Lab Midterm , Bones of the Lower Limb and Joints, Axial Skeleton and Upper Limb
1/507
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
508 Terms
anatomical position
axial
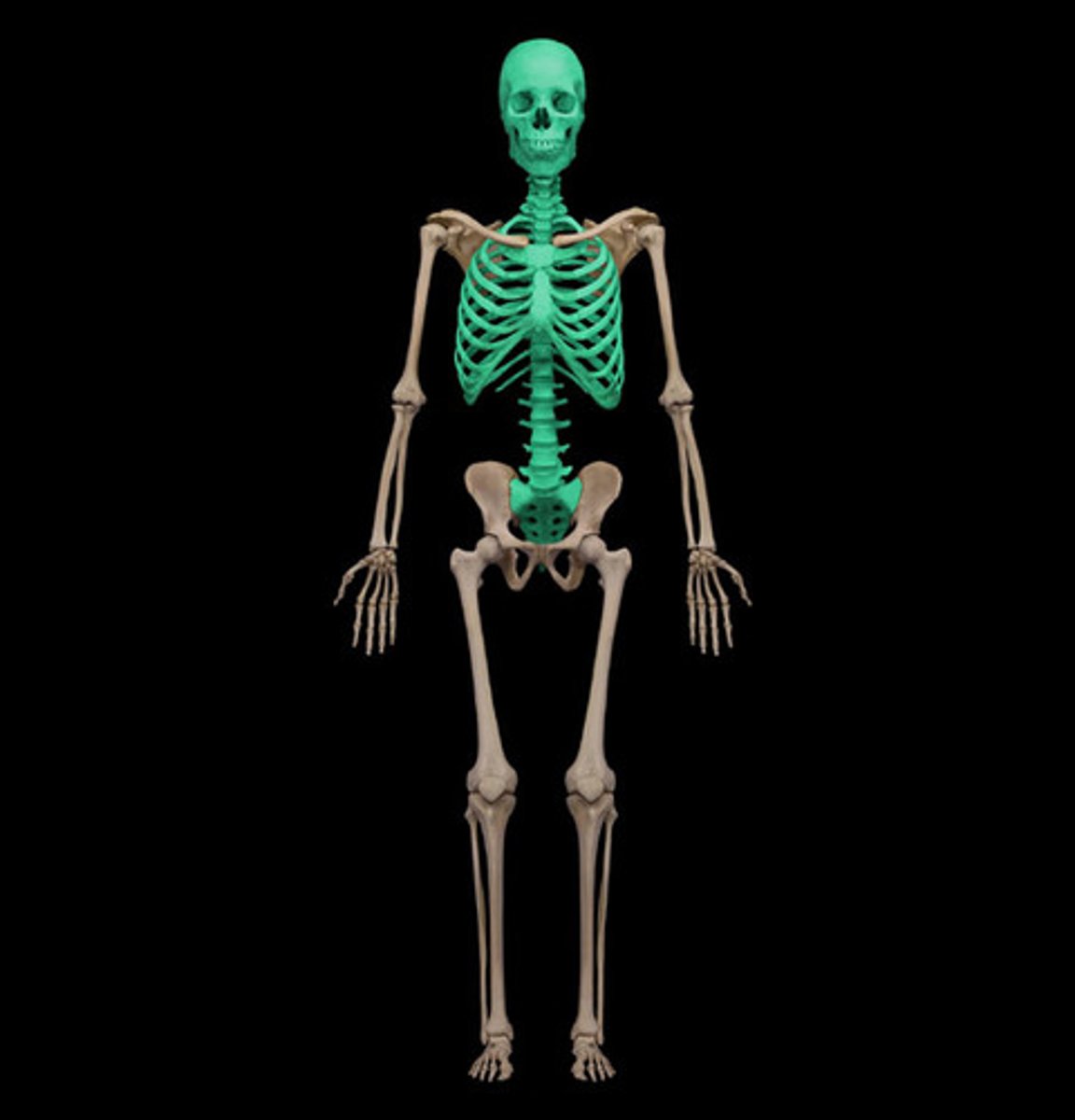
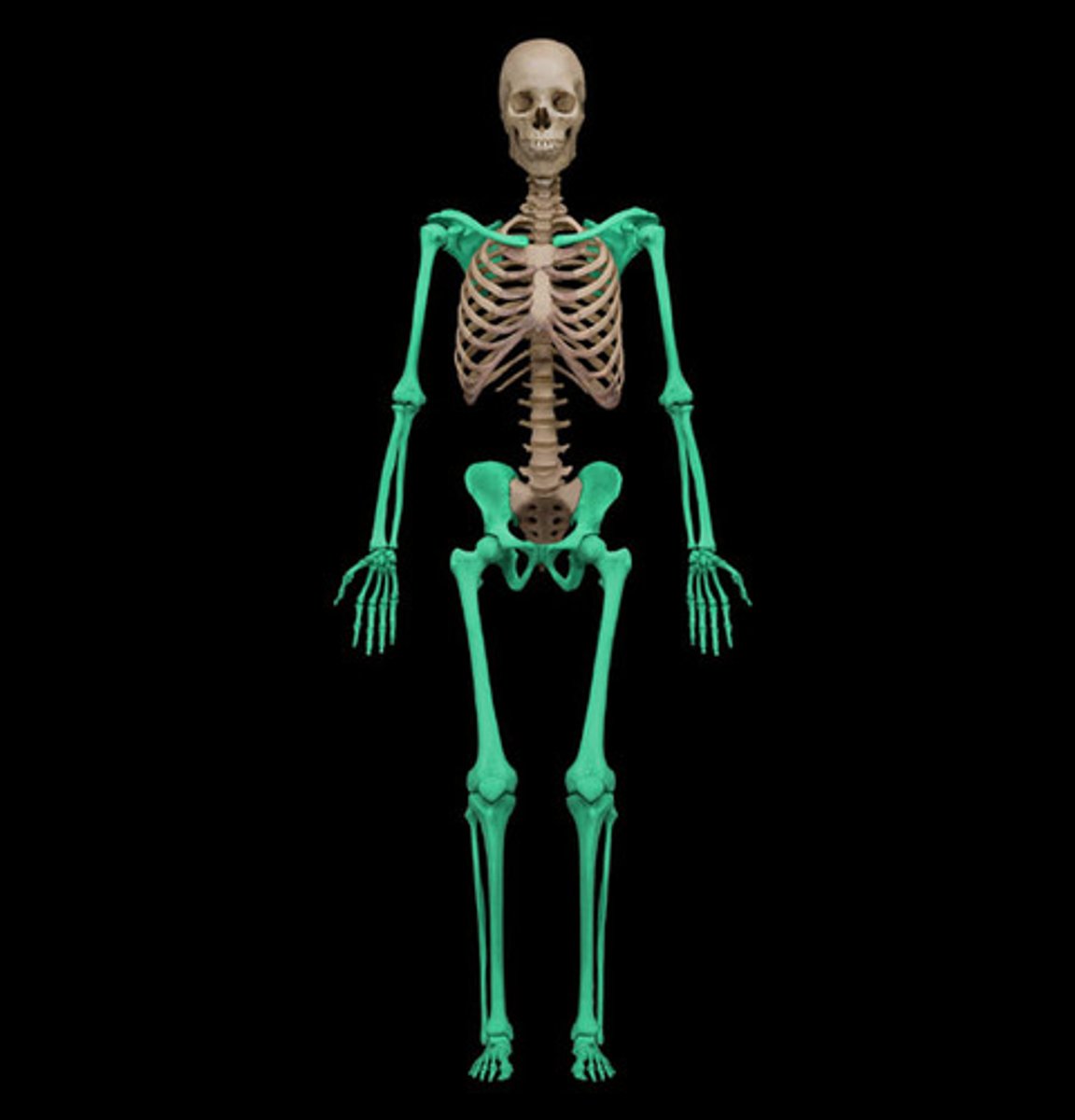
appendicular
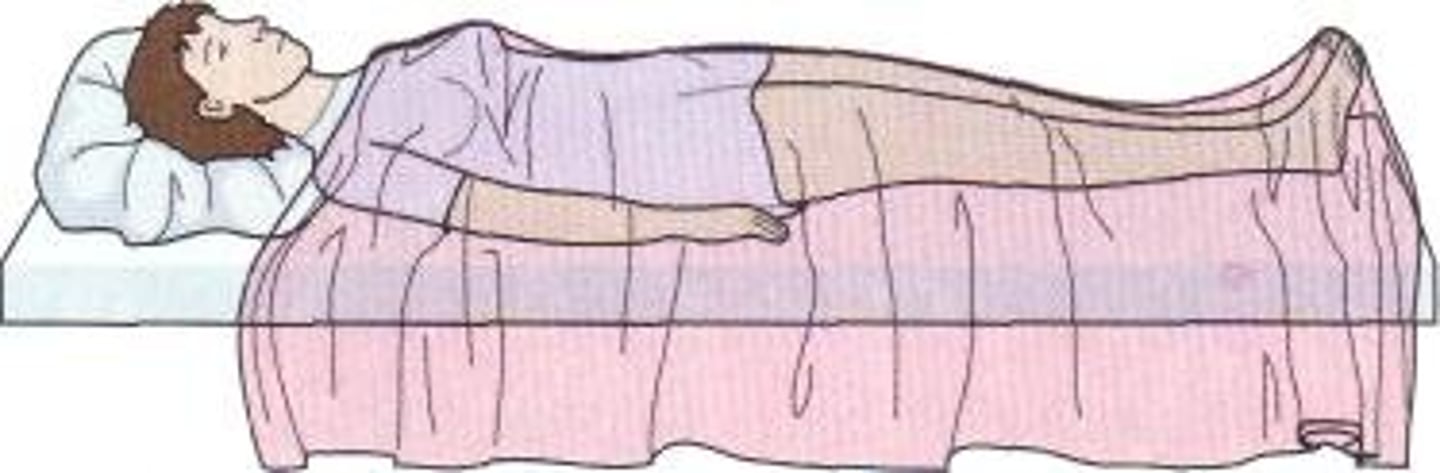
prone
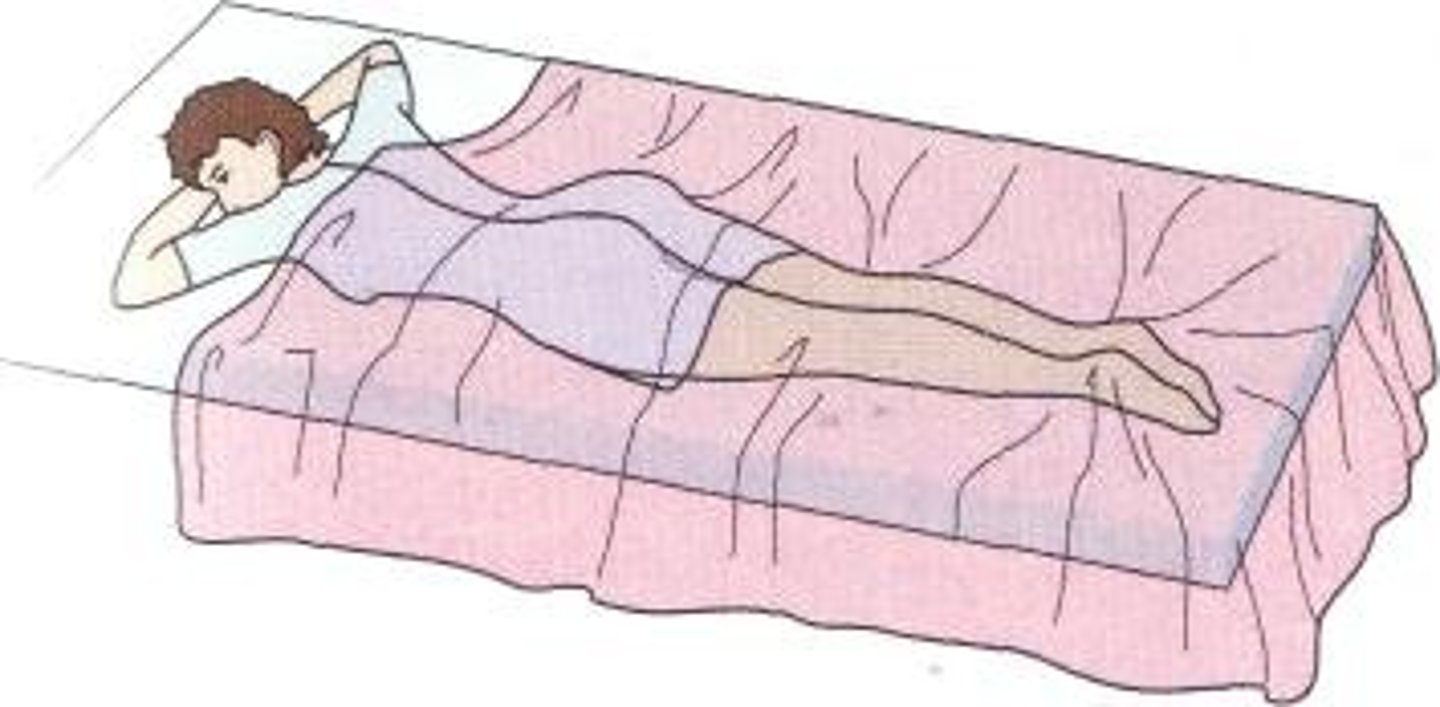
supine
superior
above
inferior
below
anterior
towards front
posterior
towards back
cephalic
towards the head
caudal
toward the tail
medial
toward the midline of the body; on the inner side of
lateral
away from the midline
superficial
close to the surface
deep
away from the surface
