RBC 13 study document
1/31
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
32 Terms
I. Normal Red Blood Cell Physiology
1. Developmental Sites of Hematopoiesis
• Yolk Sac: Initial site in very early embryogenesis.
• Liver & Spleen: Predominant in newborns.
• Bone Marrow:
o Children: Active (red) marrow in axial and appendicular skeleton.
o Adults: Active marrow in axial skeleton only (appendicular skeleton has yellow
marrow).
2. Bone Marrow Features
2. Bone Marrow Features
• Cellularity: Ratio of hematopoietic cells to fat.
• Megakaryocytes: Platelet precursors.
• M:E Ratio: Normal myeloid to erythroid ratio ~3:1.
• Other Features:
o Myeloid & erythroid maturation.
o Plasma cells, lymphocytes, hemosiderin (storage iron), possible foreign cells.
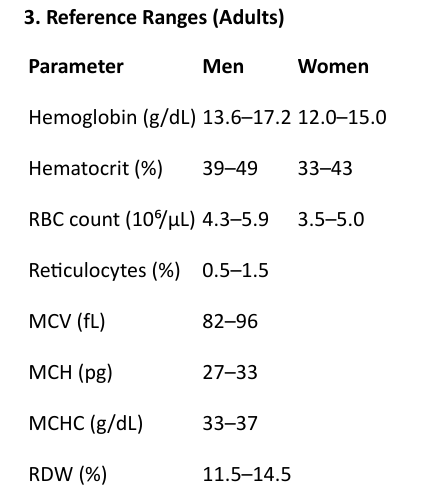
3. Reference Ranges (Adults)
II. Anemias
Defined as reduced oxygen-carrying capacity of the blood. Can result from loss, destruction, or
decreased production of red cells.
General Features of Anemia
• Pallor (skin, mucosa)
• Fatigue, weakness
• Dyspnea (due to hypoxia)
• Palpitations, tachycardia
• High-output heart failure (compensatory)
III. Classification of Anemias, A. Blood Loss
A. Blood Loss
1. Acute:
• Due to trauma.
• Normocytic, normochromic anemia initially.
2. Chronic:
• GI lesions, gynecologic disturbances.
• Often presents like iron-deficiency anemia.
III. Classification of Anemias, B. Hemolytic Anemias (Increased Destruction)
B. Hemolytic Anemias (Increased Destruction)
Life span of RBCs <120 days, increased erythropoietin, marrow hyperplasia, elevated bilirubin, serum
HGB.
Types:
a) Hereditary:
• Membrane Defects: Hereditary spherocytosis.
• Enzyme Defects: G6PD deficiency.
• Hemoglobinopathies: Sickle cell disease, thalassemias.
b) Acquired:
• Membrane Defect: Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH).
• Immune-mediated: Transfusion reactions, autoantibodies.
• Mechanical: Valves, microangiopathies (TTP, HUS).
• Drugs/Infections: Toxins, malaria, DIC.
Hemolysis Types:
• Intravascular: Within vessels; hemoglobinemia, hemoglobinuria.
• Extravascular: Spleen and liver.
Key Modifiers:
• MCV: Micro/macrocytosis
• MCH, MCHC: Hypochromia
• RDW: Anisocytosis
III. Classification of Anemias, C. Decreased Production (Impaired Erythropoiesis)
C. Decreased Production (Impaired Erythropoiesis)
Mechanisms:
• Stem cell disturbances (Aplastic anemia, pure red cell aplasia)
• DNA synthesis defects (B12, folate deficiency → megaloblastic anemia)
• Heme synthesis defects (iron deficiency)
• Globin synthesis defects (thalassemia)
1. Hereditary Spherocytosis
1. Hereditary Spherocytosis
• Autosomal dominant.
• Defective ankyrin, spectrin.
• Spherocytes, anemia, jaundice, splenomegaly, gallstones.
2. G6PD Deficiency
2. G6PD Deficiency
• X-linked recessive.
• Triggers: fava beans, infections, oxidant drugs.
• Heinz bodies, hemolysis, hemoglobinuria.
3. Sickle Cell Disease
3. Sickle Cell Disease
• HbS (β6 Glu→Val); autosomal recessive.
• Vaso-occlusion, pain crisis, autosplenectomy, infections.
4. Thalassemias
4. Thalassemias
• Impaired α or β globin synthesis.
• Microcytic, hemolytic anemia.
• Skull "crew cut" on x-ray.
o Hemoglobin H Disease: 3 α-globin gene deletions.
o Hydrops Fetalis: 4 α-globin gene deletions.
5. Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)
5. Paroxysmal Nocturnal Hemoglobinuria (PNH)
• Acquired mutation in PIGA gene.
• Deficient GPI-anchored proteins → complement-mediated lysis.
6. Immunohemolytic Anemias
6. Immunohemolytic Anemias
• Antibodies against RBCs.
• Warm (IgG): idiopathic, malignancy, drugs.
• Cold Agglutinin (IgM): Mycoplasma, mono.
• Cold Hemolysin (IgG): Paroxysmal cold hemoglobinuria.
• Coombs Test:
o Direct: Detect Ab on RBC.
o Indirect: Detect Ab in serum.
V. Non-Hemolytic Anemias (↓ RBC Production) 1. Megaloblastic Anemias
V. Non-Hemolytic Anemias (↓ RBC Production)
1. Megaloblastic Anemias
Defective DNA synthesis, most commonly due to Vitamin B12 or Folate deficiency.
