PL100 WPR3 Lesson 22-26
1/39
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
40 Terms
Define Intelligence
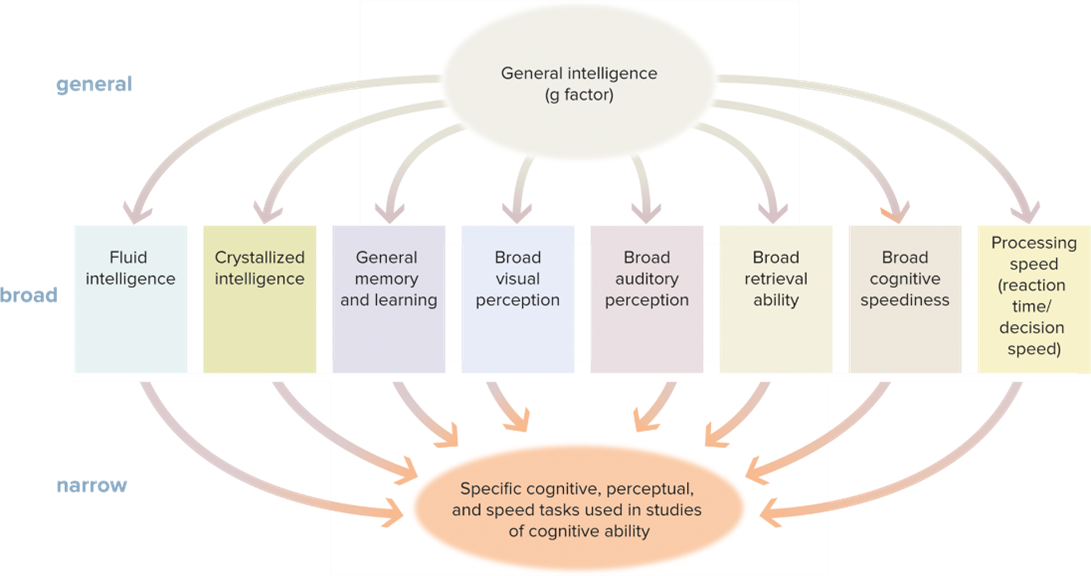
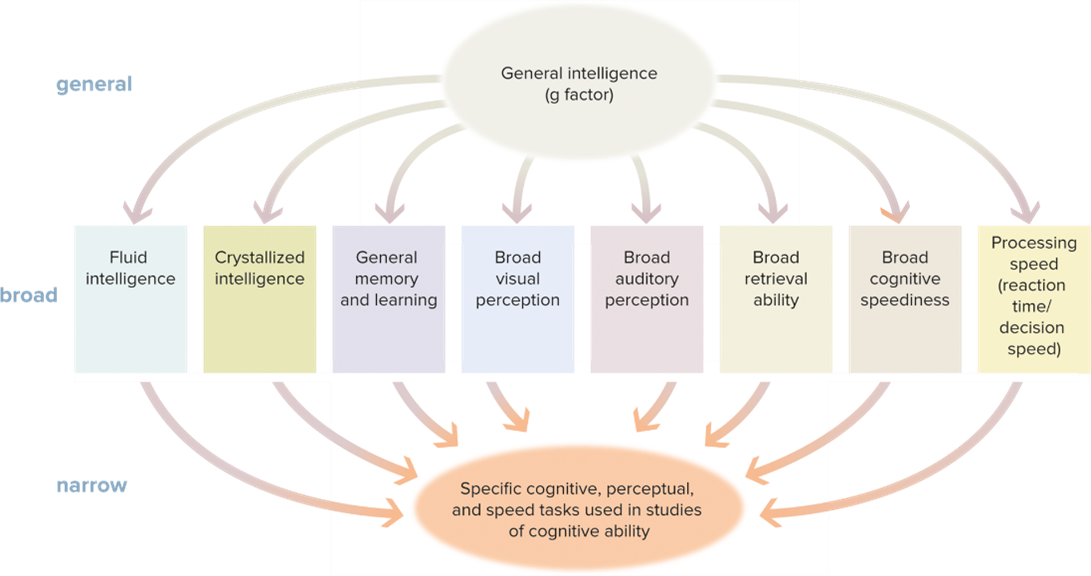
A set of cognitive skills that includes abstract thinking, reasoning, problem solving, and the ability to acquire knowledge. IQ score. Verbal, Spatial, quantitative
Explain Spearmans G Factor Theory.
