IMED1001 - Anatomical Terminologies (Learning Anatomy)
1/74
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
75 Terms
(Prefix) Cardi-
heart
(Prefix) Osteo-
bone
(Prefix) Neuro-
nerve
(Prefix) Myo-
muscle
(Prefix) Auto-
self
(Prefix) Peri-
around
(Prefix) Somato-
body
(Prefix) Epi-
upon, on, above
(Prefix) Hyper-
above (normal)
(Prefix) Hypo-
below (normal)
(Suffix) -ology
study of
(Suffix) -itis
inflammation
(Suffix) -ectomy
removal of
(Suffix) -pathy
disease of
(Suffix) -physis
growth of
(Suffix) -al
pertaining to
(Suffix) -ic
pertaining to
(Suffix) -chondria
cartilage
(Suffix) -gastric
stomach
(Suffix) -cyte
cell
(Root Word) Viscera
internal organs
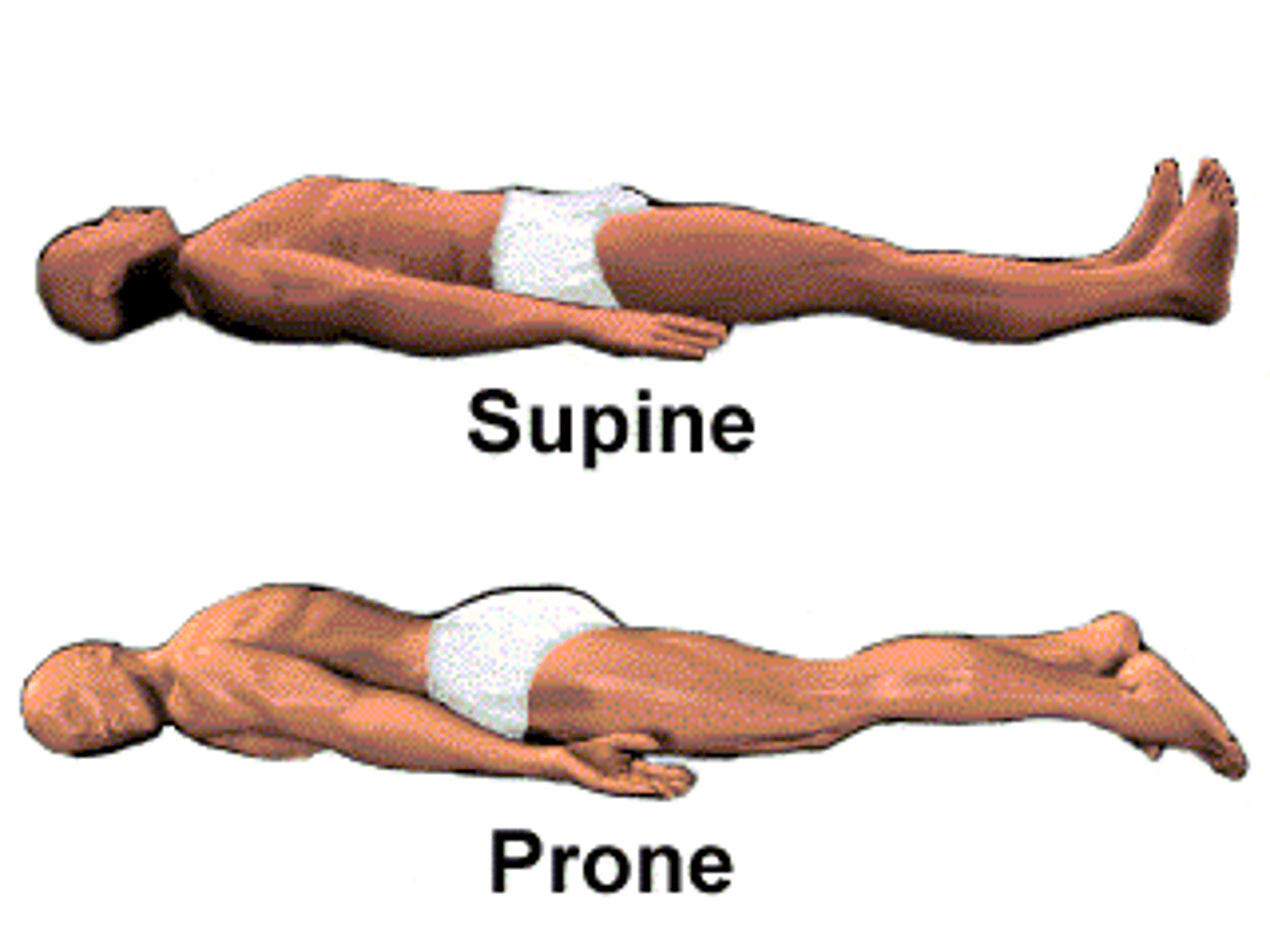
Supine
person lying face up
