BIOL 2460 Chapter 2
1/58
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
59 Terms
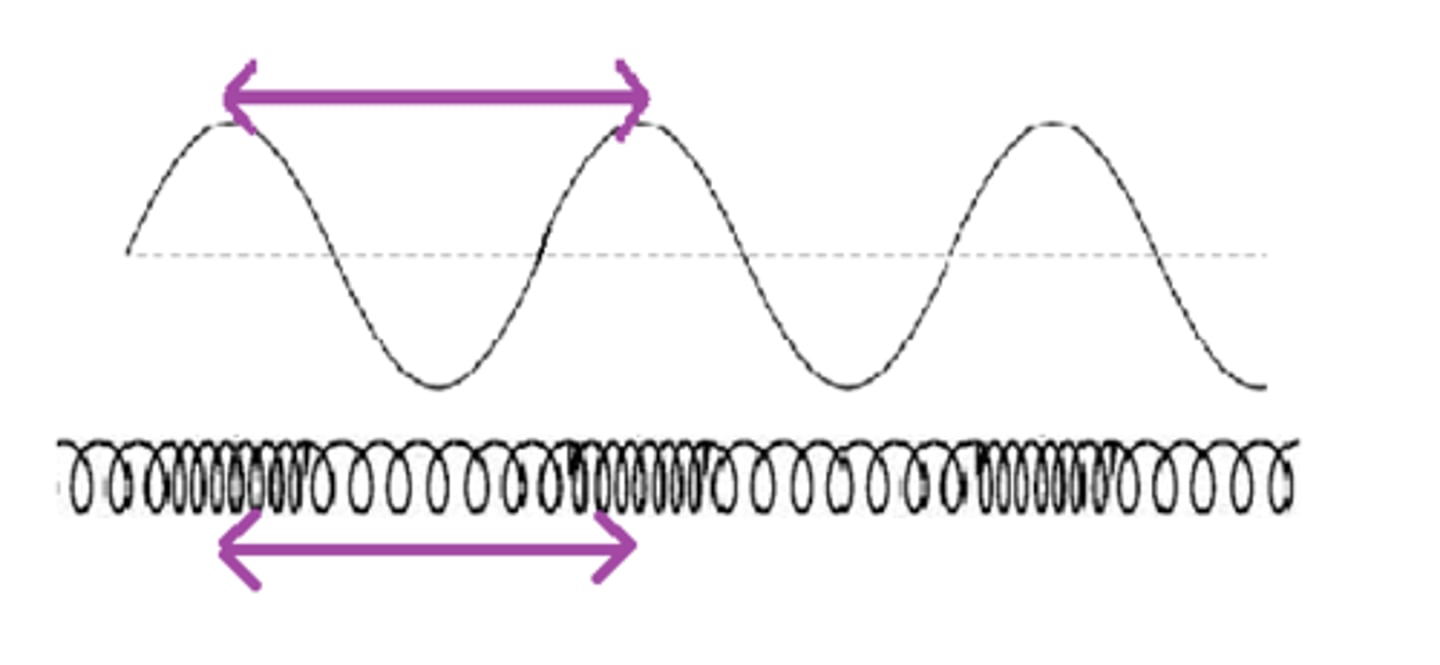
Wavelength
length between peaks
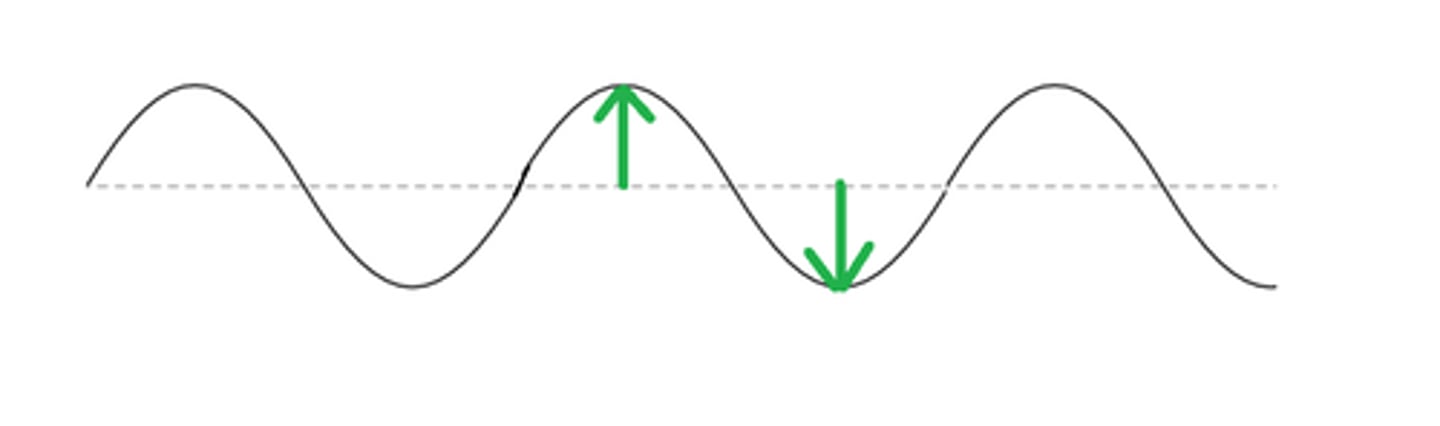
Amplitude
height of peaks
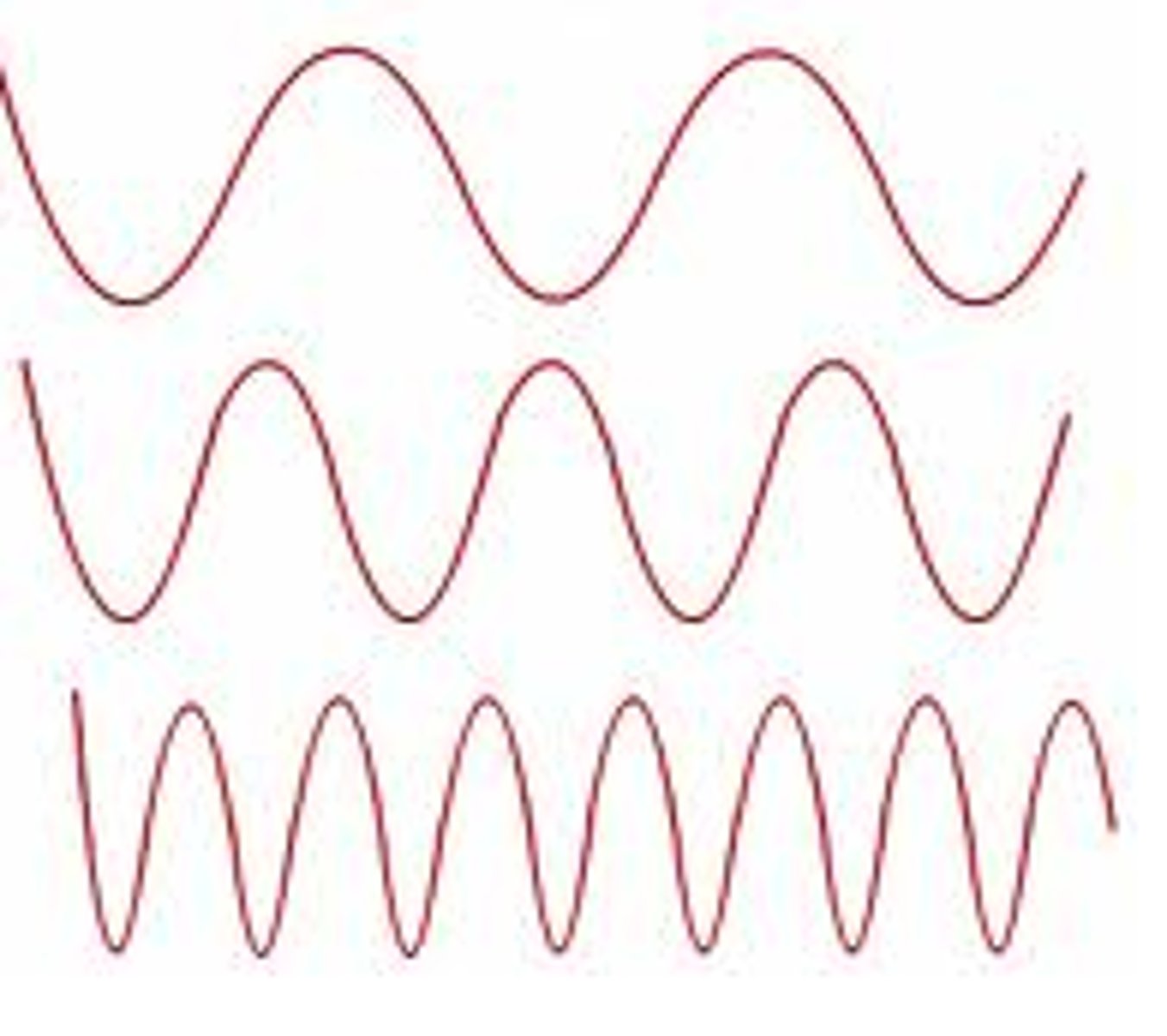
Frequency
rate of peaks in time
Reflection
wave bounces off material
Absorbance
wave is captured
Transmission
Wave travels through
Interference
the interaction between waves that meet
Diffraction
bending or scattering of a wave by object opening
Refraction
Change in direction and/or speed
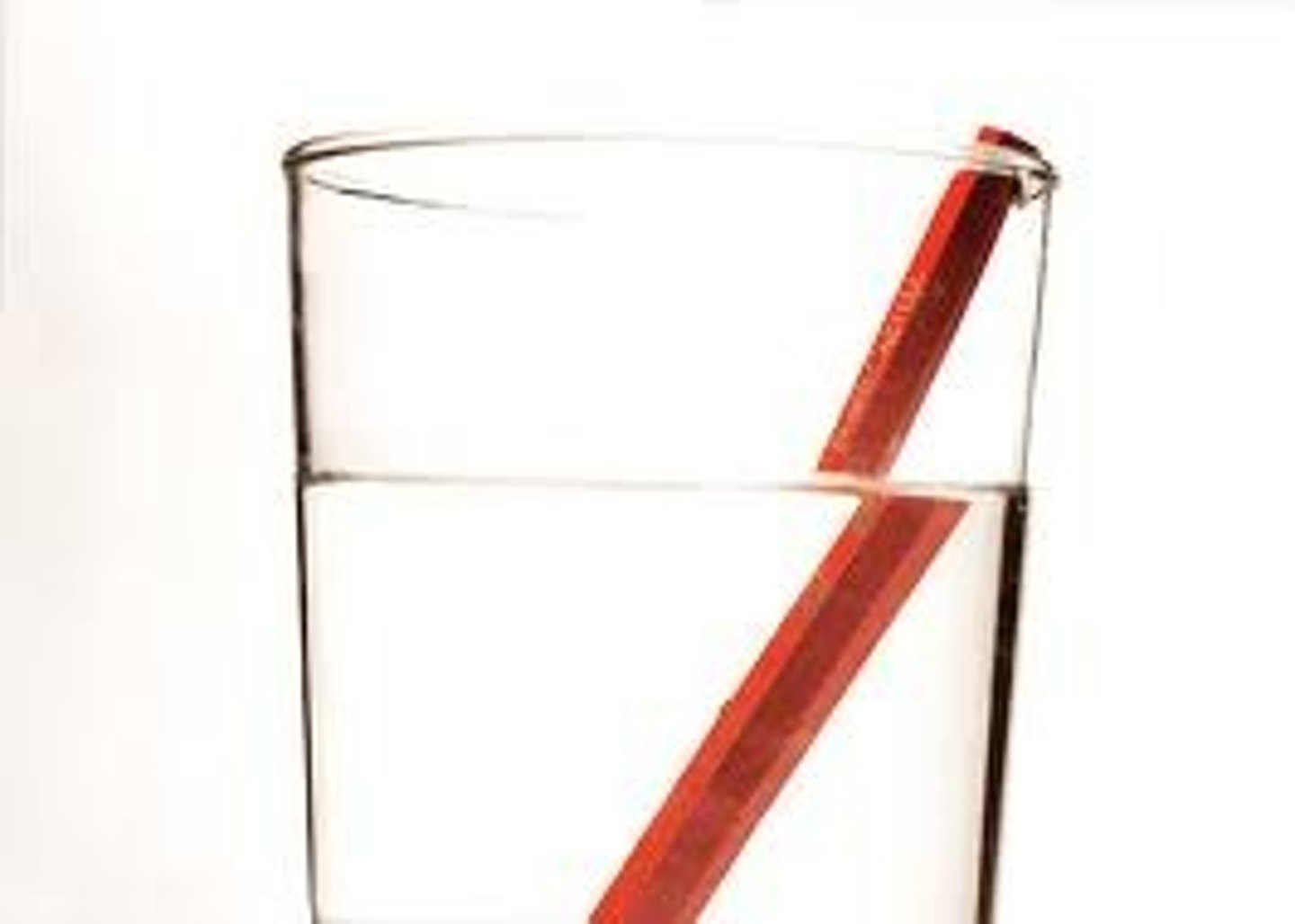

Refractive index
degree of change in transmission speed= speed of light in vaccum/ speed of light through material
If light enters a substance with a ___________ refractive index it _____________ and bends __________ the normal line (_________from the boundary)
