ANHB3323 (9) - cell-cell interactions
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
19 Terms
2 Main ways animal cells are bound together
Epithelial cells:
Anchored cell to cell and cell to ECM
Mesenchymal cells (Cancer Type):
cell-ECM dominant
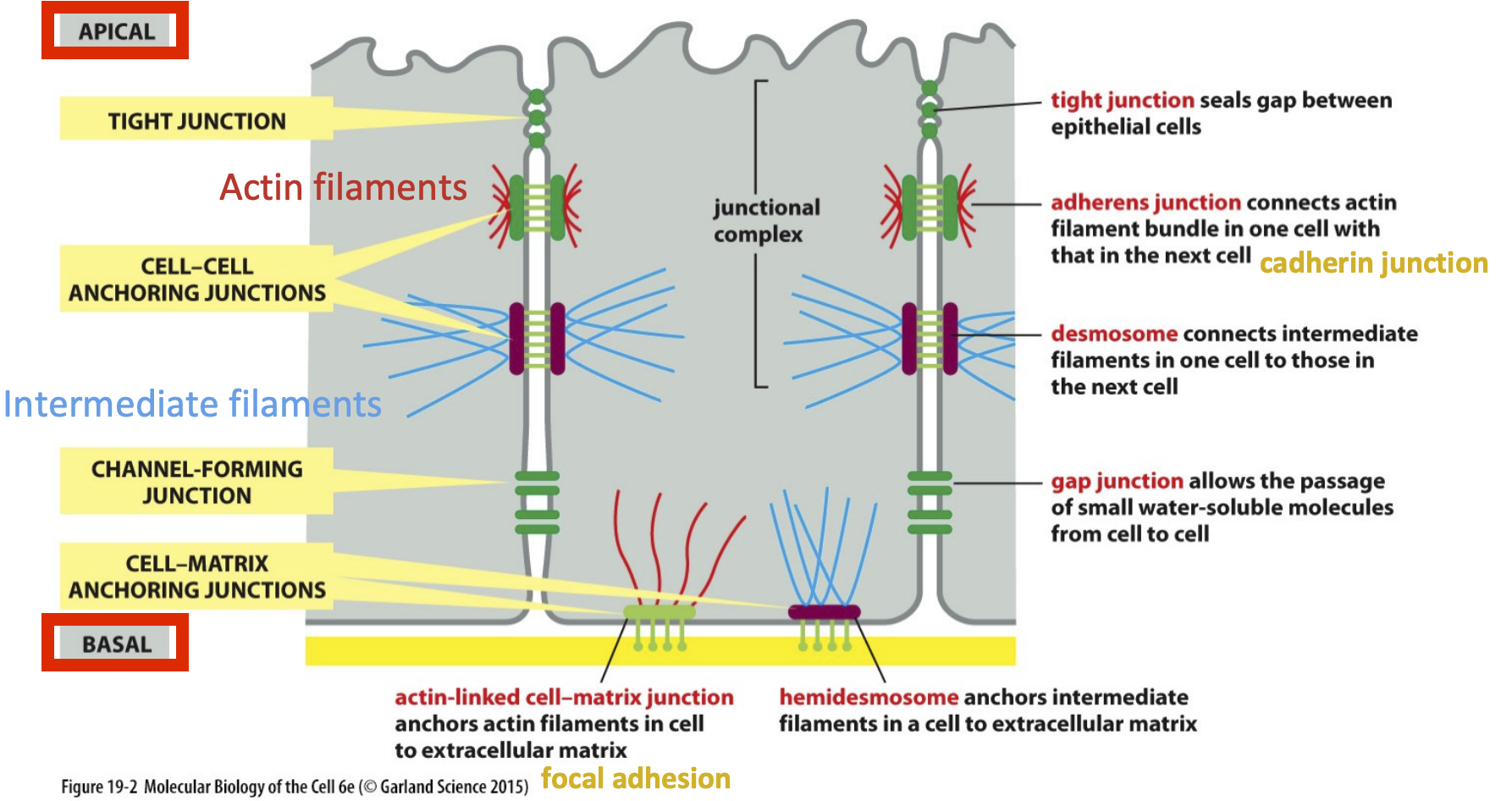
Cell Junction types
1. tight junction
2. cell-cell anchoring junctions
3. channel-forming junctions
4. cell-matrix anchoring junctions
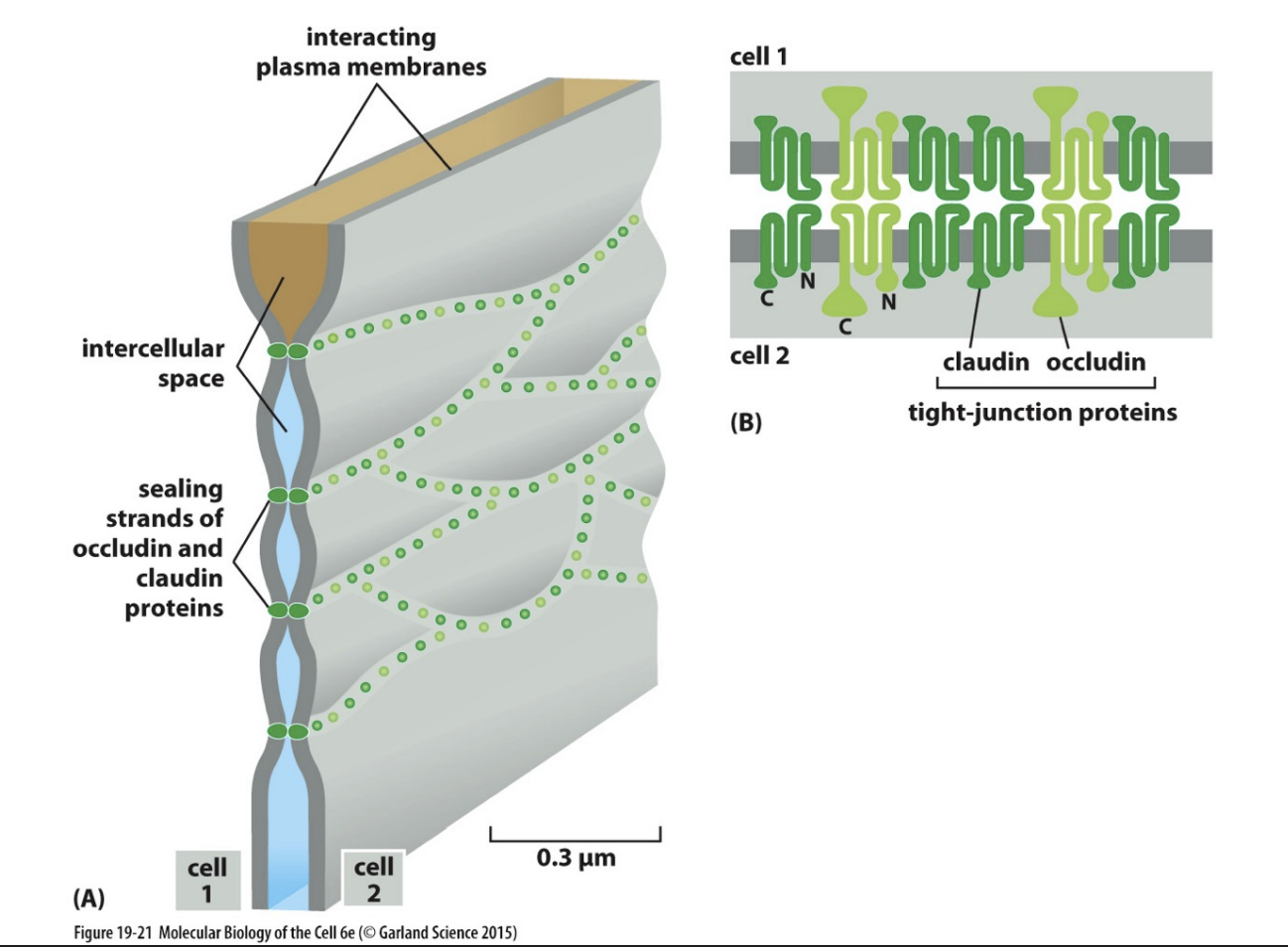
Tight junctions
seals gap between epithelial cells - prevent uncontrolled molecule movement