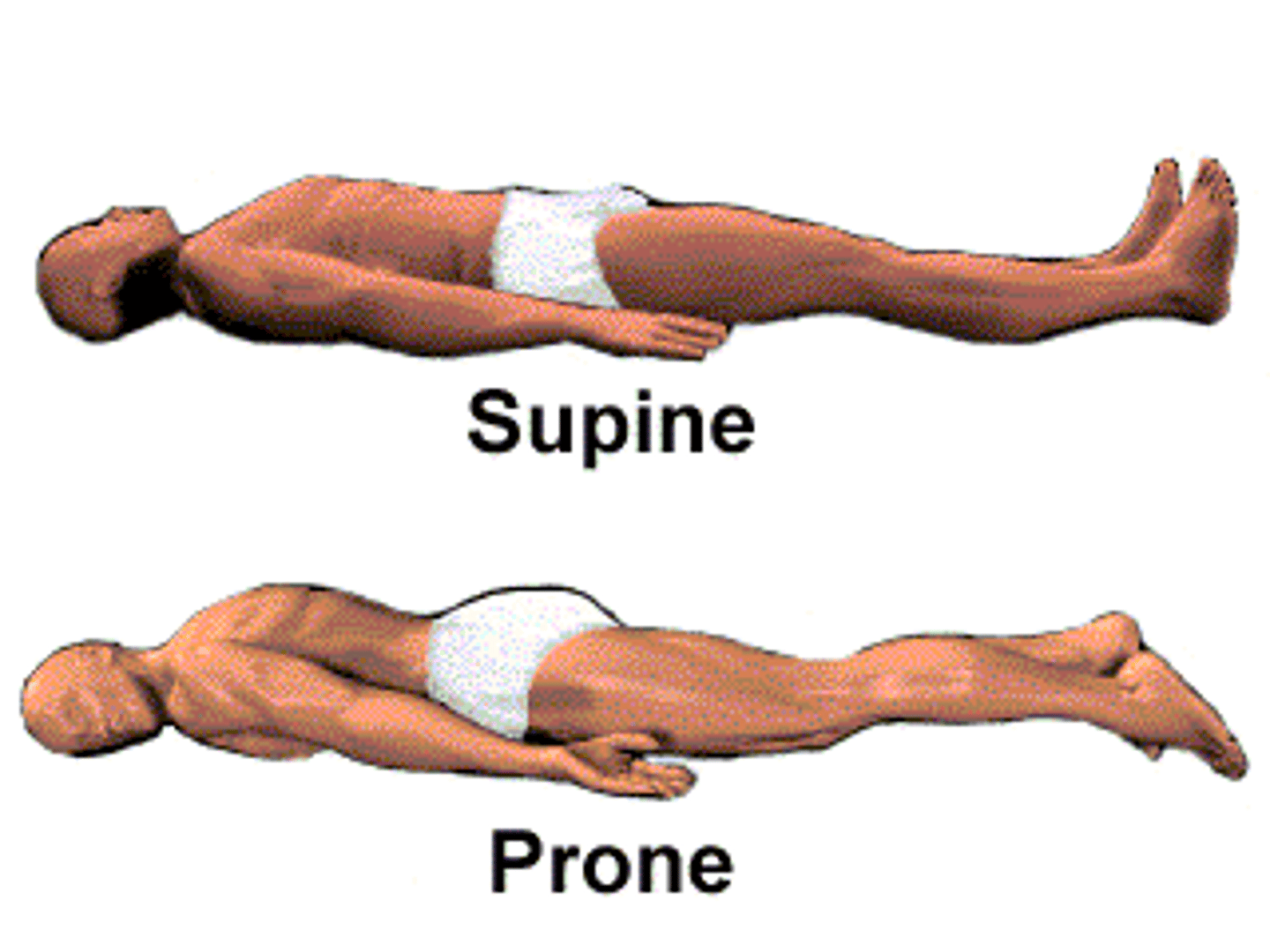
Prone
person lying face down
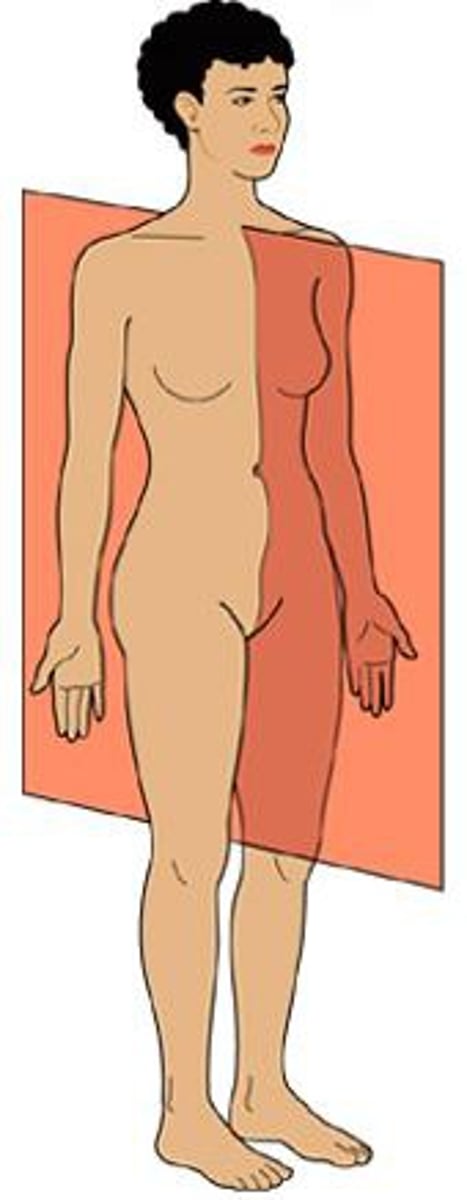
Sagittal Plane
- vertical plane, divides into left and right portions
- Midsaggital/Median: through midline.
- Para-sagittal: parallel to mid-sagital
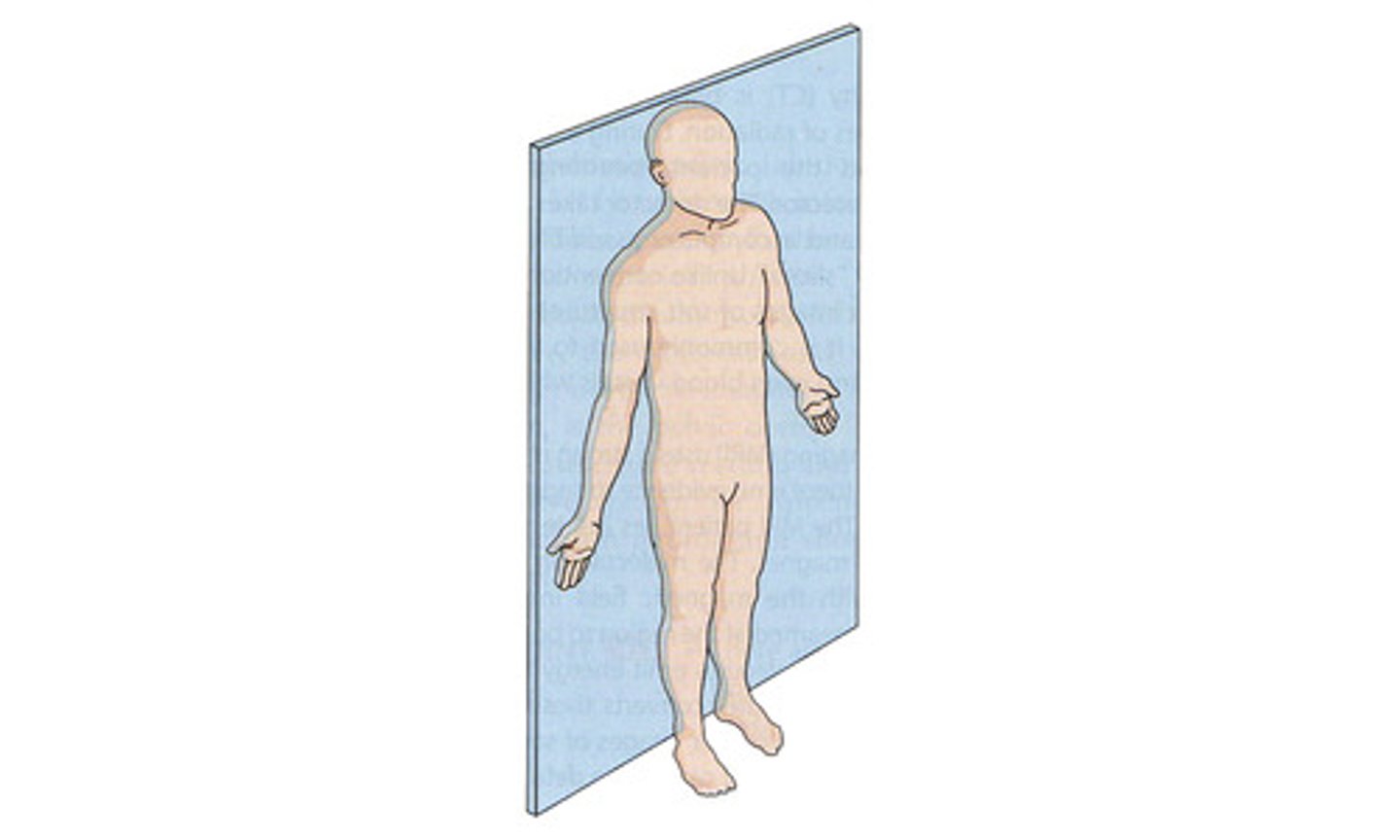
Frontal/Coronal Plane
vertical plane, divides into anterior (front) and posterior (back) portions
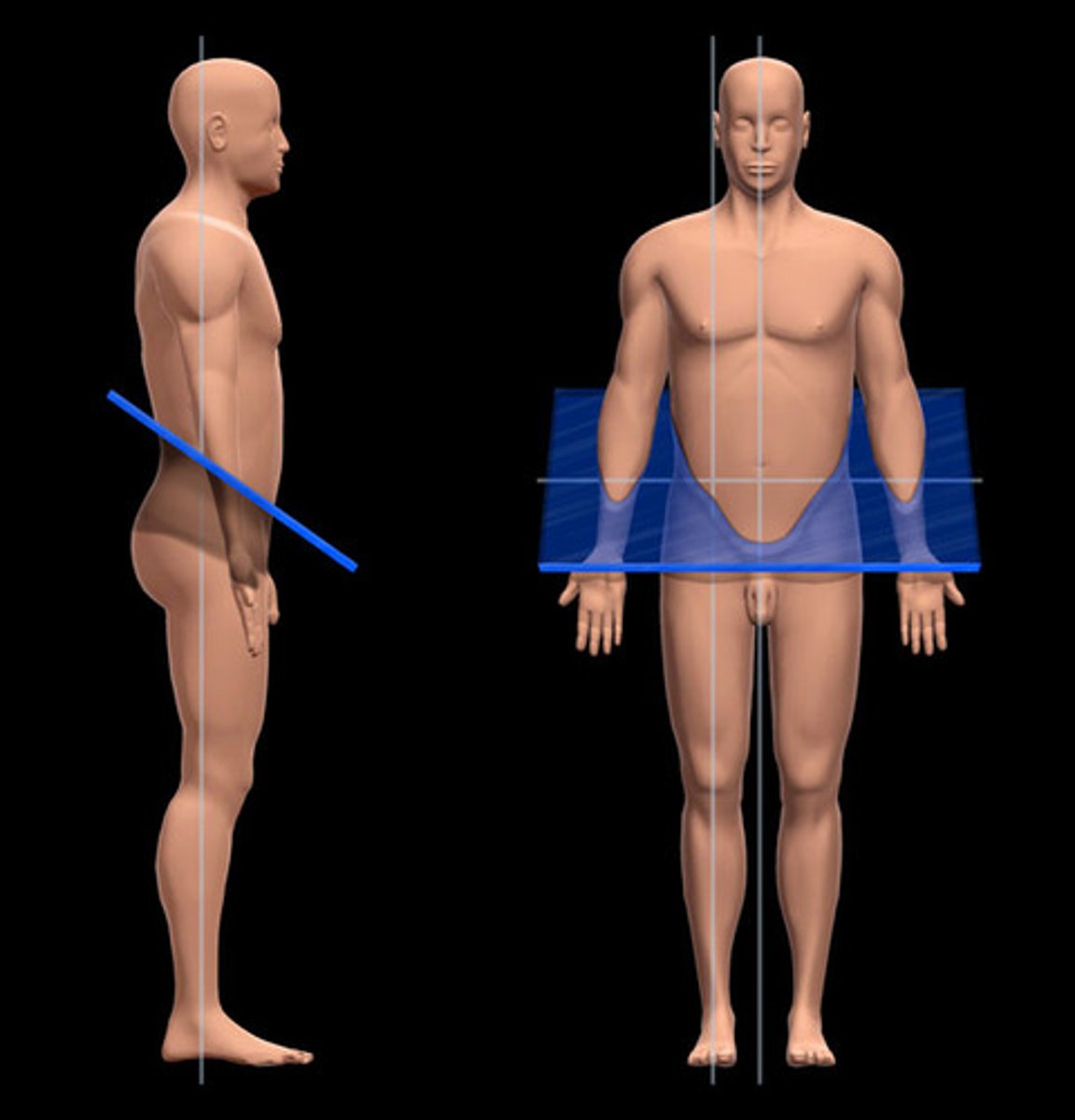
Transverse/Horizontal Plane
- perpendicular to length, divides into superior (top) and inferior (bottom)
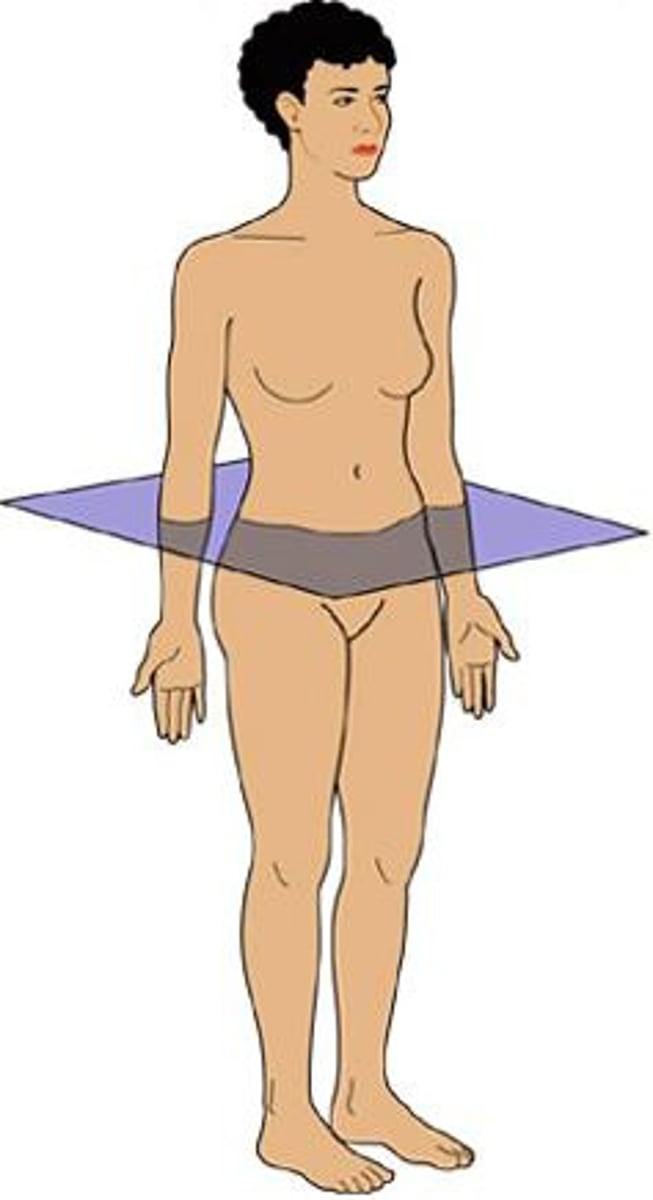
Oblique Plane
all other non-standard planes
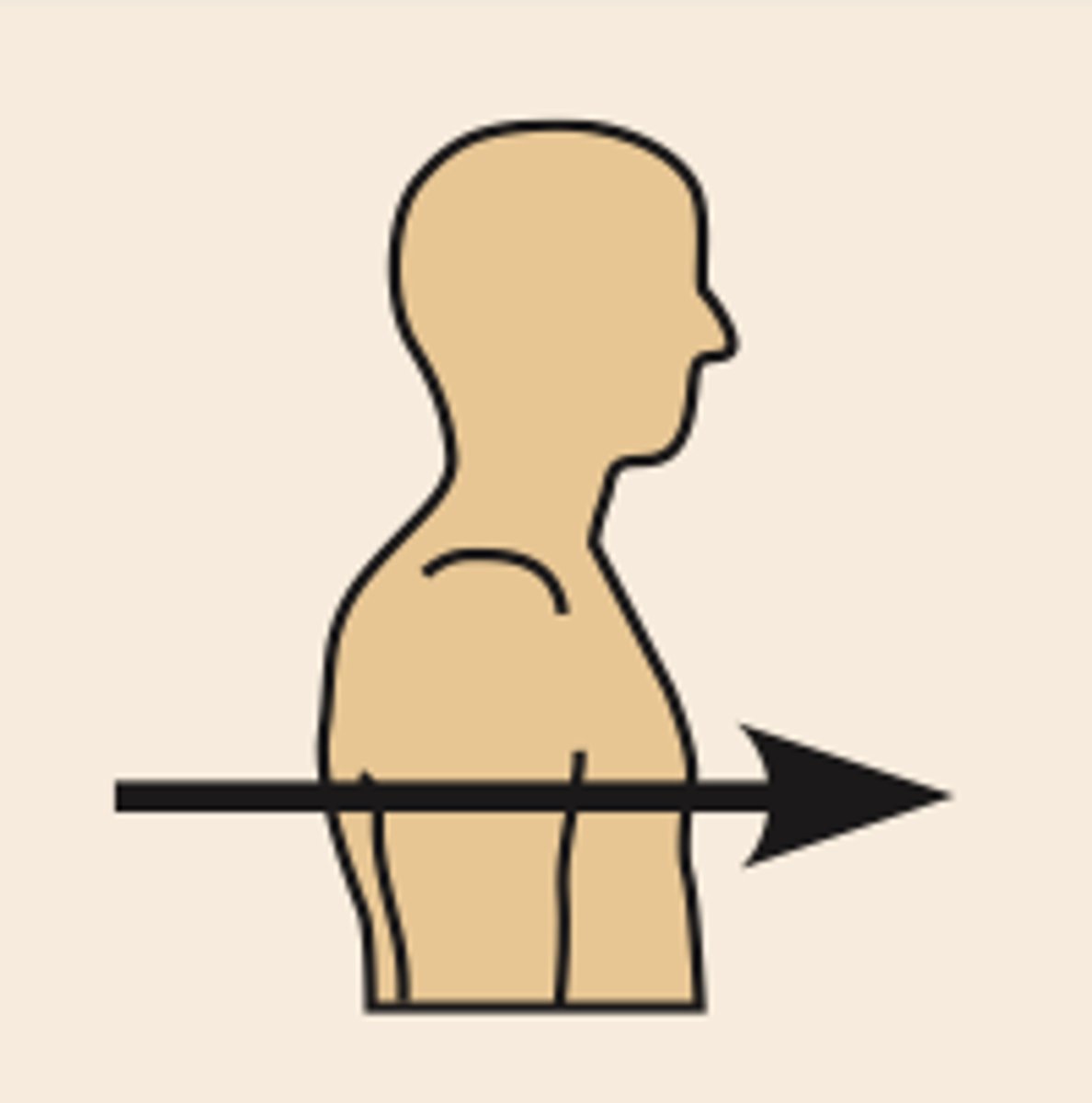
(Direction) Ventral
toward the front or belly
(Direction) Dorsal
toward the back or spine
