Chapter 3- Cell Biology Pt 1
1/66
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
67 Terms
Cells
basic unit of all living things
components of cells
plasma membrane
nucleus
cytoplasm-
contains organelles
Functions of the cell
Cell metabolism and energy use
Synthesis of molecules
Communication
Reproduction and inheritance
Cell metabolism and energy use
all chemical reactions in the cell
often involve energy transfer
many reactions release heat and play a role in regulating body temperature
Synthesis of molecules
structural and functional characteristics of cells are determined by the types of molecules they produce
Communication
use chemical and electrical signals for communication
Reproduction and inheritance
Reproduction
passing genes from one cell to the next during cell division
Inheritance
transmission of traits from one generation to the next, gamete production
Components of the plasma membrane
Proteins (45-50%)
Lipids(45-50%)
phospholipids
cholesterol
Carbohydrates (4-8%)
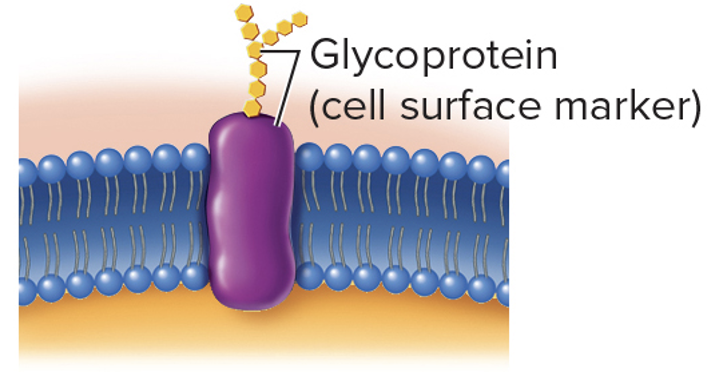
Glycocalyx
glycoproteins and glycolipids on the outer suface of the plasma membrane
Functions of the Plasma Membrane
Boundary separating the intracellular substances from the extracellular substances
Encloses and supports the cell contents
Attaches cells to the extracellular environment or to other cells
Allows for recognition and communication between cells
Determines movement of material into and out of the cell
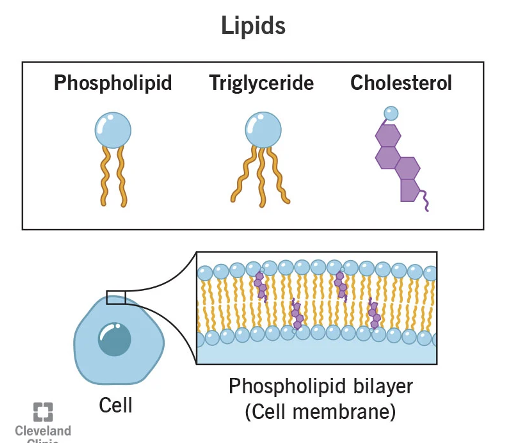
Membrane lipids
phospholipids
cholesterol
Phospholipids
form th elipid bilayer due to amphipathic nature
Cholesterol
Interspersed among the phospholipids
1/3 of the total lipids in the plasma membrane
hydrophilic hydroxyl group allows it to associate with the hydrophilic membrane surface
determines the fluid nature of the membrane by limiting movements of phospholipids
Fluid Mosaic Model
membrane is not rigid or static structure
highly flexible
changes shape and composition
