Chemistry SOLO 2
1/50
Earn XP
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
51 Terms
Glycolysis
metabolism of glucose molecule to pyruvate or lactate for production of energy
gluconeogenesis
formation of glucose-6-phosphate from noncarbohydrate sources
glycogenolysis
breakdown of glycogen to glucose for use as energy
glycogenesis
conversion of glucose to glycogen for storage
lipogenesis
conversion of carbohydrates to fatty acids
lipolysis
decomposition of fat
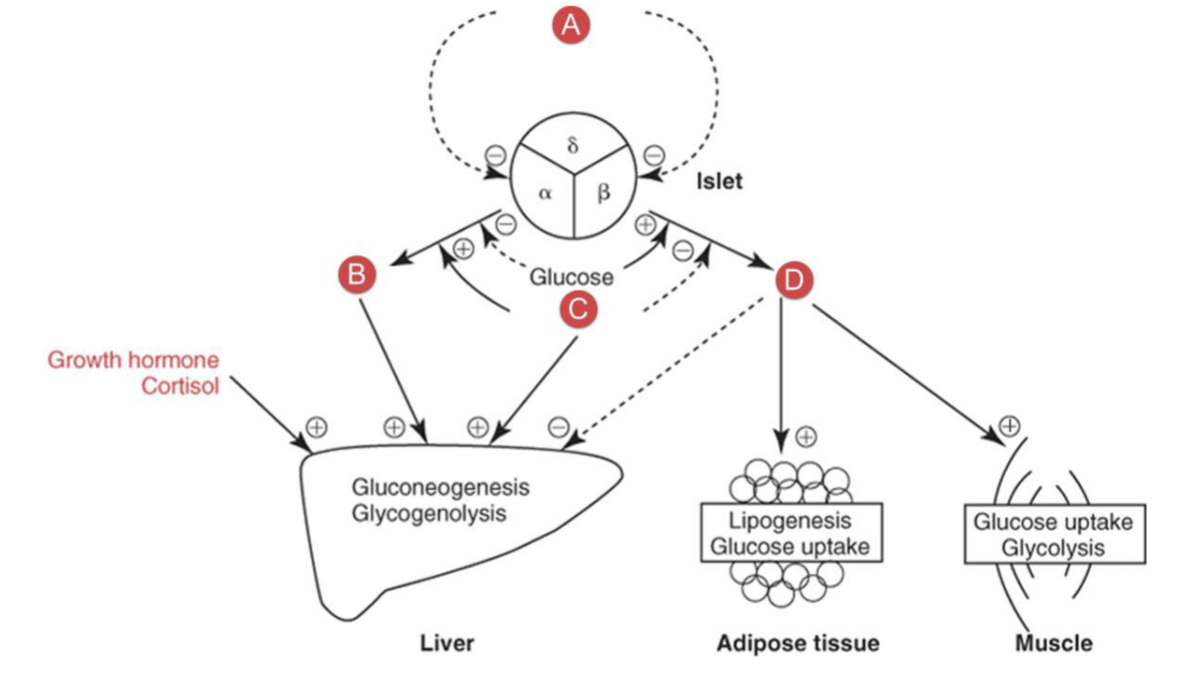
What hormone is A?