HIGHER , SLOWS DOWN, TOWARD , AWAY
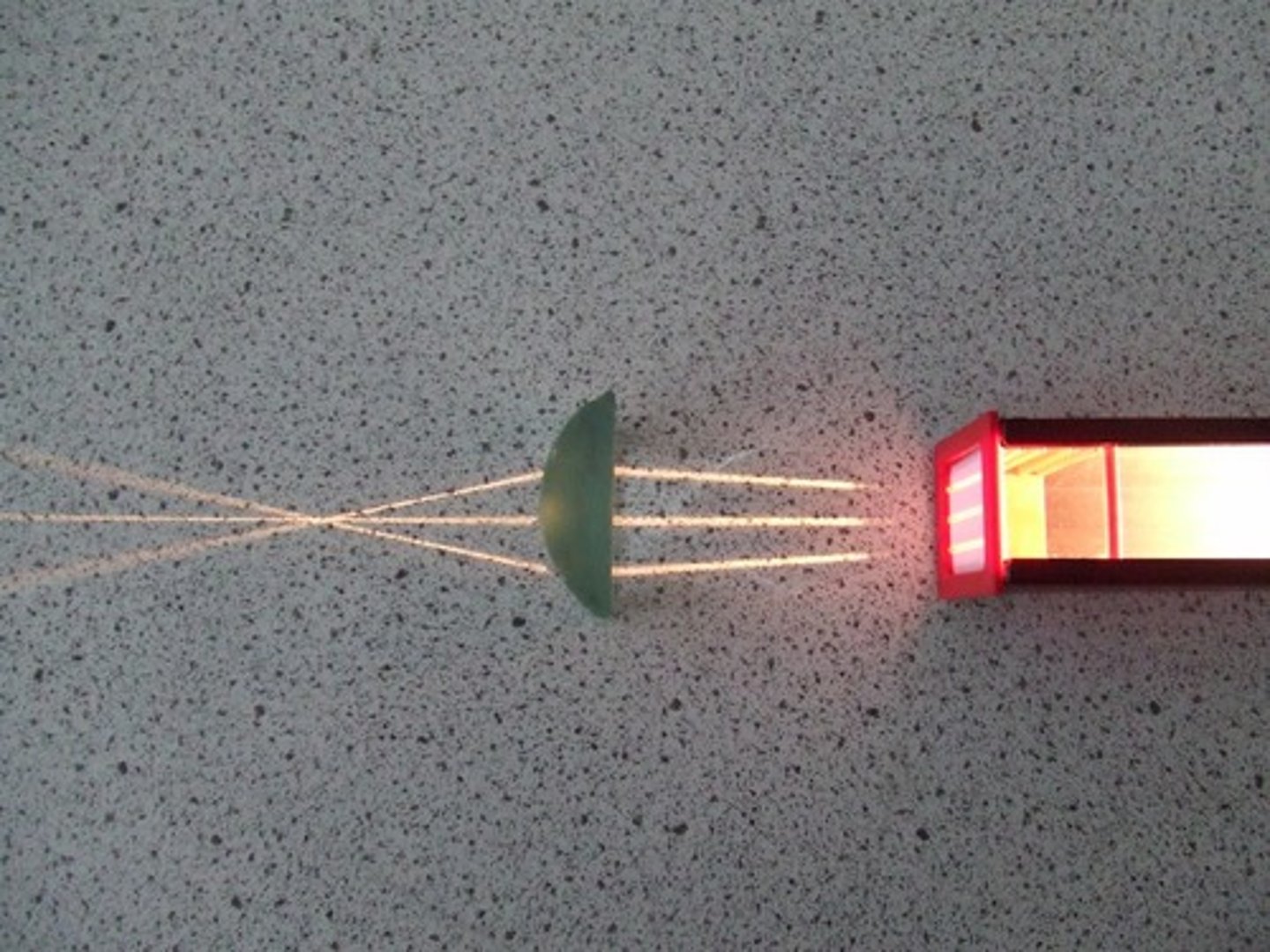
Convex lens
A lens that is thicker in the middle than at the edges that bends light rays towards one another. Occurs on a curved boundary to meet a focal point (microscope, glasses, contacts)
Concave lens
a lens that is thicker at the edges than in the middle that bends light rays away from one another. refracts light away from a focal point. (flashlights)
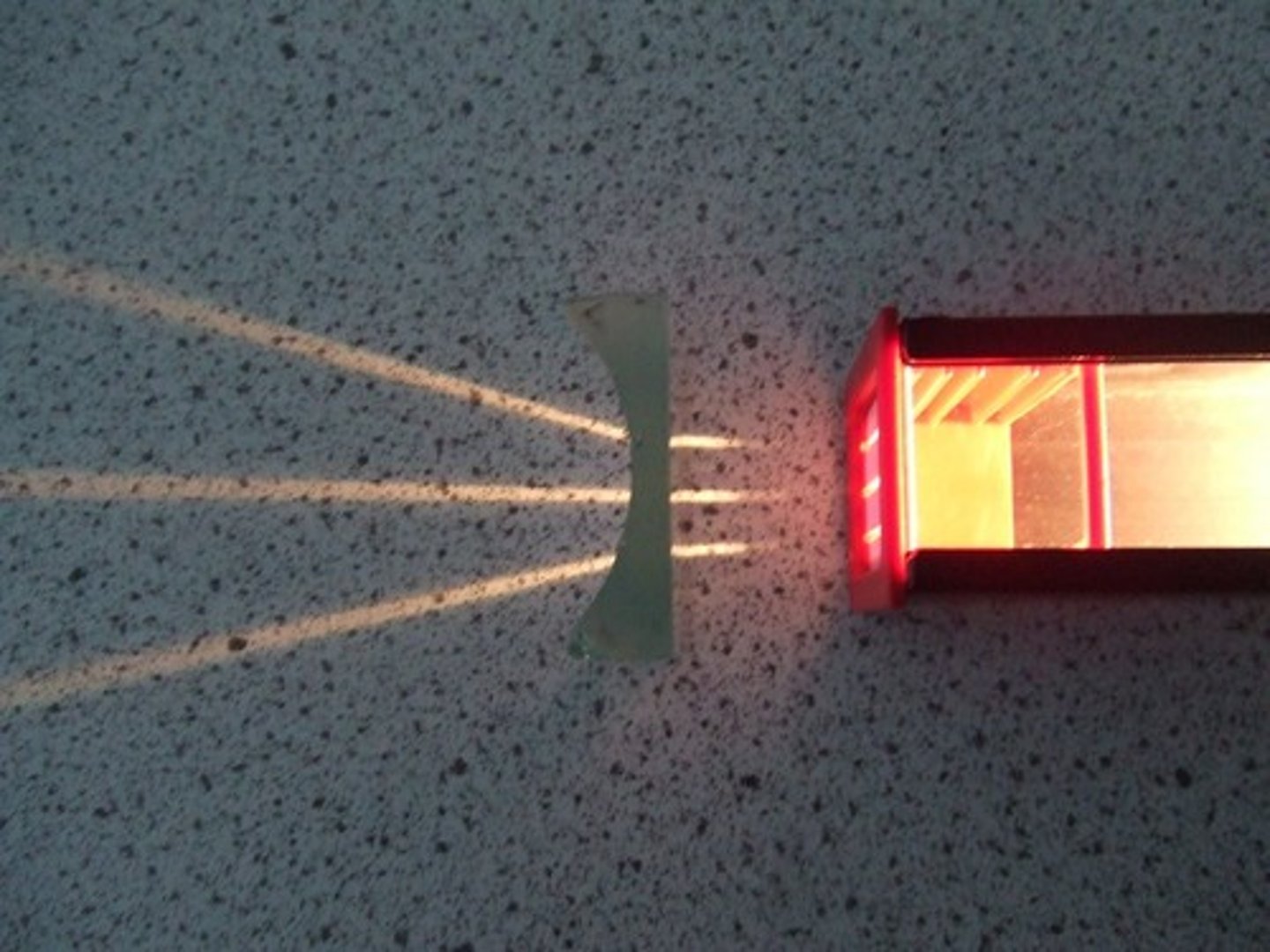
Higher frequency waves have
higher energy (protons move faster)
Ultraviolet
Have the most energy
Infrared
Have the least energy
Magnification
ability of a lens to enlarge the image of an object
Contrast
creation of stark difference in coloration
Resolution
ability to tell that two separate points/objects are separate (clarity)