(Direction) Anterior
toward the ventral side
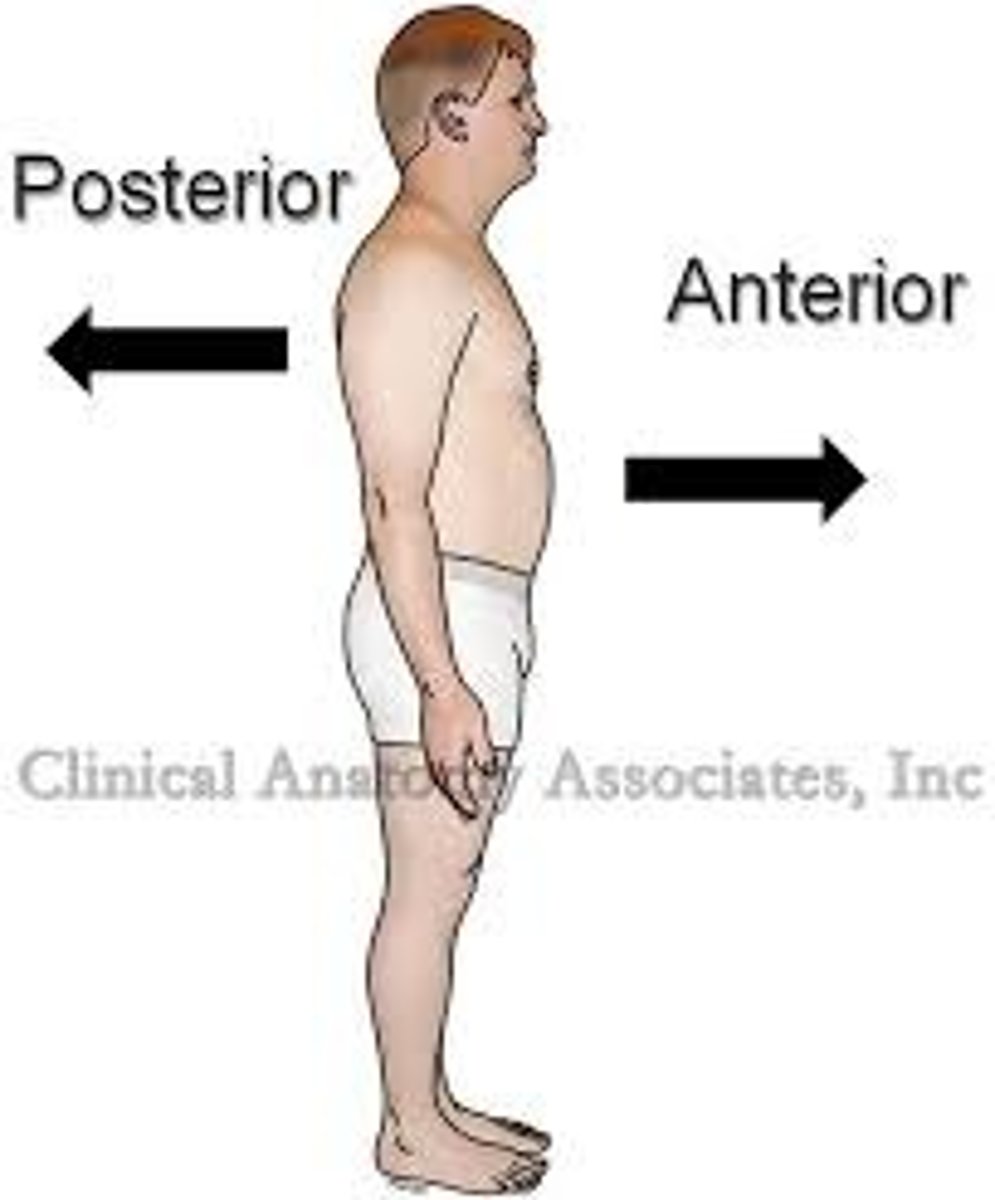
(Direction) Posterior
toward the dorsal side
(Direction) Cephalic
Toward the head or superior end (aka cranial)
(Direction) Rostral
toward the forehead or nose
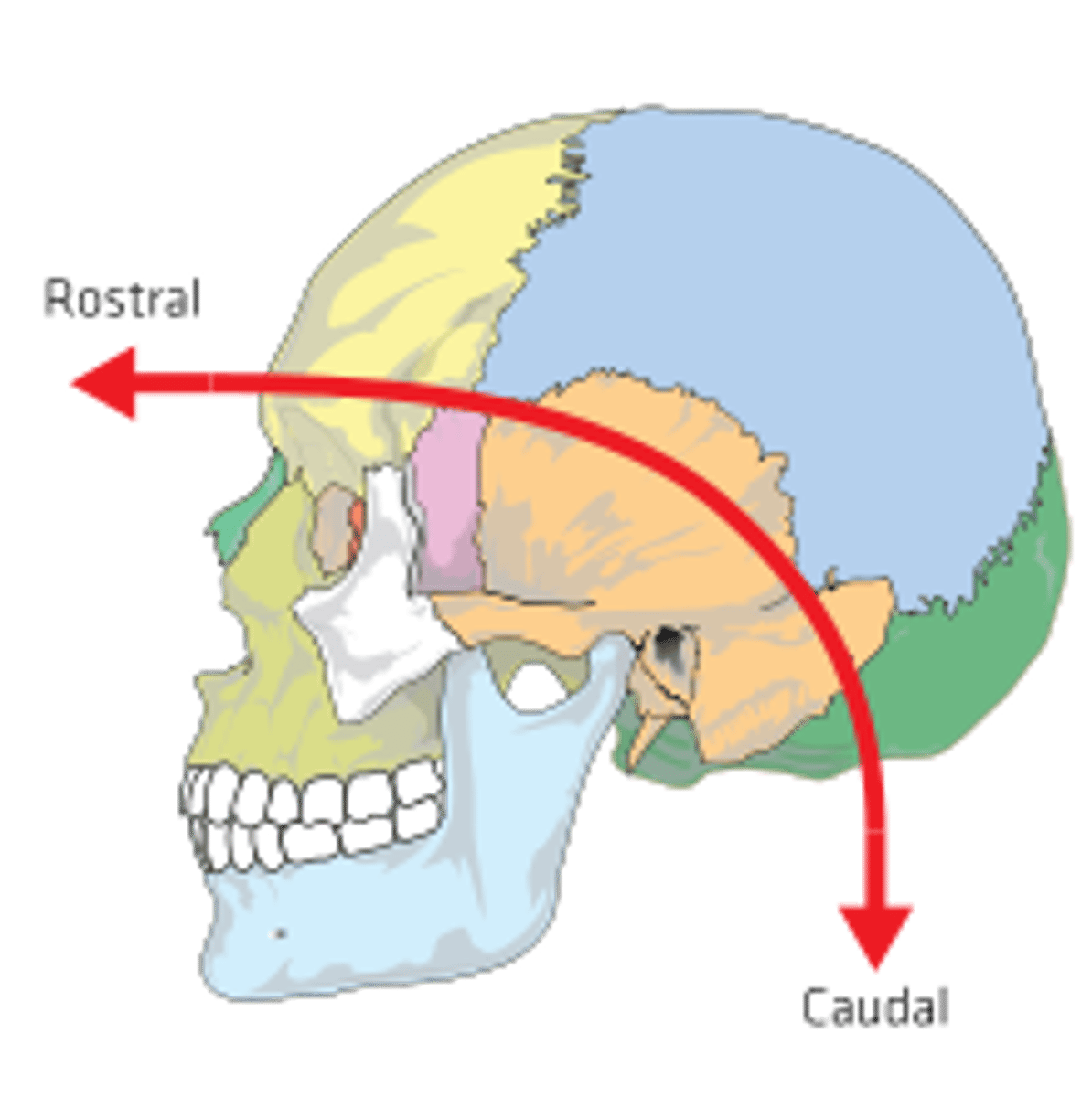
(Direction) Caudal
toward the tail or inferior end
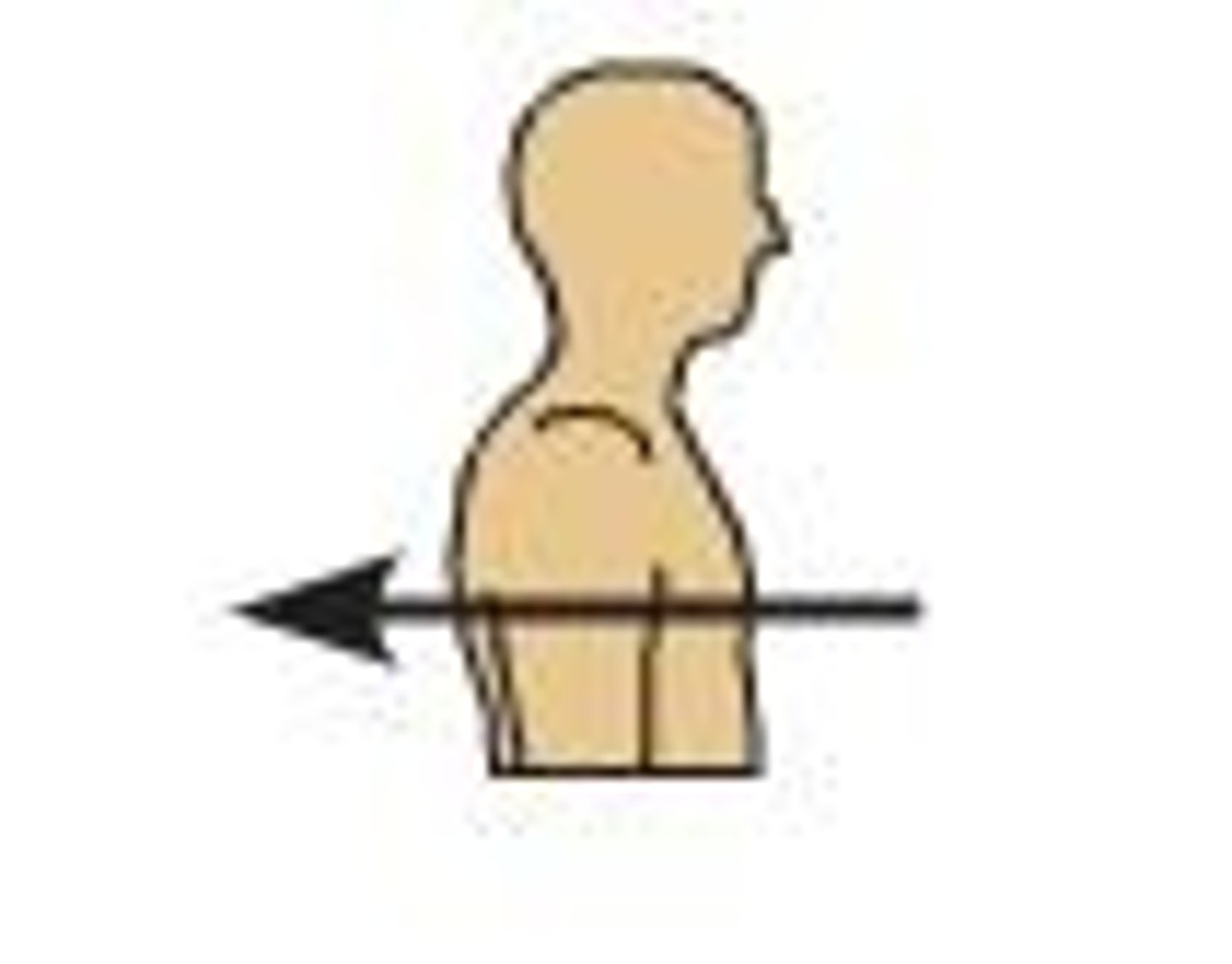
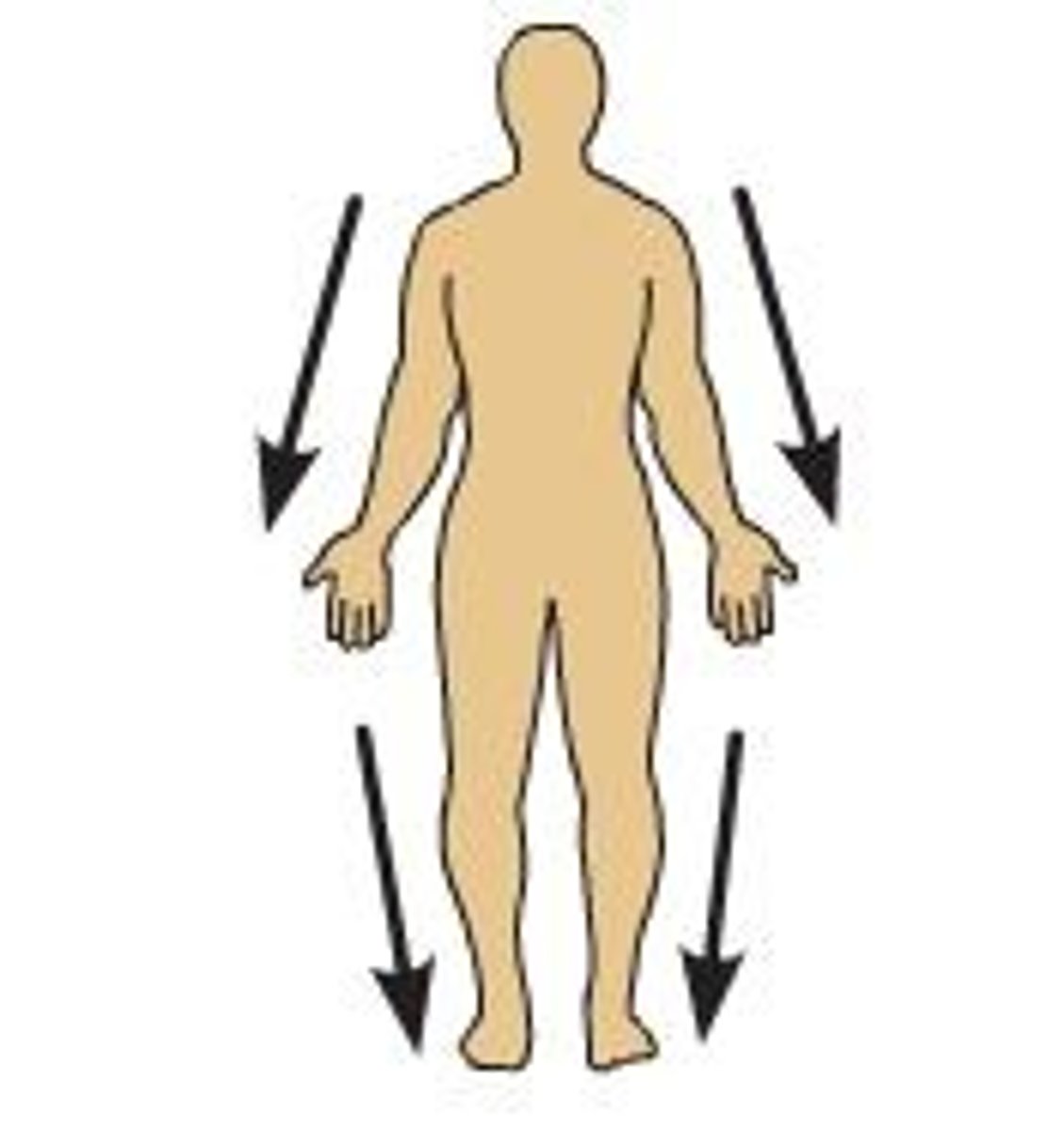
(Direction) Superior
Above
(Direction) Inferior
Below
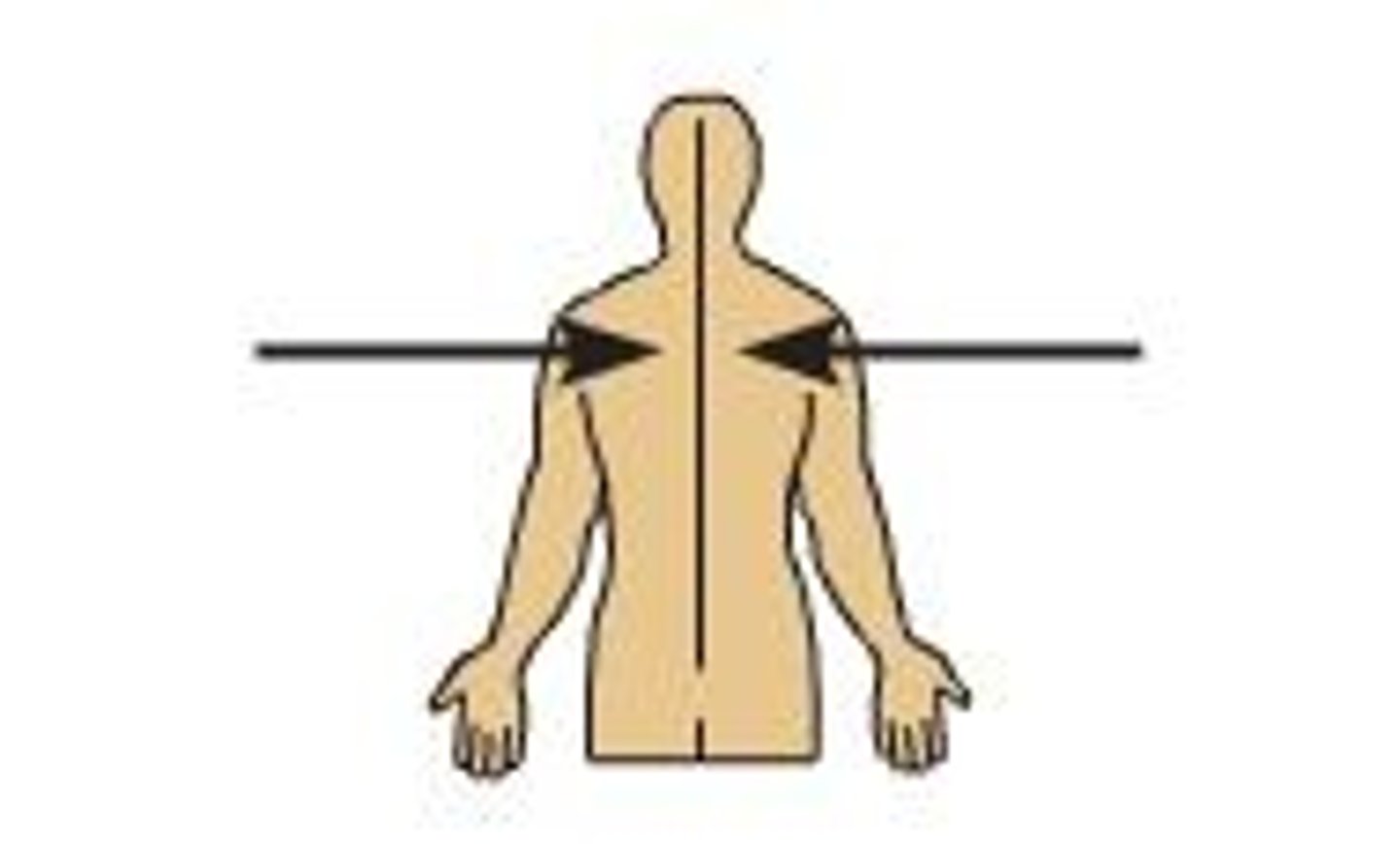
(Direction) Medial
Toward the median plane
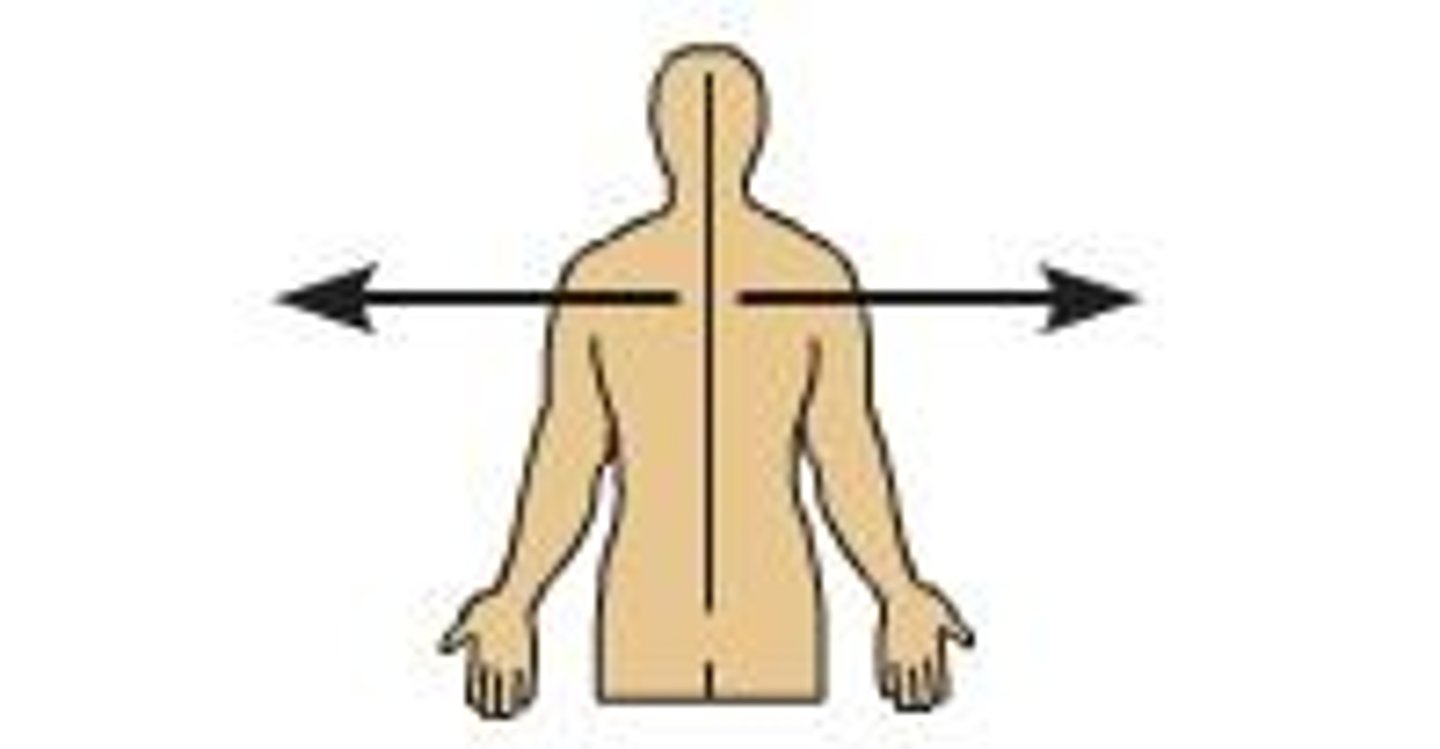
(Direction) Lateral
away from the median plane
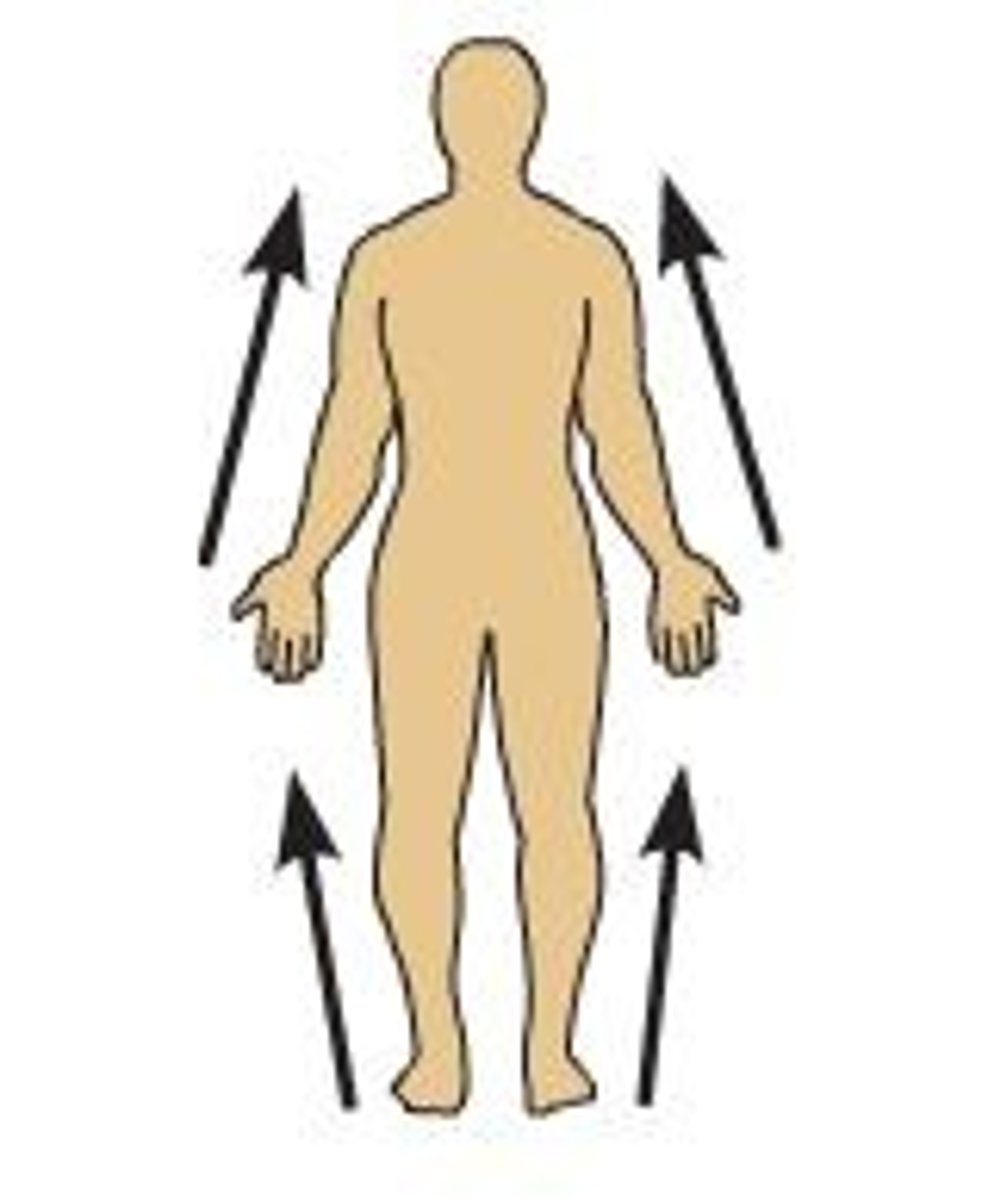
(Direction) Proximal
closer to the point of attachment or origin
