CSCC 1190 Exam 1 Review
1/65
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
66 Terms
X-rays were discovered by
W. C. Roentgen
X-rays were discovered on
November 8th, 1895
X-rays were discovered in
Wurzburg, Germany
The proper term for the image or picture produced using x-ray is a
radiograph
__________ means that credentials issued in one area are recognized in another.
Reciprocity
X-ray images of blood vessels is termed
angiography
GXMO's must be under __________ when performing x-rays
direct supervision
GXMO's cannot perform
mammography, computed tomography, or mobile radiography
MRI
uses a magnetic field and radio waves to generate sectional images of the body
Ultrasonography
uses sound waves to make images of the body
Radiation Therapy
is using radiation to treat cancer tissue
Nuc Med
is utilizing radioactive pharmaceuticals to determine organ function
Mammography
is specialized imaging of the breast
CT
is the use of x-ray to make sectional images or three-dimensional images of the body
Can LXMO's perform routine chest x-rays and assist patients to the radiographic room?
Yes
Can LXMO's perform CT's of the head and administer contrast for angiograms?
No
Scatter Radiation
Comes primarily from the patient, is secondary
Primary Radiation
Comes from the x-ray tube
Remnant Radiation
Radiation resulting after the x-ray beam exits the patient
Collimator
Limits the size of the x-ray field
Grid
Reduces the amount of scatter that reaches the image receptor
Detent
Stops tube movement in a specific location (aligned with Image receptor)
Image Receptor
Device that receives the energy of the x-ray beam and forms an image of the body part
Film Screen
Cassette containing film receives the x-ray beam
CR
Cassette containing phosphor plate receives x-ray beam, plate will be processed and scanned by a laser which will emit light in proportion to x-ray energy received, info is used to form a digital image
DR
Flat panel detector, receives beam and produced electronic signal which is sent directly to the computer for processing
Moving the x-ray tube side to side across the patient
Transverse movement
Moving the x-ray tube from head to toes of the patient
Longitudinal movement
Moving the x-ray tube closer or further from the image receptor
Vertical movement
Tilting the x-ray table so the foot is above the head
Trendelenburg position
ALARA