contain strands of transmembrane adhesion proteins
Proteins:
Claudin and Occludin
Mice with no claudin-1 gene
fail to make tight junctions = lose water rapidly
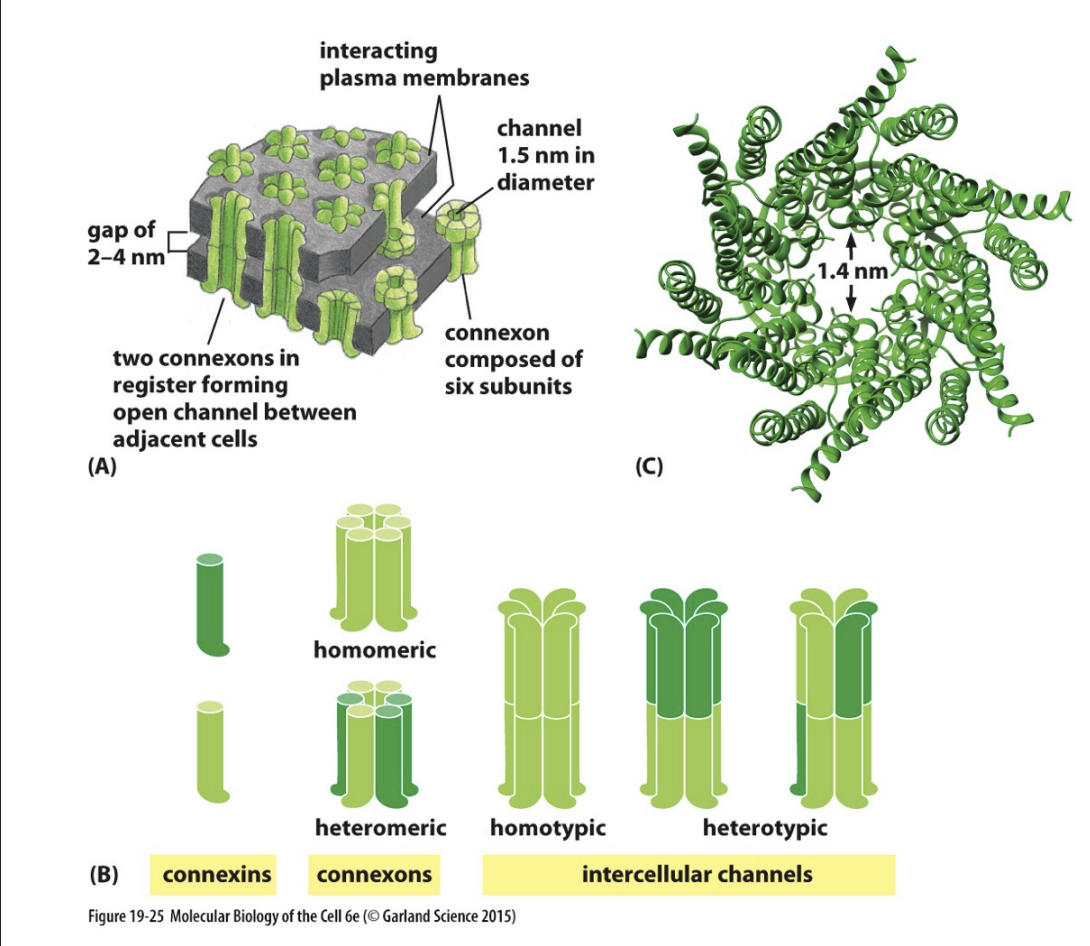
Gap Junctions - channel forming
Allows passage of small water-soluble molecules from cell to cell
connect cells electrically (ions) and metabolically (molecules)
Diameter of gap dictates size of molecules that can pass
Gap junction structure
Connexins
2 types of proteins that make up the channel
Connexon
Half og channel