Spearman’s theory that intelligence is a single general (g) factor made up of specific components. finds How intelligent are you. IQ test
Explain the Triarchic Theory of Intelligence (Sternberg).
The idea that intelligence consists of distinct dimensions and is not just a single factor. Analytical, practical, creative. finds How are you intelligent.
Describe Convergint and Divergent thinking problems.
a. convergent thinking problems- Problems that have known solutions and require analytic thinking and the use of learned strategies and knowledge to come up with the correct answer.
b. divergent thinking problems- Problems that have no known solutions and require novel solutions.
Describe the three solution strategies used to solve problems.
a. Algorithms- A step-by-step procedure or formula for solving a problem.
b. Eureka insight (insight solution)- A sudden solution that comes to mind in a flash. a solution you use right now.
c. Thinking outside the box- An approach to problem solving that requires breaking free of self-imposed conceptual constraints and thinking about a problem differently in order to solve it. a solution you use later.
Describe how fixation, mental set, and functional fixedness serve as obstacles to solutions.
a. Fixation- to focused on one thing. The inability to break out of a particular mind-set in order to think about a problem from a fresh perspective. Like rooster, only focused on one thing. Focused on getting there, but not on time.
b. mental set- A tendency to continue to use problem-solving strategies that have worked in the past, even if better solutions are available. Guy that went to fast and lost his team, he didn’t pause and consider, going fast worked before, itll work now.
c. functional fixedness- A mindset in which one is blind to unusual uses of common, everyday things or procedures. When your to focus on the way things are meant to be used for. Equipment. We can take everyday things and using them differently. Example, maverick uses the Radar (which is used for mapping) and used it differently to train them.
Define emotional intelligence and describe how it relates to standard/general intelligence.
empathic understanding, and skills for regulating emotions and being able to describe in oneself and others.
5 categories:
Self-awareness be able to understand what your feeling.
Self-regulation- ability to internally control you feelings.
Social skills-
empathy- being able to understand how someone else feels.
motivation- the desire and need to do something.
general intellegence is spearmans G factor
Describe how emotional intelligence influences behavior in schools.
children who participate in emotional intelligence programs have better attendance and exhibit less disruptive classroom behavior; they enjoy school more and have higher GPAs.
Fluid Intelligence
Fluid Intelligence- thinking outside the box, different approaches. You don’t learn prior, on the spot.
Crystalized intelligence
skill, you have prior knowledge and have learned it.
Social vs Emotional Intelligence
emotional ability to recognize emotions in yourself and regulate your own emotions.
social- ability to accurately read our social environments, picking up social ques.
Summarize the adaptive functions of positive and negative emotions
a. Positive emotions, BLUF- aquire new skills becuase you will be thinking more in a cognitive way.
such as contentment, happiness, love, and amusement, solve different kinds of adaptive problems. According to the broaden-and-build model, positive emotions widen our cognitive perspective, making our thinking more expansive and enabling the acquisition of new skills and enhanced well-being.
B. Negative emotions- Negative emotions promote a narrow, vigilant way of looking at the world. sympathetic neverous system develop physical and strategic skills that may be useful for hunting, escaping, or defensive fighting.
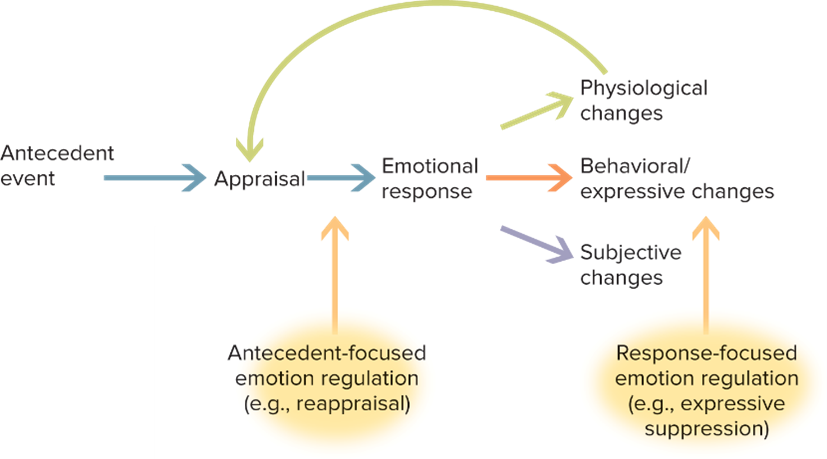
Describe emotion as a process.
Reaprasial- you reevaluate you emotions.
