most simple method to study the brain
used for sleep studies bc the brain emits diff waves at diff levels of consciousness - waves get slower deeper into sleep
used for someone who’s been in an accident that affected their brain to see if they’re emitting the wrong waves for their consiousness
ablation
destroying brain issue where it can not be reversed by surgically removing it
irreversible (no remaining plasticity)
most invasive technique to study the brain
ex. lobotomy, split-brain procedure l
lesion
an area of damage or abnormality within the brain tissue
plasticity
the brain can “heal” itself to an extent
CT scan/ CAT scan (computerised tomography)
“sophisticated X-ray”
a series of x ray photos taken from diff angles and combined by a computer to create composite images of the brain’s structure to show injuries, tumours or strokes
pros: cheap & easy
cons: images are not super clear
MRI (magnetic resonance imaging)
constructs an image of the brain by passing a magnetic field and radio waves over the head to produce detailed images of the brain’s soft tissue & structure
pros: provides very clear images
cons: high costs, high maintenance, takes longer