stomatostatin
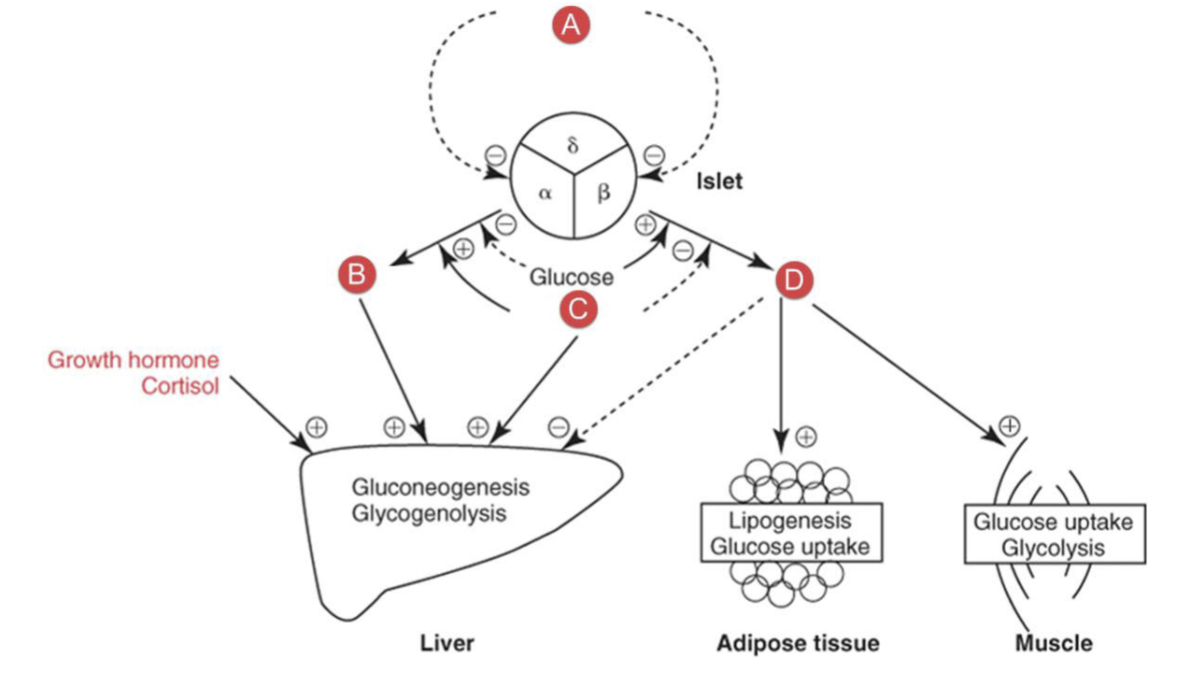
What hormone is B?
glucagon
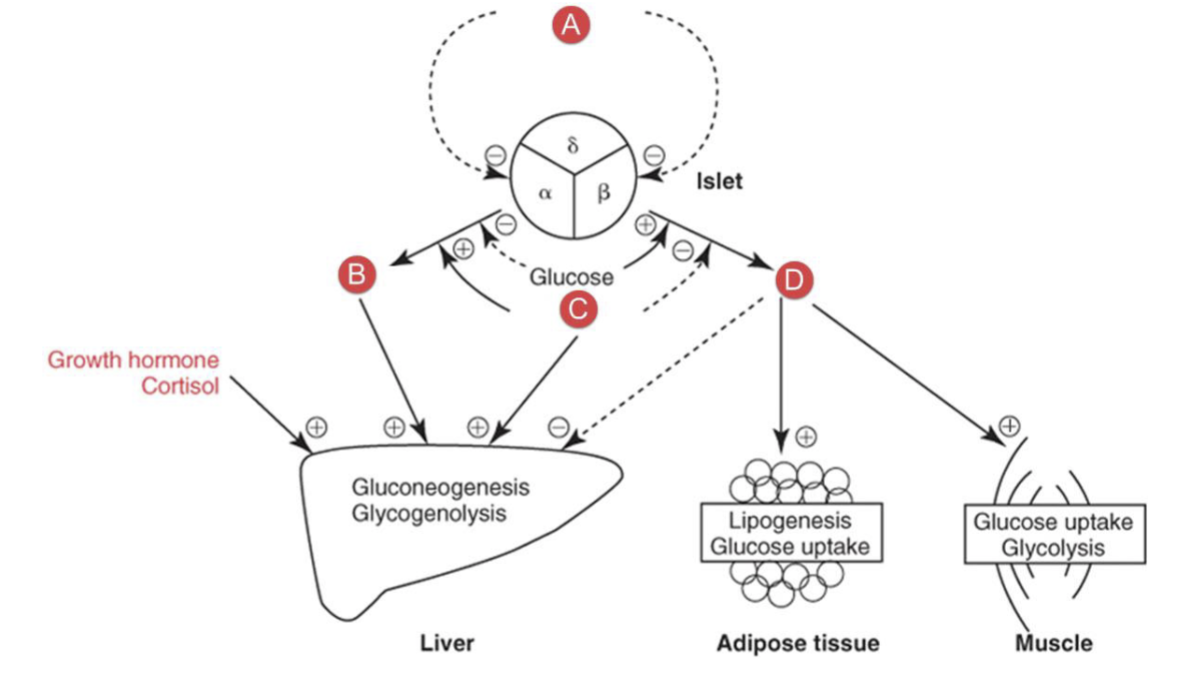
What hormone is D?