Heteromeric (mix of the two types of connexins)
Homomeric (only one type of connexin)
Intercellular channel
both sides of the channel from each cell combines
Cell-cell anchoring junction types
Adherens junction (actin filament)
Desmosomes (intermediate filaments)
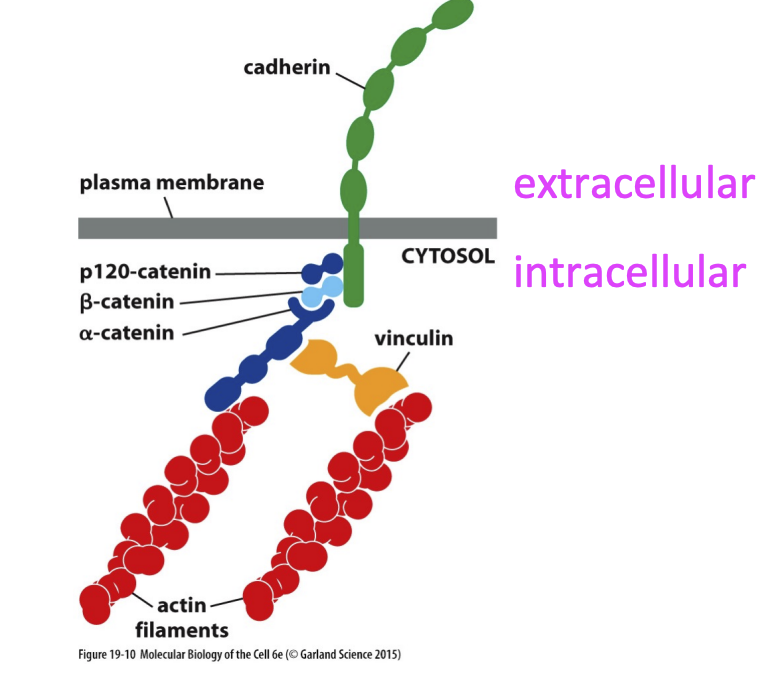
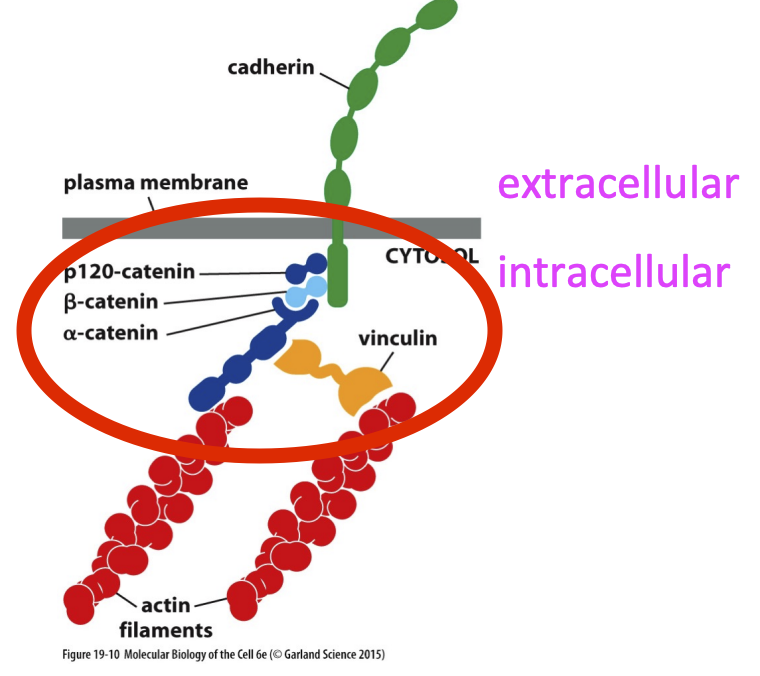
Adherens junction
connects actin filament bundle in one cell with that in the next cell
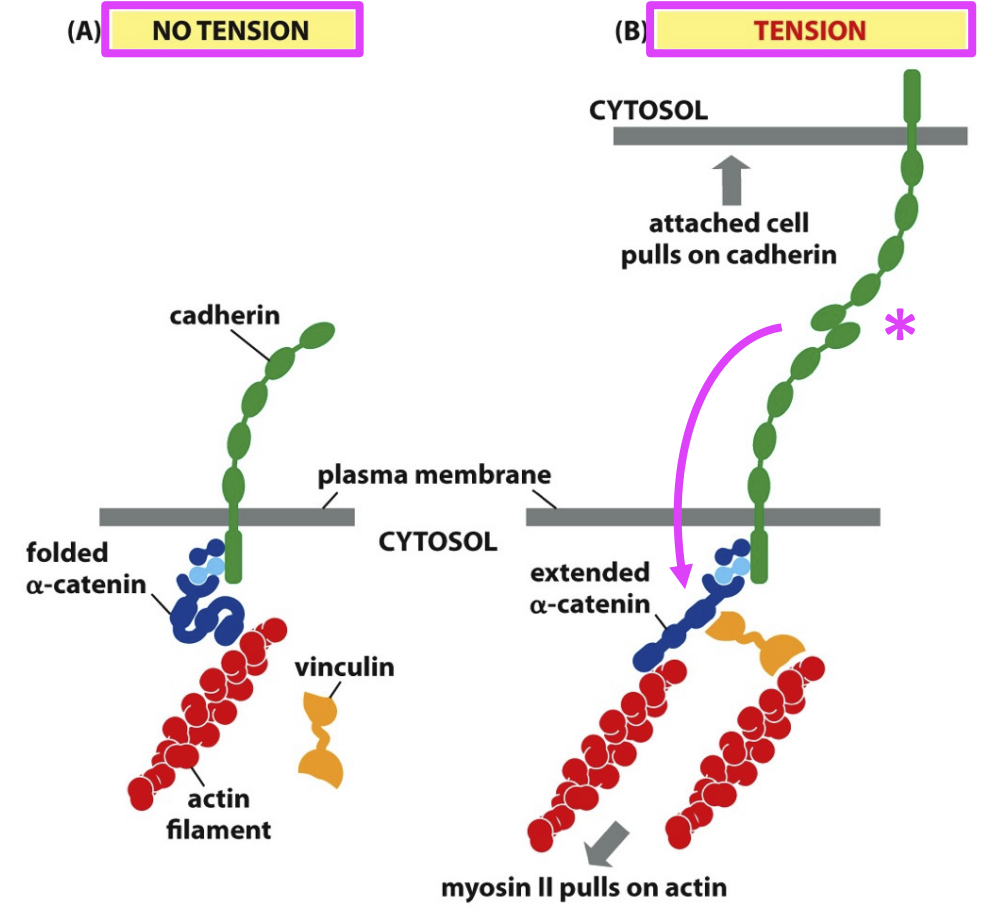
Adherens junction mechanism