(Direction) Distal
farther away from the point of attachment or origin
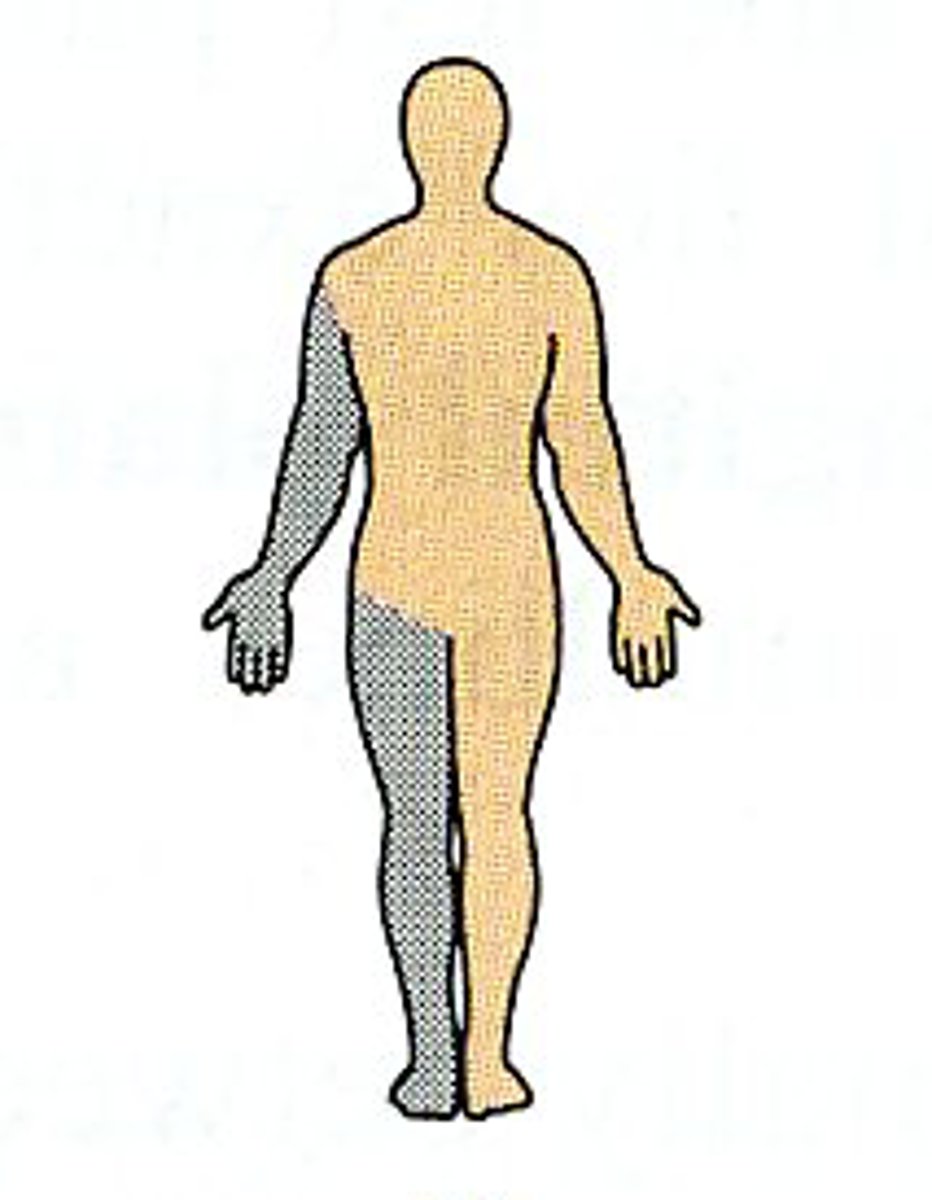
(Direction) Ipsilateral
on the same side of the body (left or right)
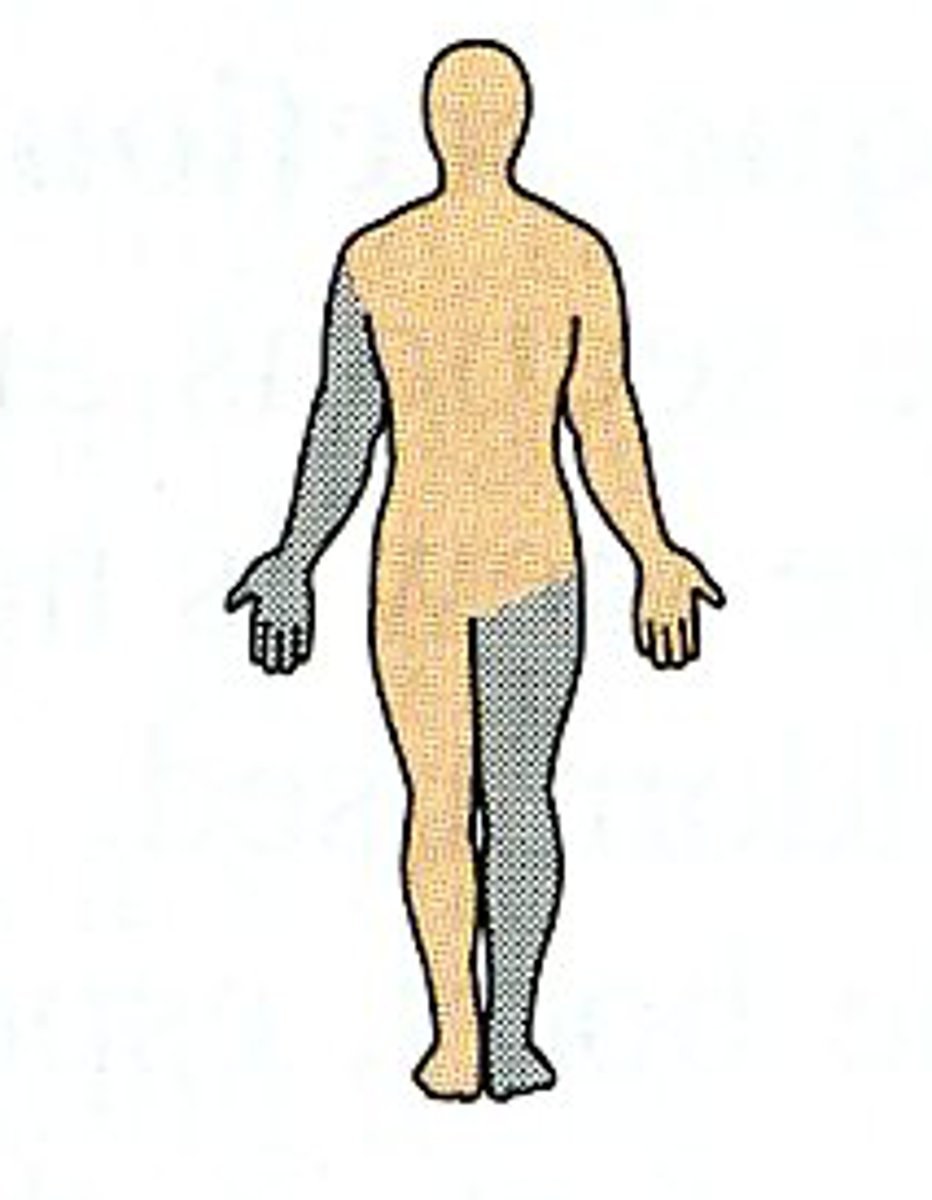
(Direction) Contralateral
on opposite sides of the body (right and left)
(Direction) Superficial
Closer to the body surface
(Direction) Deep
farther from the body surface
(Direction) Palmar
toward the palm side of the hand
(Direction) Plantar
toward the sole of the foot
(Region) (Associated Viscera, Membranous Lining) Cranial Cavity
- Associated Viscera: Brain
- Membranous Lining: Meninges
(Region) (Associated Viscera, Membranous Lining) Vertebral Canal
- Associated Viscera: Spinal Cord
- Membranous Lining: Meninges