dense liquid with proteins suspended in it
allows for:
distribution of molecules in the plasma membrane
repair of slight damage
membrane fusion
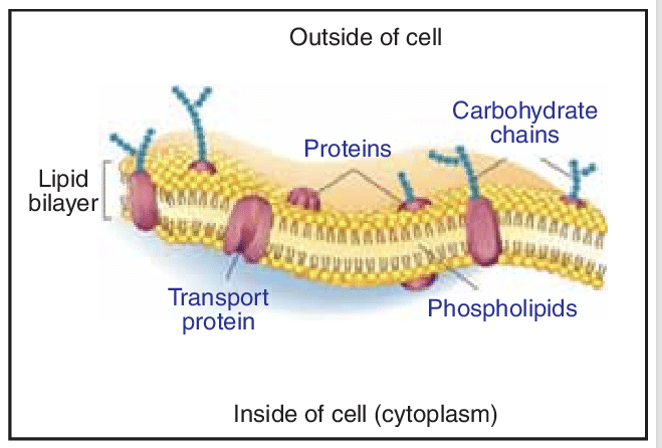
Membrane Proteins
carry out diverse functions in the plasma membrane
marker molecules, attachment proteins, transport proteins, receptor proteins, enzymes
Integral membrane proteins
penetrate deeply into the lipid bilayer
Peripheral membrane proteins
attach to the inner or outer surface of th elipid bilayer
can be bound to the integral proteins
Proteins: Marker Molecules
allow cells to identify other cells or other molecules
mostly glycoproteins and glycolipids
Attachment Proteins
integral proteins that allow cells to attach to other cells or extracellular molecules
often also attach to cytoplasmic molecules
Includes:
CADHERINS
INTEGRINS
cadherins
attach cells to other cells
integrins
attach cells to extracellular molecules
also attach to cytoplasmic molecules to allow for cellular communication
transport proteins
integral proteins that allow ions or molecules to move across the plasma membrane
Characteristics
specificity
competition
saturation
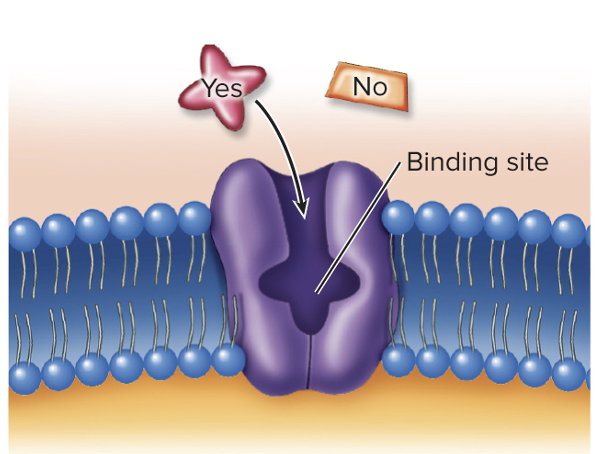
Transport proteins Characteristics- Specificity
bind only a certain type of molecule or ion
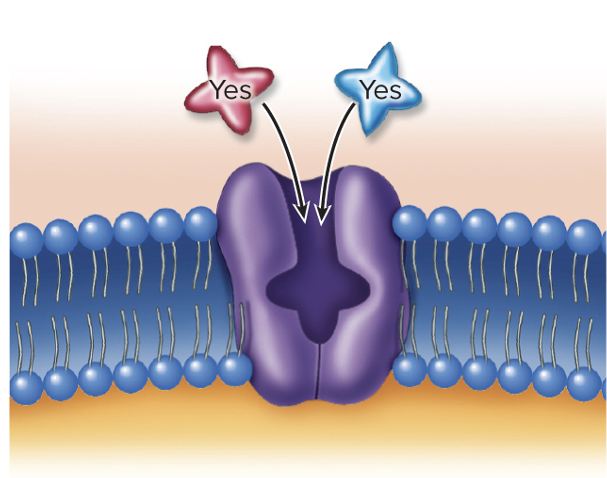
Transport proteins Characteristics- Competition
similarly shaped molecules can compete for the same binding site
Result of molecules of similar shape binding
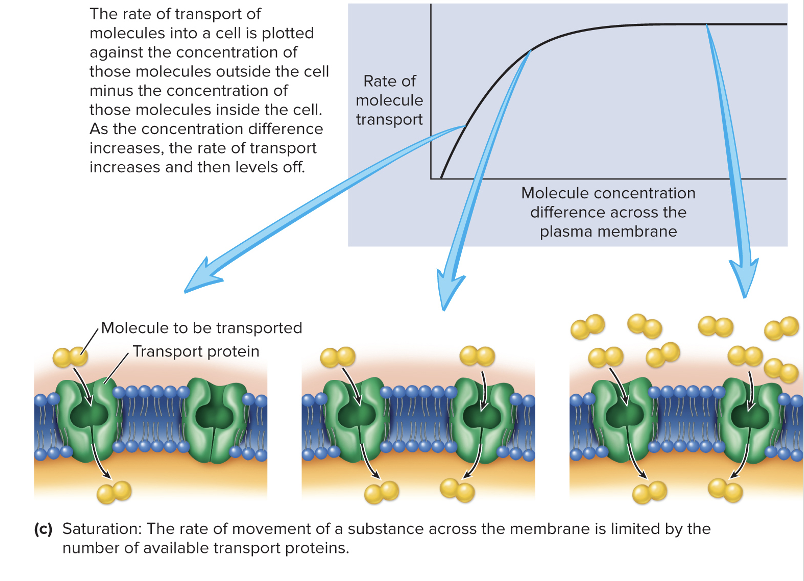
Transport proteins Characteristics- Saturation
rate of movement of the molecule is limited by the number of transport proteins
Classes of Transport Proteins
Channel Proteins
Carrier Proteins
ATP-powered pumps
Channel Proteins
One or more integral proteins that form a tiny channel through the plasma membrane
Hydrophobic regions face outward, hydrophilic portion face inward to determine ions that can pass through
Includes:
Leak ion channel
Gated ion channel
leak ion channels
