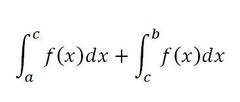Integrals
4.0(1)Studied by 14 people
Card Sorting
1/97
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 7:01 PM on 9/20/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
98 Terms
1
New cards
∫dx
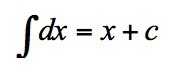
2
New cards
∫uⁿ du
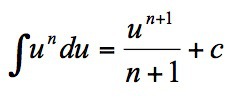
3
New cards
∫e^u du
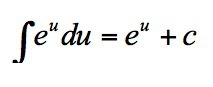
4
New cards
∫b^u*ln(b) du
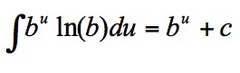
5
New cards
∫b^u du
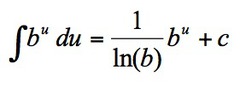
6
New cards
∫cosu du
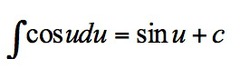
7
New cards
∫-sinu du
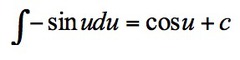
8
New cards
∫sinu du
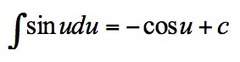
9
New cards
∫sec²u du
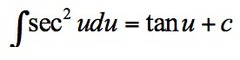
10
New cards
∫-cscu*cotu du
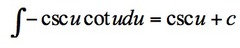
11
New cards
∫cscu*cotu du
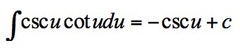
12
New cards
∫secu*tanu du
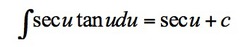
13
New cards
∫-csc²u du
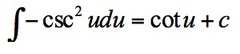
14
New cards
∫csc²u du
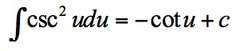
15
New cards
∫du/√(1-u²)
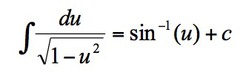
16
New cards
∫-du/√(1-u²)
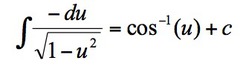
17
New cards
∫du/(1+u²)
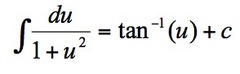
18
New cards
∫-du/u√(1-u²)
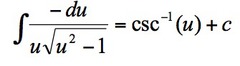
19
New cards
∫du/u√(1-u²)
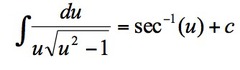
20
New cards
∫-du/(1+u²)
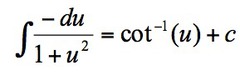
21
New cards
∫du/u
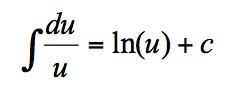
22
New cards
∫tan u du
-ln|cos u|+C
23
New cards
∫cot u du
ln|sin u|+C
24
New cards
∫sec u du
ln|sec u+tan u|+C
25
New cards
∫csc u du
-ln|csc u+ cot u|+C
26
New cards
f(x)g'(x) + g(x)f'(x)
derivative of the multiplaction of two functions
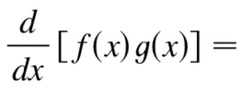
27
New cards
d/dx [f(x)/g(x)] =
quotient rule
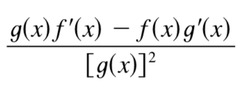
28
New cards
f'(g(x))g'(x)
chain rule
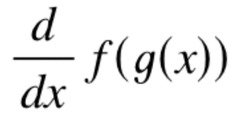
29
New cards
d/dx [ln|x|] =
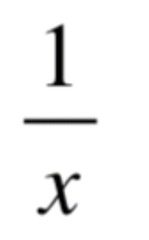
30
New cards
d/dx [a^x] =
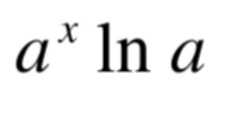
31
New cards
d/dx [log_a X] =
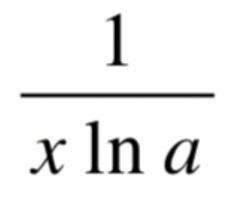
32
New cards
∫- sinx
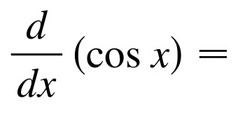
33
New cards
∫secxtanx
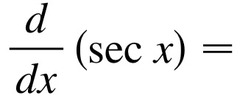
34
New cards
∫- cscxcotx
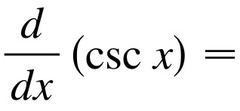
35
New cards
d/dx [tanx]
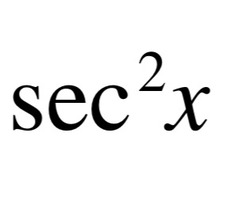
36
New cards
d/dx [cotx]
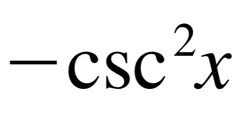
37
New cards
∫cosx
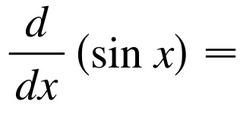
38
New cards
quotient rule
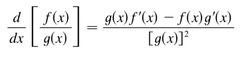
39
New cards
derivative of a power
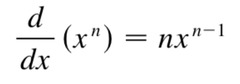
40
New cards