Visceral Layer
covers the organs
Parietal Layer
lines the cavity
(Joint Movement) Flexion
- brings ventral surface together, decreasing the angle between two body parts
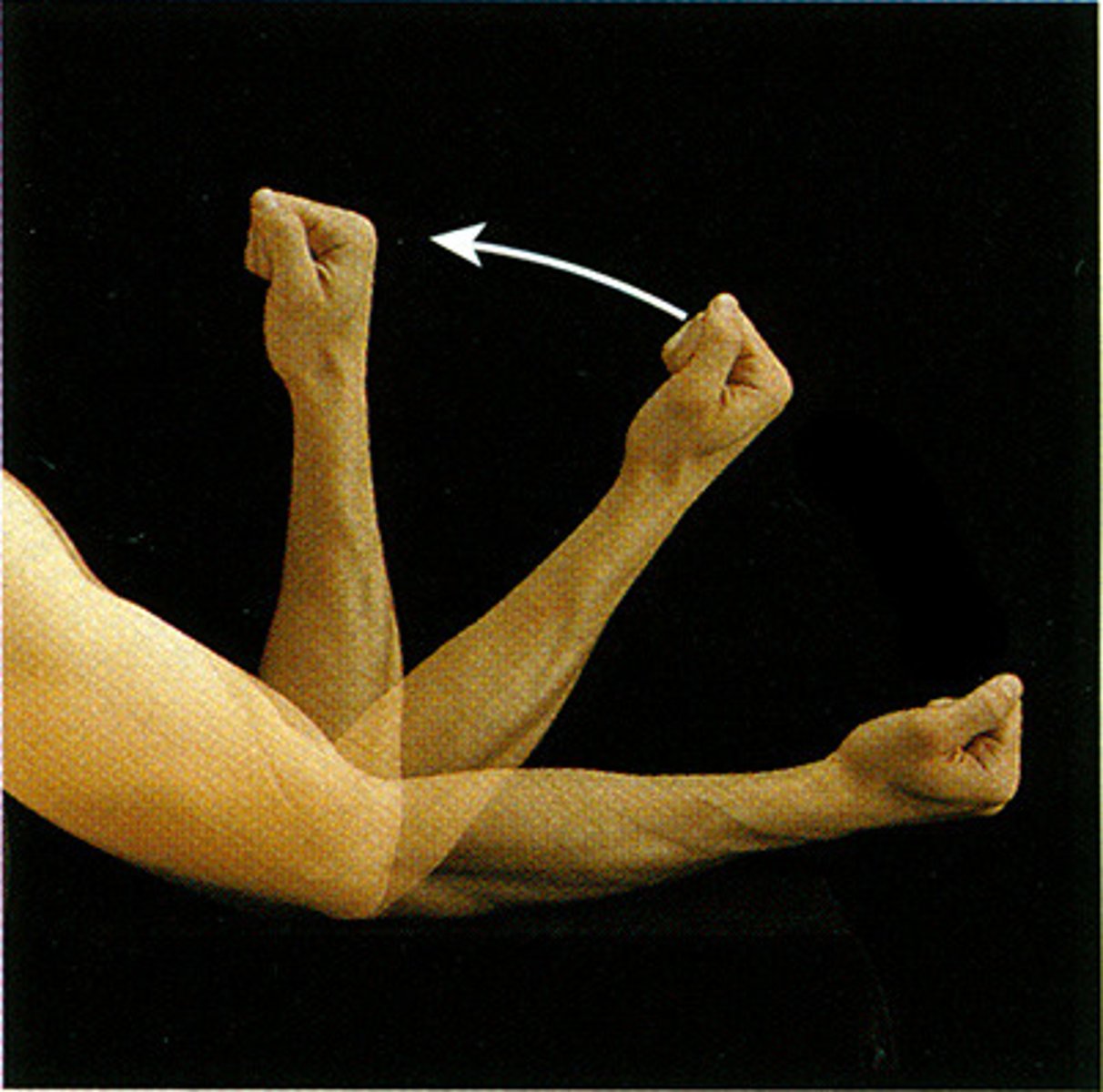
(Joint Movement) Extension
- moves ventral surfaces apart, increasing the angle between two body parts
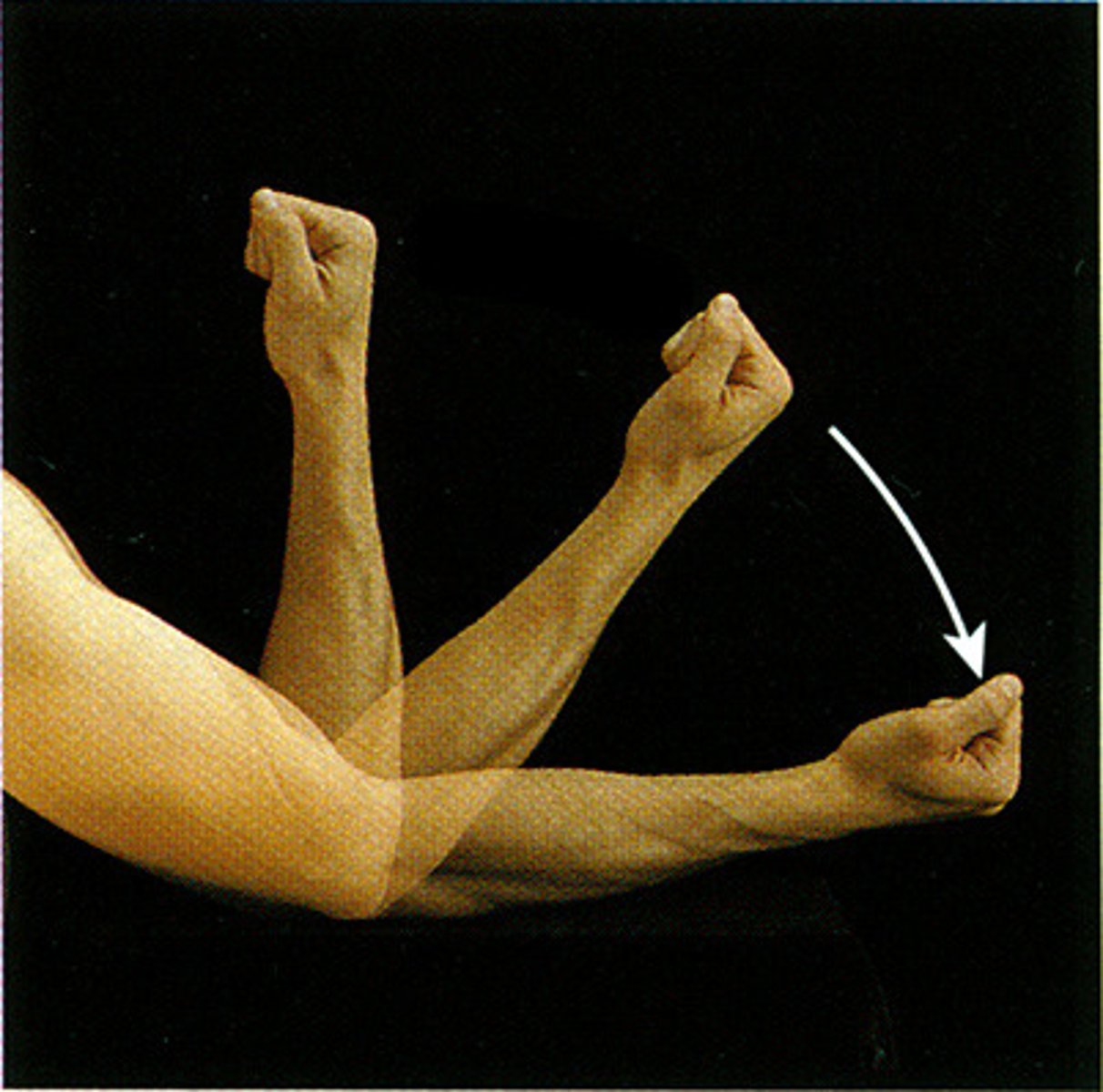
(Joint Movement) Hyperextension
- extension that extends beyond anatomical position
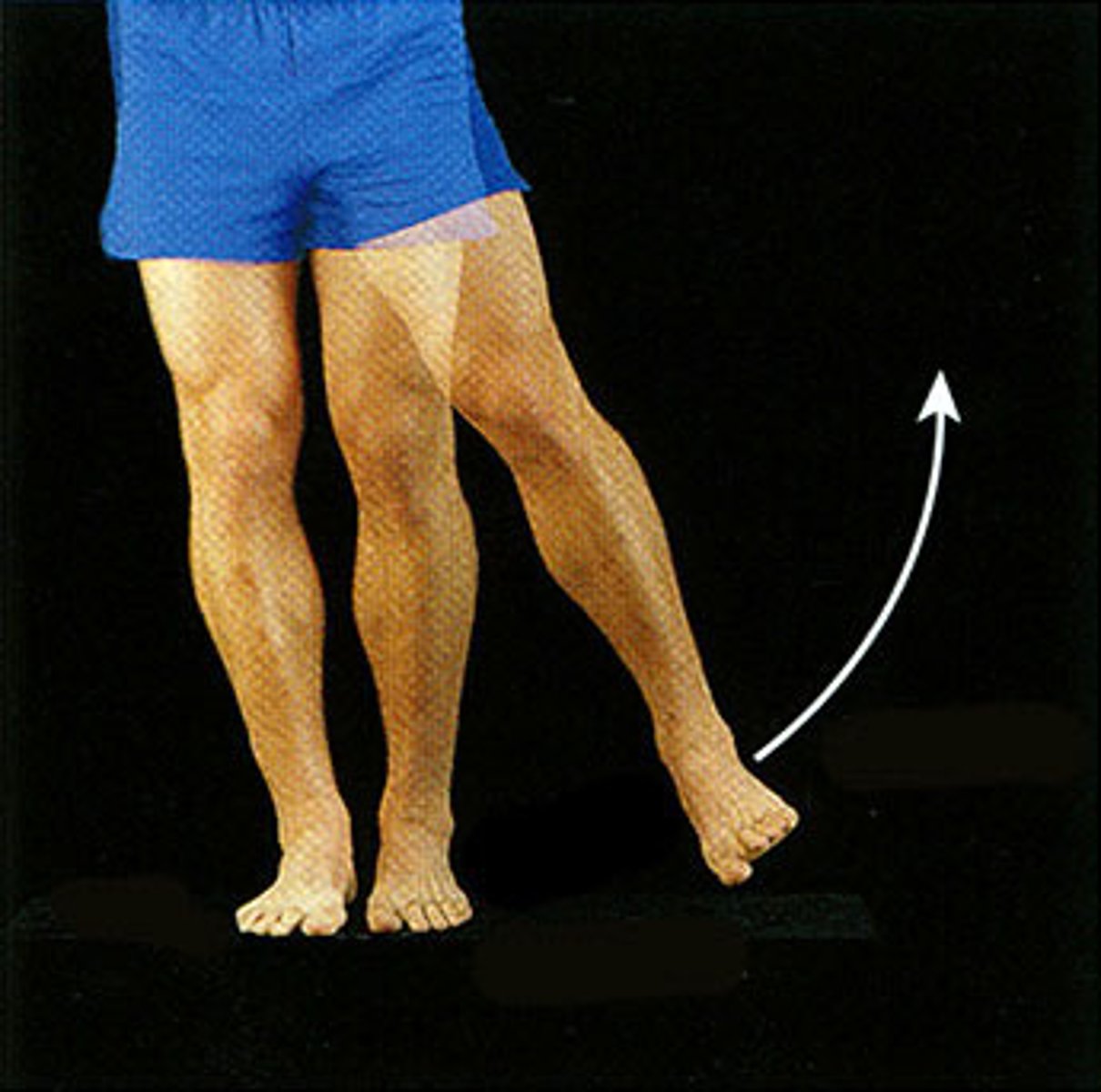
(Joint Movement) Abduction
- to move away from the midline
(Joint Movement) Adduction
- to move toward the midline
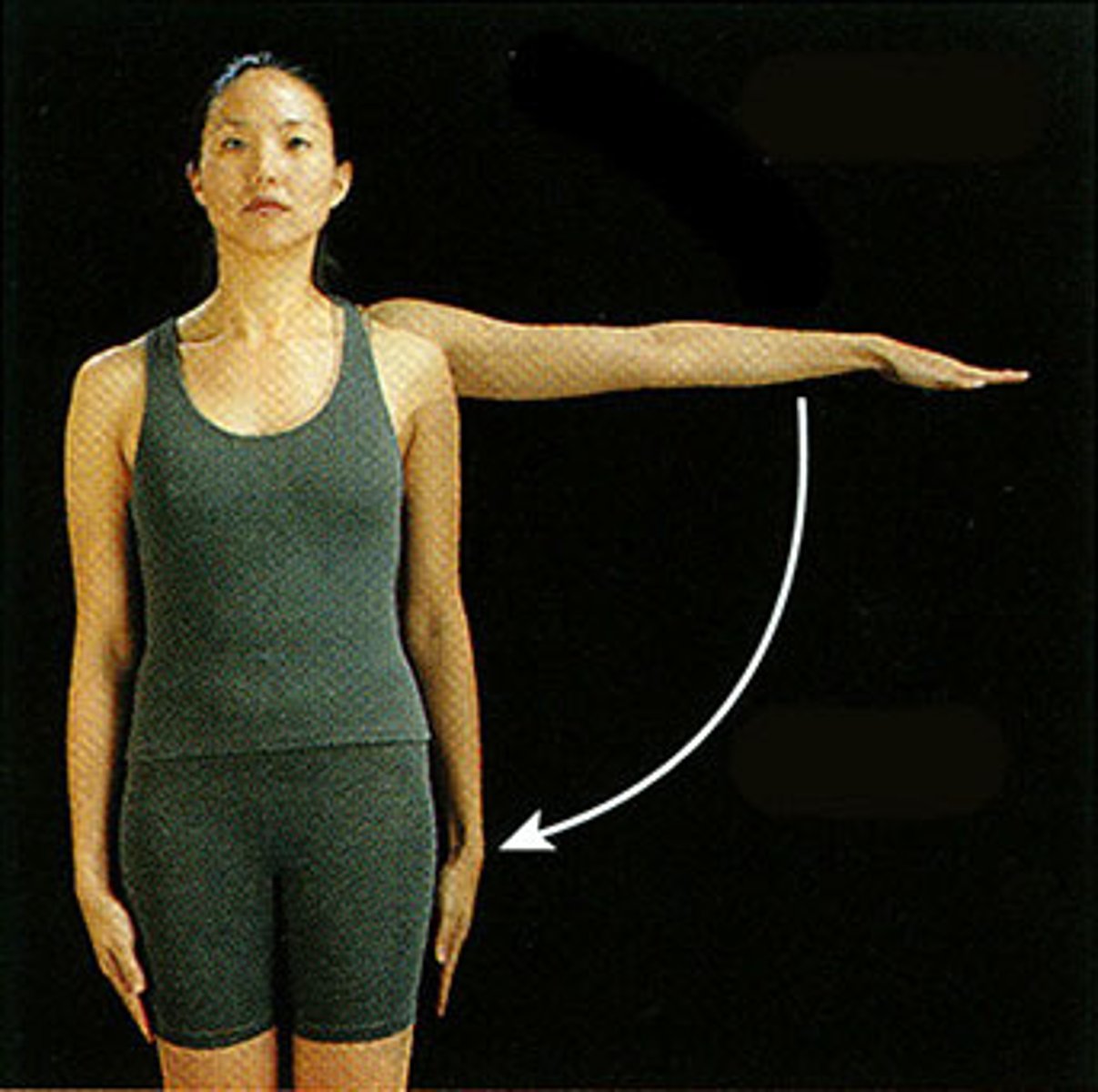

(Joint Movement) Circumduction
- one end stays fairly stationary, while the other end makes a circular motion