Physiological changes- sweating, adrenaline, sympathetic nervous system
Behavioral changes- ducking, action changes
Subjective- 4 theories
self-conscious emotions
you associate your emotions and motivation based on society and being normal. Fake
aymgdila and hypothalums
amygdala- component of brain, regulating fear and anger
Hypothalamus- generates pleasure and awards with certain emotions.
Differentiate among the following theories of emotion discussed in the text:
James-Lange;
facial-feedback;
Cannon-Bard;
Schachter-Singer:
James-Lange theory of emotion suggests that emotions occur as a result of physiological reactions to events. Heart rate and arousal cause emotions
Cannon-bard. First, he suggested, people can experience physiological reactions linked to emotions without actually feeling those emotions. Cannon also suggested that emotional responses occur much too quickly to be simply products of physical states arousal and emotion are independent, they don’t cause each other.
Schacter- singer. This theory suggests that the physiological arousal occurs first, and then the individual must identify the reason for this arousal to experience and label it as an emotion. A stimulus leads to a physiological response that is then cognitively interpreted and labeled, resulting in an emotion. Stimulus causes arousal, the interpretation/cognition of the stimulant, then causes the emotion.
Facial feedback- people based on their face. Smile makes you feel happy.
Define stress and stressors.
a. Stress- A response elicited when a situation overwhelms a person’s perceived ability to meet the demands of the situation.
cortazol id the stress horomone
b. Stressor- Events that trigger a stress response.
Differentiate among the stimulus, response, and relational views of stress.
a. Response- view of stress focuses on the physiological changes heart reaching and adrenalin. that occur when someone encounters an excessively challenging situation. Increase blood pressure, start sweating.
b. Relation-defines stress as a particular relationship between people and the situations in which they find themselves. If you about to be late for something you didn’t even want to go to, it might not be that bad, vs missing first born child, will be more.
c. Stimulus- an event. Stuck in traffic
Differentiate between primary and secondary appraisal in the stress process.
a. primary appraisal- A quick assessment of the meaning of a given environmental event for the individual.
b. secondary appraisal- Self-assessment of the resources available to cope with stress. only happens with stress
1. Describe the physiology of stress, to include explanations of the neuroendocrine systems, the adrenal-medullary system, and the hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis.
a. neuroendocrine system- The hormonal produced, and systems involved in emotions and stress.
adrenal gland- produces adrenalin
Purptary glad- master glad, will release the most important
b. adrenal-medullary system- hypothalumus tells brain to acatavite symothtic nerous.
c. hypothalamic-pituitary-adrenal (HPA) axis- A major neuroendocrine pathway relevant to the stress response involving the hypothalamus, pituitary gland, and adrenal cortex.
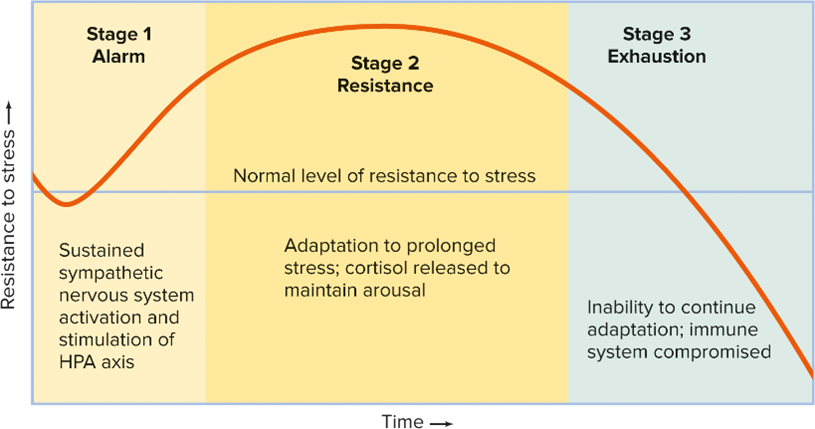
1. Describe the three phases of Selye’s General Adaptation Syndrome and their effects on health.
As defined by Hans Selye, a generalized, nonspecific set of changes in the body that occur during extreme stress.
GAS ARE- General Adaptation Syndrome
Alarm reaction: The initial symptoms the body experiences when under stress.
Resistance phase: The body begins to repair itself.
