L9: Functional Anatomy of the PNS
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
what kind of neurons carry SENSORY information from receptors in the skin and organs TO the CNS?
Afferent Neurons
Where are the cell bodies of afferent neurons located?
Outside of the spinal cord and brainstem
What kind of neurons carry MOTOR information FROM the brain to the PNS?
Efferent neurons
Where are the cell bodies of efferent neurons located?
In the ventral horn of the spinal cord
What are the 4 types of somatosensory receptors?
1- Mechanoreceptors
2- proprioceptors
3- Thermoreceptors
4- Nociceptors
Which kind of somatosensory receptor detects touch, pressure, stretchings, and vibration?
Mechanoreceptors
What kind of somatosensory receptor provides continuous information about the body and limb position?
Proprioceptors (spacial awareness)
What kind of somatosensory receptor consists of free nerve endings that respond to temperature?
Thermoreceptors
What kind of somatosensory receptors consists of free nerve endings that respond to extreme mechanical, thermal, or chemical stimuli and initiate the sensation of pain?
Nociceptors
Sensory receptors convert stimuli into ____ impulses that are transmitted by _____ neurons from the ______ to the brainstem or ____ ____.
electrical
Sensory
PNS
Spinal cord
What 2 factors of a neuron influence the conduction velocity of action potentials?
1- neuron diameter
2- myelination
Is conduction velocity of a neuron faster or slower when myelination is present?
FASTER
Is conduction velocity of neurons faster or slower with a smaller neuron diameter?
SLOWER
What is a spinal reflex?
A rapid, predictable, involuntary response to a stimulus involving the spinal cord
What is a stretch reflex?
Quick stretch of a muscle (activated muscle spindles) that causes contraction of the muscle being stretched
What is a withdrawal reflex?
Protective reflex that withdraws a body part from a painful stimulus
If a lower limb is involved in a withdrawal reflex, what happens to the lower limb on the opposite side?
Opposite side extensors contract to support the body
_____ ______ give rise to spinal nerves that branch into posterior (dorsal) rami and anterior (ventral) rami
Spinal segments
Posterior (dorsal) rami innervate?
Deep back muscles and skin over the back
Anterior rami innervate?
Muscles and skin in the extremities, front and sides of the neck, thorax, and abdomen
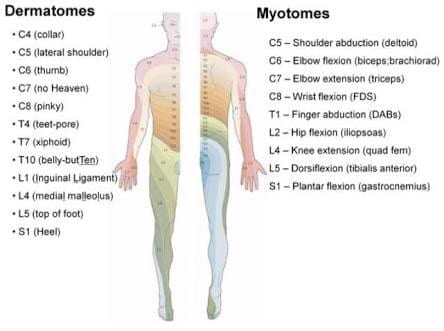
What is the area of skin supplied by a spinal cord segment/spinal nerve called?
Dermatome
is there overlap between adjacent dermatomes?
YES
What are the regional dermatome ranges discussed in class?
C2-C4: neck
C5-T2: upper extremity
C4-L1: trunk
L1-S4: lower extremity
S3-coccygeal nerve: perineum
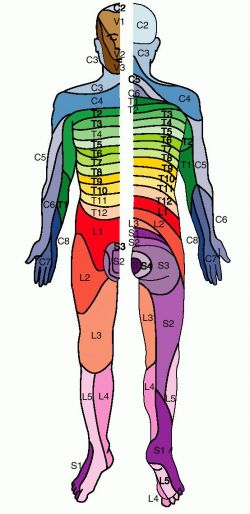
What are the spinal segment innervations of muscle called?
Myotomes
What are the two major myotomes discussed in class?
upper extremity: C5-T1
Lower extremity: L1-S3
What spinal segments make up the cervical plexus?