always open, responsible for membrane permeability at rest
gated ion channels
open and close depending on conditions of the cell
Carrier Proteins
Transporters
Integral proteins that move ions or molecules from one side of the membrane to the other
Types:
Uniporter
Symporter
Antiporter
Uniporter
moves one ion or molecule
Symporter
moves two different ions or molecules in the same direction
Antiporter
moves two different ions or molecules in opposite directions
ATP-Powered Pumps
require ATP to move specific ions or molecules
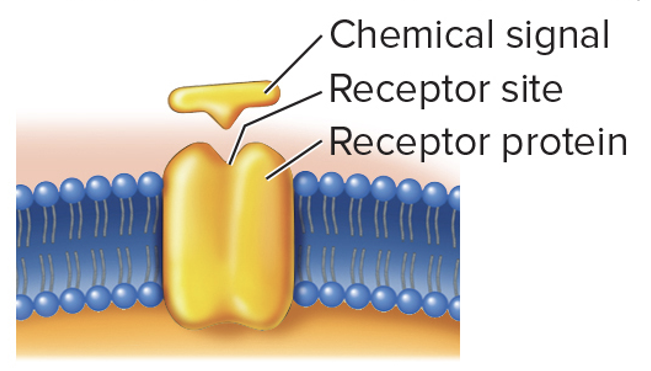
Receptor Proteins
Membrane proteins or glycoproteins that have a receptor site
Used for intercellular communication
Receptor in receptor proteins can be coupled to
channel proteins
G protein complexes
Enzymes
Catalyze chemical reactions on either side of the plasma membrane
Can be always active or activated by membrane bound receptors of G protein complexes
Plasma Membrane
selective permeable
cell volume must remain constant
must maintain the differences between intracellular and extracellular material
selective permeable
allows certain substances to pass through
Intracellular
enzymes, other proteins, glycogen, K+
Extracellular
Na+, Ca2+, Cl-
simple diffusion
net movement of particles from a place of high concentration to an area of low concentration, down a concentration gradient
how oxygen and steroid hormones enter cells and carbon dioxide leaves
DOES NOT USE ENERGY
nonpolar and hydrophobic substances diffuse through lipid regions of membranes
hydrophilic substances diffuse through protein channels in the membrane
osmosis
net movement of water through a selectively permeable membrane from area or relatively low concentration of solutes to the area of relatively high solute concentration
tonicity
ability of a solution to affect intracellular pressure and volume
determined by concentration of solutes that cannot pass through the plasma membrane
isotonic
hypertonic
hypotonic
isotonic