Shorter wavelengths-
Longer wavelengths
Higher resolution
Lower resolution
Numerical aperture
ability to gather light by lens
Antonie van Leeuwenhoek utilized
1st simple microscope
Galileo Galilei used a
Compound Microscope
Robert Hooke
first to observe "small chambers" in cork and call them cells.
Who invented the mircroscope?
unknown
Brightfield microscope
A microscope that uses visible light for illumination; the specimens are viewed against a white background.
Darkfield microscope
Specimens appear bright against a dark background; no staining is required, live specimens may be observed

Phase-contrast microscope
light microscope that uses refraction and interference to enhance contrast; useful in examining living, unstained cells (endospores and organelles)
Differential interference contrast microscope
This microscope, similar to the phase contrast, is used to observe minute surface irregularities but at a higher resolution. However, the use of polarized light limits the variety of observable specimen containers.
Fluorescence microscopy
uses a fluorescent dye that emits fluorescence when illuminated with ultraviolet radiation. Used to distinguish living from dead cells, and find pathogens and specific molecules
Confocal microscopy
a light microscope that uses fluorescent stains and laser to make two- and three-dimensional images, Useful for examining thick specimens such as biofilms
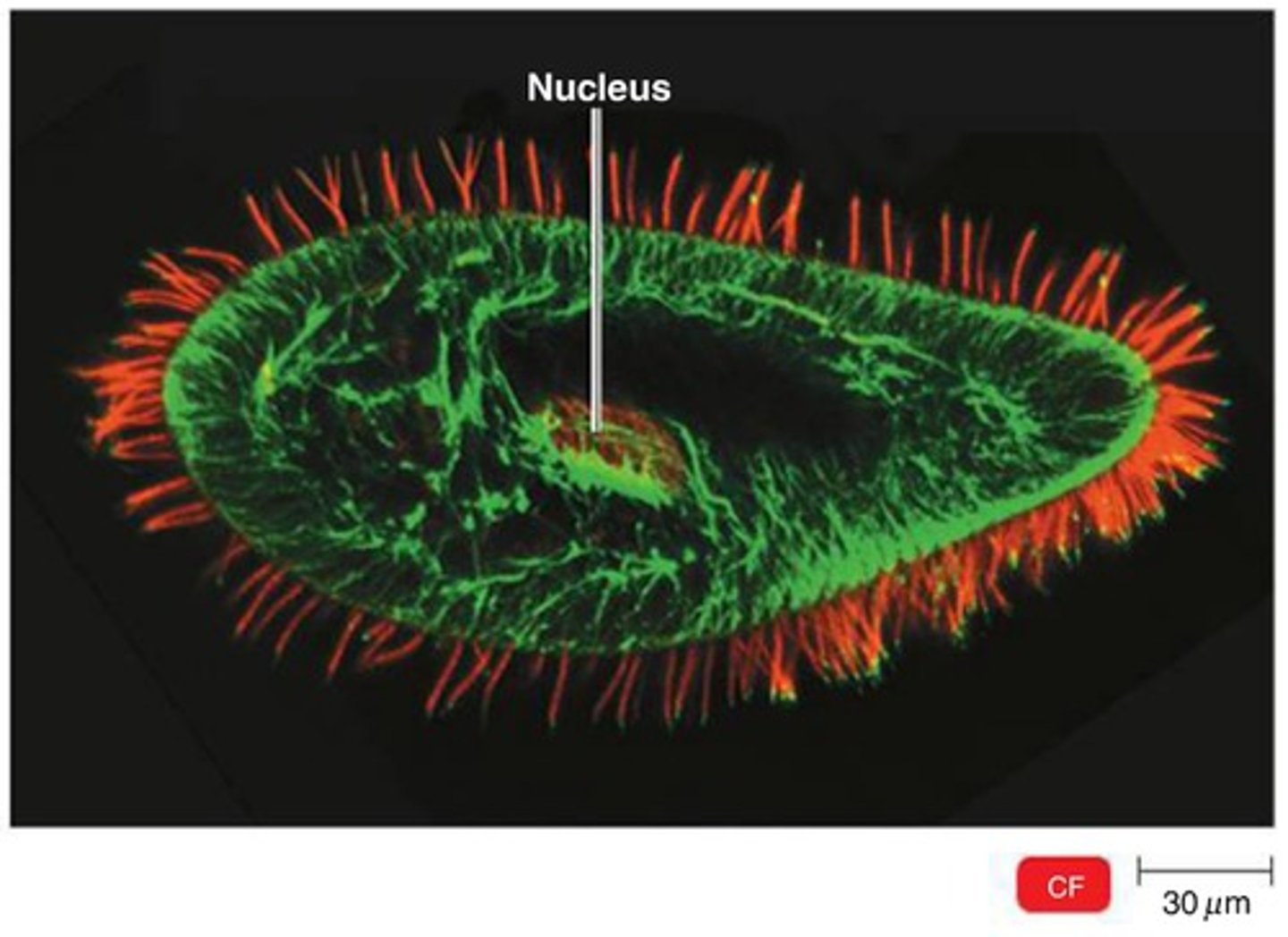
Two-Photon Microscopy
Cells are stained with fluorochrome dyes. Two photons of long-wavelength (red) light are used to excite the dyes. Good for viewing thicker material (e.g. brain slices, embryos, organs, etc.)