chain rule
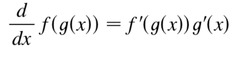
41
New cards
derivative of an exponential function
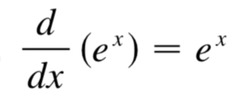
42
New cards
derivative of a natural log
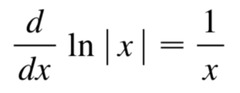
43
New cards
d/dx [a^x]
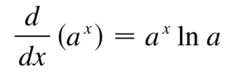
44
New cards
derivative of a log base a
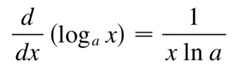
45
New cards
d/dx [sinx]
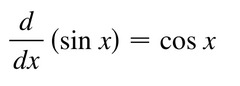
46
New cards
d/dx [cscx]
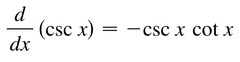
47
New cards
d/dx [cosx]
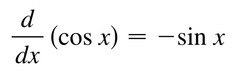
48
New cards
d/dx [secx]
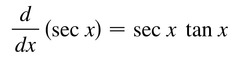
49
New cards
d/dx [tanx]
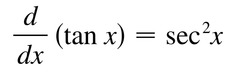
50
New cards
d/dx [cotx]
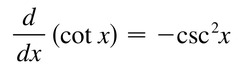
51
New cards
d/dx [arcsinx]
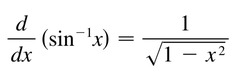
52
New cards
d/dx [arccscx]
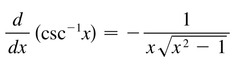
53
New cards
d/dx [arccosx]
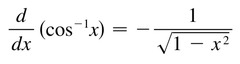
54
New cards
d/dx [arcsecx]
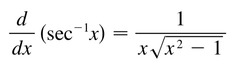
55
New cards
d/dx [arctanx]
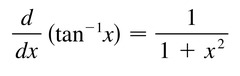
56
New cards
d/dx [arccotx]
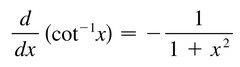
57
New cards
product rule
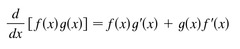
58
New cards
f is continuous at x=c if...
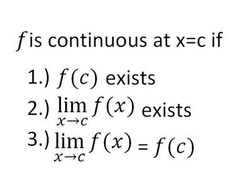
59
New cards
Intermediate Value Theorem
If f is continuous on [a,b] and k is a number between f(a) and f(b), then there exists at least one number c such that f(c)=k
60
New cards
Global Definition of a Derivative
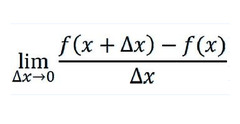
61
New cards
Alternative Definition of a Derivative
f '(x) is the limit of the following difference quotient as x approaches c
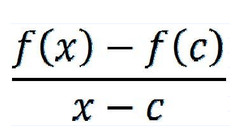
62
New cards
∫-sin(x)
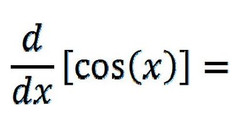
63
New cards
∫sec²(x)
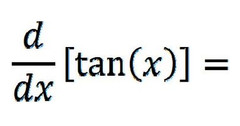
64
New cards
∫-csc²(x)
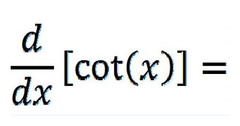
65
New cards
∫sec(x)tan(x)
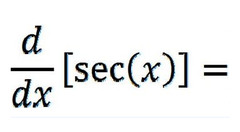
66
New cards
Extreme Value Theorem
If f is continuous on [a,b] then f has an absolute maximum and an absolute minimum on [a,b]. The global extrema occur at critical points in the interval or at endpoints of the interval.
67
New cards
Rolle's Theorem
Let f be continuous on [a,b] and differentiable on (a,b) and if f(a)=f(b) then there is at least one number c on (a,b) such that f'(c)=0 (If the slope of the secant is 0, the derivative must = 0 somewhere in the interval).
68
New cards
Mean Value Theorem
The instantaneous rate of change will equal the mean rate of change somewhere in the interval. Or, the tangent line will be parallel to the secant line.
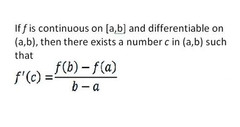
69
New cards
First Derivative Test for local extrema