proximal
close to the point of attachment
distal
far from the point of attachment
cephalic region
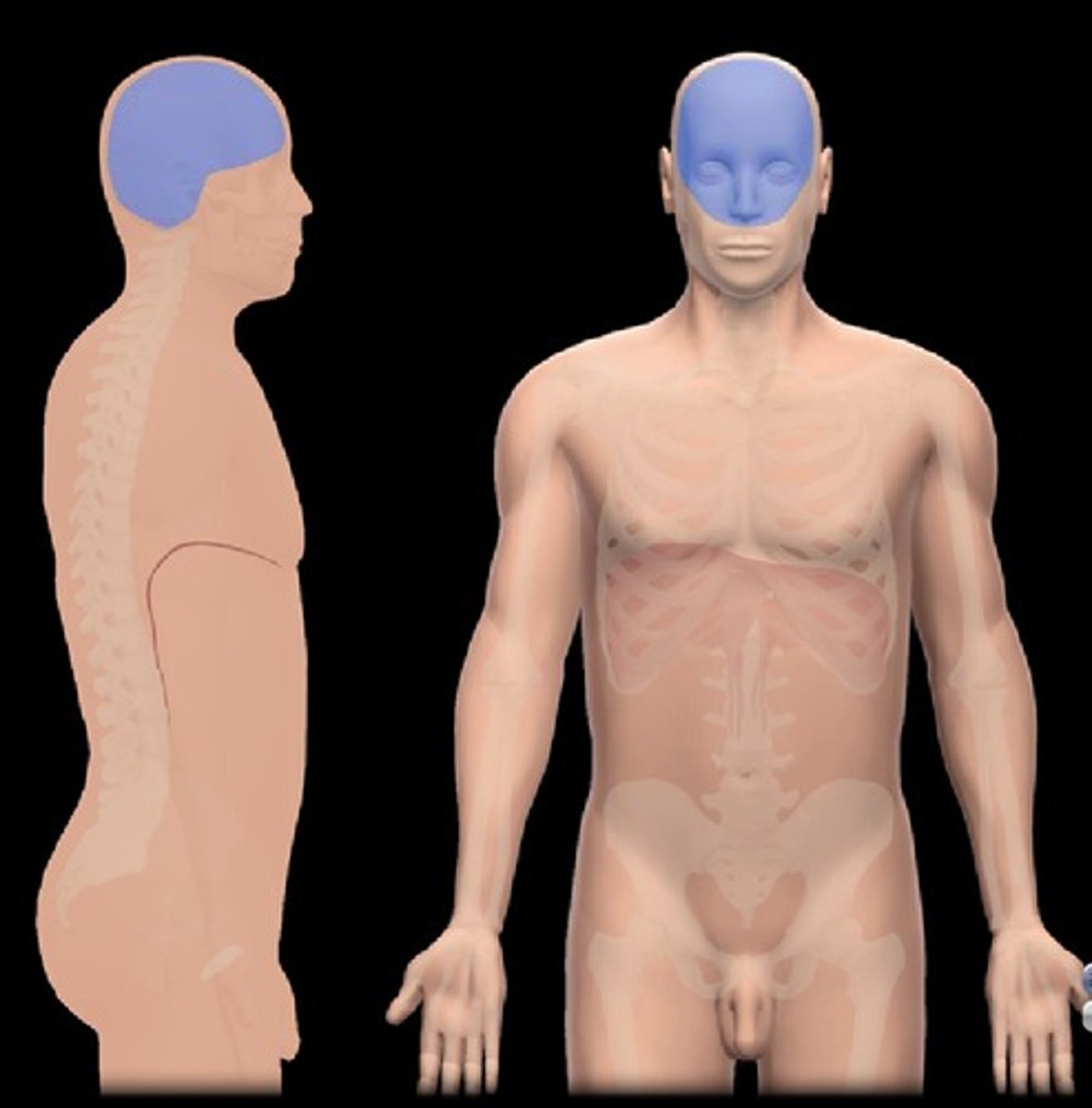
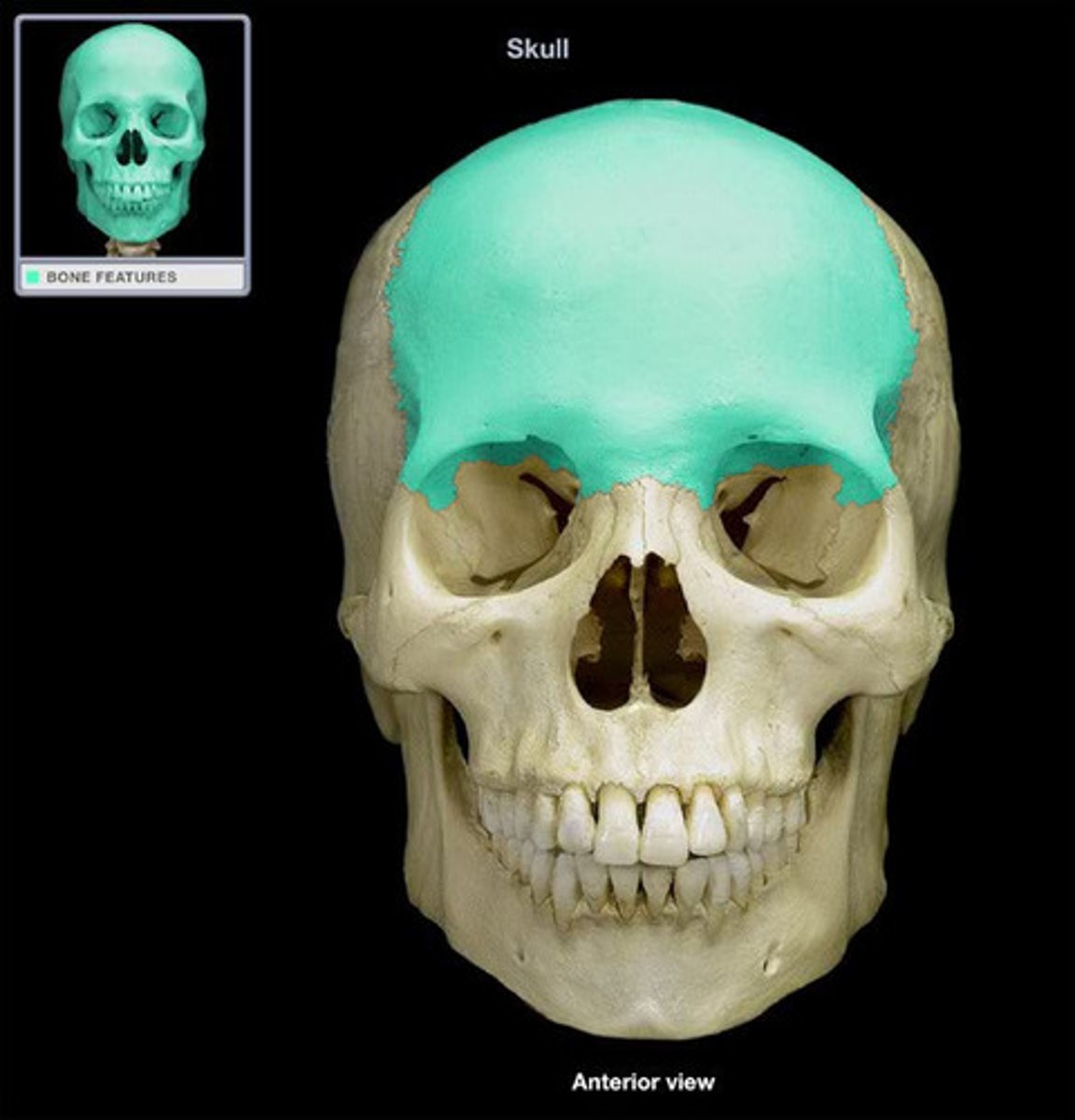
frontal
forehead
orbital
eye

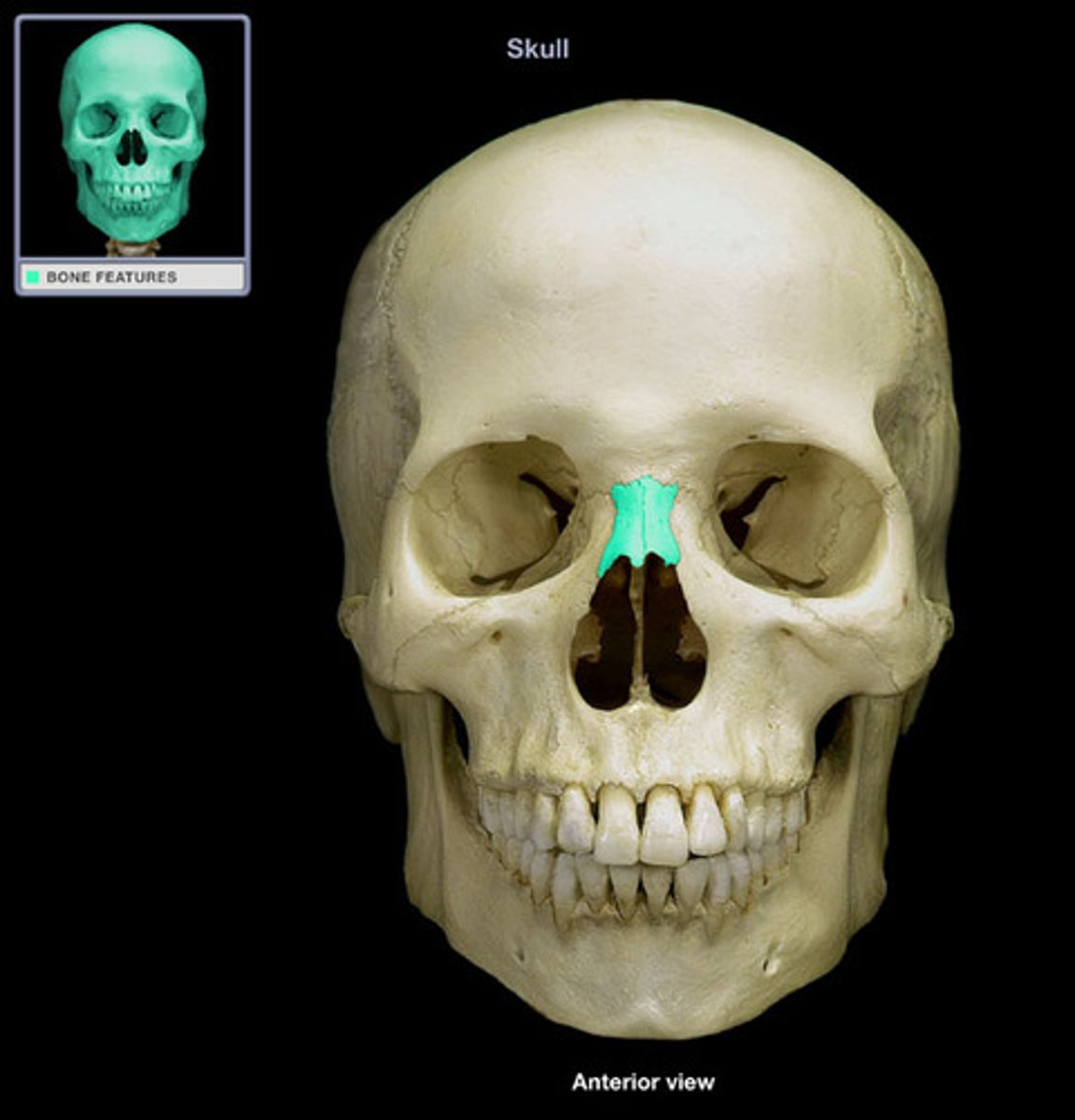
nasal
nose
oral
mouth
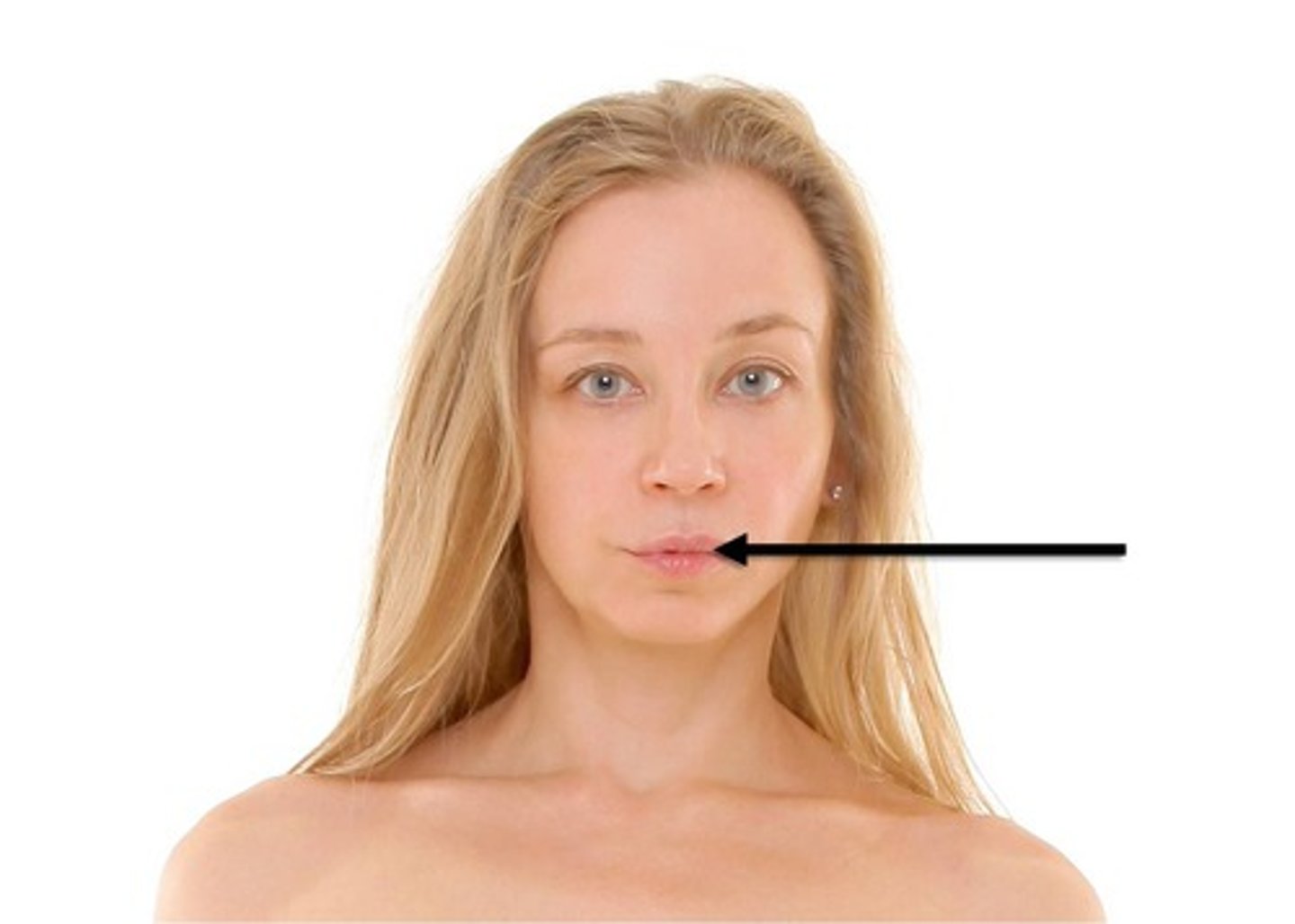
mental
chin
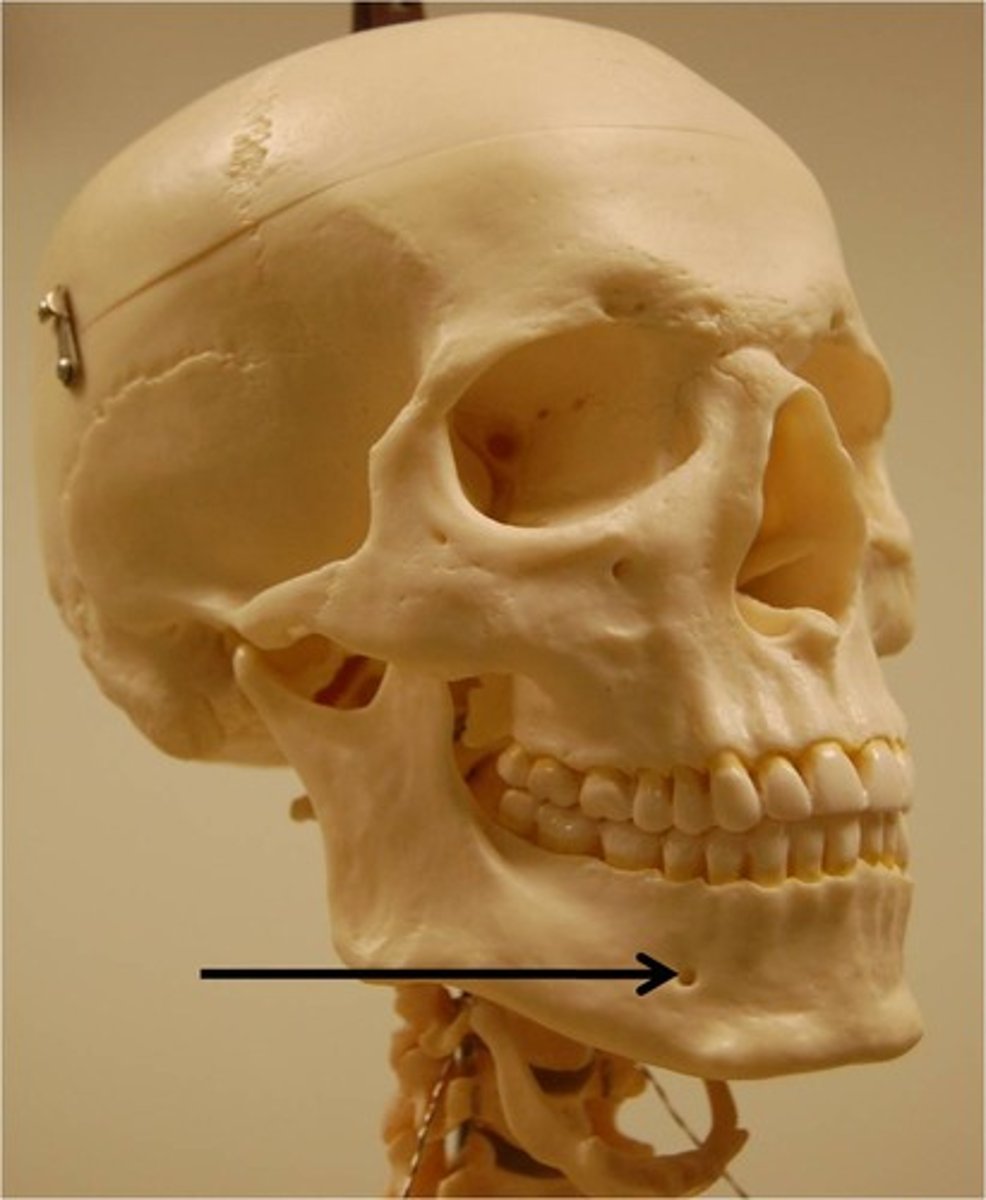
buccal
cheek area
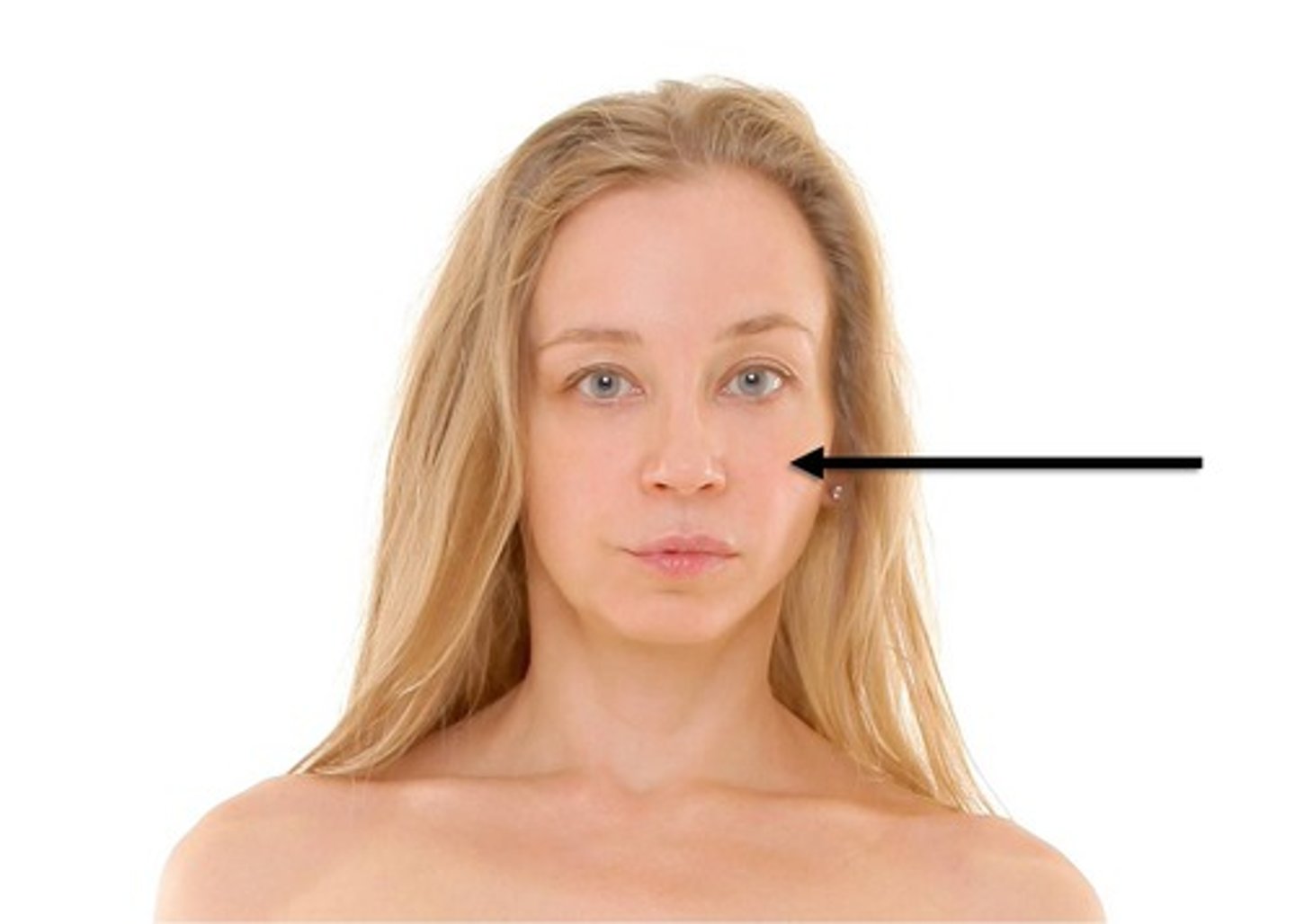
cervical
neck area
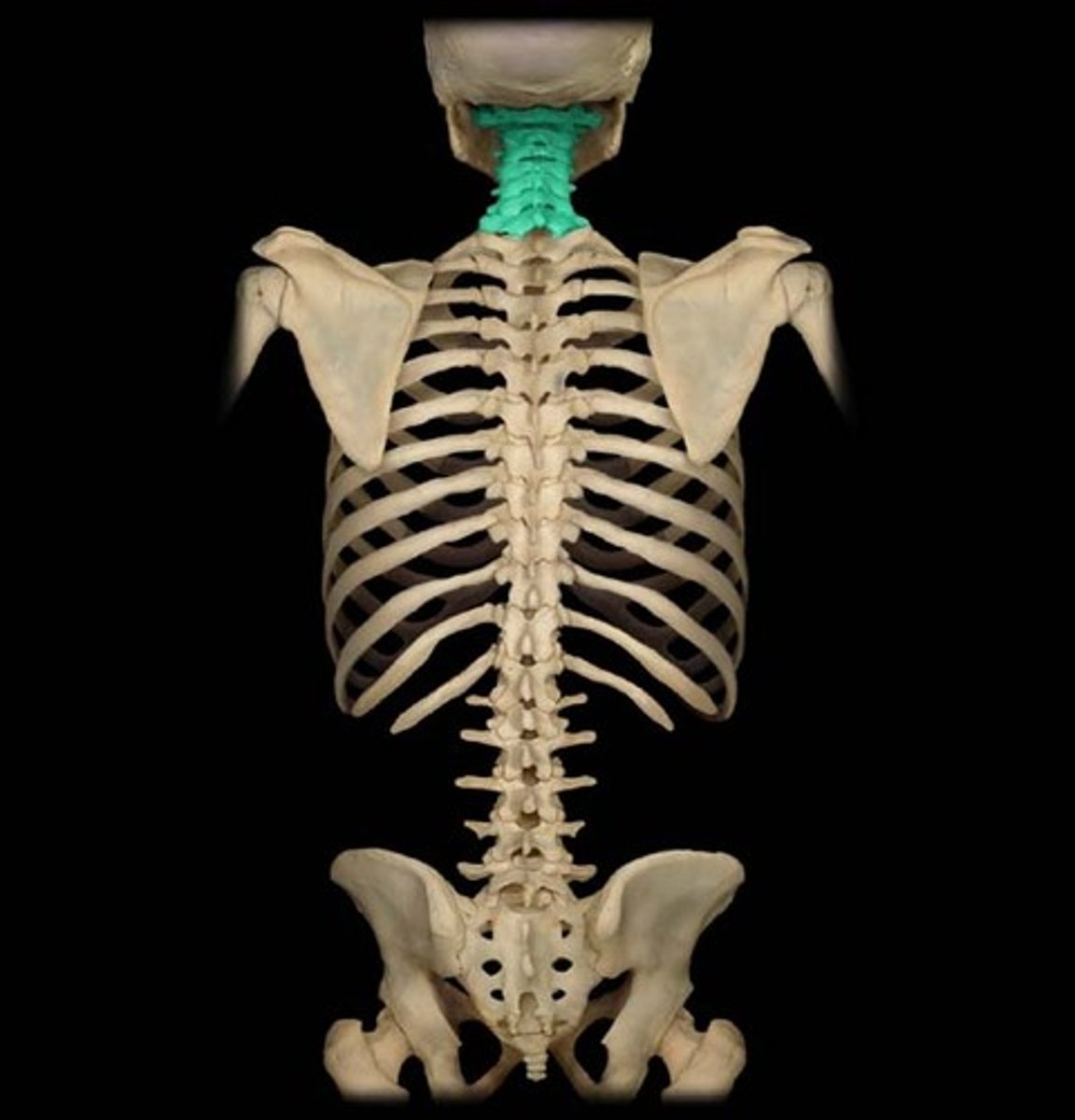
trunk
acromial
shoulder area
thoracic/pectoral
chest
mammary
breast
sternal
middle of thorax
abdominal
abdomen
umbilical
belly button
pelvis