have the same tonicity, cells gain and lose water at the same rate
hypertonicity
ECF has a higher concentration than ICF, water leaves the cell
hypotonic
ECF has a lower concentration than ICF, water enters the cell
facilitated diffusion
type of carrier-mediated. transport
use carrier proteins in the plasma membrane
moves molecules that could not pass through the plasma membrane
glucose
solute moves down its concentration gradient
does not require ATP (energy)
active transport
type of carrier-mediated transport
moves molecules up its concentration gradient
requires ATP (energy)
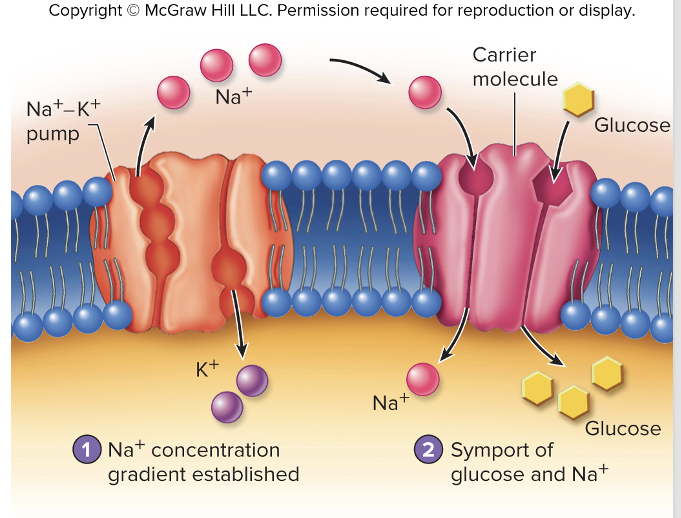
sodium-potassium (Na+-K+) pump
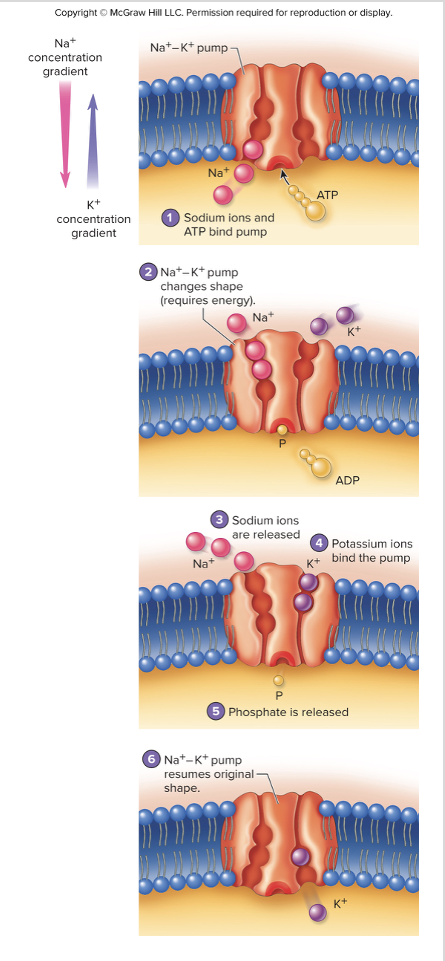
secondary active transport
involves active transport of an ion out of the cell
then its movement down the concentration gradient provides the energy necessary to move a different ion/molecule into the cell
vesicular transport
moves larger particles or droplets of fluid through the membrane
requires ATP
Endocytosis
Exocytosis
Endocytosis
moves matter into the cell
Phagocytosis
Pinocytosis
Receptor-mediated endocytosis
Exocytosis
moves matter out of the cell
transcytosis
substances like large molecules, fluid, and even pathogens are transported across a cell, from one side to the other
cytoplasm
cellular material outside the nucleus and inside the plasma membrane
about half cytosol and half organelles
cytosol
cytosol
fluid portion of the cytoplasm
viscous solution containing dissolved ions and molecules with suspended molecules (enzymes, cytoskeleton, cytoplasmic inclusions)
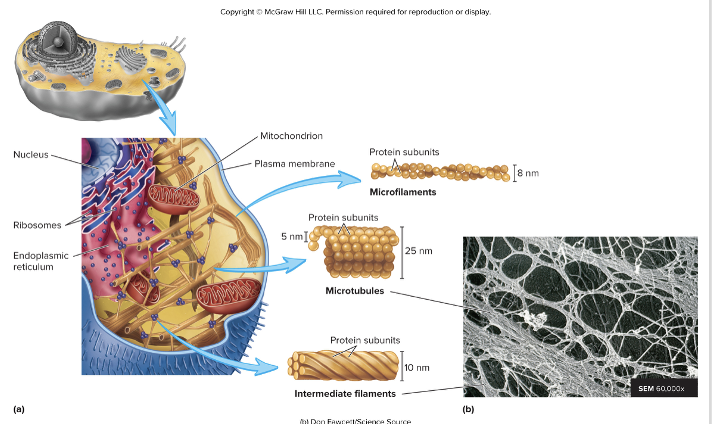
cytoskeleton
support the cell
holds the nucleus and organelles in place
help change the cell shape
movement of cell organelles
consists of:
microtubules
microfilaments (actin filaments)
intermediate filaments
cytoplasmic inclusions
aggregates of chemicals
produced in the cell or taken in by the cell
includes:
lipid droplets
glycogen granules
organelles