70
New cards
Point of inflection at x=k

71
New cards
Combo Test for local extrema
If f'(c) = 0 and f"(c)

72
New cards
Horizontal Asymptote
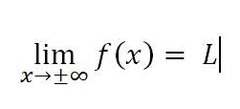
73
New cards
L'Hopital's Rule
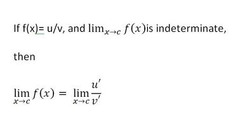
74
New cards
x+c
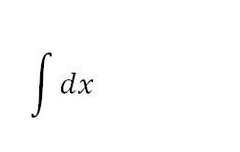
75
New cards
sin(x)+C
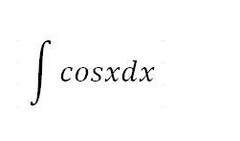
76
New cards
-cos(x)+C
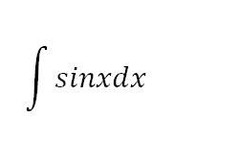
77
New cards
tan(x)+C
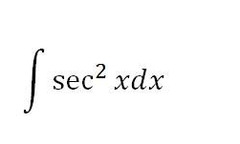
78
New cards
-cot(x)+C
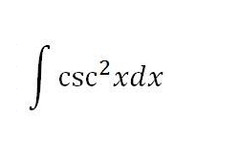
79
New cards
sec(x)+C
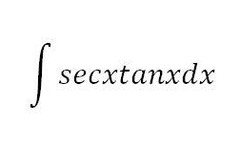
80
New cards
-csc(x)+C
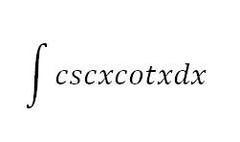
81
New cards
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus #1
The definite integral of a rate of change is the total change in the original function.
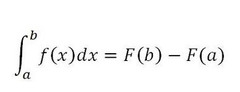
82
New cards
Fundamental Theorem of Calculus #2
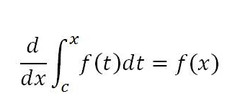
83
New cards
Mean Value Theorem for integrals or the average value of a functions
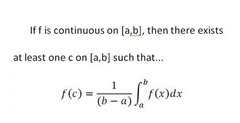
84
New cards
ln(x)+C
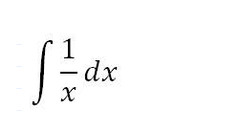
85
New cards
-ln(cosx)+C = ln(secx)+C
hint: tanu = sinu/cosu
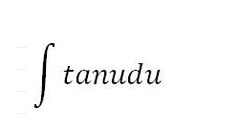
86
New cards
ln(sinx)+C = -ln(cscx)+C

87
New cards
ln(secx+tanx)+C = -ln(secx-tanx)+C

88
New cards
ln(cscx+cotx)+C = -ln(cscx-cotx)+C

89
New cards
If f and g are inverses of each other, g'(x)
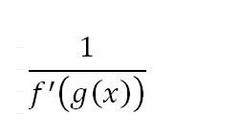
90
New cards
Exponential growth (use N= )
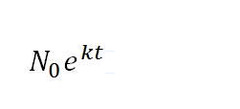
91
New cards
Formula for Disk Method
Axis of rotation is a boundary of the region.
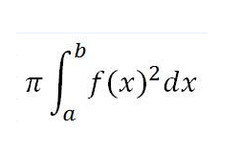
92
New cards
Formula for Washer Method
Axis of rotation is not a boundary of the region.
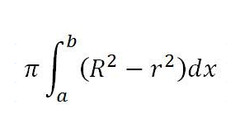
93
New cards
Inverse Secant Antiderivative
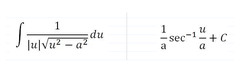
94
New cards
Inverse Sine Antiderivative

95
New cards
Derivative of eⁿ
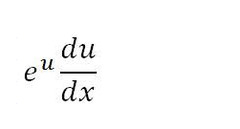
96
New cards
ln(a)*aⁿ+C
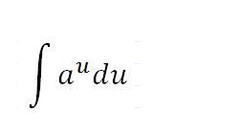
97
New cards
Derivative of ln(u)
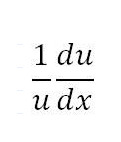
98
New cards
Antiderivative of f(x) from [a,b]