Insulin
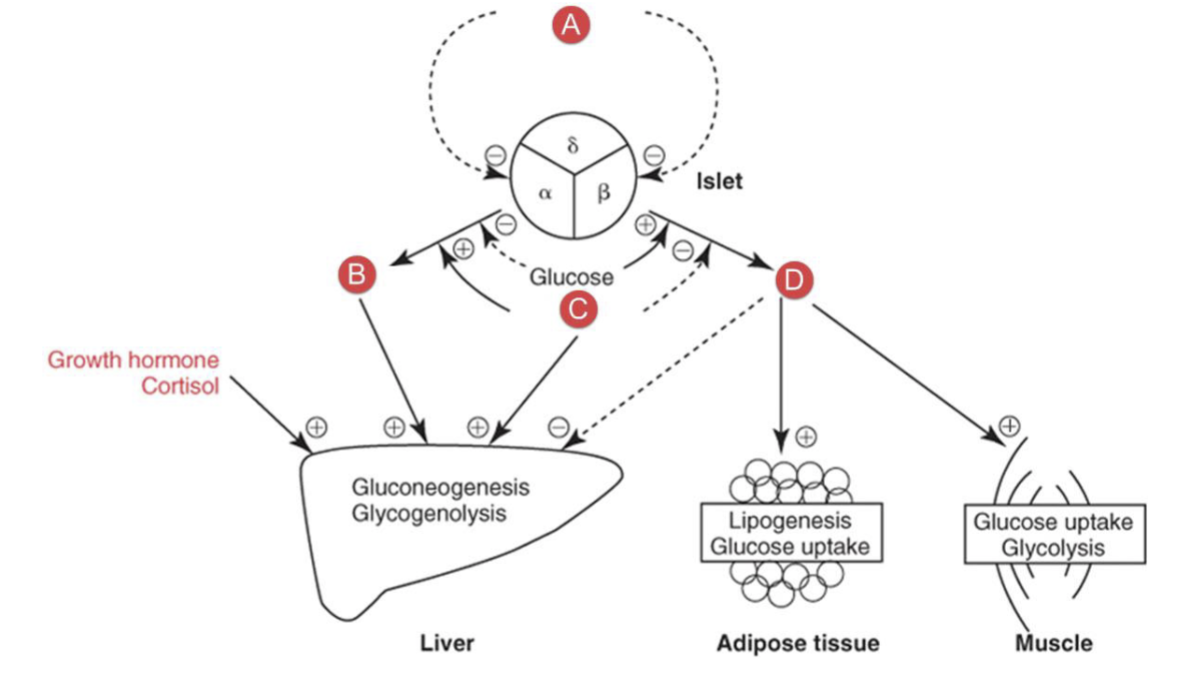
What hormone is C?