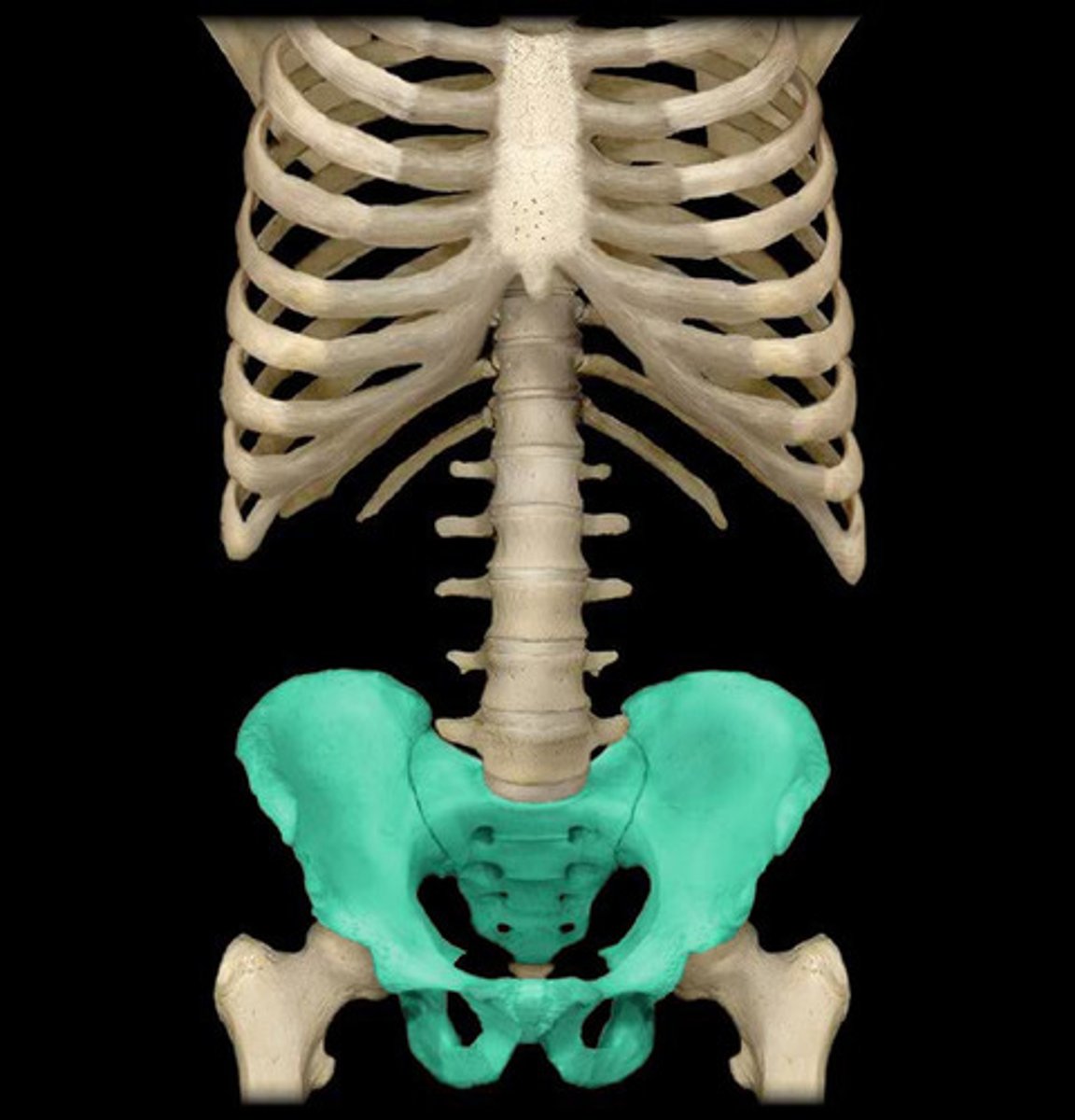
coxal
hip
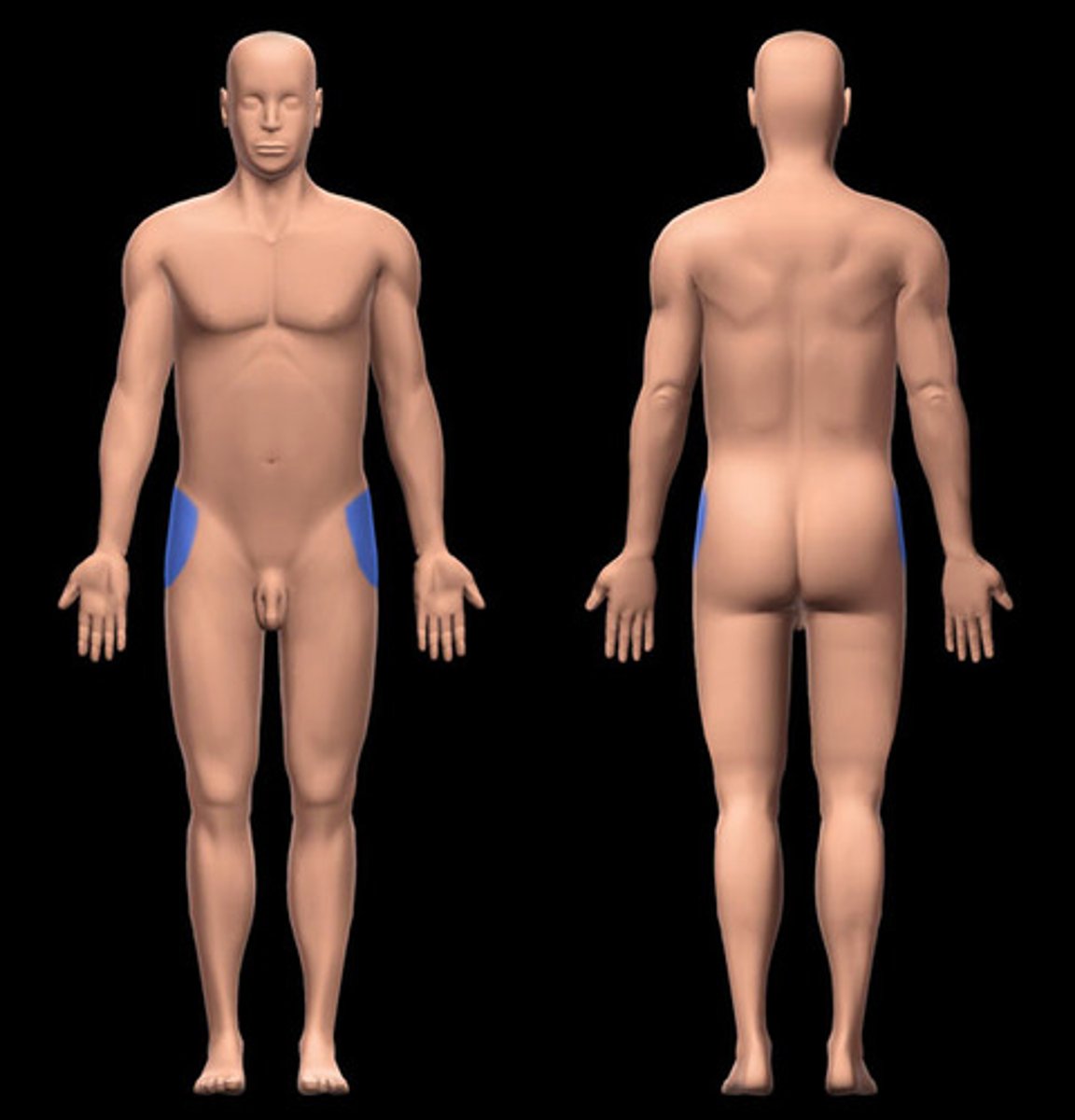
inguinal
groin area
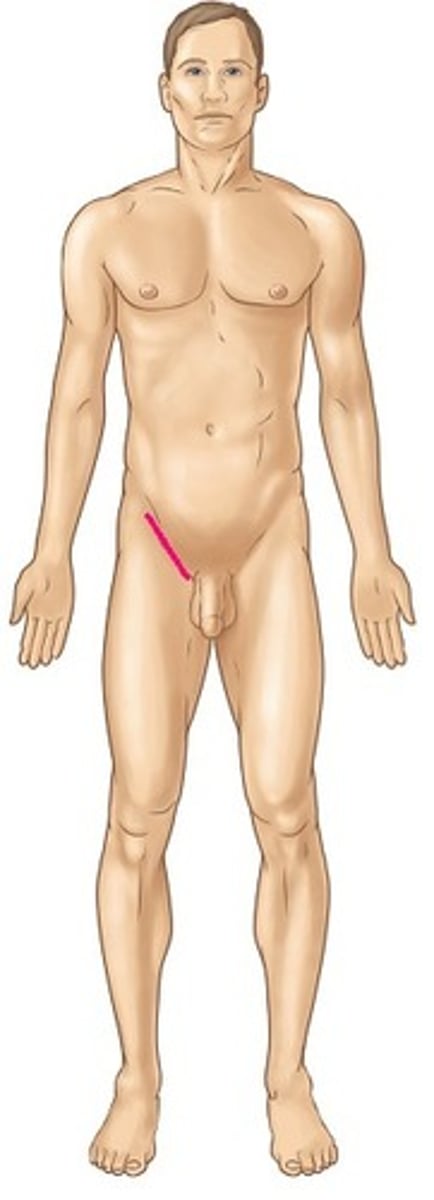
perineal
area between anus and reproductive organs
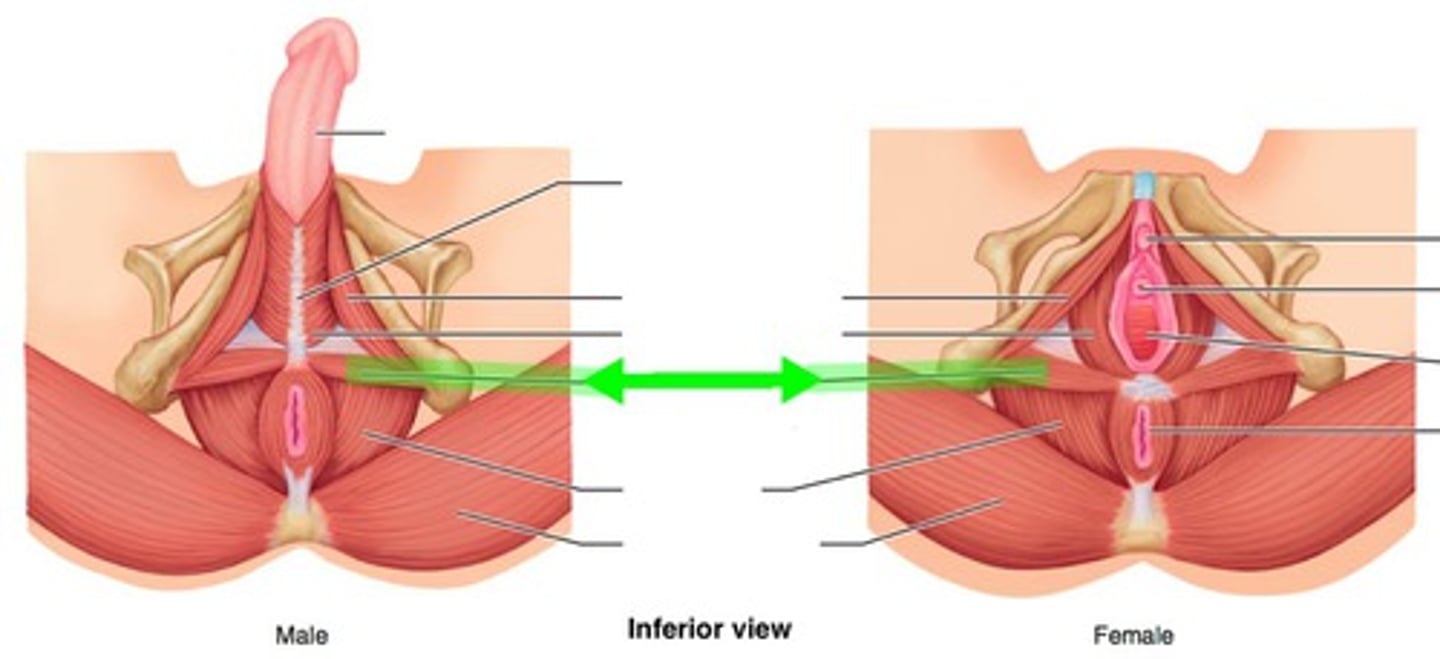
pubic
genitals
pudendal
external genitalia
octic
ear area
occipital
back and bottom of the head
vertebral spine
scapular
shoulder blade region
cervical
neck
thoracic
back
lumbar
back from ribs to hips
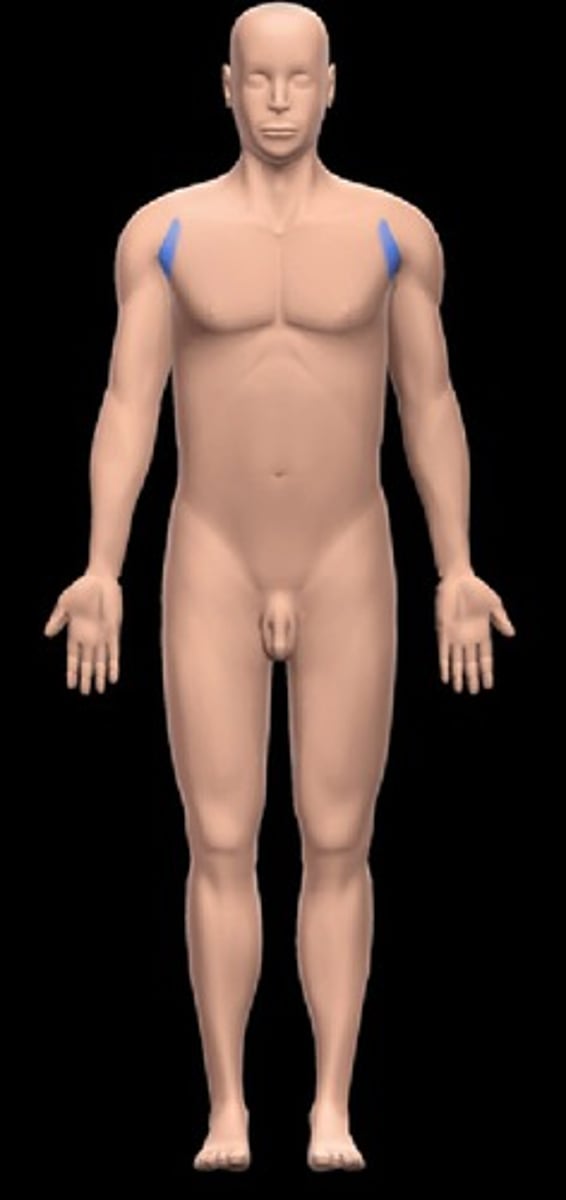
axillary
armpit area
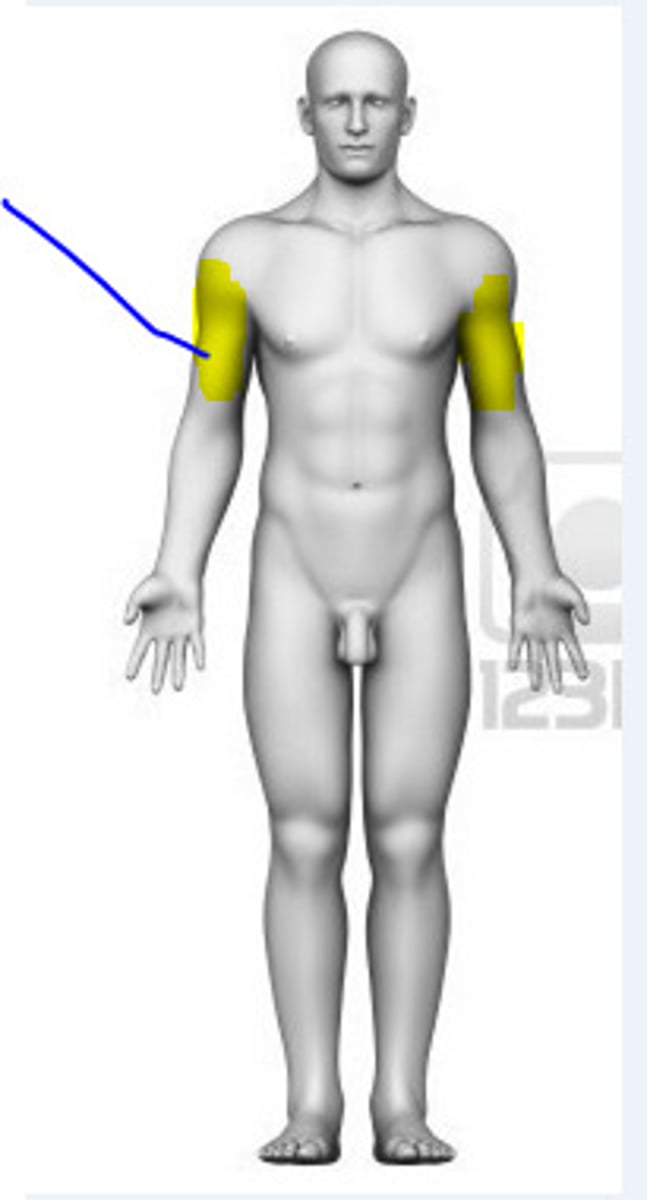
brachial
arms
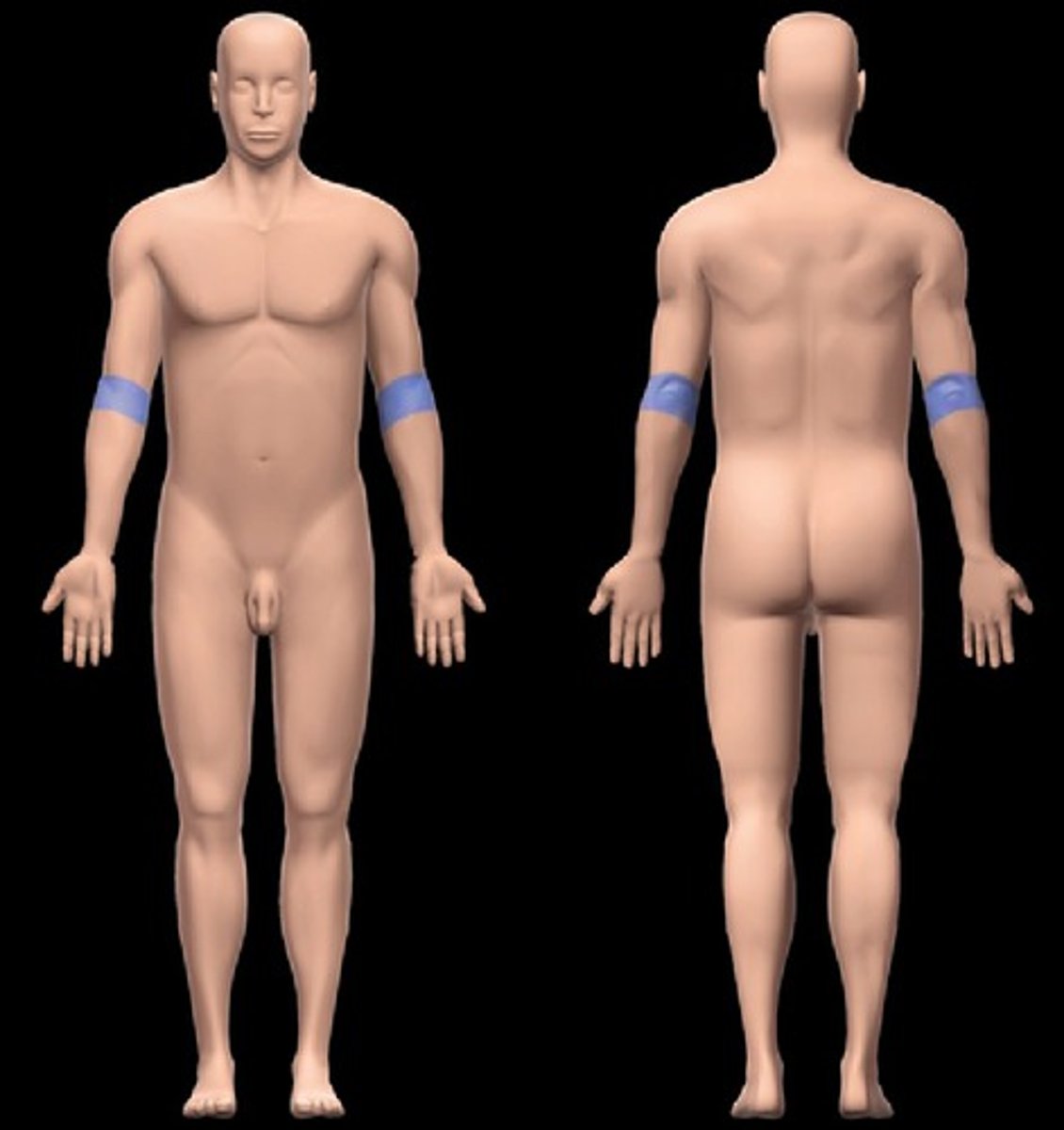
cubital
elbow
olecranon
bump of the elbow