Tension (extracellular) is required to expose the binding side of the actin fimalent and unfold the alpha-catenin molecule
allows for binding of vinculin
Junction is activated by tug of war tension between cadherins
Desmosomes
connects the intermediate filaments in one cell with that in the next cell
utilise non-classic cadherin proteins
Connected to hemidesmosomes via intermediate filament
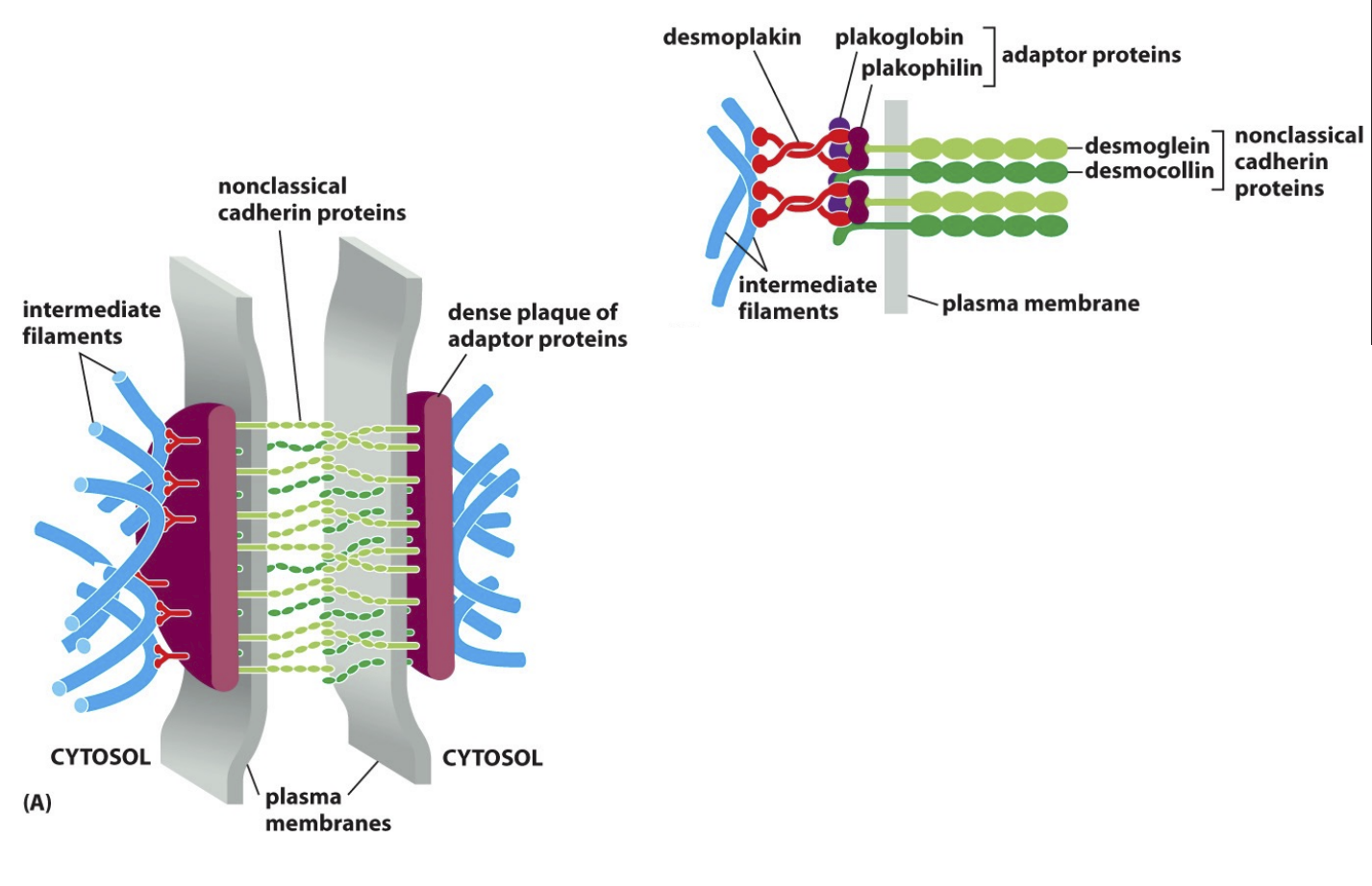
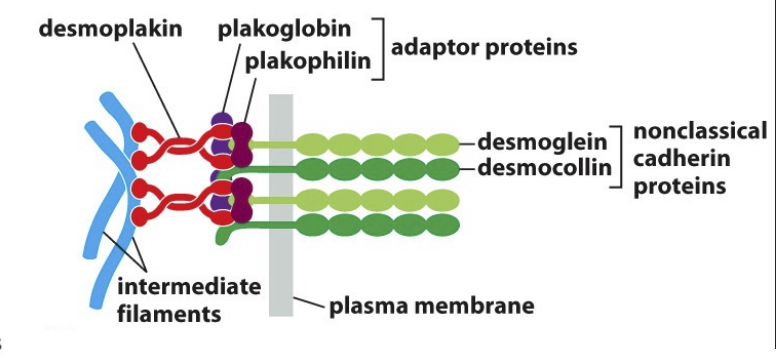
Desmosome elements and their protein types
Cytoskeleton→ Intermediate filament
Intracellular adaptor protein