General Features:
• Macrocytic (MCV > 100)
• Hypersegmented neutrophils
• Bone marrow: megaloblasts
Vitamin B12 Deficiency (Pernicious Anemia)
Vitamin B12 Deficiency (Pernicious Anemia)
• Causes:
o ↓ intake (vegetarians),
o ↓ absorption (IF deficiency, gastrectomy, ileal disease)
o Tapeworm, blind loop syndrome
• Neurologic signs (posterolateral spinal cord demyelination)
• Low serum B12
• Failed Schilling test
• Achlorhydria
Folate Deficiency
Folate Deficiency
• Causes:
o Poor diet (alcoholics, infants)
o Drugs (methotrexate, anticonvulsants)
o Increased demand (pregnancy)
• No neurologic symptoms
2. Iron Deficiency Anemia
2. Iron Deficiency Anemia
• Most common anemia worldwide.
• Causes:
o ↓ intake (rare)
o ↑ loss (GI bleeding in men/postmenopausal women; menstruation in
premenopausal women)
• Microcytic, hypochromic
• Low serum ferritin
• Diagnosis:
o Serum ferritin (BEST test)
o Prussian blue stain of marrow (iron stores)
3. Anemia of Chronic Disease
3. Anemia of Chronic Disease
• Chronic infections, immune diseases, cancer, renal failure.
• Functional iron deficiency with abundant hemosiderin in marrow.
• Resembles iron-deficiency anemia.
4. Aplastic Anemia
4. Aplastic Anemia
• Pancytopenia due to stem cell failure.
• Idiopathic or caused by:
o Drugs (chloramphenicol, chemo)
o Viruses (EBV, Hepatitis, VZV)
o Radiation, insecticides
• Fanconi Anemia: Only inherited form.
• “Pure” red cell aplasia = only RBCs affected.
5. Myelophthisic Anemia
5. Myelophthisic Anemia
• Marrow failure due to space-occupying lesions, e.g., metastasis.
VI. Polycythemia
VI. Polycythemia
Types:
• Relative: Hemoconcentration (dehydration).
• Absolute:
o Primary (Polycythemia Vera): Myeloproliferative disorder; low EPO.
o Secondary: High EPO (hypoxia, tumors, EPO doping, high altitude).
VII. Bleeding Disorders (Hemorrhagic Diatheses)
VII. Bleeding Disorders (Hemorrhagic Diatheses)
Categories:
1. Blood vessel wall abnormalities
2. Platelet disorders:
o ↓ Number (thrombocytopenia)
o ↓ Function
3. Clotting factor deficiencies
4. DIC
A. Vessel Wall Abnormalities
A. Vessel Wall Abnormalities
• Infectious: Meningococcemia, RMSF
• Immune/Drug: Vasculitis
• Hereditary:
o Ehlers-Danlos
o Hereditary hemorrhagic telangiectasia
• Other: Scurvy, amyloid, Cushing
B. Thrombocytopenias
B. Thrombocytopenias
Mechanisms:
• ↓ Production (aplastic anemia, leukemia, drugs, viruses)
• ↑ Destruction (ITP, DIC, drugs, HIV)
• Sequestration (hypersplenism)
• Dilutional (massive transfusion)
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
Immune Thrombocytopenic Purpura (ITP)
• Chronic ITP: Adults, autoimmune
o Anti-platelet antibodies
o ↑ megakaryocytes in marrow
o Rx: Steroids
• Acute ITP: Children, post-viral, self-limited
Drug-Induced Thrombocytopenia:
Drug-Induced Thrombocytopenia:
• Quinine, quinidine, sulfa, heparin
HIV:
• Causes both decreased production and increased destruction.
C. Thrombotic Microangiopathies
C. Thrombotic Microangiopathies
• TTP (Thrombotic Thrombocytopenic Purpura)
• HUS (Hemolytic Uremic Syndrome)
• Both involve:
o RBC fragmentation
o Platelet consumption
o High mortality
D. Qualitative Platelet Disorders
D. Qualitative Platelet Disorders
• Inherited:
o Bernard-Soulier (GpIb deficiency)
o Glanzmann thrombasthenia (GpIIb/IIIa deficiency)
o Storage pool diseases
• Acquired: Aspirin use (irreversible COX inhibition)
E. Clotting Factor Deficiencies
E. Clotting Factor Deficiencies
Congenital:
• Hemophilia A: Factor VIII deficiency, X-linked
• Hemophilia B: Factor IX deficiency (Christmas disease), X-linked
Acquired:
• Vitamin K deficiency: Affects Factors II, VII, IX, X
• Liver disease: Impaired synthesis of clotting factors
F. von Willebrand Disease
F. von Willebrand Disease
• Most common inherited bleeding disorder (1%)
• Autosomal dominant
• ↓ vWF → defective platelet adhesion and low Factor VIII
• Prolonged bleeding time, normal platelet count
VIII. Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
VIII. Disseminated Intravascular Coagulation (DIC)
Widespread activation of coagulation → consumption of platelets and clotting factors → bleeding.
Causes:
• Obstetric complications (e.g., abruption, toxemia)
• Infections (e.g., meningococcemia)
• Malignancy (APL)
• Trauma, burns
Features:
• Widespread fibrin deposition
• Organ dysfunction
• High mortality
IX. Laboratory Tests Summary