antebrachial
lower arm
carpal
wrist area
digital
fingers
manual
hand area
femoral
front of thigh
geniculate
knee
patellar
front of knee
popliteal
back of knee
fibular
lateral lower leg
crucal
lower leg
sural
calf region
tarsal
ankle region
calcaneal
heel of foot
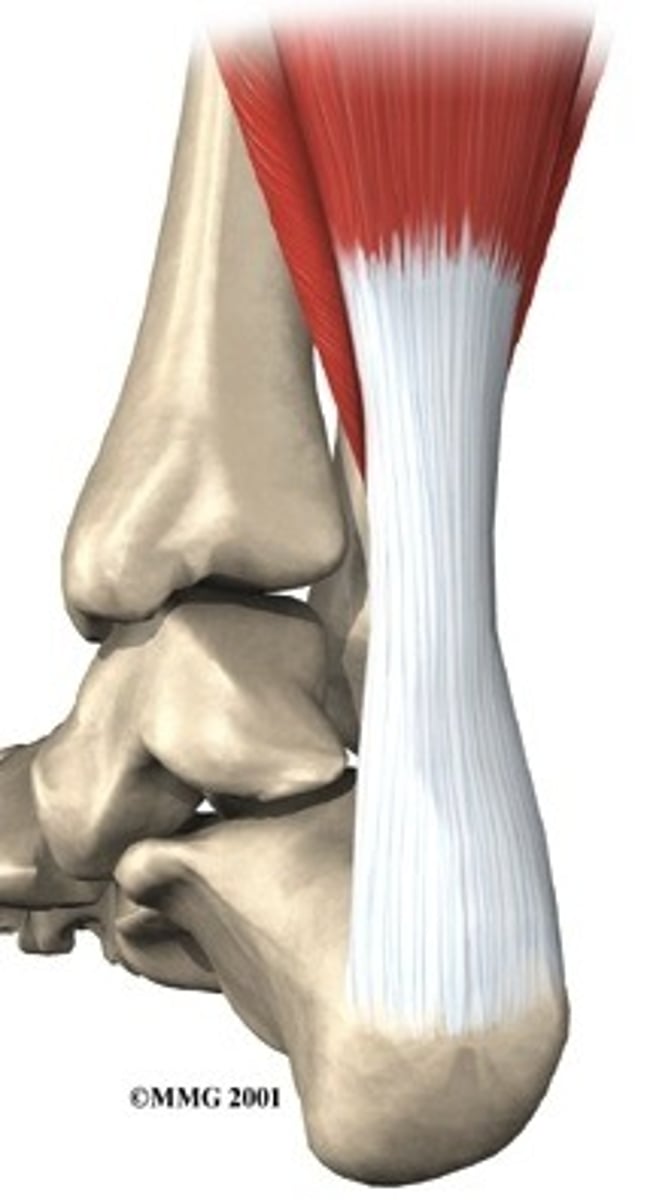
pedal
foot area
dorsum
top of foot
plantar
sole of foot
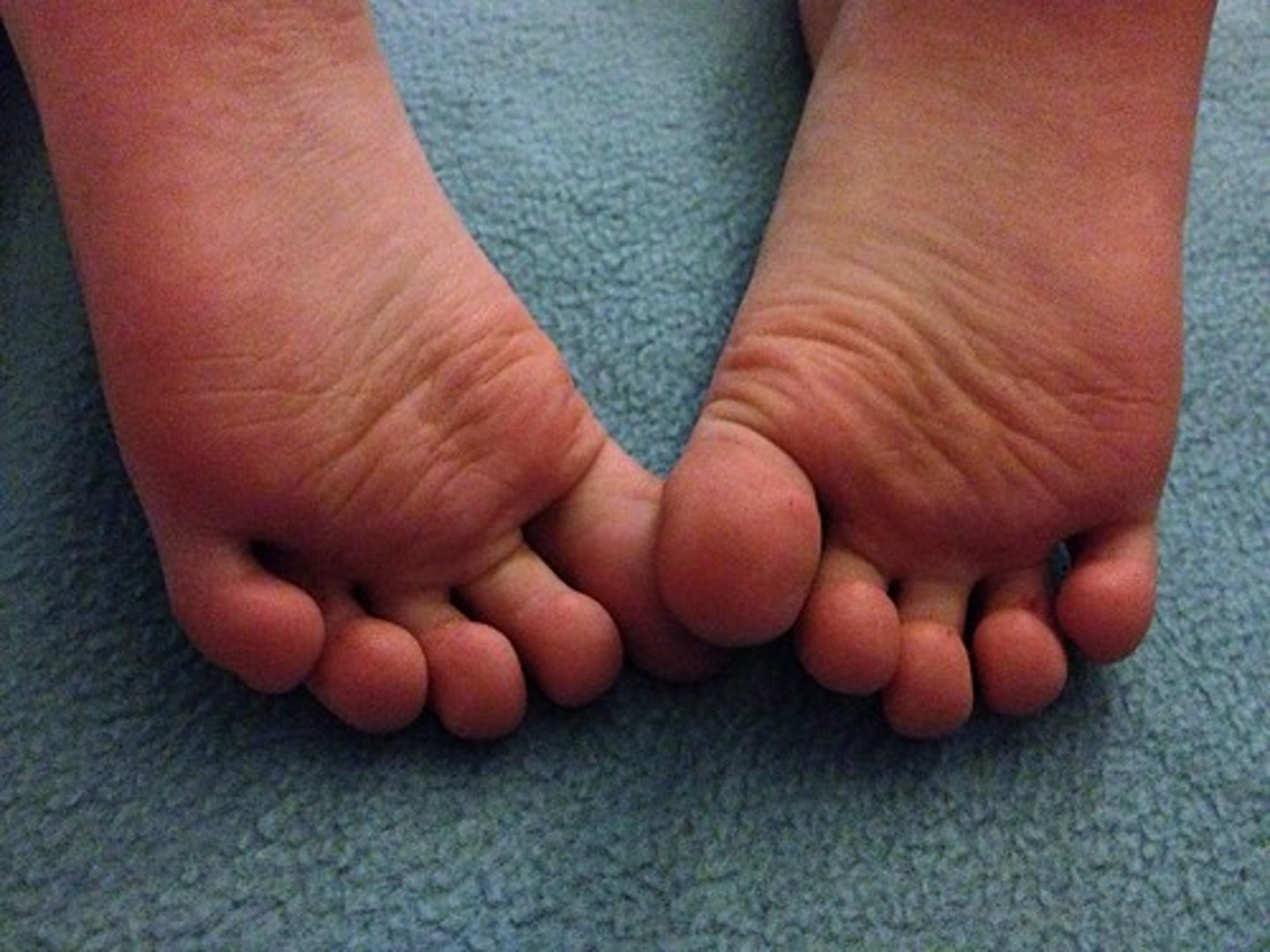
digital
toe area
saggital
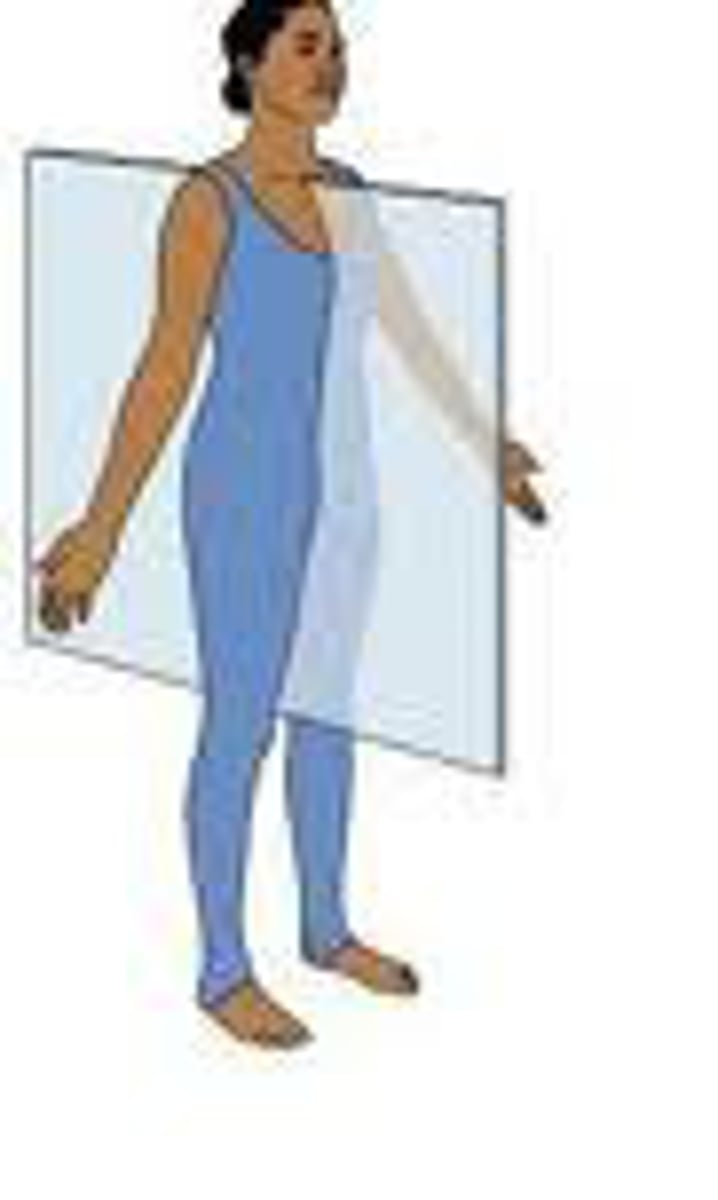
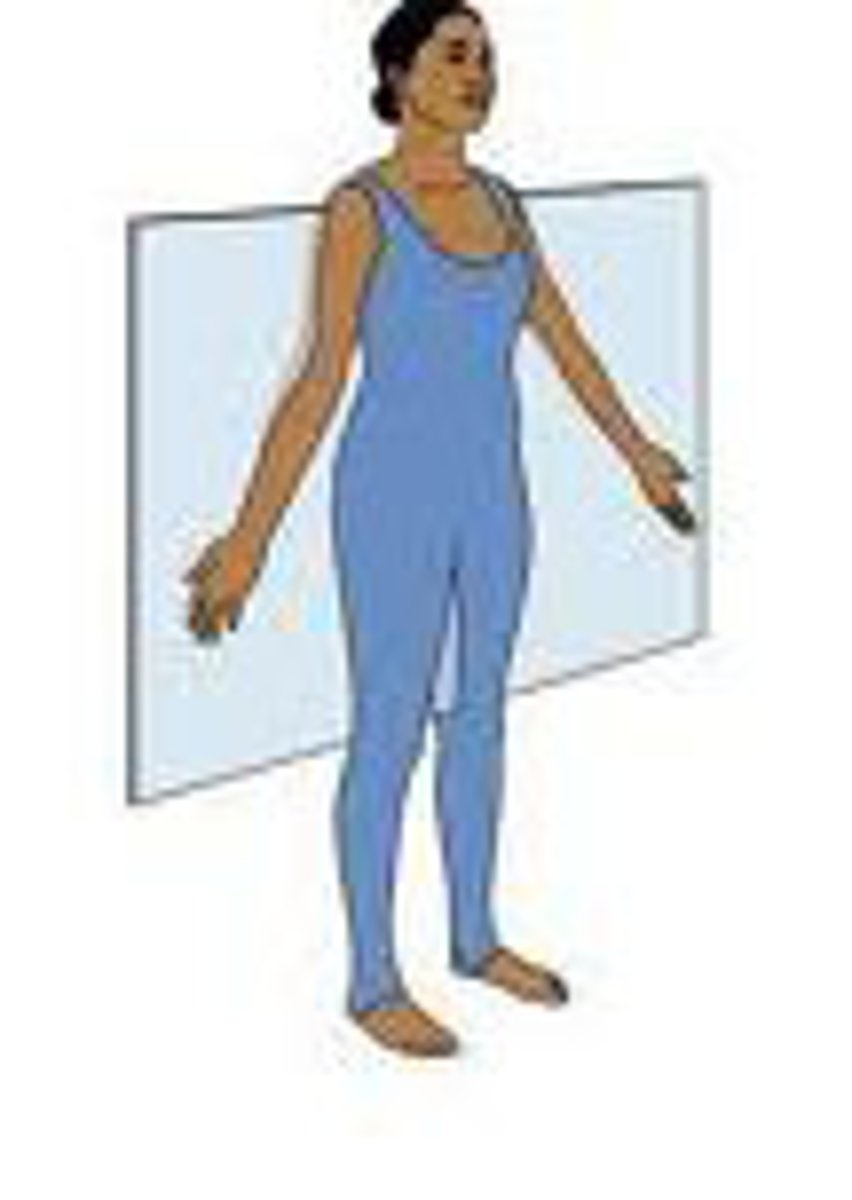
coronal

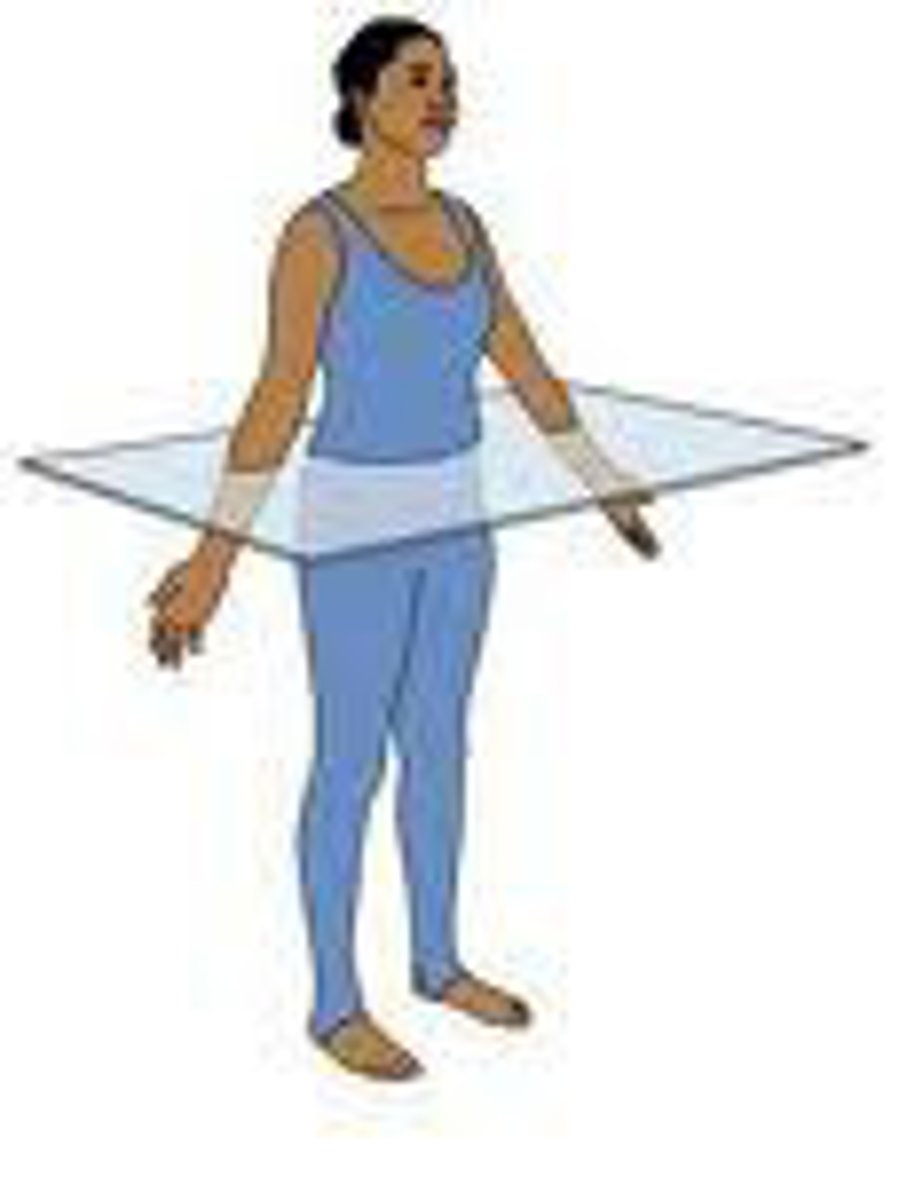
transverse
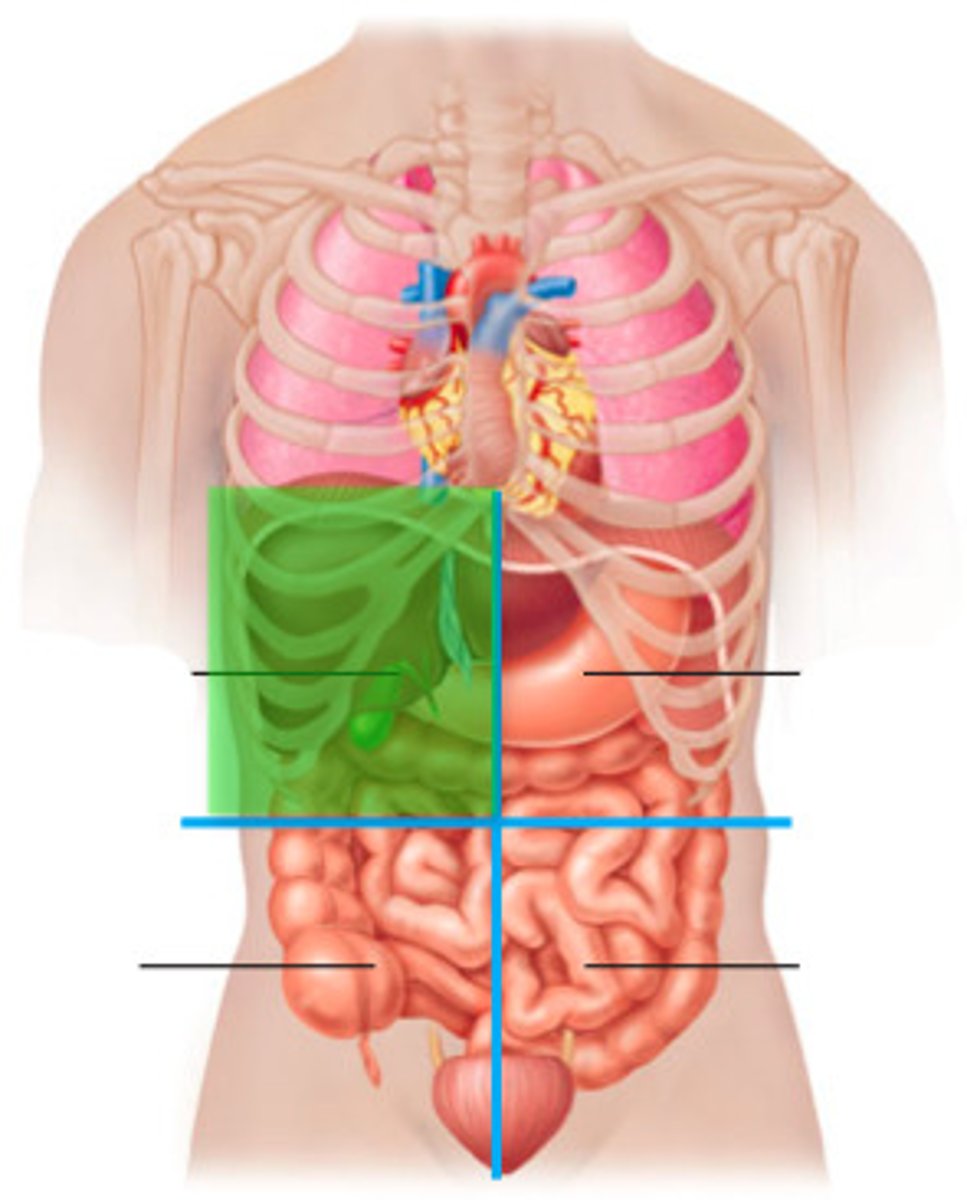
right upper quadrant