plakoglobin, plakophilin, desmoplakin
Transmembrane Adhesion protein
desmoglein, desmocollin (non-classical cadherin proteins)
Extracellular Ligand
desmoglein, desmocollin
Cell-matrix anchoring junctions (types)
Actin linked cell-matrix junction
Hemidesmosome
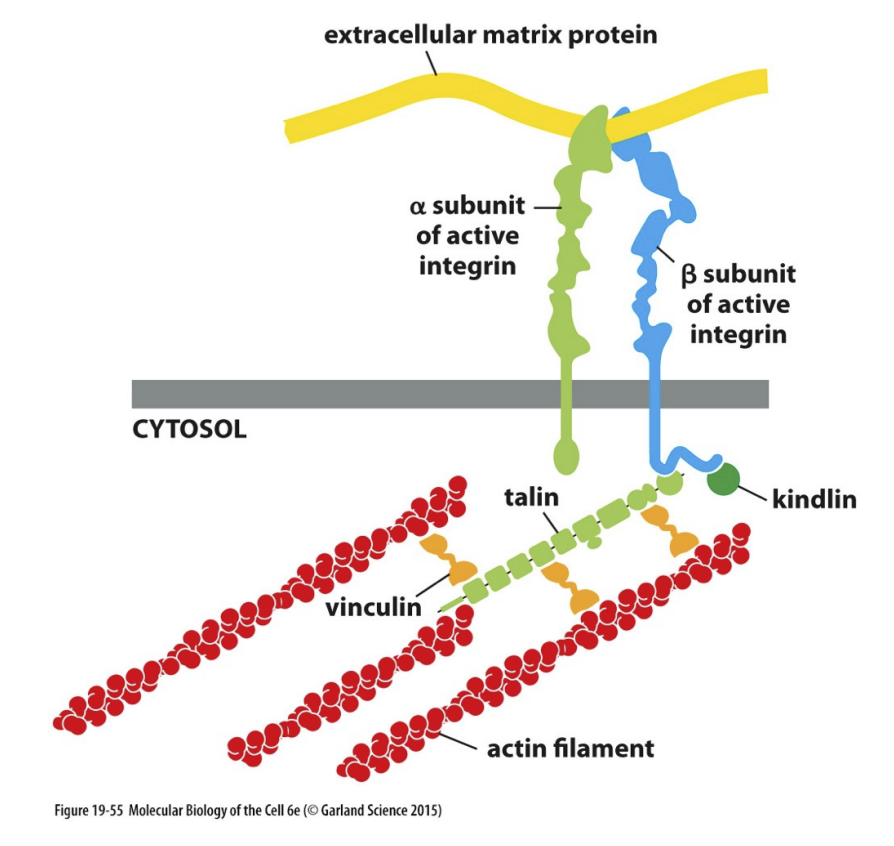
Actin-linked cell matrix junction
Anchors actin filaments in cell to extracellular matrix
Adhesion proteins:
Integrin heterodimer (with alpha (24) and beta (8) subunits)
Adaptor proteins:
Talin & Vinculin
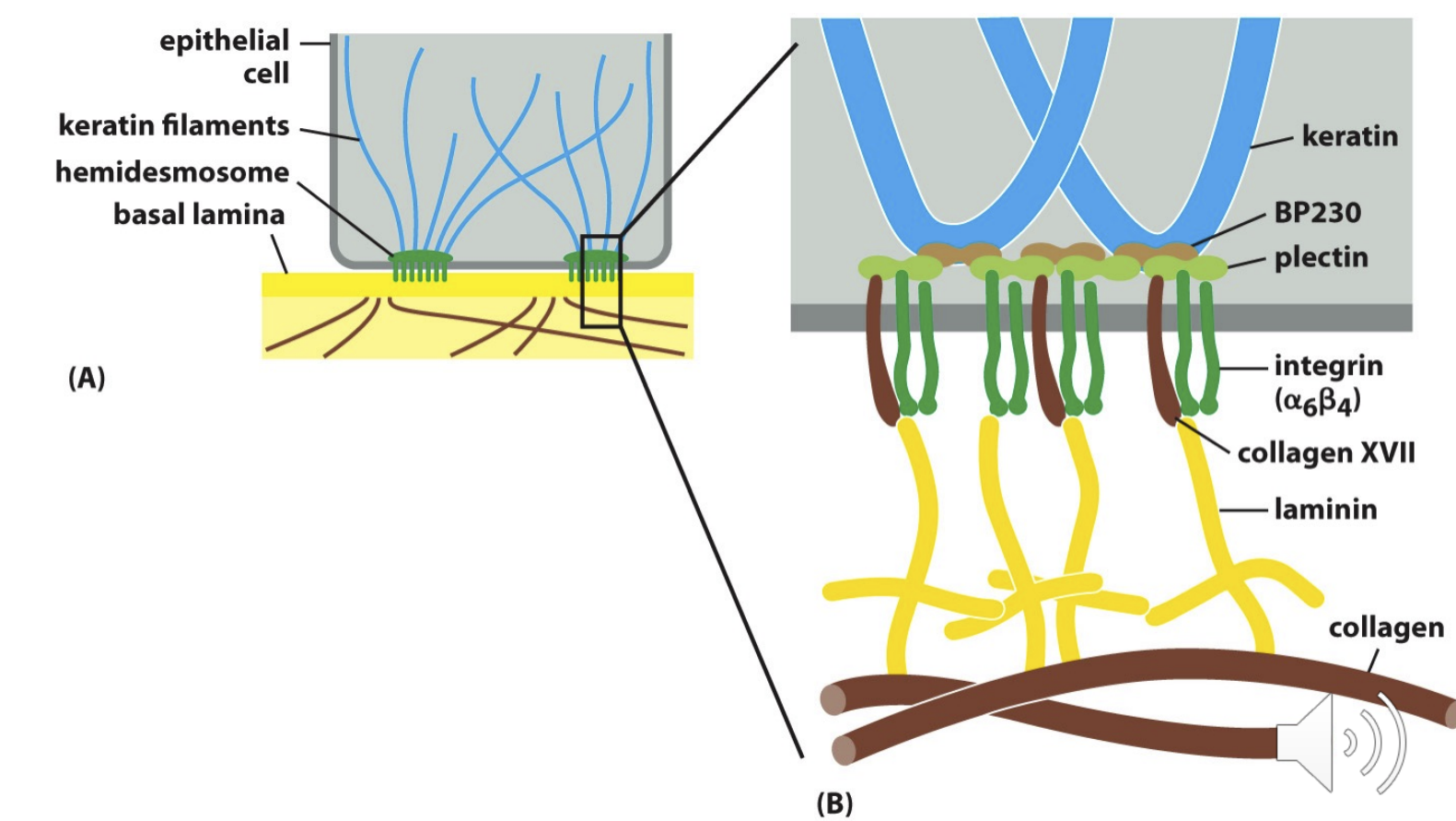