(Joint Movement) Medial (internal) rotation
Movement around a central axis toward the midline
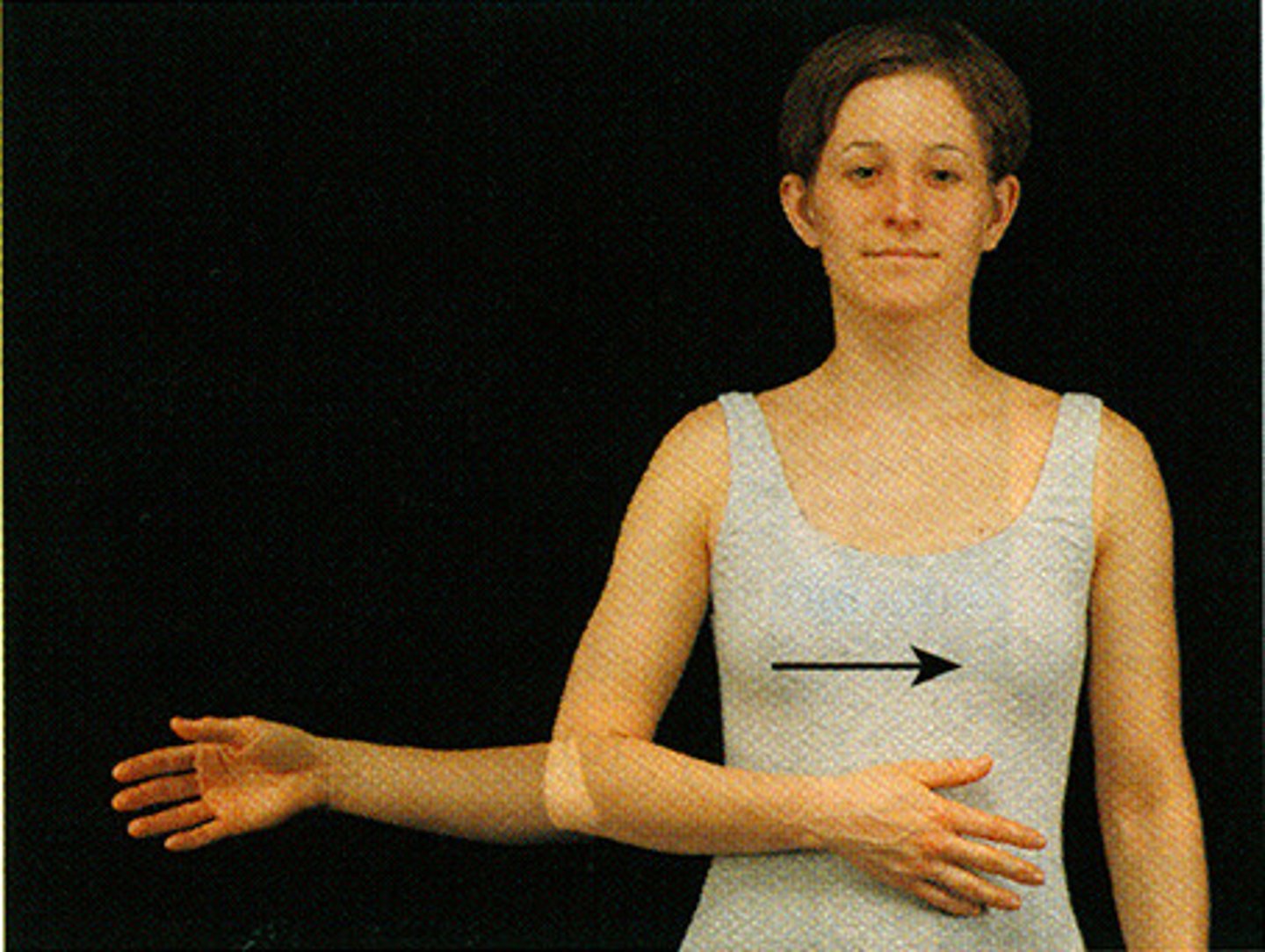
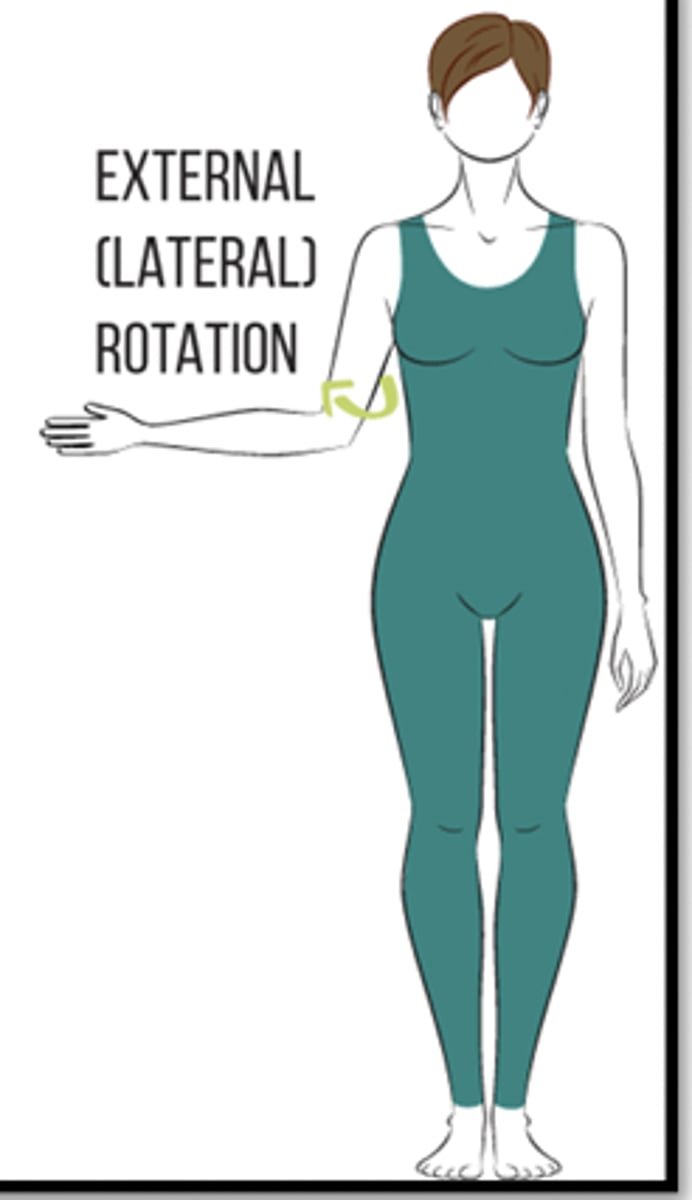
(Joint Movement) Lateral (external) rotation
Movement around a central axis away from the midline
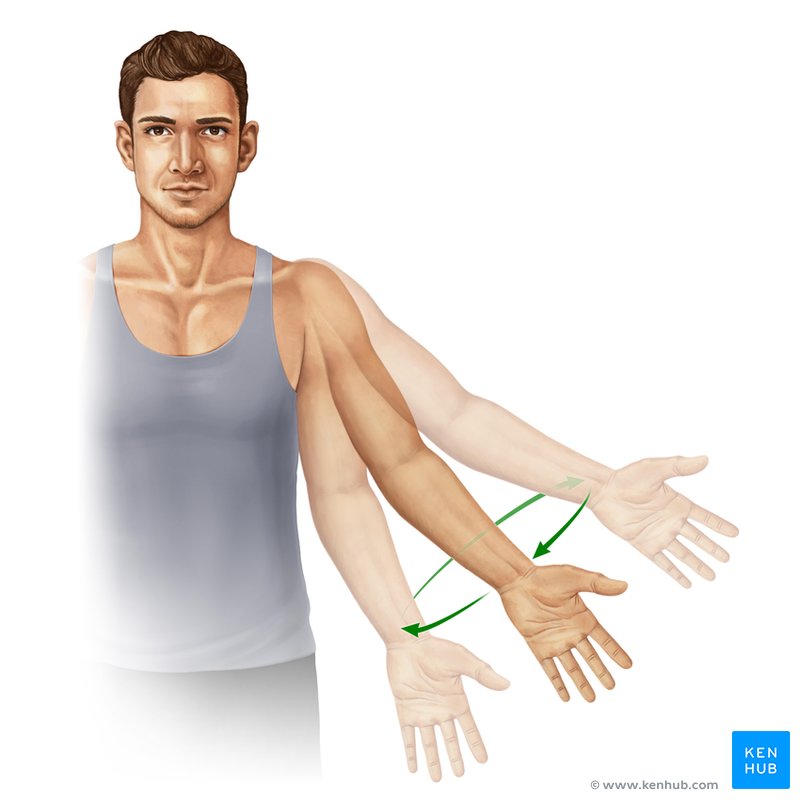
(Joint Movement) Pronation
rotation of the forearm so the palm faces posteriorly (palm facing backward)
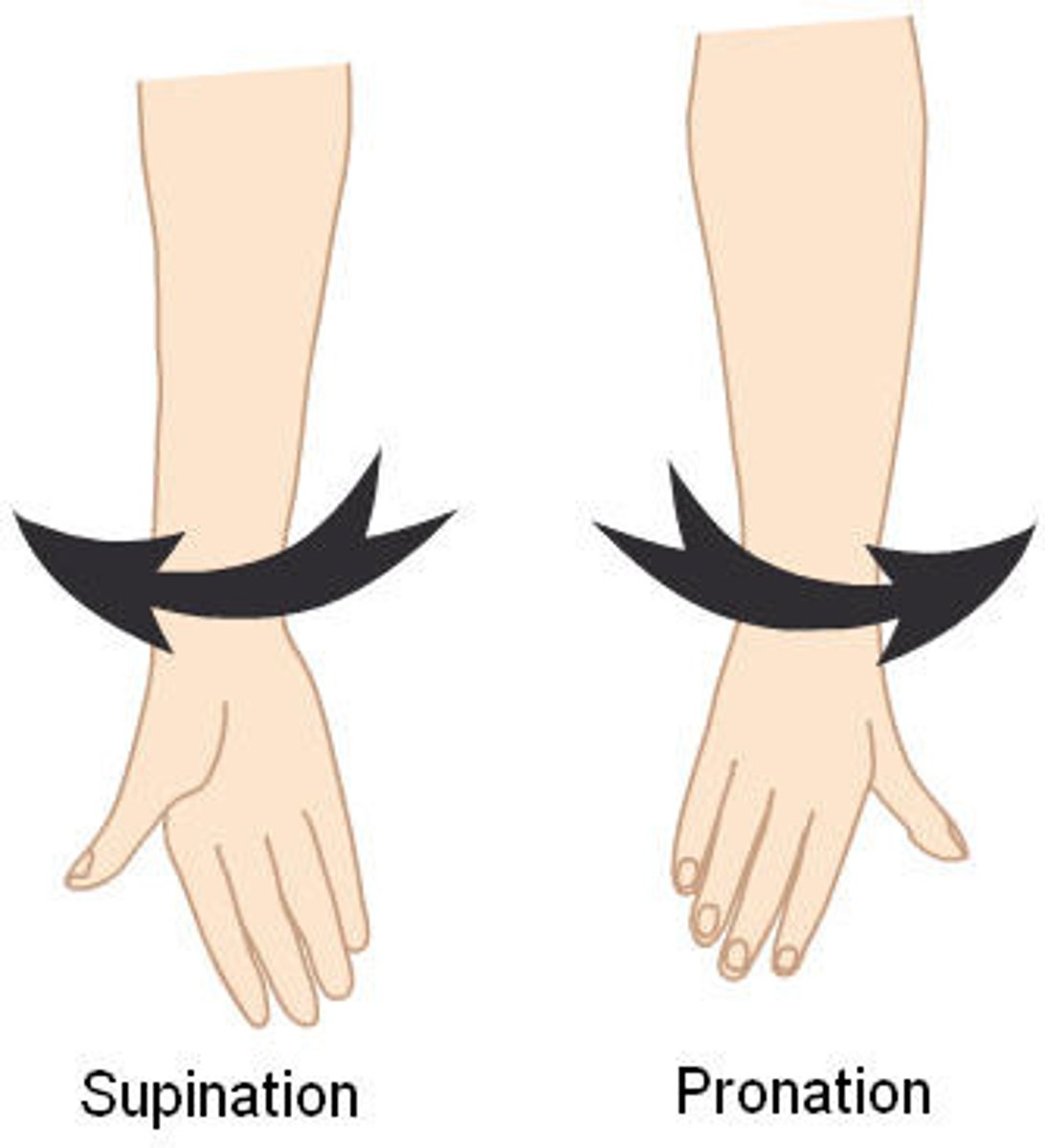
(Joint Movement) Supination
rotation of the forearm so the palm faces anteriorly (palm facing forward)
(Joint Movement) Elevation
raises a body part vertically in a frontal plane
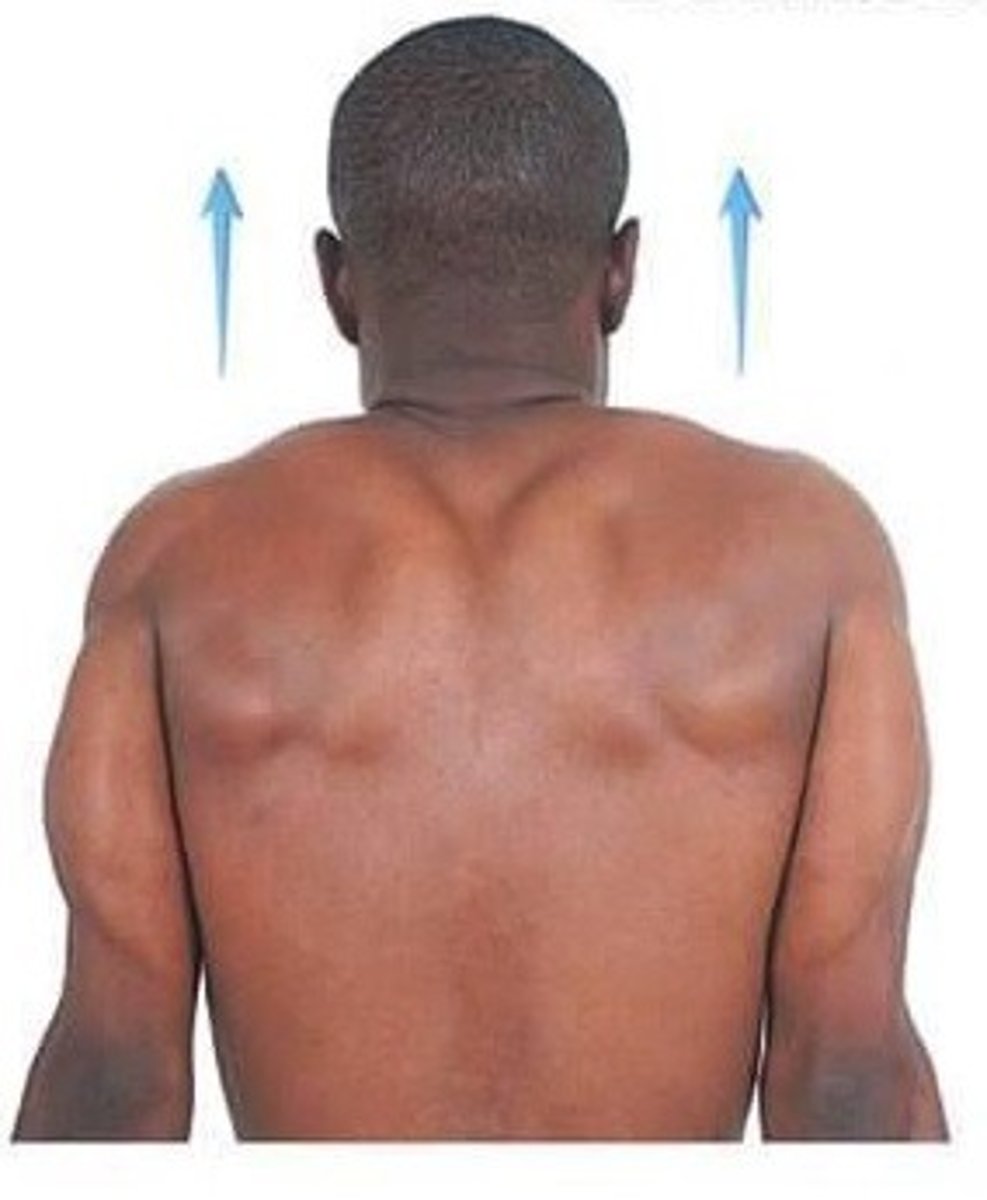
(Joint Movement) Depression