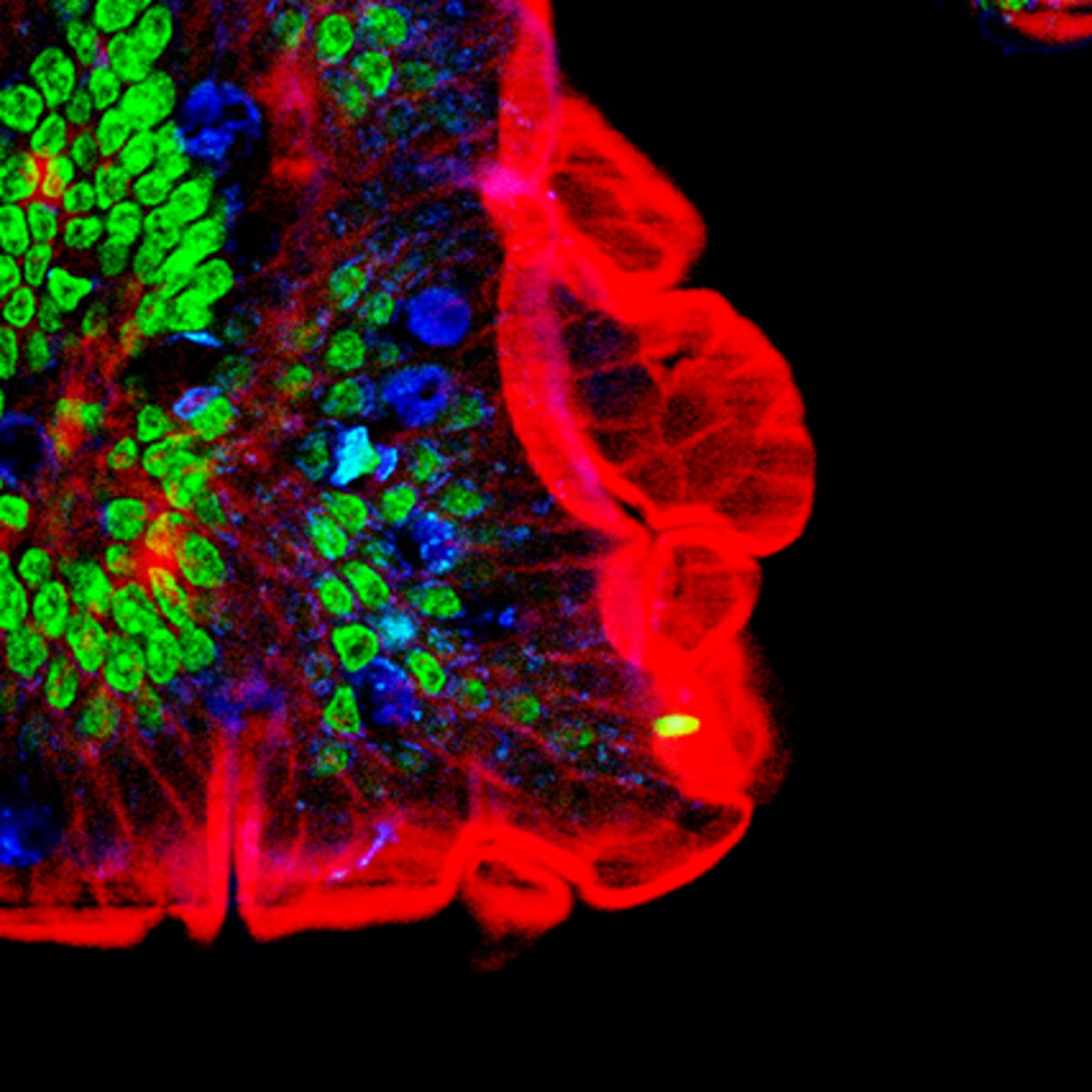
Transmission electron microscope (TEM)
a microscope that passes an electron beam through very thin sections (ultramicrotome). Can only view specimens that are cut into thin, dehydrated slices. Stained with electron-dense heavy metals
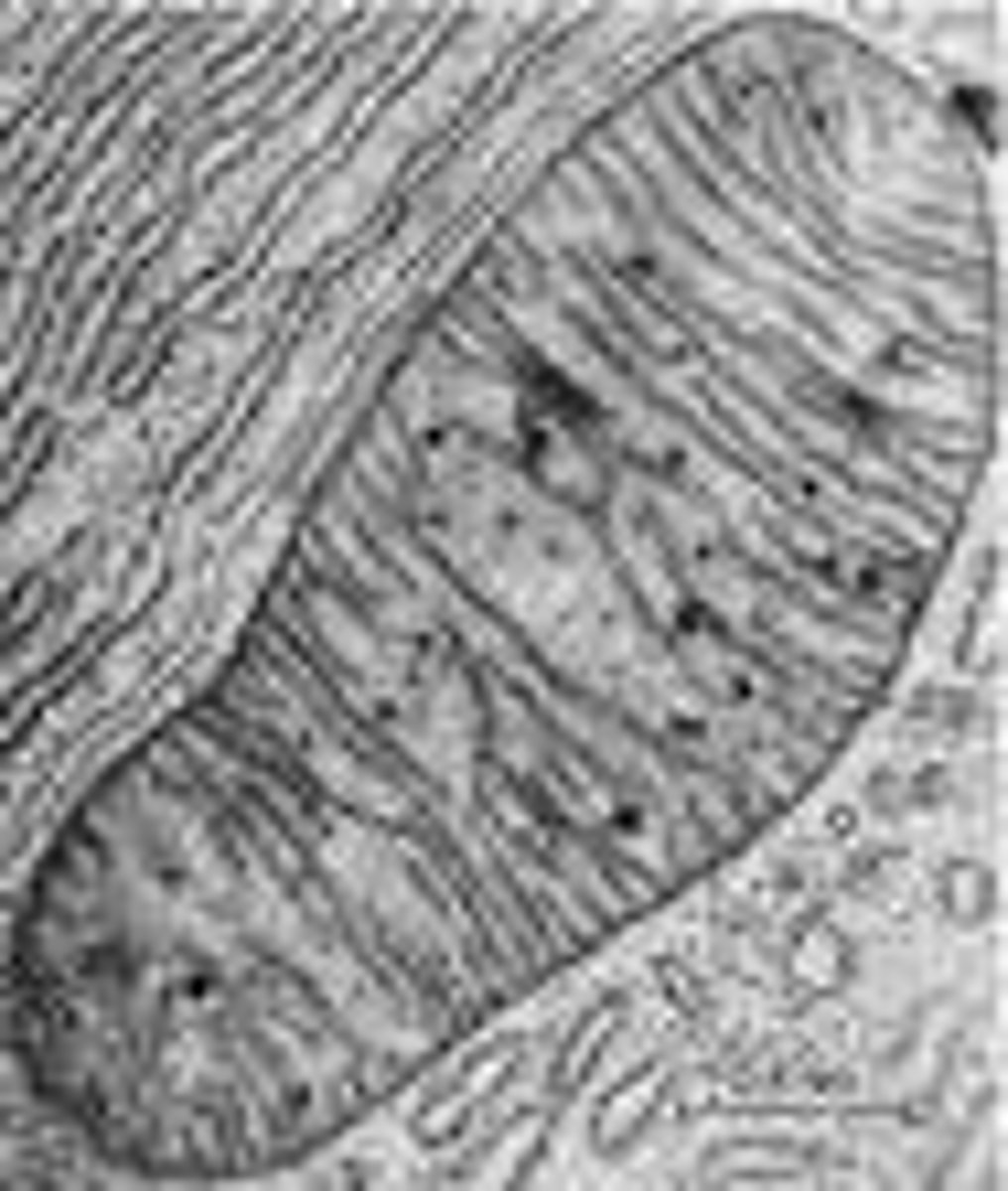
Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM)
A microscope that uses an electron beam to scan the surface of a sample, coated