Exhaustion phase: The body's resources are depleted and it can no longer cope with the stressor.
info from General Adaptation Syndrome (GAS): Stages and Triggers (verywellhealth.com)
Compare and contrast homeostasis and allostasis.
a. Homeostasis- if your hungry you eat. Bodu needs to get back to the setpoint. if your thirsty you heat. the principle of homeostasis suggests that unless we are being provoked by something, we are humming along at an even-keeled baseline state, and we return to the same state after the stress. Moreover, homeostasis implies that just one system in the body struggles to return to baseline at a time (homeo- means “same”)
b. Allostasis- body is changing in an environment EX. if im in a colder enviorment, my body will set an alliostate for a little,The process by which the body achieves stability through physiological change.
Describe the psychological risk factors for heart disease. Include: type A and anger and the Type A Behavior Pattern (TABP) Cardiovascular Reactivity model (CVR).
hositlity- dictor in heart dieses. road rage, more hostile
impatientness
competivness
Describe how smoking, drinking alcohol, diet/eating, exercise, and meditation can affect your health.
Smoking and drinking activates the fight or flight, lowers 10 years
exercise and meditaion are good
Differentiate between good stress, tolerable stress, and toxic stress.
Good stress- competition, pushes you to be better.
Tolerable stress- have no dicision, somone dies and, have good coping mecnisems. studying for a test can reduce it. Tolerable
Toxic- when it imitates that fight or flight mentality. leads to trumama and cant deal with it.
Describe the four Ds and how they can be used to determine if a behavior or condition could be considered a disorder.
in order for anything to classify as a pyscological disorder, it must follow the four D. 4 Ds” should be used to confirm the presence of a mental disorder:
a. Disturbance of thought, emotion, or behavior
b. Dysfunction of biological or developmental processes. there not doing anything so there dyfunctioning ther biological needs. EX not going outside, cant get vitamen D.
c. Distress (or Disability) in everyday life (especially relationships or work) leads to discomfort and pain
d. Deviant social. not viewed normal by society thought, emotion, or behavior, but only if also dysfunctional; deviance alone is not enough.
Explain what makes depression different than feeling blue.
Feeling Blue is like being sad for a day or two, Depression is A mood disorder characterized by pervasive low mood, lack of motivation, low energy, and feelings of worthlessness and guilt that last for at least 2 consecutive weeks.
Differentiate major depressive disorder from bipolar disorder.
a. Major Depressive Disorder- A mood disorder characterized by pervasive low mood, lack of motivation, low energy, and feelings of worthlessness and guilt that last for at least 2 consecutive weeks.
b. Bipolar- A mood disorder characterized by substantial mood fluctuations, cycling between very low (depressive) and very high (manic) moods. moods last a week stright
Describe the following anxiety disorders.
a. Generalized Anxiety Disorder
b. Panic Disorder
c. Social Phobia (social anxiety disorder)
d. Specific Phobias
e. obsessive compulsive disorder
f. Post-traumatic stress disorder
a. Post-traumatic stress disorder- A type of trauma- and stressor-related disorder that involves intrusive and persistent cognitive, emotional, and physiological symptoms triggered by catastrophic or horrifying events.
b. obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) - An anxiety disorder in which uncontrollable thoughts lead to repeated, unwanted behaviors.
Manic- feeling really energized. you dont sleep, to energized
others on photo
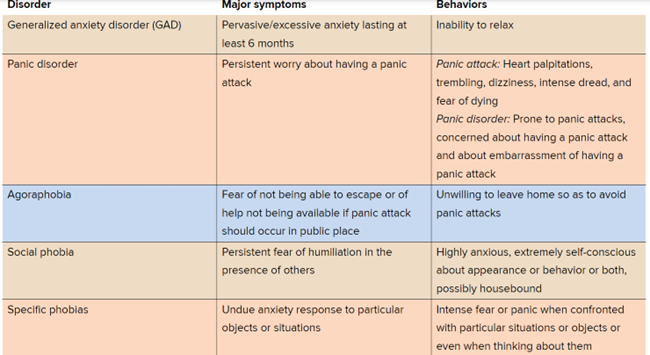
Panic vs axiity attack
Panic there is no trigger, anxitiy is a trigger
Summarize how biological, psychological, and sociocultural factors interact to lead to the development of psychological disorders.
it will be more accaptable or less acceptial to have these dissorders based on these three. severity of it
Differentiate between Anorexia Nervosa and Bulimia Nervosa.
a. Anorexia Nervosa- An eating disorder in which people cannot maintain 85% of their ideal body weight for their height, have an intense fear of eating, and have a distorted body image
b. Bulimia Nervosa- An eating disorder characterized by binge eating and a perceived lack of control during the eating session. then purge it up.