lowers a body part vertically in a frontal plane
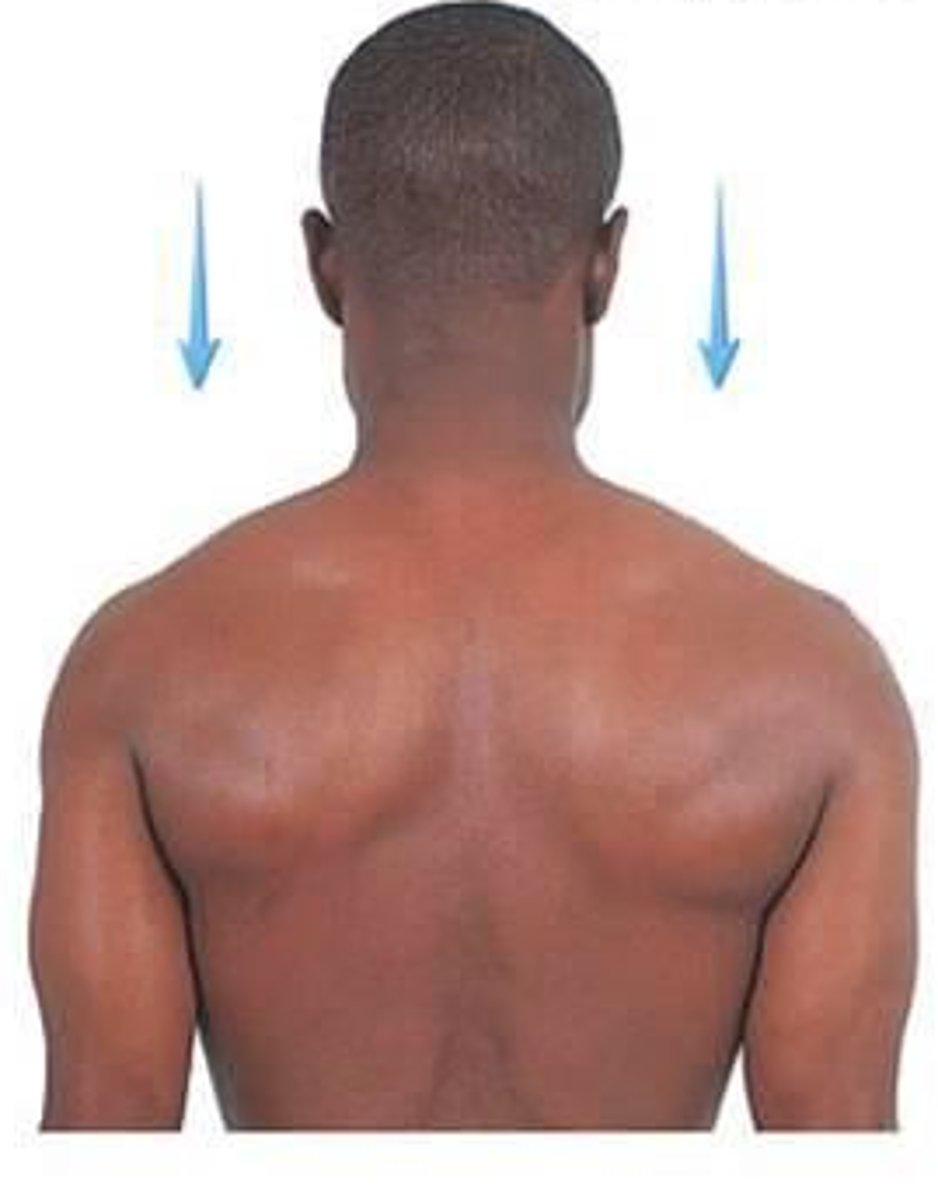
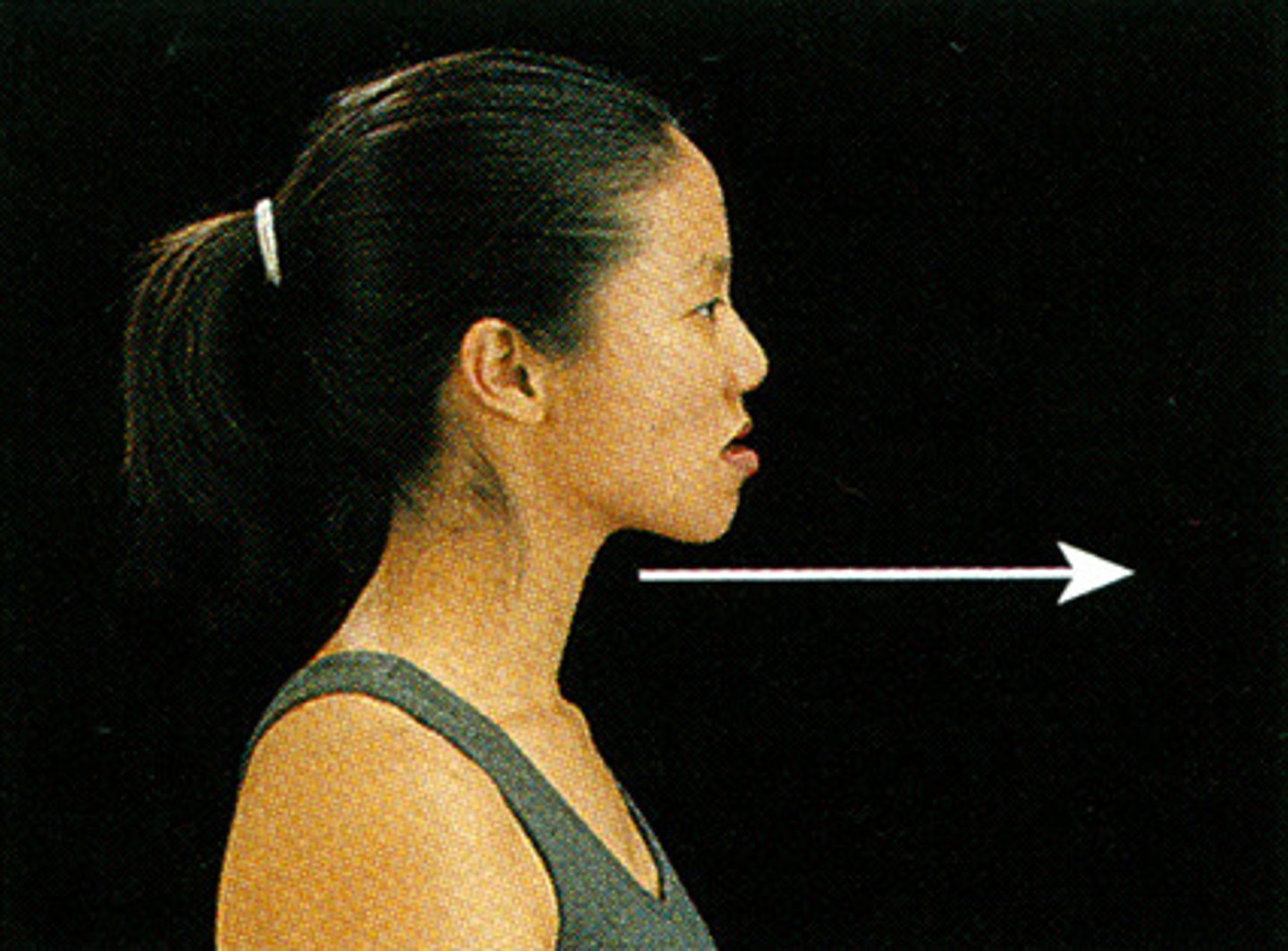
(Joint Movement) Protraction
anterior movement in a transverse plane
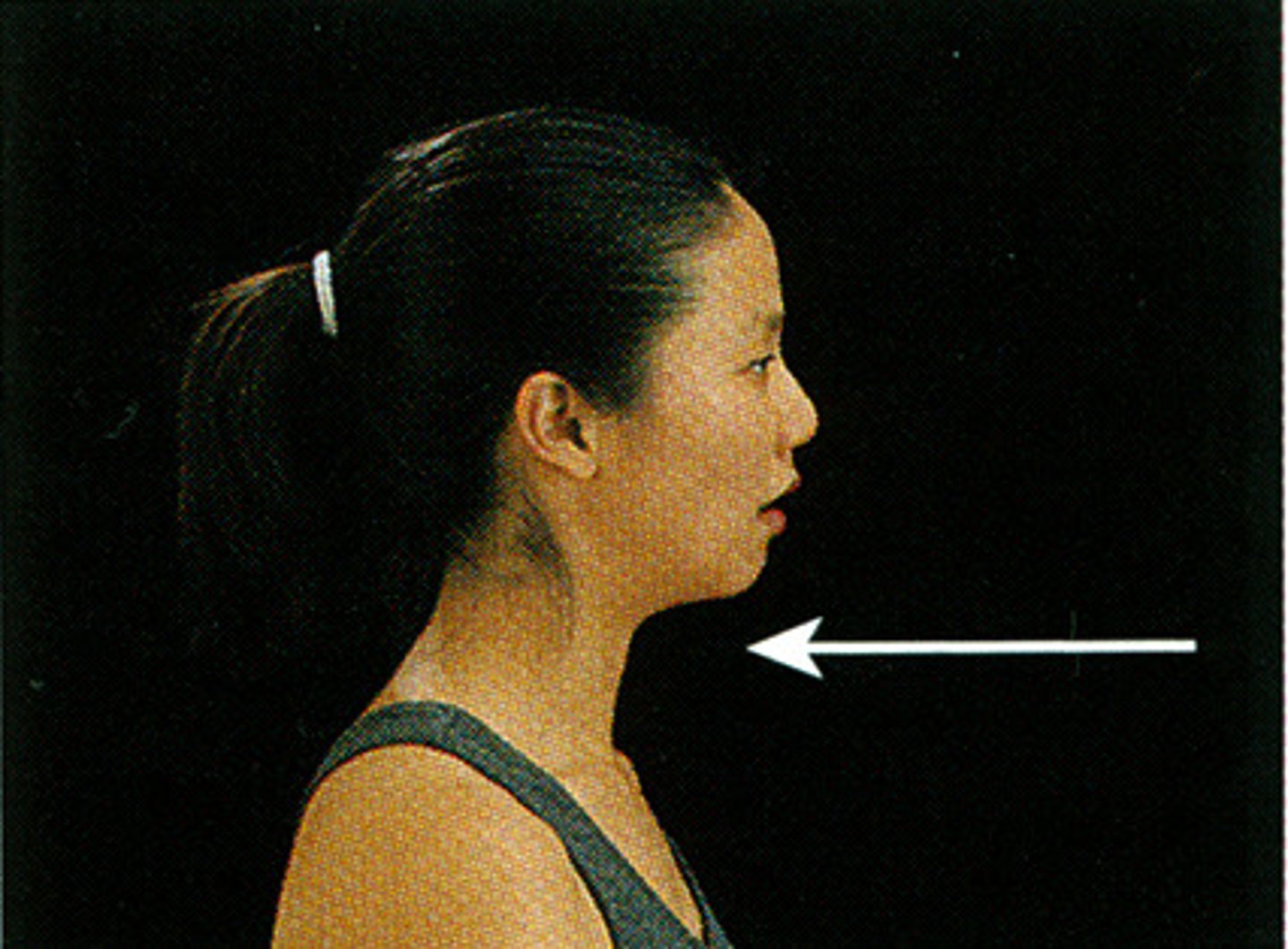
(Joint Movement) Retraction
posterior movement in a transverse plane
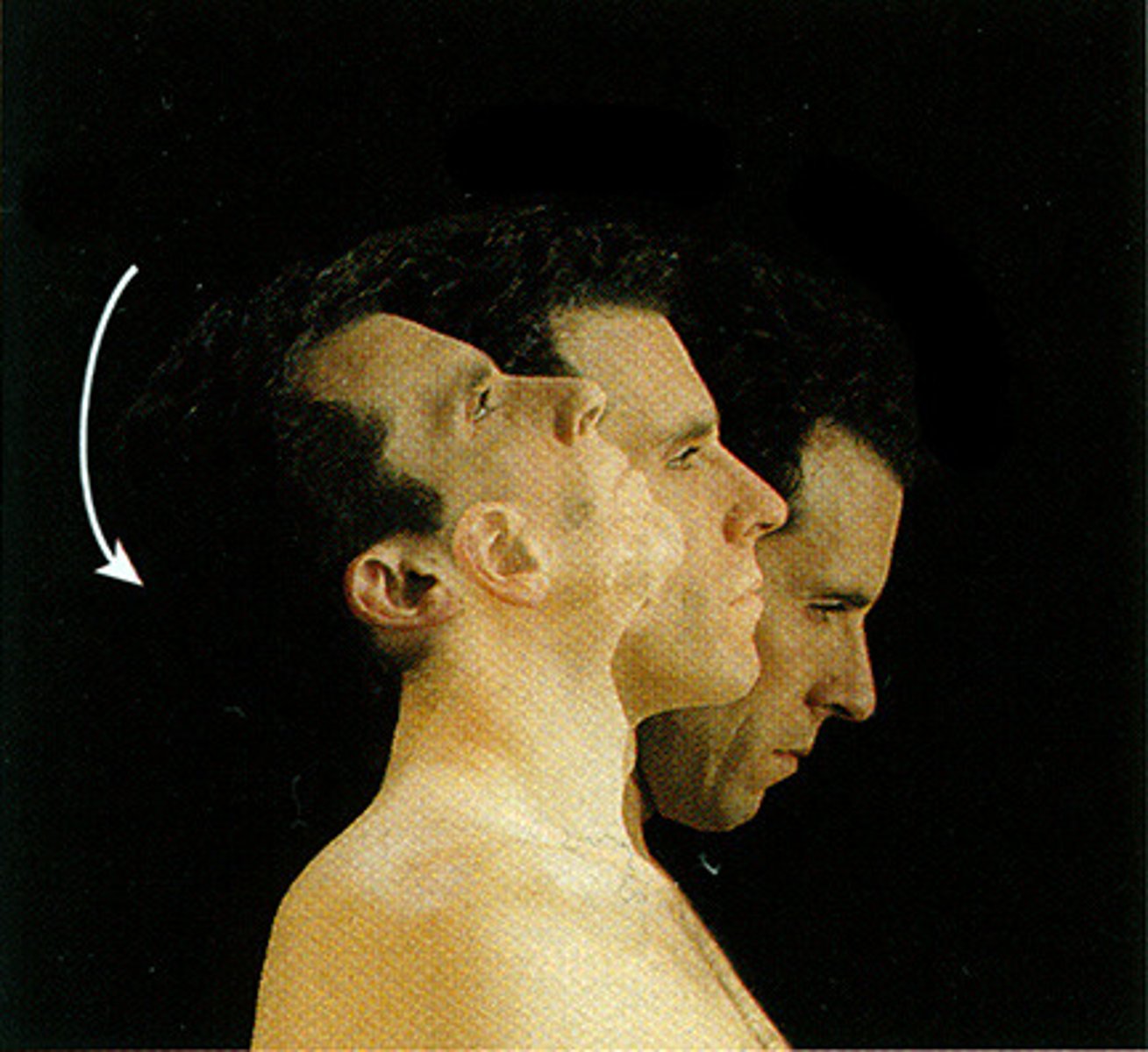
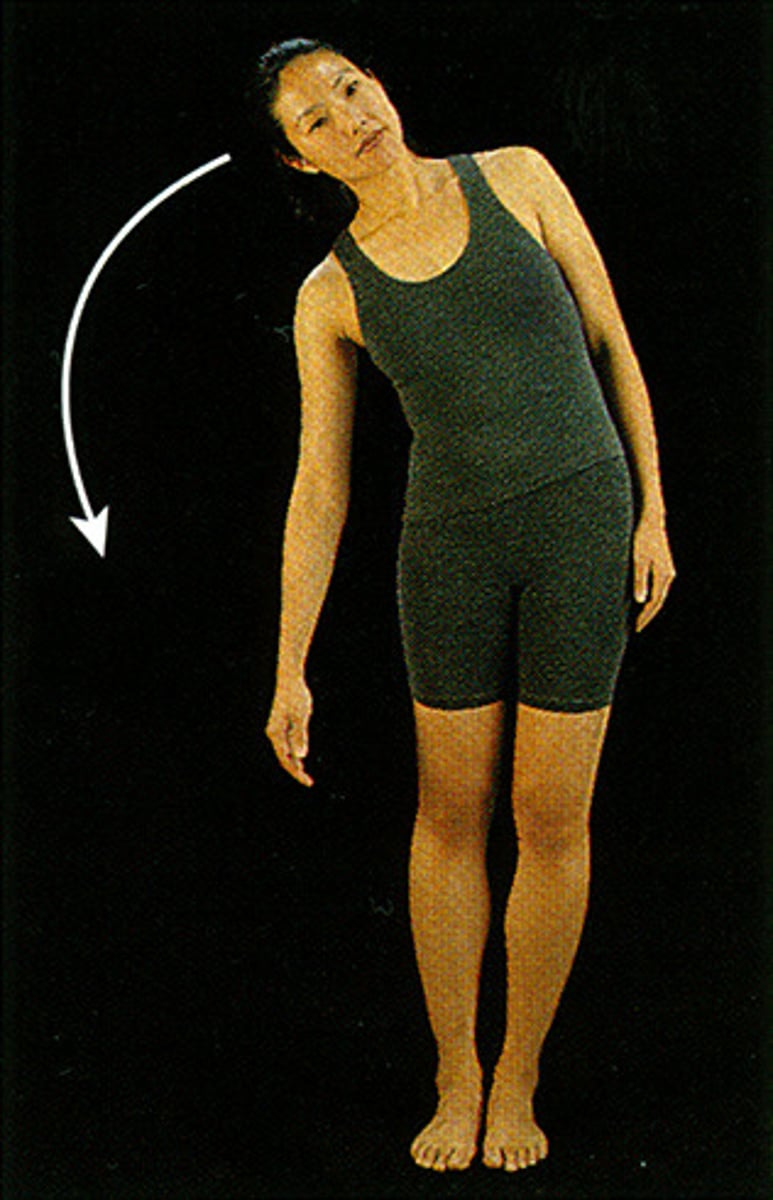
(Joint Movement) Lateral Flexion
tilting the head or trunk to the right or left of the midline
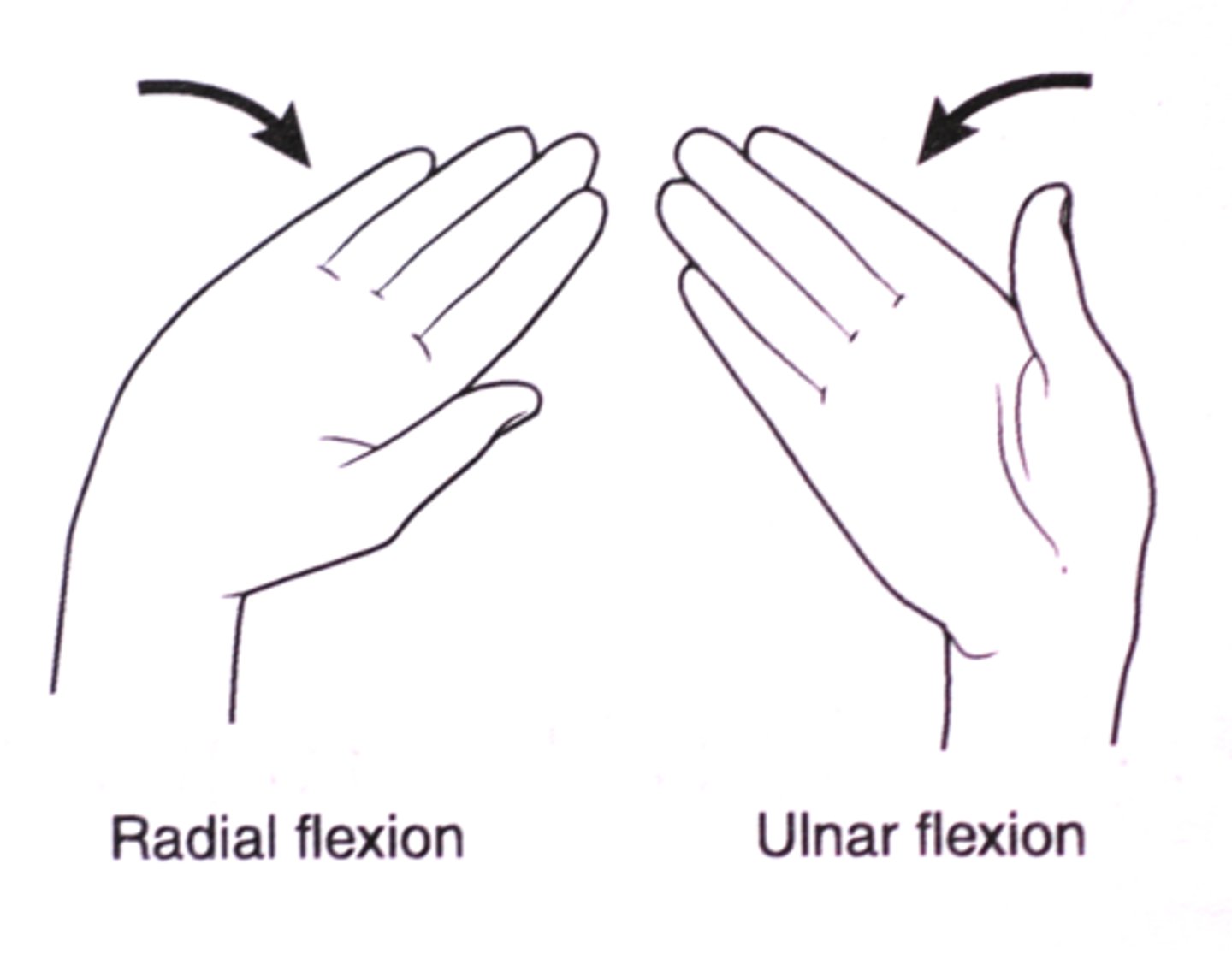
(Specialised Hand Movement) Radial Flexion
see diagram
(Specialised Hand Movement) Ulnar Flexion
see diagram
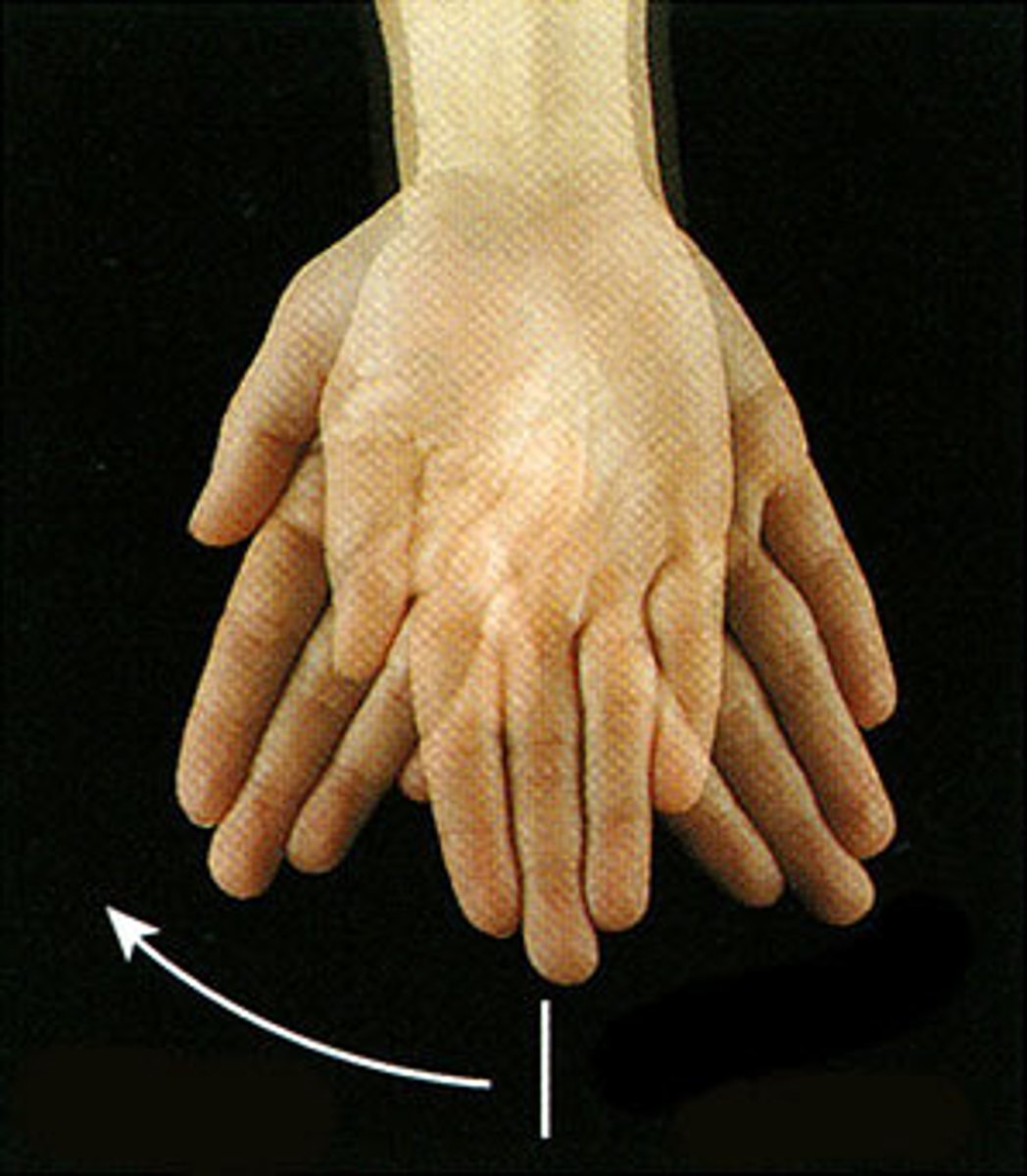
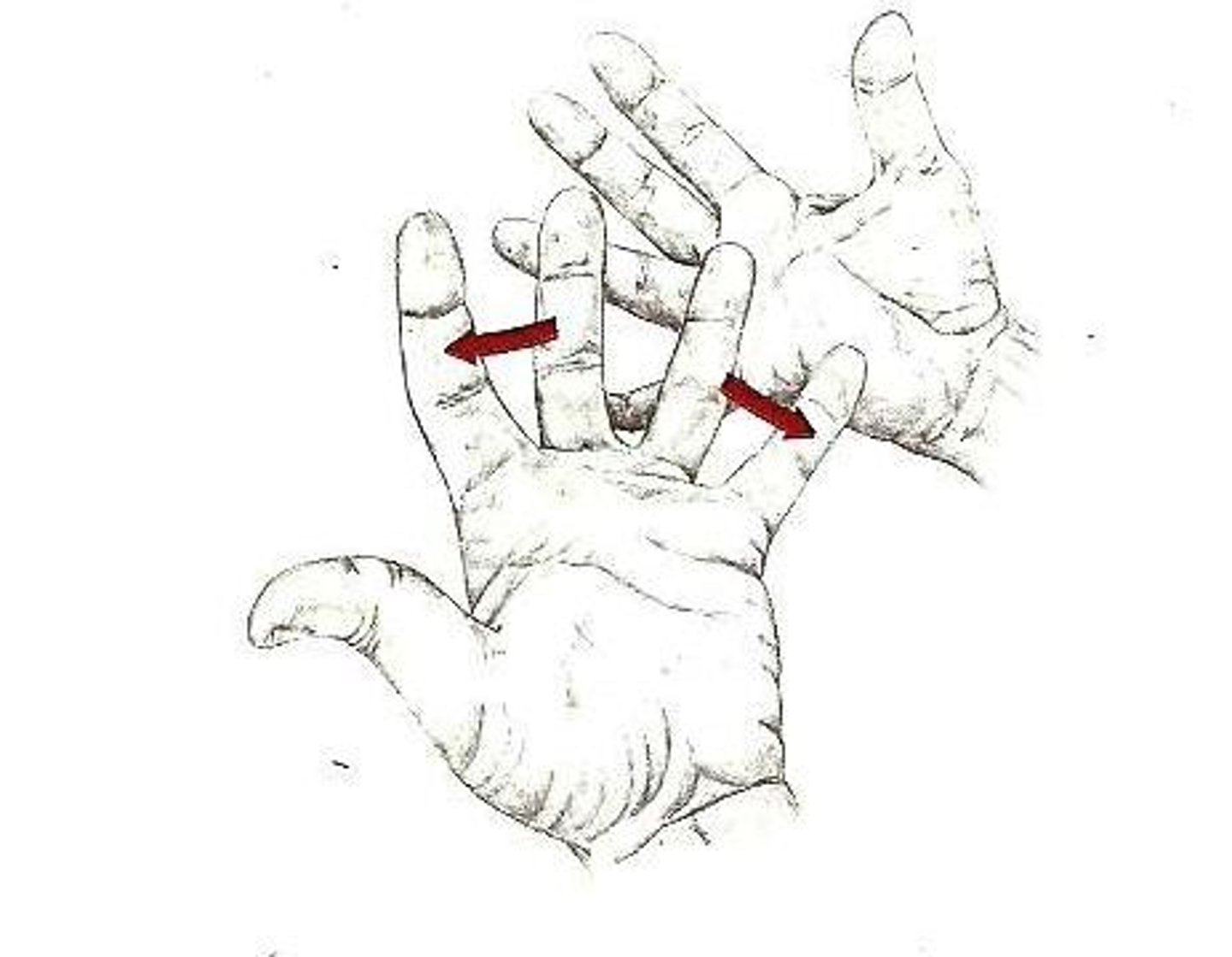
(Specialised Hand Movement) Abduction of Fingers