with metal atoms. Examines the surface of specimens on a 3-D detailed image. More dehydrated (critical point dying with liquid CO2), sputter-coated with metal.
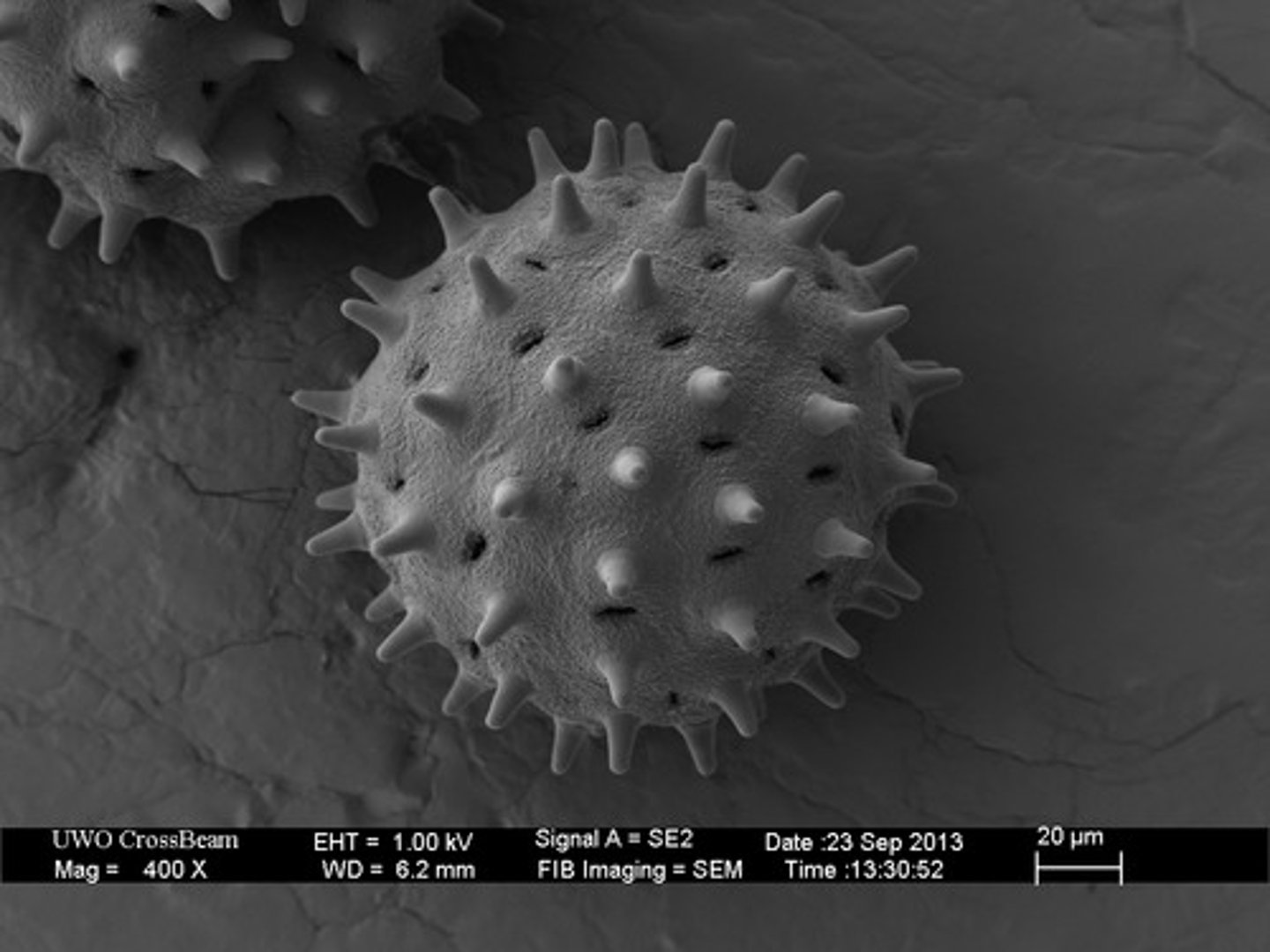

Scanning Tunneling Microscope (STM)
microscope that measures electrons that leak or "tunnel" from the surface of the specimen. Shows a sample's surface atom by atom with ultra-high resolution, without the use of electron beams or light.