Epinephrine
Type 1 diabetes
beta cell destruction leading to absolute insulin deficiency and development of autoantibodies
Type 2 diabetes
insulin resistance with an insulin secretory defect due to progressive loss of adequate beta cell insulin secretion (relative insulin deficiency)
other diabetes
monogenic diabetes syndromes
neonatal and maturity onset
diseases of the exocrine pancreas
drug or chemical induced
gestational diabetes
glucose intolerance during pregnancy diagnosed in the second or third trimester of pregnancy
lab findings of hyperglycemia
decreased/absent insulin
increased glucose in plasma/urine
increased urine specific gravity
increased serum and urine osmolality
ketones in serum and urine
decreased blood/urine pH
electrolyte imbalance
HbA1c diabetes diagnostic criteria
>/= 6.5%
Fasting plasma glucose diabetes diagnostic criteria
>/= 126 mg/dL
2h/random plasma glucose diabetes diagnostic criteria
>/= 200 mg/dL
Oral glucose tolerance test normal
2h pg </= 140 mg/dL
Oral glucose tolerance test impaired
2h pg = 140-199 mg/dL
Oral glucose tolerance test diabetes
2h pg >/= 200 mg/dL
Level 1 hypoglycemia
glucose alert value
<70mg/dL
Level two hypoglycemia
clinically significant hypoglycemia
<54 mg/dL
Level 3 hypoglycemia
severe hypoglycemia
no specific glucose threshold
associated with severe cognitive impairment
methods of glucose measurment
glucose oxidase
hexokinase
clinitest
Methods of glycosylated hemoglobin measurement
affinity chromatography
cation-exchange chromatography
latex immunoagglutination inhibition
high performance liquid chromatography
electrophoresis
Nondiabetic patient reference value for glucose, plasma or serum fasting
70-99 mg/dL
Nondiabetic patient reference value for HbA1c
4.0-5.6
Nondiabetic patient reference value for microalbumin in urine
<25 mg/g creatinine
autoantibody markers for type 1 diabetes
islet cell cytoplasmic autoantibodies
glutamic acid decarboxylase autoantibodies
insulinoma-associated-2 autoantibodies
insulin autoantibodies
zinc transporter 8
Microvascular diabetes complications
diabetic retinopathy
diabetic nephropathy
neuropathy
macrovascular diabetes complications
cardiac
cerebral
peripheral large vessels
monosaccharides
termed aldoses or ketoses
glucose
galactose
fructose
disaccharides
composed of two monosaccharides
maltose
lactose
sucrose
polysaccharides
large numbers of monosaccharides linked together
Starch
major carbohydrate storage in plants
composed of amyloses and amylopectins that contain glucose residues
glycogen
major carbohydrate storage in animal
a heavily branched polysaccharide containing many glucose residues
most abundant in the liver and skeletal muscle
insulin
a protein produced and secreted by the beta cells of the islets of langerhans in the pancreas
decreases blood glucose by stimulating the uptake of glucose into fat and muscle and stimulated glycolysis
promotes conversion of glucose into glycogen or fat for storage
inhibits glucose production by the liver
stimulated protein synthesis and inhibits protien breakdown
glucagon
protein hormone secreted by the alpha cells of the pancreas that increases blood glucose through glycogenolysis and gluconeogenesis in the liver
increases lipolysis and enhances ketogenesis
levels increased during stree and exercise and in hypoglycemic episodes
epineprhine
catecholamine secreted by the adrenal gland that stimulates glucagon secretion and inhibits insulin secretion
increased production in physical or emotional stress and in pheochromocytomas
growth hormone
secreted by the anterior pituitary gland
stimulates gluconeogenesis
enhances lipolysis
opposes insulin stimulated glucose uptake
cortisol
“stress hormone”
stimulates gluconeogenesis
thyroxine
increases the rate of intestinal glucose absorption
stimulates glycogenolysis and gluocneogenesis
somatostatin
inhibits secretion of insulin, glucagon, and growth hormone
ketones
produced when the body doesn’t have enough carbohydrates for clls to burn for energy and it burns fat instead
ketones examples
acetone
Beta-hydroxybutyrate
acetoacetic acid
Normally long chain fattty acids are:
taken up by the liver
re-esterified to triglycerides
stored in the liver or incorporated in VLDL
returned to plasma
Ketone bodies may form due to:
decreased availability of carbohydrates
decreased use of carbohydrates
diabetic ketoacidosis
complication from T1DM
without enough insulin, the body can’t use sugar properly for energy
this prompts the release of hormones that break down fat as fuel, which produces acidic ketones
excess ketones build up in the blood and eventually “spill over” into the urine
hyperosmolar nonketotic coma
characterized by hyperglycemia, extreme dehydration, hyperosmolar plasma, and altered conciousness
complications: coma, seizures, death
most often occur in T2DM in the setting of physiological stress, which increases hormones that favor elevated glucose hormones
hyperglycemia → fluid shift from cells to blood→ increased urine output→ dehydration
Whipple’s triad
symptoms are known or likely to be caused by hypoglycemia
low glucose is measured when symptoms occur
relief of symptoms occurs when glucose is increased to normal