Thermochemistry
1/39
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Study of chemical reactions and the energy changes involving heat.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
40 Terms
Potential Energy
energy an object possesses by virtue of its position or chemical composition
First Law of Thermodynamics
Energy can be converted from one form to another, but it is neither created nor destroyed.
Energy is released when bonds are
Formed
Energy is consumed when bonds are
Broken
Open System
can exchange heat and mass with its surroundings.
Closed System
can only exchange heat with the surroundings (not mass).
Isolated System
cannot exchange heat or mass with the surroundings.
The “system” refers to the
chemicals
The “surroundings” refer to
everything else (aka NOT chemicals)
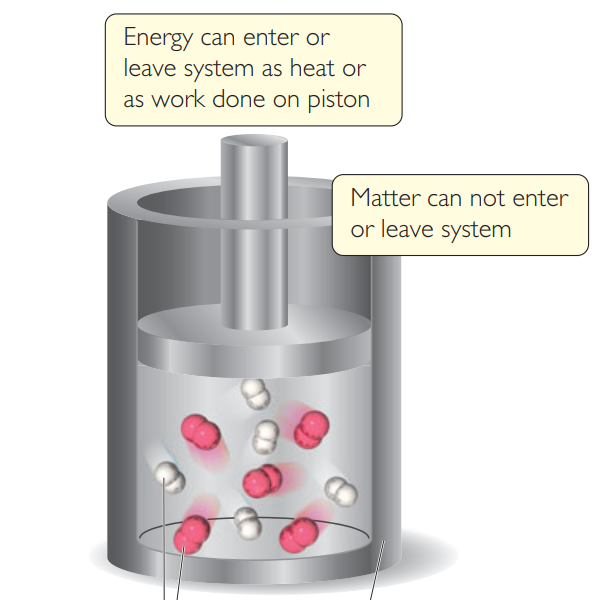
What kind of system is this?
Closed
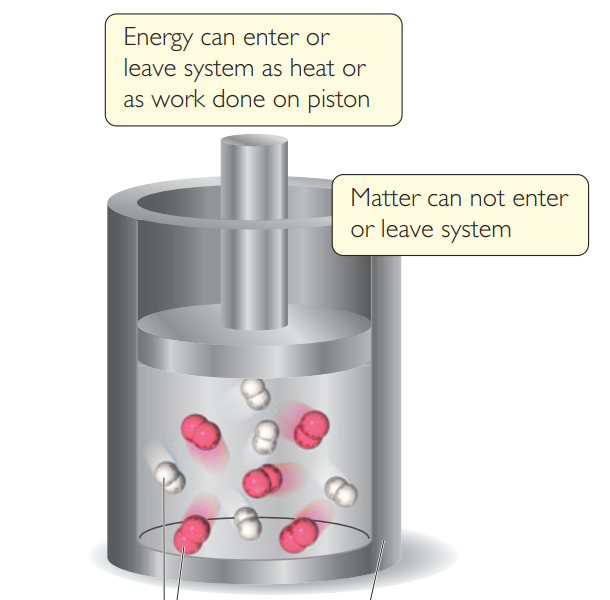
In this photo, hydrogen and oxygen is
the system
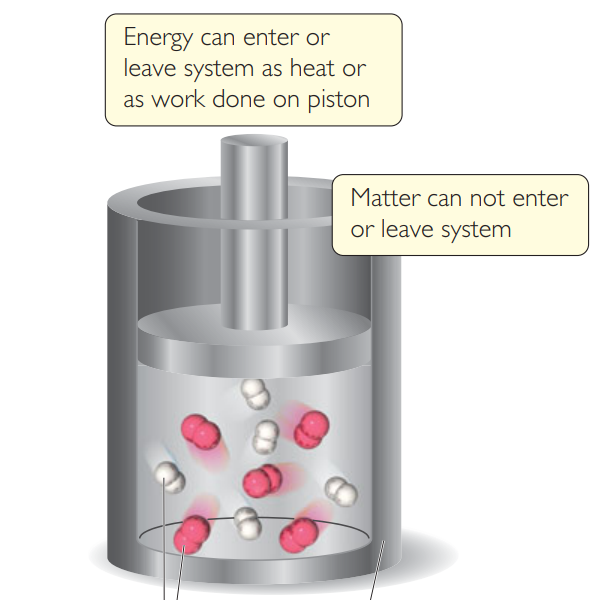
In this photo the cylinder is
The surroundings
What is Internal Energy (E)?
sum of all kinetic and potential changes of the system.
We generally don’t know (E), we only know…
how it changes
In a chemical reaction, the initial state of the system (E initial)
refers to the reactants.
In a chemical reaction, the final state of the system (E final)
refers to the products
In this example
H2 (g)+ O2 (g) —> 2H2O (l)
The system will…
Lose energy because bonds are beings formed.
Exergonic
When the system releases energy from the surroundings.
Exergonic will give a ______ value
negative
As a system undergoes a change,
its internal energy can change, and energy can be transferred
When the system gains heat, q will have a _____ value.
positive
When the system loses heat, q will have a ______ value.
negative
When the work is done by the system on the surroundings
(w) will have negative values.
When the work is done on the system by the surroundings (w)
will have positive values.
Endergonic
When a system absorbs energy from the surroundings.
Endothermic
Heat is absorbed by the system from the surroundings
Exothermic
Heat is released by the system into the surroundings.
Because internal energy (E) is a state function,
it depends on the current state of matter, but not how it got to that state of matter.
Enthalpy
The internal energy plus the product of pressure and volume
The value of enthalpy cannot be measured but..
the change of enthalpy can
When a process takes place in constant pressure, and only volume and pressure do work
then we can account for heat flow by measuring the enthalpy of the system.
Enthalpy of reaction ΔH
The change in enthalpy, or also known as change in heat
The process is endothermic when the ΔH value
is positive
The process is exothermic when the ΔH value
is negative
Enthalpy is an _____ property, meaning it _______ on mas
extensive; depends
Enthalpy is a _____ function.
state
The enthalpy change for a reaction is _____ in magnitude, but ______ in sign.
equal; opposite
What is Internal Energy (E)?
sum of all kinetic and potential changes of the system.
Enthalpy is useful for
discussing heat flow in processes that occur under constant pressure.
state function (or state variable)
depends on the current state of matter, however it does not care how it got to that state.