Hemidesmosome
Anchors intermediate filaments in a cell to extracellular matrix
adhesion proteins
Integrin a6B4 + Collagen XVII
adaptor proteins
BP230 + Plectin
Transmembrane adhesion proteins
Go through the cell membrane to adhere to something outside
connects to intracellular adaptor proteins → which link to the filaments
(found in anchoring junctions, cell-cell or cell-ecm)
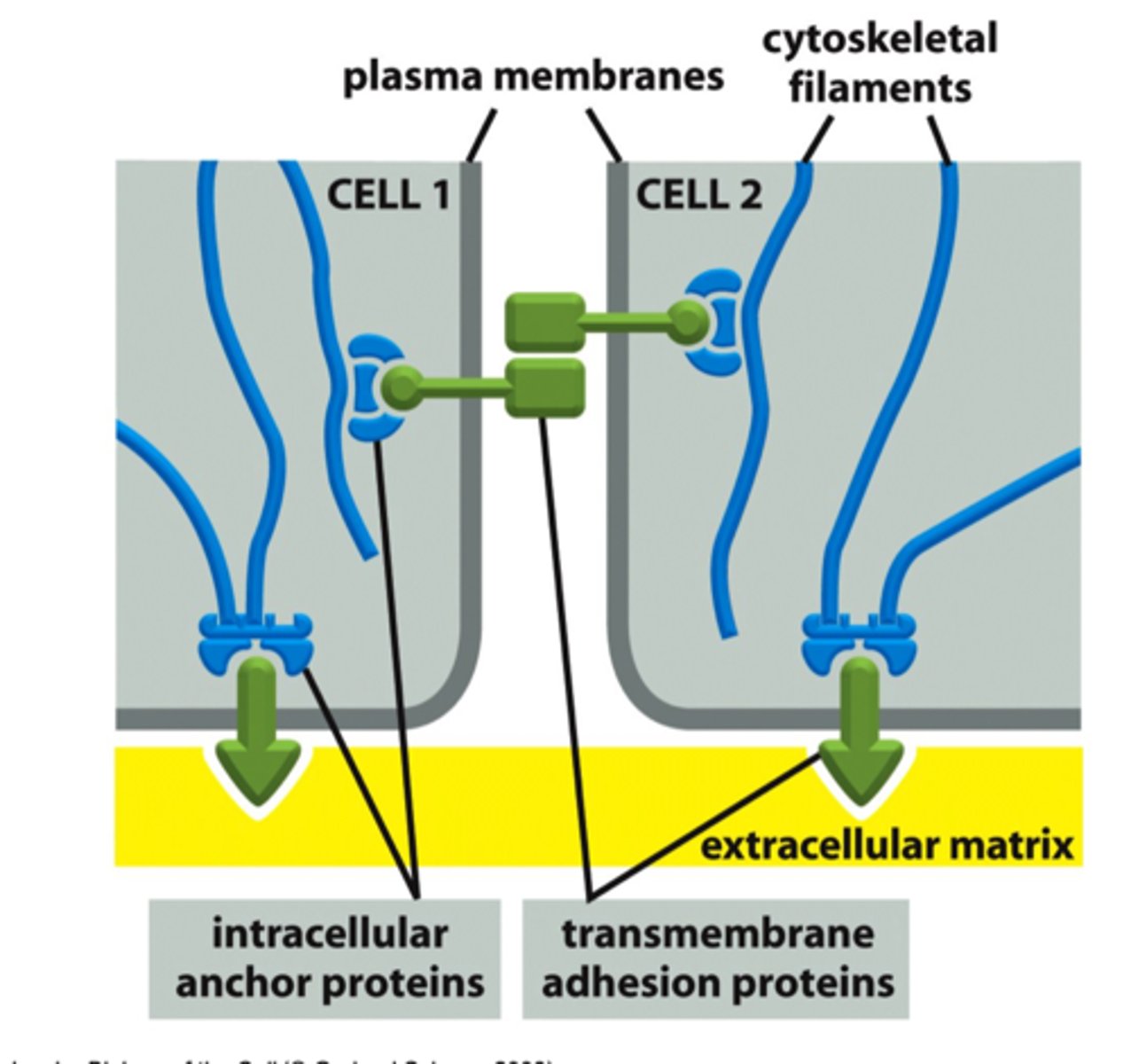
Intracellular adaptor proteins
Connect the cytoskeleton filaments to the transmembrane adhesion membrane.