Liver, Right Kidney, Colon, Pancreas, Gallbladder
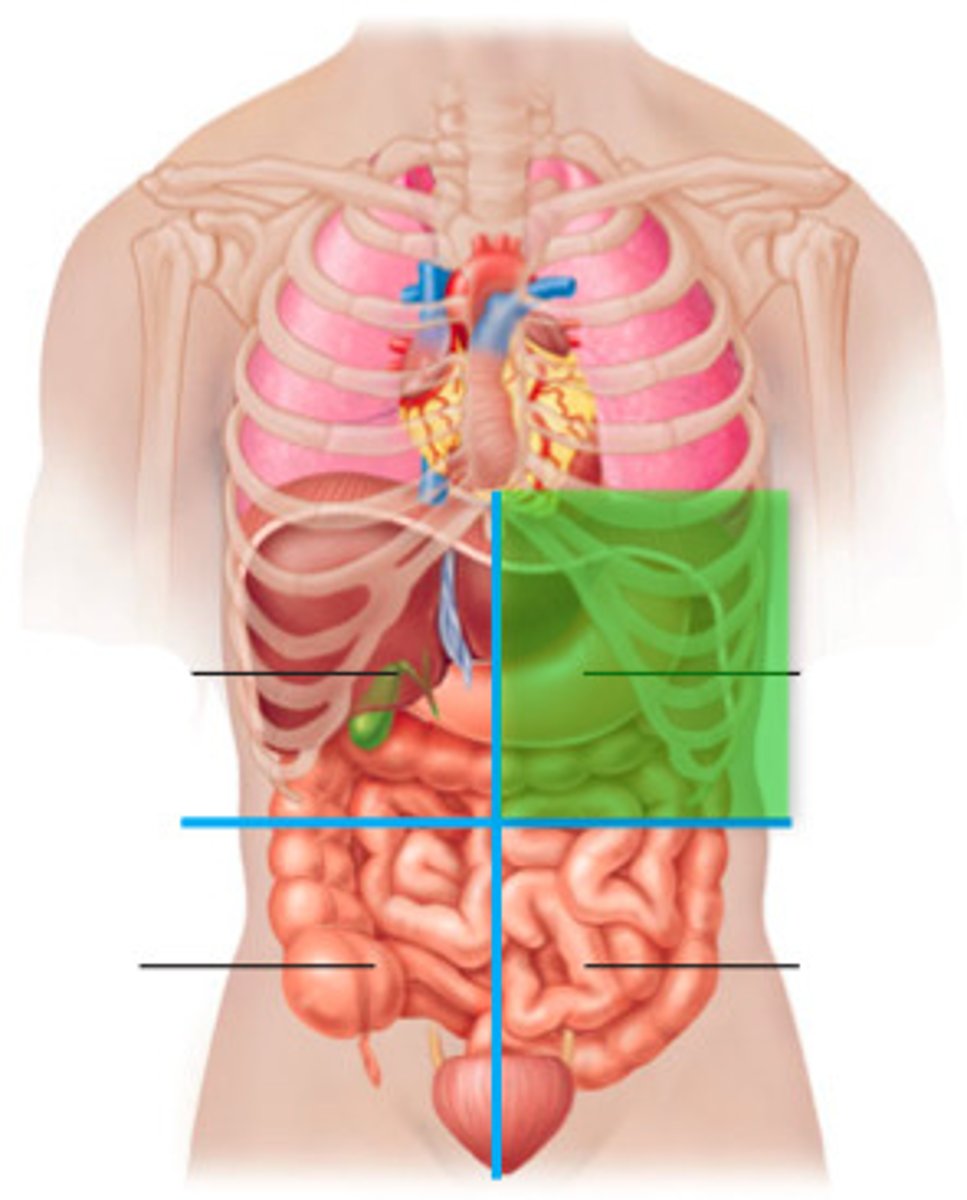
left upper quadrant
liver, spleen, left kidney, stomach, colon, pancreas
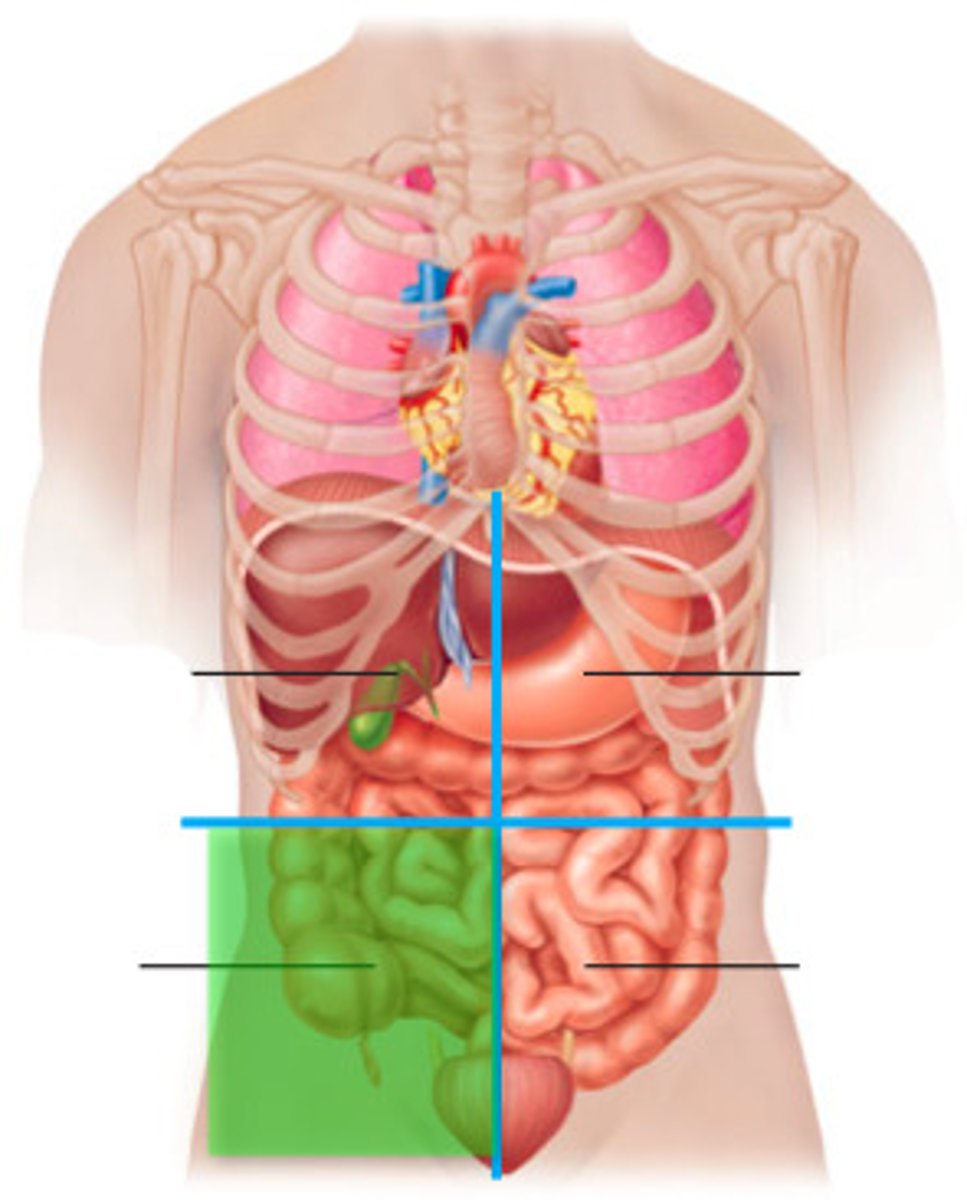
right lower quadrant
cecum, appendix, right ovary and tube, right ureter, right spermatic cord
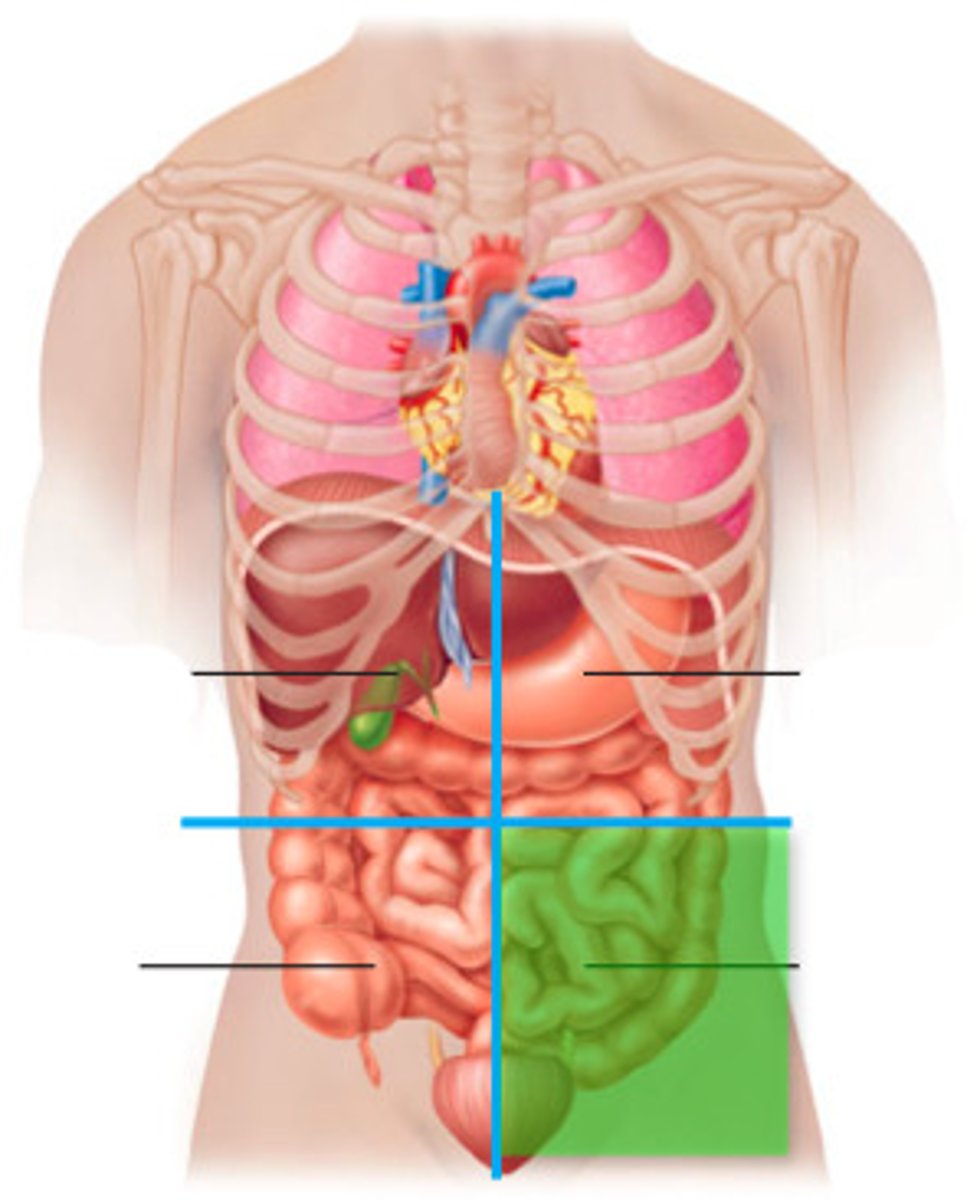
left lower quadrant
Part of descending colon
Sigmoid colon
Left ovary and tube
Left ureter
Left spermatic cord
integumentary system
skin, dermis, and glands
function of integumentary system
regulation and protection; prevents water loss
skeletal system
bones, cartilages, and tendons
function of the skeletal system