C1-C4
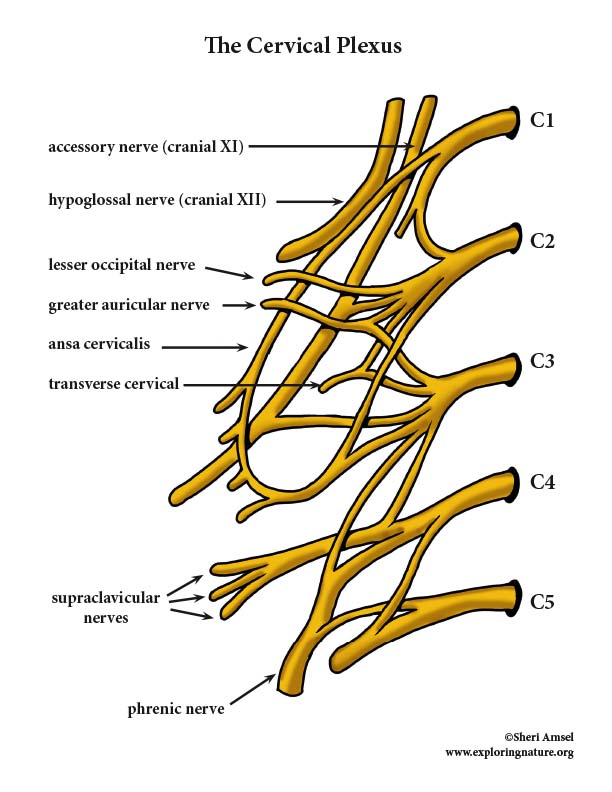
What does the cervical plexus innervate?
Skin of the anterior and lateral neck, some anterior neck muscles, and the phrenic nerve
What spinal segments make up the brachial plexus?
C5-T4
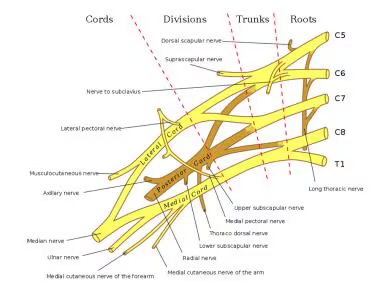
What does the brachial nerve innervate/what are its branches?
provides motor and sensory to the upper limb
Major nerves: axillary, radial, musculocutaneous, median, and ulnar