“little organs”
structures where individual functions of the cell take place
nucleus
largest organelle
most cells have only one nucleus
mature red blood cells have none, skeletal muscle cells can have dozens of nuclei
nuclear envelope
nuclear pores
nucleoli
nuclear envelope
two layer-membrane surrounding the nucleus
nuclear pores
openings in the nuclear envelope
nucleoli
one or more per nucleus, structure where ribosomes are built
nucleus
chromosomes
thread like bodies of DNA and protein found in the nucleus
46 chromosomes in most human cells
nucleosomes
structural unit of chromosomes made of DNA wrapped around histones
chromatin
very fine filament broadly dispersed throughout the nucleus of non-dividing cells
ribosomes
small granules made of protein and ribonucleic acid (RNA)
produced in the nucleus
“read” genetic code from the nucleus and build proteins from amino acids
can be found attached to the nuclear envelope or rough ER or free in cytoplasm
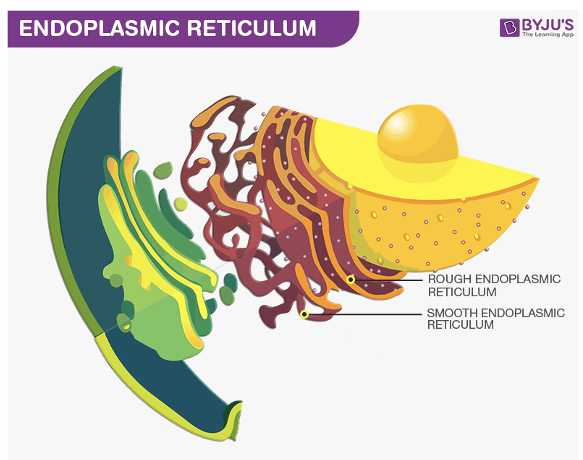
Endoplasmic Reticulum
membrane bound system of interconnected channels (cisternae)
Rough endoplasmic reticulum
flat parallel cisternae covered with ribosomes
continuous with the outer membrane of the nuclear envelope
functions:
produces phospholipids and proteins of the plasma membrane
produces secreted proteins
produces secreted proteins
produces proteins stored in lysosomes
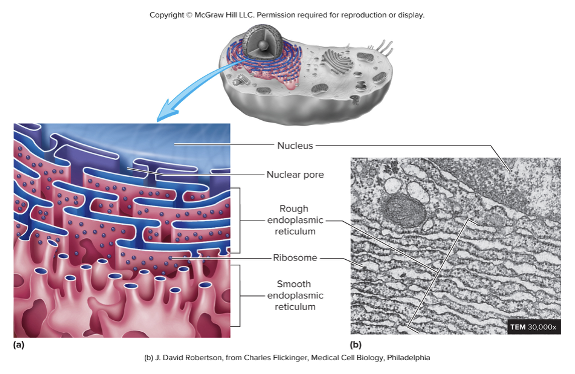
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
tubular shaped cisternae with more branching
lacks ribosomes
continuous with the rough ER
functions:
synthesizes steroids and other lipids
detoxifies alcohol and other drugs
manufactures the cells internal and surface membranes
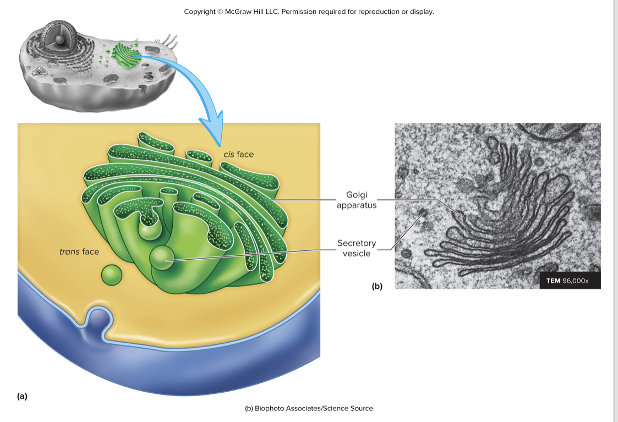
Golgi Complex
cluster/stack of cisternae
synthesize carbohydrates and finalize processing of proteins and glycoproteins
pinches off Golgi Vesicles
some are lysosomes
some incorporate into the plasma membrane
some become secretory vesicles