cell-cell vs cell-ecm transmembrane adhesion proteins
Cell-cell = connect same kind of adhesion proteins
Cell-ECM = asymmetric
Classical Cadherins - adhesion molecules
A transmembrane membrane adhesion protein
The extracellular part has 5 domains, separated by flexible hinge regions
Each hinge has calcium channels that create a velcro-like mechanism holding cells together
Present homophilic bonding which allows for sorting by types and level of expression
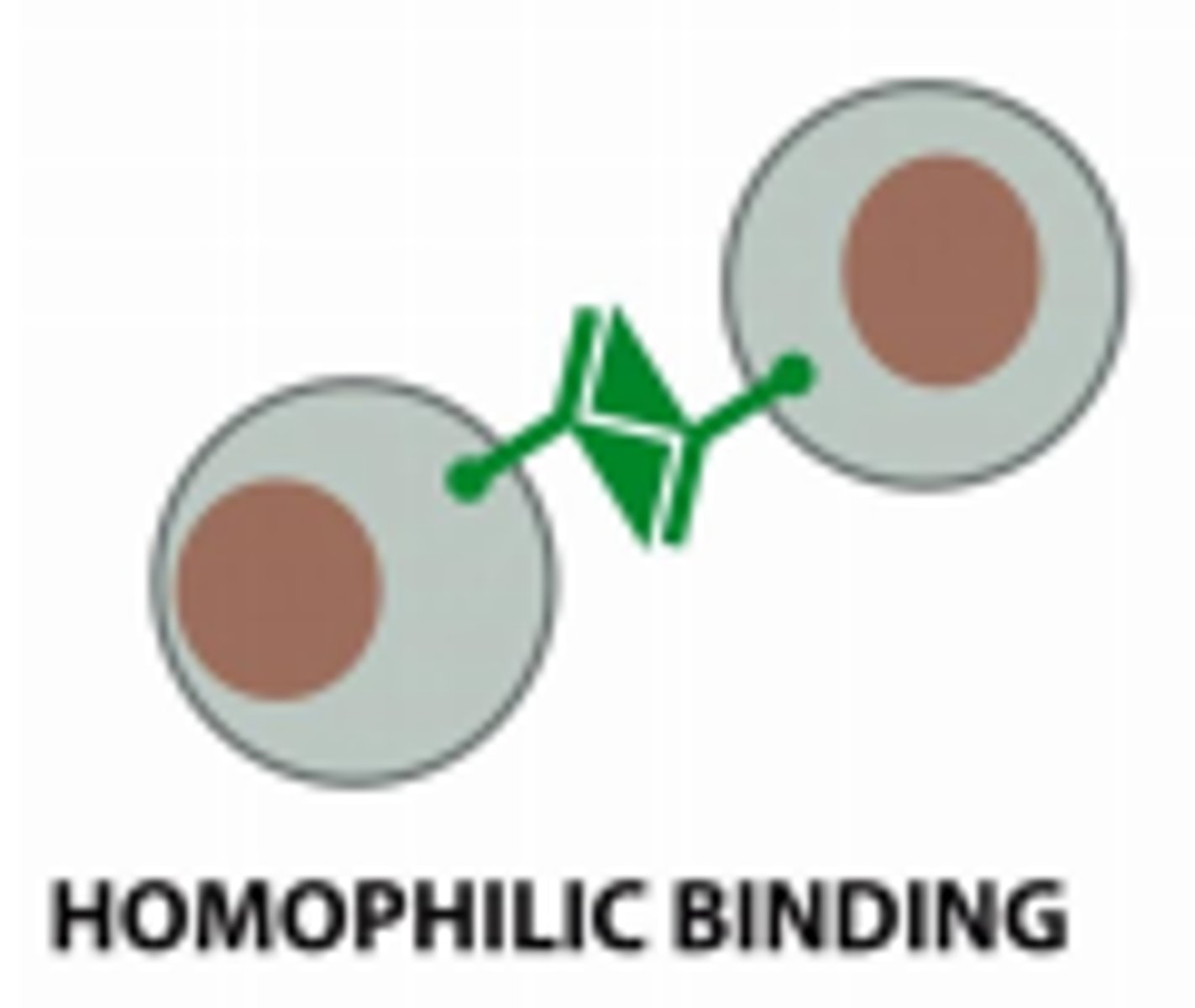
What do Cadherins use to connect to cytoskeleton?