What spinal segments make up the lumbosacral plexus?
L1-S4
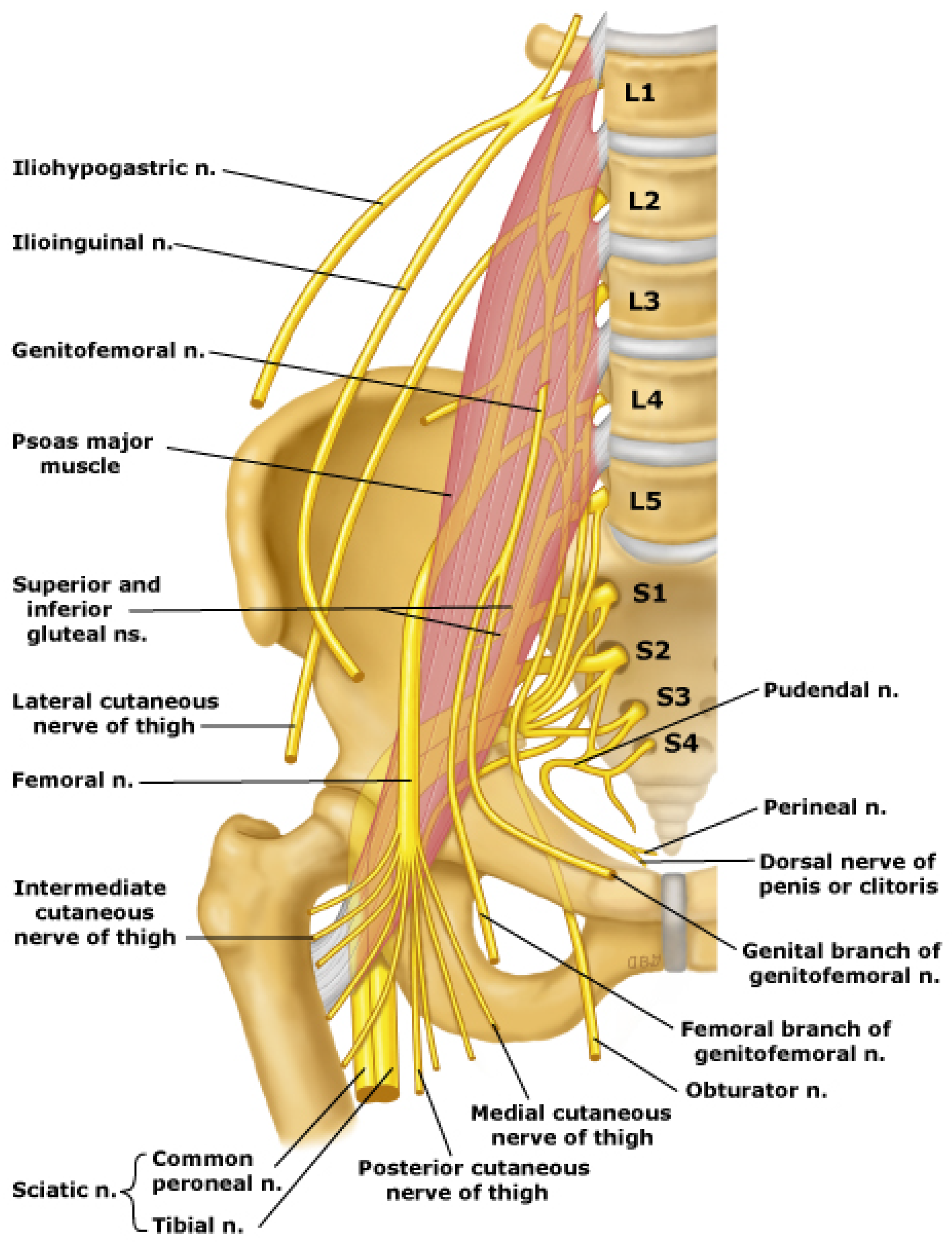
Where does the lumbosacral plexus supply innervation to?
The lower extremity and perineum
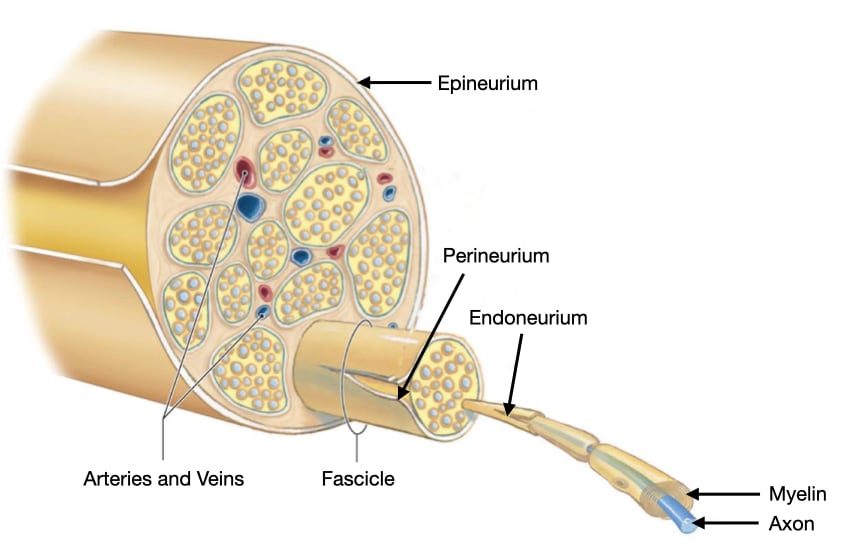
What is the function of connective tissue in nerves?
Protection and support
Does the connective tissue in nerves contain blood vessels?
YES
What are the layers, from superficial to deep, of the connective tissue in nerves?
Epineurium → perineurium → endoneurium