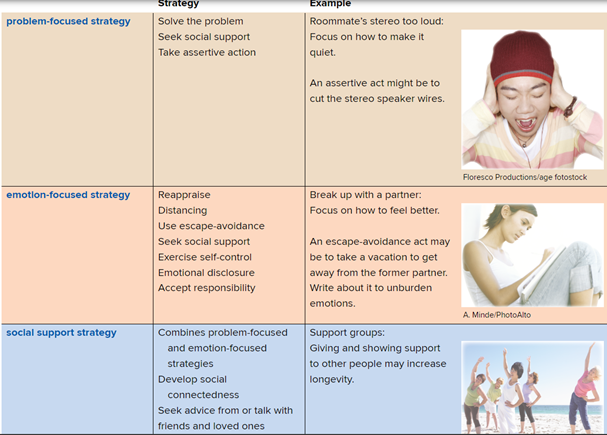
Summarize the three broad classes of coping strategies and their relationships
to health and well-being.
Problem focused- A way of dealing with stress that aims to change the situation that is creating stress. i can contol it.
Emotion focused- A way of dealing with stress that aims to regulate the experience of distress.
Social Support- relying on others. mixing of the other two stratiges
Summarize how the following positive psychology factors help people cope more effectively with stressful events.
positive traits/ positive emotions
finding meaning in stressful events
a) Positive traits, positive emotions- Some people approach the world in a positive way, and as a result, their experience of distress is reduced compared to that of others. Optimists tend to emphasize the positive, Positive emotions may facilitate recovery from the physiological effects of negative emotions. Better health and blood pressure
b) Finding meaning in stressful life events- Positive psychological traits and states do play a big role in whether people are able to find meaning in stressful and tragic events People with terminal illnesses who notice beauty amidst their pain and find opportunities for positive experiences are happier than those who don’t, and they may even live longer.
Explain under what conditions emotion-focused and problem-focused.
strategies are likely to be most effective.
Stress due to Feeling sad or upset is more emotion focused,
while more anger related stress is problem focused.
Explain how meditation reduces stress and affects health.
Mindfulness meditation involves both paying attention to the present moment and being aware that everything that may arise in one’s mind, be it a thought, an emotion, or a sensation, will eventually fade away. The meditator is trained to note experiences as they occur, without clinging to or ascribing value to them. These skills allow one to keep thoughts and emotions in perspective and avoid an unhealthy obsession with negative emotions
Explain the relationship between defense mechanisms and anxiety.
Defense mechanisms operate at an unconscious level and help ward off unpleasant feelings (i.e., anxiety) or make good things feel better for the individual.
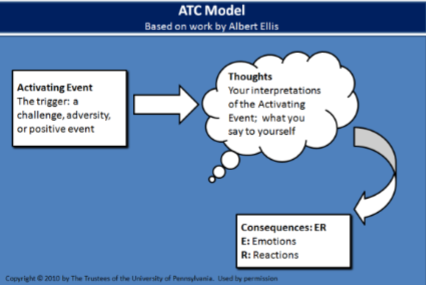
Illustrate the processes associated with the ATC model and “Detecting Icebergs.”
Explain how “Hunting the Good Stuff” can improve your performance or the performance of others.
Seeking the good things in your life helps to build positive emotion, optimism and gratitude. This leads to better health, better sleep, better relationships, more optimal performance, greater life satisfaction, and lower depression. counteracts negativity bias. Negativity bias is a tendency to pay more attention to bad events; you can counteract this by simply keeping track of the positive events and experiences in your life.
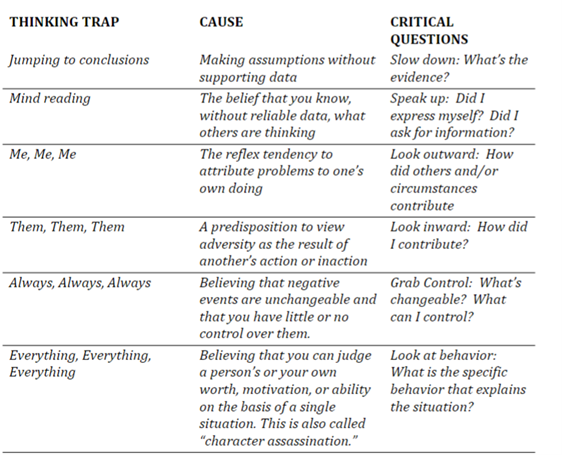
Identify and describe the 6 common thinking traps.