SLP 201 Disorders of the Ear, Auditory Nerve Pathways, Vestibular system
1/62
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
63 Terms
Syndromic
-signs and symptoms affecting multiple parts of the body
-HL + something else
-can be genetic
Nonsyndromic
-no other signs or symptoms
-HL only
-can be genetic
Autosomal Dominant Genes
if you have ONE copy of the gene, you will have the trait/disorder
*unless it is spontaneous mutation, one parent has trait/disorder
Autosomal Recessive Genes
you must have TWO copies of the gene to have the trait/disorder
*your parents may be carriers and not have the trait/disorder
X-Linked Recessive Genes
Gene is carried on the X chromosome
- females are generally carriers; males have trait/ disorder
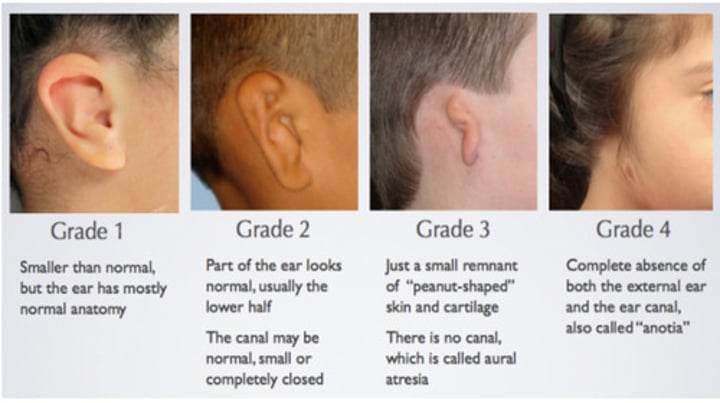
Microtia "small ear"
-more common unilaterally
-more common in males
-more common in right ear
-congenital malformation
treatment: surgical reconstruction, mainly cosmetic
Stenosis
narrowing of canal
-congenital malformation
Atresia "no hole"
-unilaterally 6x more common than bilateral
-more common in males
-more common in right ear
-congenital malformation
Obstructions of Outer Ear
-amniotic fluid (newborns)
-cerumen (ear wax)
-insects
-foreign bodies
-osteoma or exostosis (surfer's ear)
treatment; epithelial migration, medical removal
Otitis Externa (Swimmer's Ear)
-bacterial
-fungal
-painful
caused by cold water in the ear
treatment- prevention, medical
Cellulitis
skin, but no swelling
-bacterial infection; red, hot inflamed skin
Perichondritus
swelling
Carcinoma
Cancer
Outer Ear Injuries
-burns
-frostbite
-chemical
-injuries
-radiation
Outer ear Disorders affect..
deflection, collection, direction, resonance enhancement
Collapsing Canals
babies and elderly
-pressure
-headphones vs. insert earphones
Middle Ear Malformations
-absence of middle ear
-absence of ossicles
-ossicular malformations
-bony malformations
treatment- surgical, may not be able to completely restore
Down Syndrome
Trisomy 21, small low set ears, structural ear anomalies related to skull formation, short neck, eustachian tube dysfunction
Branchio-oto-renal syndrome (BOR)
autosomal dominant, ossicular abnormality, cysts/clefts on neck, microtia, renal (kidney) abnormalities
Treacher Collins Syndrome
autosomal dominant, outer and/or middle ear malformations, malformations of cheeks, jaws, and/or face
no effects of intelligence
Goldenhar Syndrome
cause unknown; often unilateral, ears, nose, soft palate, lip, mandible,
Eustachain Tube Dysfunction
pressure "mismatch"
-pressure in OE>ME
treatment- eardrum retraction, nasal sprays, allergy testing
eustachian tube dysfunction to otitis media
eustachian tube does not open
middle ear cavity needs oxygen
tm becomes retracted ( pulled back into ME)
creates a vacuum in ME and intracellular fluid is pulled into ME cavity
Otitis Media
red eardrum; fluid from eustachian tube dysfunction or nasal congestion (vacuum created in ME)
treatment: Medical decongestants, antihistamines, antibiotic, surgery, pressure equalizer tube
Otitis Media with Effusion
clear fluid, purulent fluid (infected), glue ear
treatment: Medical decongestants, antihistamines, antibiotic, surgery, pressure equalizer tube
TM perforation
injury to middle ear caused by...