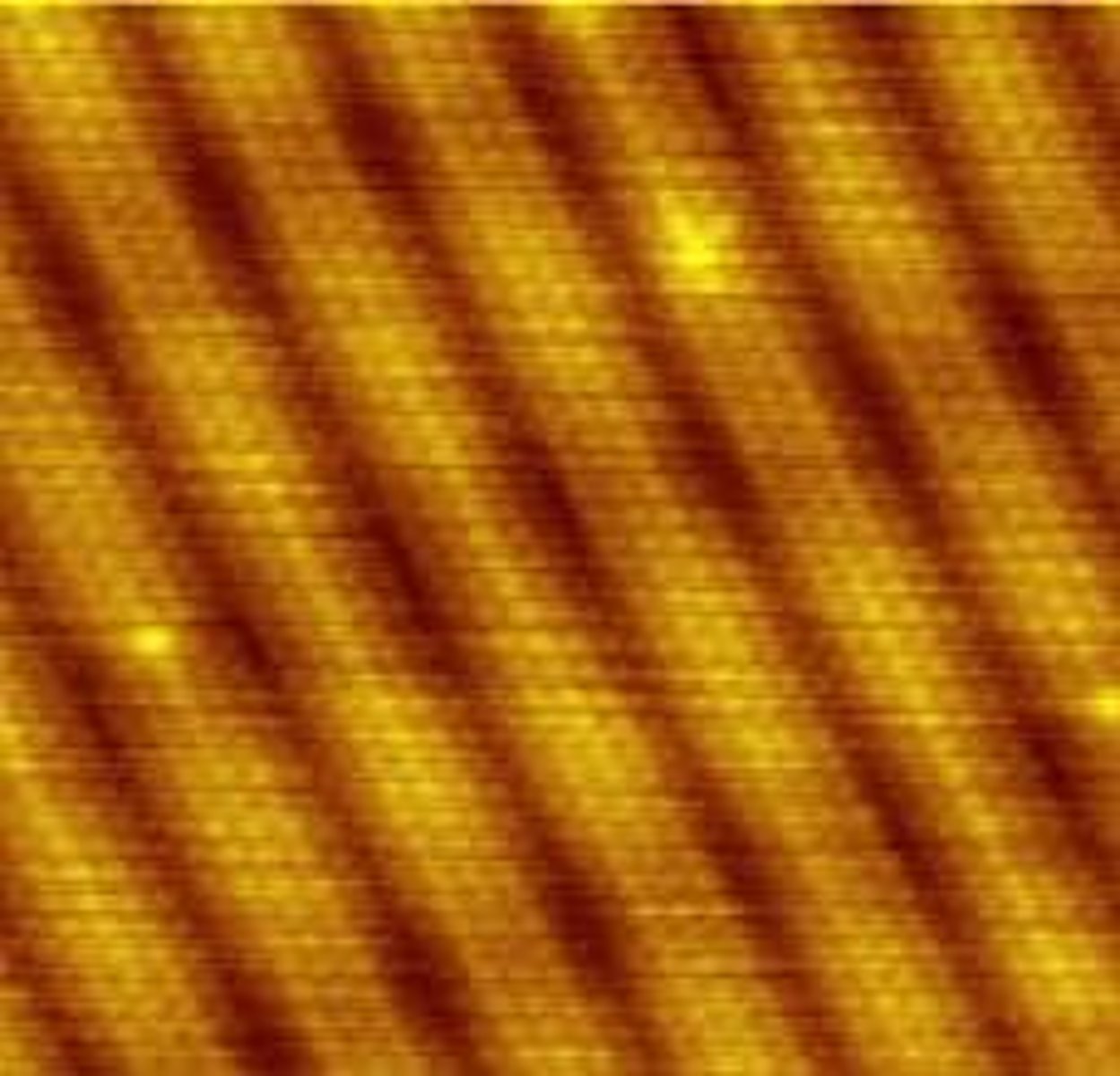
Atomic Force Microscopy (AFM)
uses a metal- and-diamond probe inserted into the specimen.
Produces three-dimensional images.
Wet mount (smear)
a glass slide holding a specimen suspended in a drop of liquid (such as water) for microscopic examination. Good for viewing live specimens
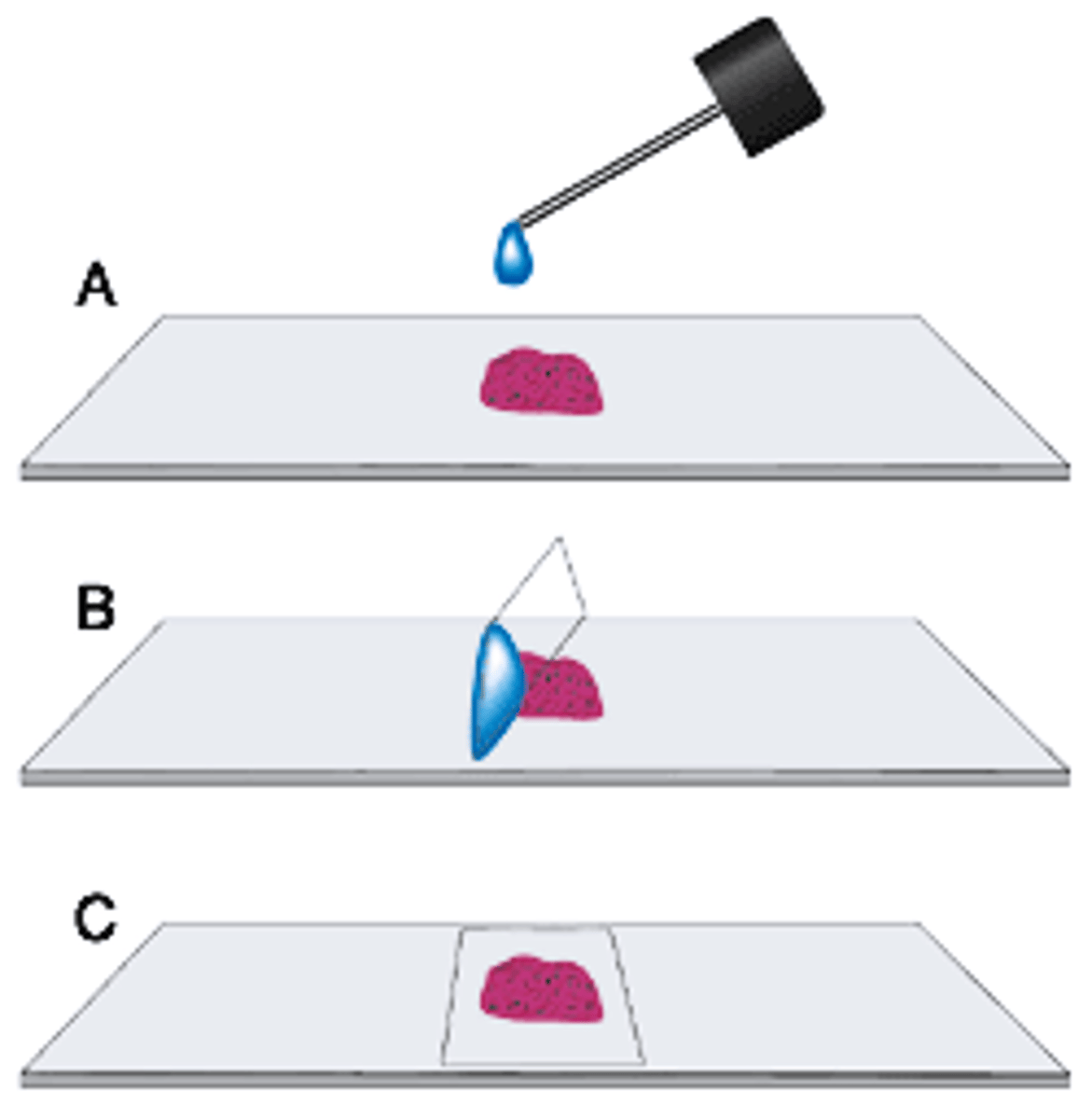
fixed mount (smear)
Good for staining since cells are stuck to the plate
Basic stain
(+) charge on the ion (cationic). Ex: Methylene Blue, crystal violet, Basic fuchsin, Malachite green. stains negatively charged molecules and structures.
Acidic stain