see diagram
(Specialised Hand Movement) Palmar Abduction of Thumb
see diagram
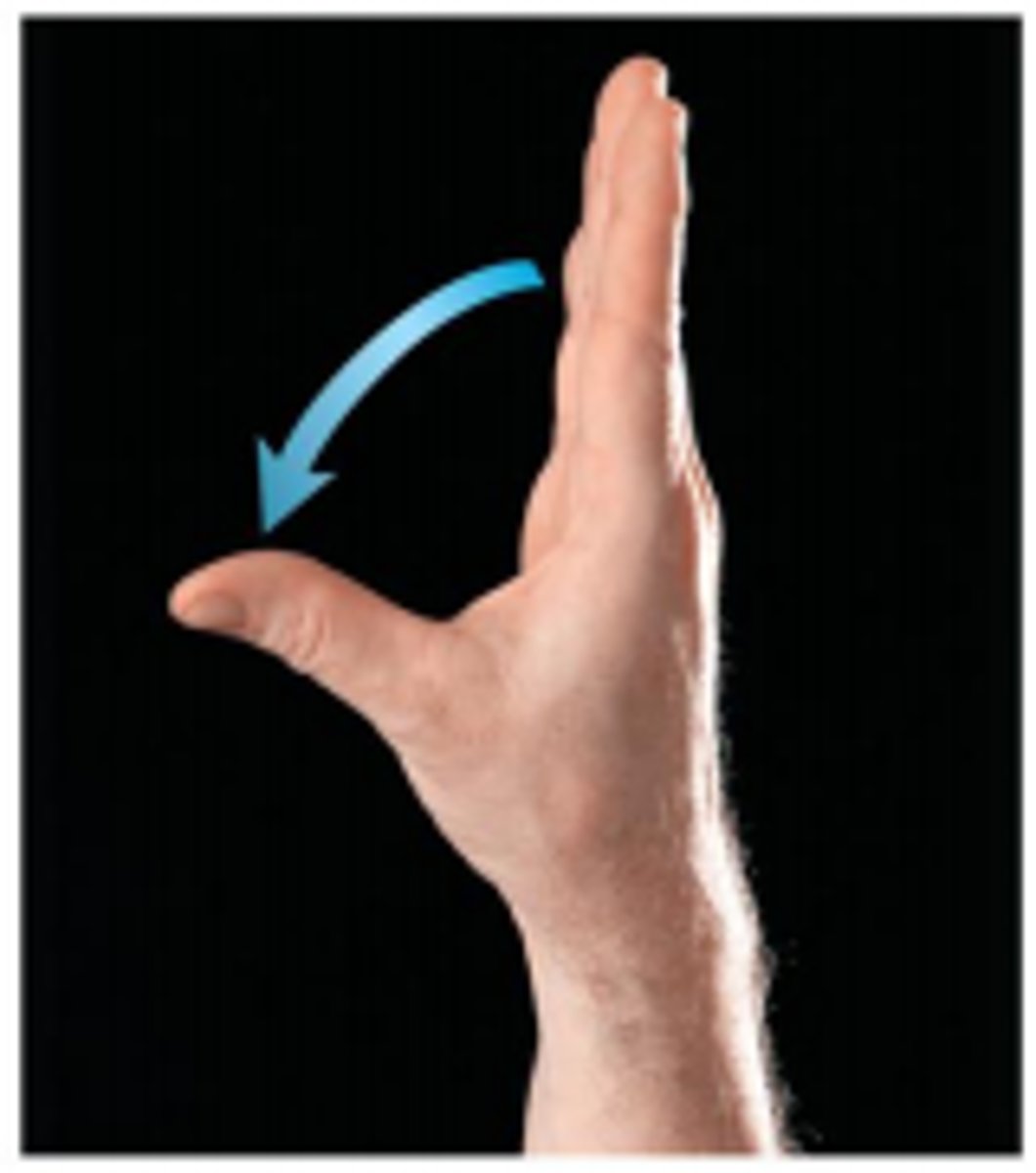
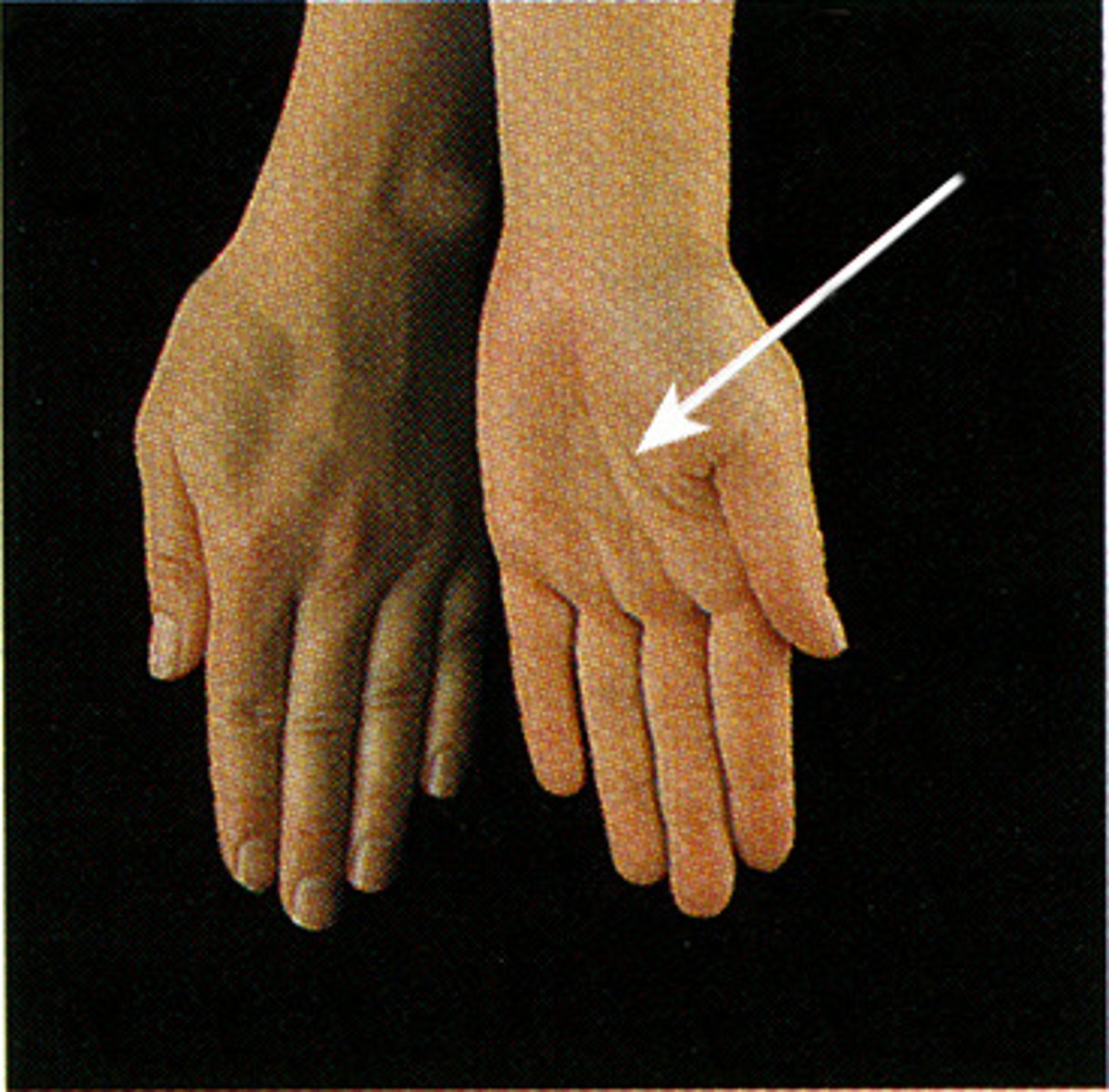
(Specialised Hand Movement) Opposition of Thumb
see diagram
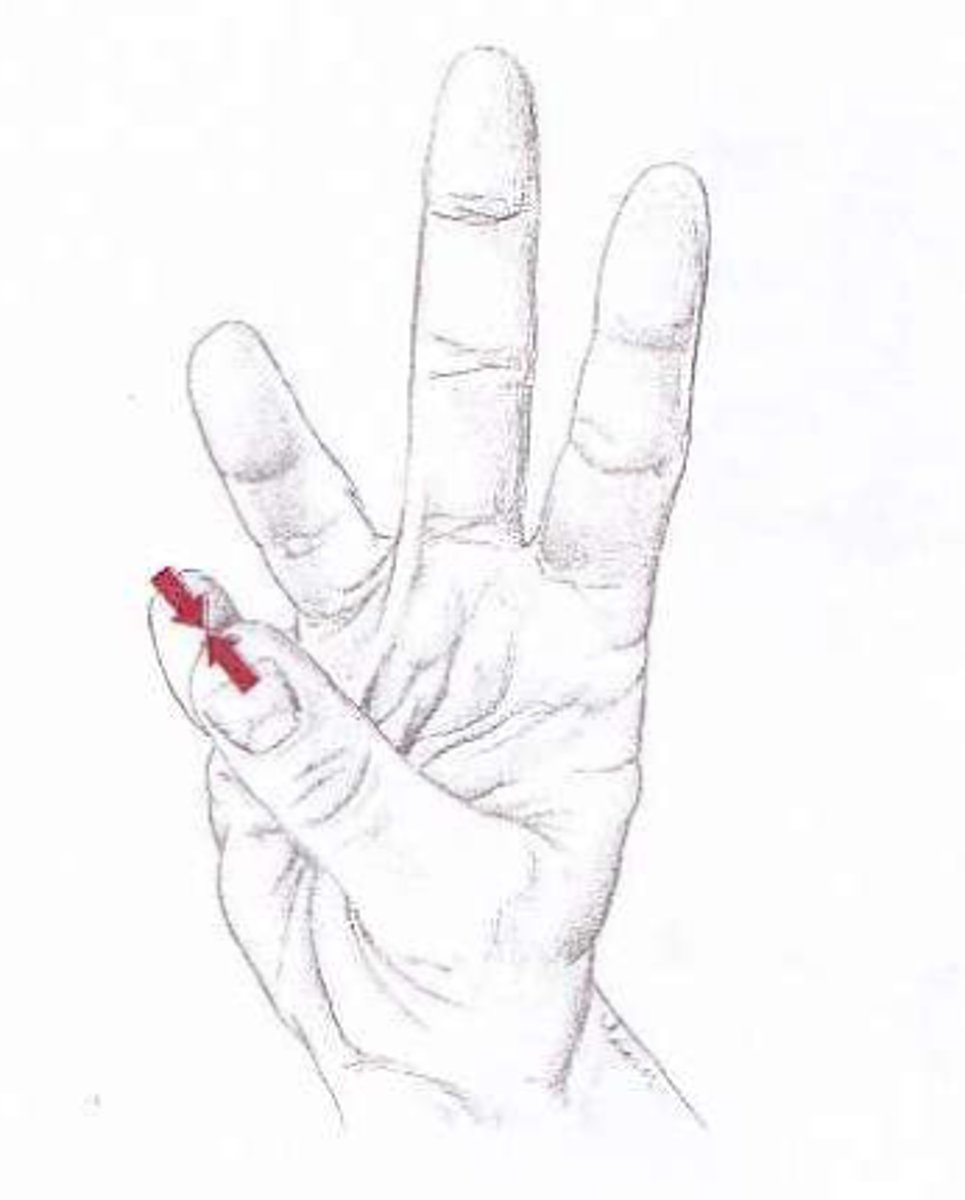
(Specialised Feet Movement) Flexion of Ankle
see diagram
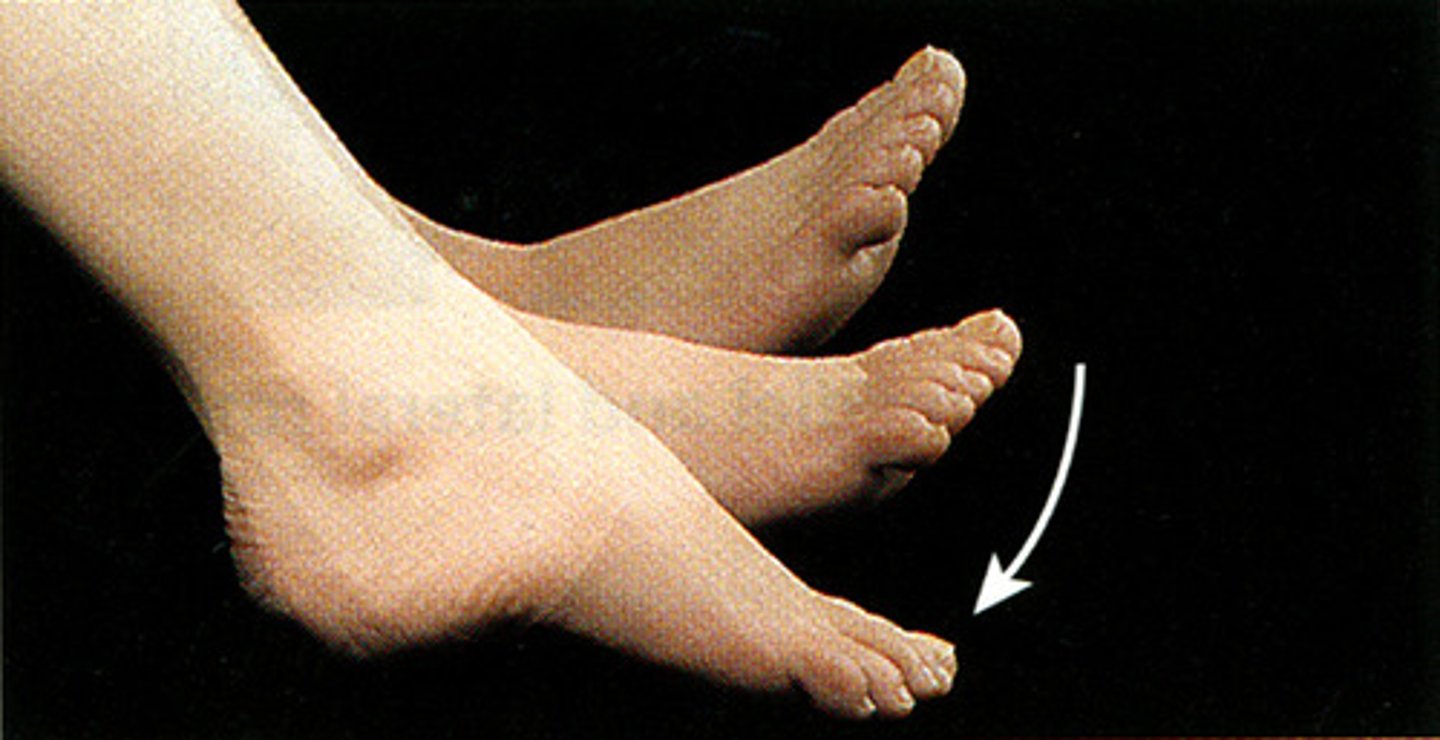
(Specialised Feet Movement) Inversion
see diagram
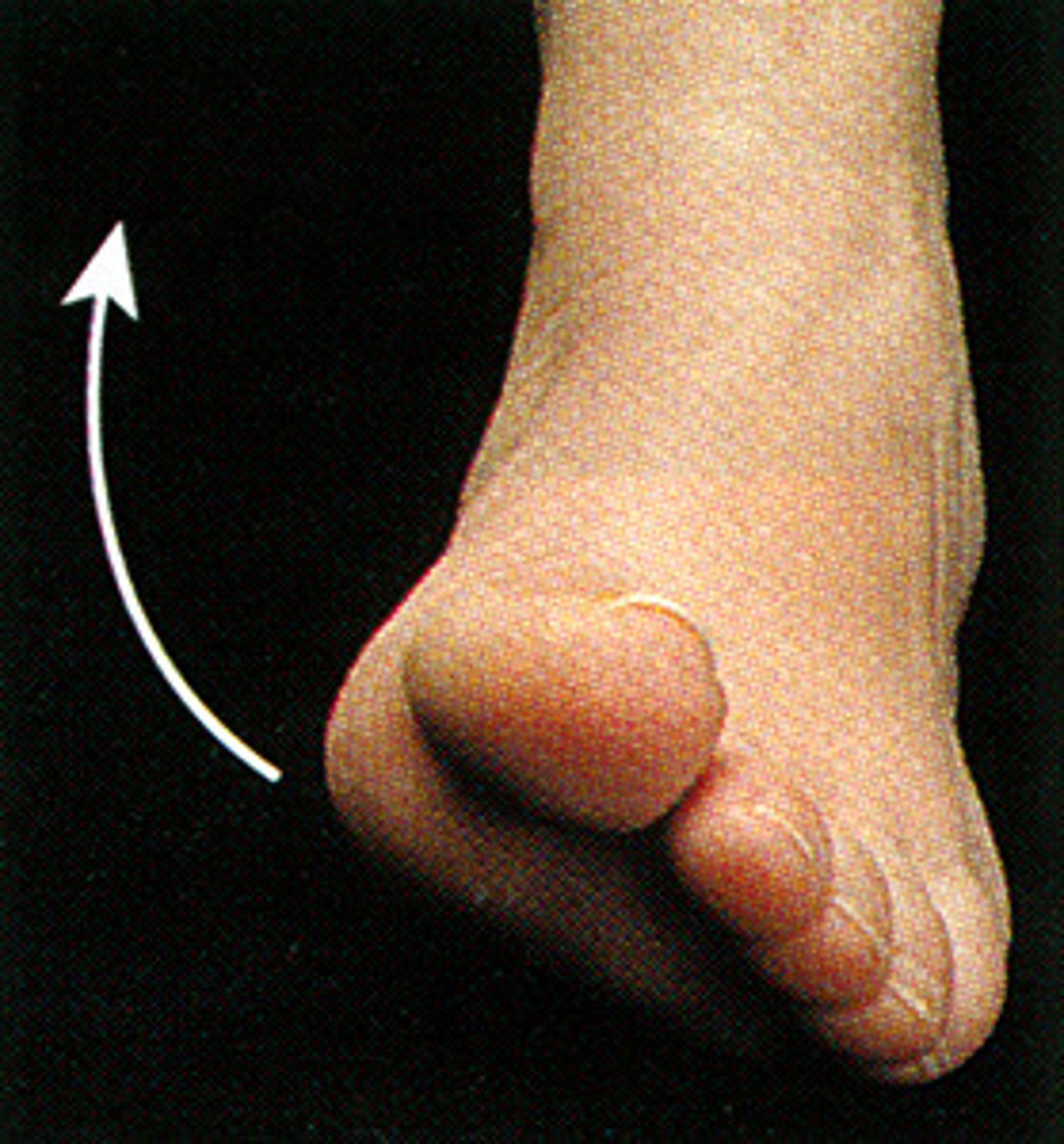
(Specialised Feet Movement) Eversion
see diagram
Applying Movement
- a movement should always be accompanied by a joint:
- E.g "Movement" at a "Joint"
- e.g Flexion at a knee joint
Good source for movement visualisation
https://www.kenhub.com/en/library/anatomy/directional-terms-and-body-planes