-pressure from effusion
-foreign body
-blow to the head
treatment: most heal quickly, surgical tympanoplasty
Tympanosclerosis
irregular white plaques on TM (think of scarring)
may come from trauma, tm perforation, me disease
Cholesteatoma
dead, exfoliate skin cells from external auditory meatus and surface of TM grow in ME; can erode ossicular chain
treatment- surgical removal, medical antibiotics
Otosclerosis
ME disease
condition in bony labyrinth of middle ear which causes the formation of bony growth over the footplate of stapes
2x women than men, bilateral, not symmetrical, mostly hereditary
Ossicular Chain Discontinuity
ME trauma ossicular discontinuity
trauma to TM
Head trauma
treatment: surgical repair
Middle ear disorders affect...
vibration, conduction, amplification
inner ear disorders affect...
sensory reception of sound waves, amplification of sound, neural encoding of sound
Michel Aplasia
-bony remnant of IE or absense (no cochlea or semicircular canals)
-anacusis (total HL)
Cochlear Aplasia
-absence of cochlea
-semicircular canals present, but may be deformed
-anacusis (total HL)
Common Cavity Deformity
-cochlea is a cavity, not a coiled structure
- 4th week gestation
-relatively common (26% of cochlear malfunctions)
-HL varies but can be progressive, but generally profound
Enlarged Vestibular Aqueduct Syndrome (EVAS)
-enlargement of the bony canal that connects IE to the cranial cavity
-filled with endolymphatic fluid
-HL may be present at birth, may be progressive, may be sudden, may fluctuate,
- symptom of pendred syndrome
Pendred Syndrome
-autosomal recessive
-EVAS
-possible cochlear malformation
-thyroid dysfunction; goiter
CHARGE Syndrome
-spontaneous mutation
-autosomal dominant
coloboma, choanal atresia, cranial nerve abnormality, ear anomalies
HL + vision loss
IE- malformed cochlea, semi circ c anals, small or absent auditory nerve
ME- malformed ossicles
-Can vary drastically for every different child
Usher Syndrome
autosomal recessive,
-congenital or early onset HL
-vestibular difficulties
-vision loss + HL
CHARGE and Usher syndrome are common causes of ...
HL and Vision loss
Waardenburg Syndrome
-pigmentation abnormalities
-wide set eyes
- generally autosomal dominant
-possible HL (25%)
Long QT Syndrome
cardiac muscle takes longer to recharge between beats; progressive HL
can lead to sudden death if not medicated
Connexin 26
*most common congenital HL
affect gap junction protein critical to chemical activity of hair cells; genetic screening of pregnant mothers
After a diagnosis of HL with an unknown cause every child should be referred for..
CT scan (ear malformations)
thryoid testing (pendred)
ophthalmological evaluation (Usher, CHARGE)
kidney function testing (BOR)
EKG (long QT)
Genetic testing (Connexin 26, otoscope test)
TORCH
in utero infection/disease
toxoplasmosis (cat feces)
other
rubella
cytomegalovirus
herpes
Maternal Rubella (German Measles)
infection during 1st/2nd trimester
may cause vision impairment, cataracts, heart disease, mental disability
- rate went down because of vaccines but it going up again because less people are getting vaccinated
CMV (maternal cytomegalovirus )
- leading cause of progressive or late onset HL in children
may cause vision impairment, mental disability, small head size, lack of coordination, seizures
- treatments: early detection, anti viral drugs
Neonates
low birth weight
prematurity
anoxia/hypoxia
jaundice
Miniere's Disease
-autoimmune disease
-typically unilateral
- low freq HL
-tinnitus
-long-lasting symptoms
- excess of endolymphatic fluid in cochlea
treatment: avoid caffeine, salt, alcohol
Presbycusis
progressive HL associated with aging
- often bilateral and symmetrical
- treatment: prevention
Ototoxic medication
drugs that are damaging to the ear/hearing
- aspirin, quinine, cisplatin, gentamicin, carboplatin, loop diuretics, ,Accutane
Noise Induced HL
-acoustic trauma; exposure brief but intense sound
-noise-induced; repeated/habitual exposure to injurious levels of sound
treatment- generally preventable, use common sense, wear ear protection
What do outer ear disorders affect?
collection, deflection, direction, resonance enhancement
What do middle ear disorders affect?
pressure mismatch, amplification, conduction, vibration
What do inner ear disorders affect?
sensory reception of sound waves, amplification of sound, neural encoding of sound
What do auditory nerve/pathway disorders affect?
neural encoding of sound, brain decoding of sound processing time, auditory functions
What do vestibular disorders affect?
body awareness, environmental awareness, locomotion, daily life activities, general feelings of health
auditory nerve and pathways disorders affect
neural encoding of sound
brain decoding of sound
processing time
auditory factors
localization, understanding
cochlear nerve deficiency
absence or underdeveloped cochlear nerve
mishomer
ANP disease, 8th nerve tumor
growth usually arises from one of vestibular nerves
HL usually unilateral and asymmetrical, progressive, tinnitus
Treatment- surgical intervention, hearing may be sacrificed
Auditory nerve pathway injury
Stroke or any other disorder affecting blood flow to brain
Anoxia / hypoxia - any trauma or disorder which deprives brain of oxygen
auditory nerve spectrum disorder (ANSD)
OHC function normally, IHS/Cochlea do not
HL can be any degree, speech scores are often lower
Risk factors- prematurity, hyperbilirubinemia (jaundice), cochlear nerve deficiency
auditory nerve and pathway central processing disorders
normal peripheral hearing sensitivity
difficulty processing auditory info into the CNS when it gets in the brain