protection and support; blood cell production
muscular system
muscles attach to bones
function of the muscular system
movements, posture, and generates heat
nervous system
brain, spinal cord, nerves, sensory receptors
function of nervous system
regulates and coordinates sensations and movements, and many other functions
endocrine system
pituitary, thymus, thyroid, parathyroid, adrenal, and pineal glands; ovaries, testes, and pancreas
function of endocrine system
regulation and maintenance of growth, metabolism
cardiovascular system
heart, blood vessels, and blood
function of cardiovascular system
transport of nutrients and waste, immune function
lymphatic system
vessels, nodes, thymus, tonsils and lymph tissue
function of lymphatic system
immune response, circulatory functions, fat absorption
respiratory system
nasal passages, pharynx, larynx, lungs, and bronchi
function of respiratory system
O2 and CO2 exchange
digestive system
mouth, esophagus, stomach, small intestine, large intestine, salivary glands, liver, gallbladder, and pancreas
functions of digestive system
mechanical and chemical breakdown of ingested foods, and absorption
urinary system
kidneys, ureters, bladder, and urethra
functions of urinary system
waste removal, regulates pH, water balance
reproductive system
testes, prostate, scrotum. penis, ovaries uterine tubes, uterus, vagina
equilibrium
no net movement of solutes within the cell
semi permeable membrane
membrane that allows only certain things to pass through
isotonic solution
a solution whose solute concentration is equal to the solute concentration inside a cell
hypotonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is less than that of the cell that resides in the solution
hypertonic solution
A solution in which the concentration of solutes is greater than that of the cell that resides in the solution
solute
A substance that is dissolved in a solution