Catenins and Vinculin used to connect to actin filament
happens via force feeling upon homophilic binding
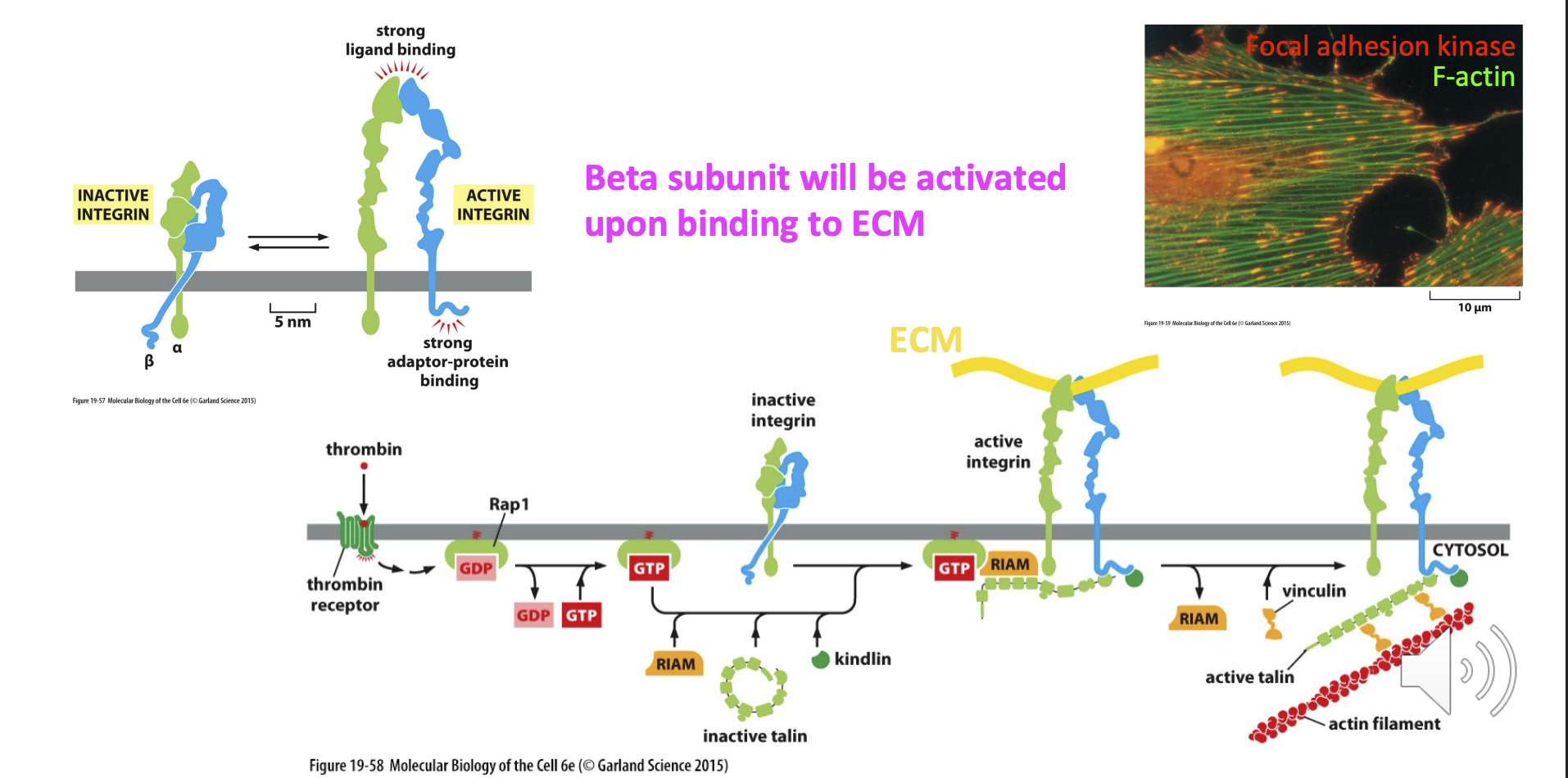
Activation of integrin leads to...
intracellular signalling
(integrin beta subunit will be activated upon binding to ECM = recruits intracellular adaptor proteins)