As Low As Reasonably Achievable
Proton
Positively charged, in nucleus of atom
Neutron
No charge, in nucleus of atom
Electron
Negatively charged, in orbital shell around nucleus of atom
Ion
Charged particle
Ion Pair
Electron and positively charged atom
Ionization
Process of electron leaving its orbit around a neutral atom
Isotropic
Equal in all directions
Energy
Ability to do work
Matter
Anything occupying space with mass
Mass
Quantity of matter
Inverse Square Law
Intensity and distance
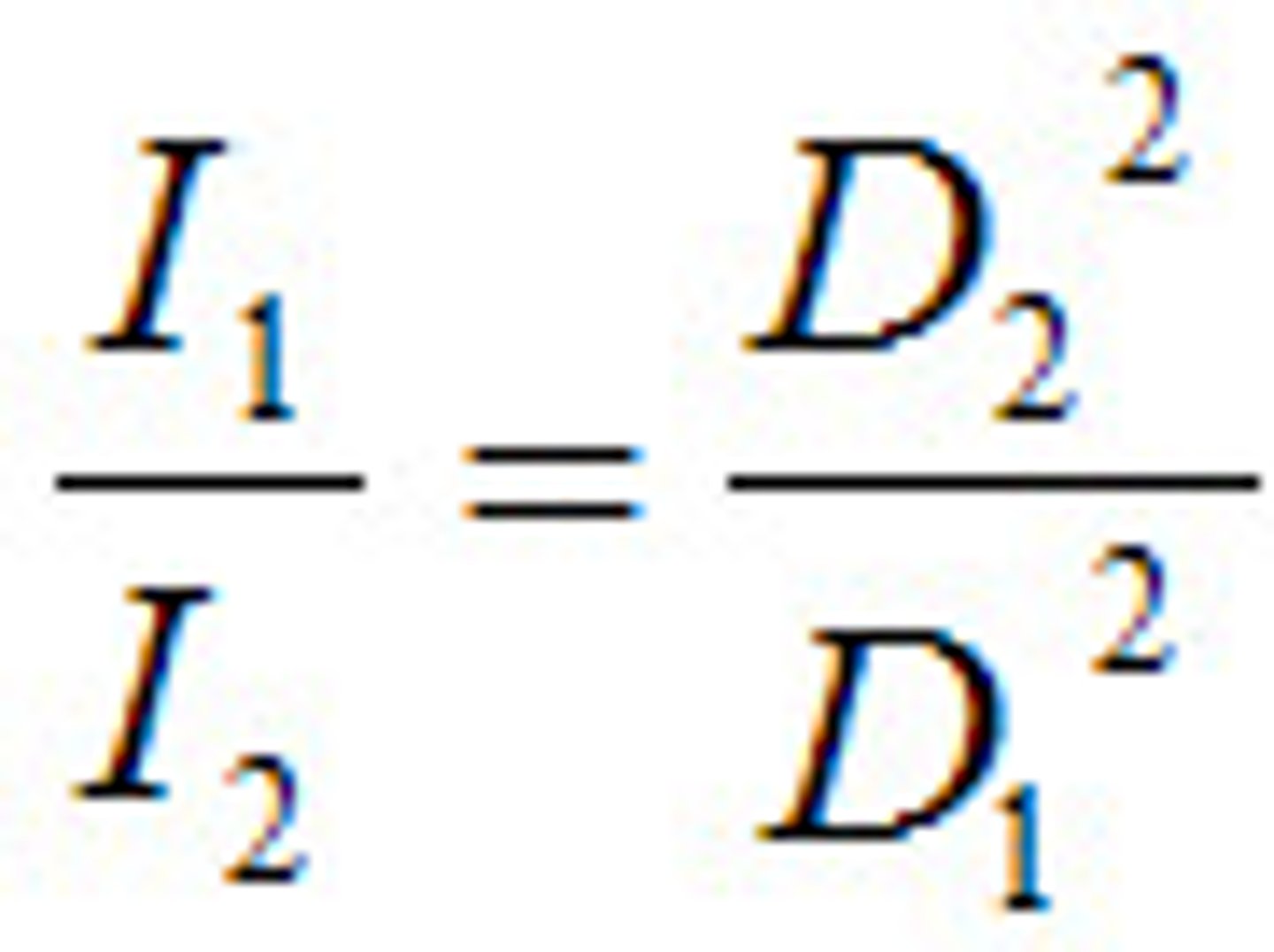
Anode
Positive charge, contains target,
Cathode
Negative charge, contains filament, often contains small AND large filament, heated to produce thermionic emission of electrons
99% of energy becomes
heat
Characteristic
Electron striking the target ejects inner shell electrons of target atom, outer shell electron fills vacancy with release of x-ray photon
Bremsstrahlung
Electron striking the target interacts with target atom nucleus, slows down, loses kinetic energy and is converted into an x-ray
Focusing Cup
Propels electrons toward a specific area of target anode
Focal Spot
Area of target which with electrons interact with
Anode
Rotates during exposure to distribute heat
Small Filament
Used to provide greater image detail
The effective focal spot is smaller than the actual focal spot, due to this anode heel effect, radiation intensity is greater at the cathode and less at the anode end of the x-ray beam
True
Autotransformer
Supplies power to kVp selection and other parts of the x-ray circuit
High Voltage Transformer
Changes incoming low voltage to high voltage, i.e. 54V to 54,000V
Rectifiers
Changes alternating current to direct current
APR
Op selects "PA CHEST" x-ray from options, machine sets corresponding exposure factors
AEC
Op selects an x-ray detector area corresponding to anatomy of interest, i.e. center cell may be selected for "AP LUMBAR SPINE" radiograph
Rapid series, high exposure, exposure on cold anode =
Failure due to overheating
kVp
Determines quality of x-ray beam
mAs
Directly related to quantity of x-ray beams
Focal Spot Size
Affects image sharpness
AEC...
requires accurate positioning, requires use of the bucky mechanism, and provides consistent radiographic density
200 mA at 0.25 seconds results in
50 mAs
Radiopaque
absorbs the x-ray
Radiolucent
Easily penetrated by the x-ray
Latent
image in film being processed