(-) Charge on the ion (anionic). Ex: India Ink, rose Bengal, Eosin, acid fuchsin. Stains negatively charged molecules and structures
Positive stain
Dye/stain is absorbed into cells
Negative stain
stains the background, not the cell
Simple stain
A method of staining microorganisms with a single basic dye emphasizes structures. Helps to highlight the cell
Differential stains
Differentiates organisms based on stain interactions, 2+ stains
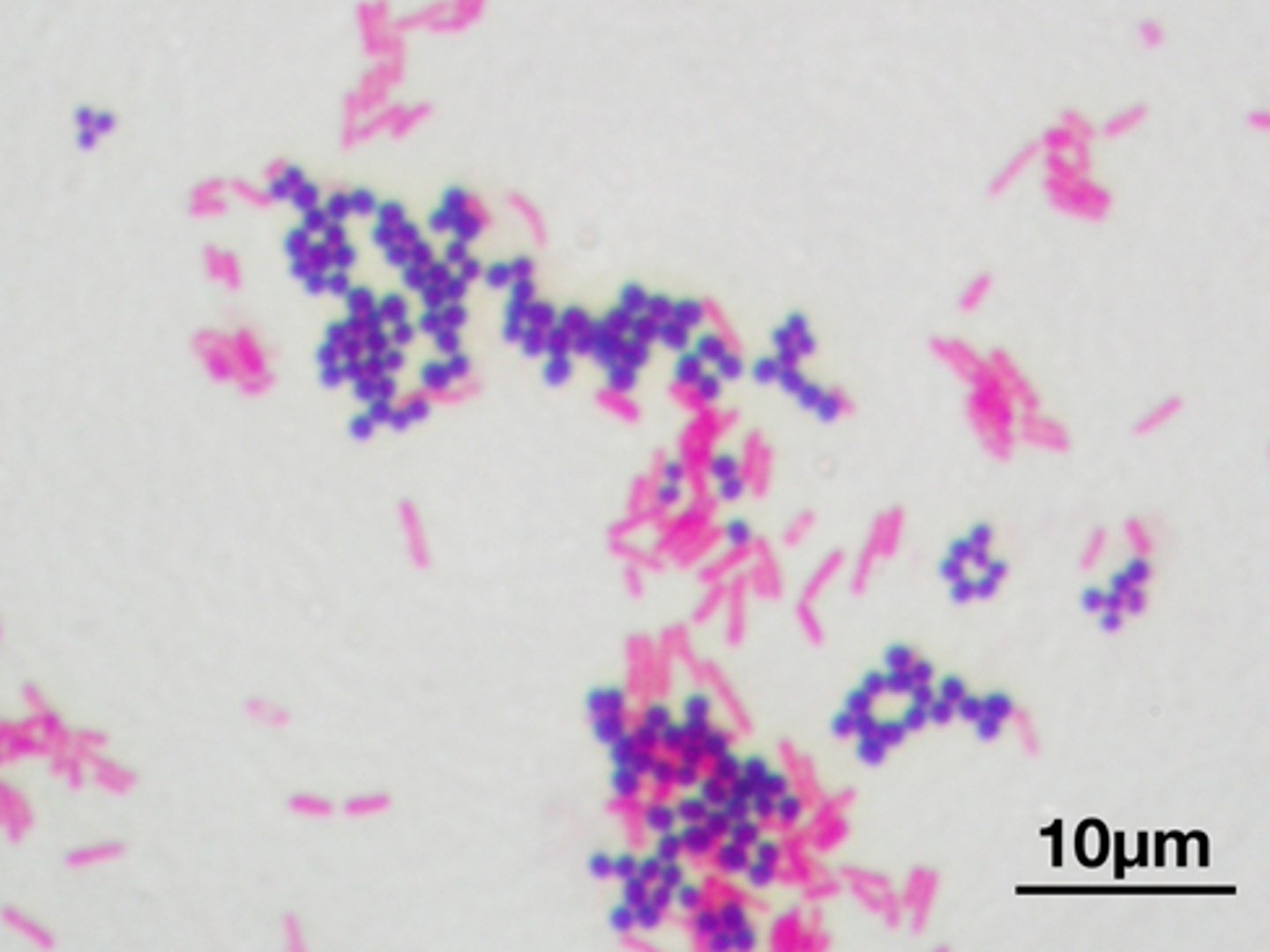
Gram stain
A staining method that distinguishes between two different kinds of bacterial cell walls. Gram-positive= thick cell wall, Gram-negative= thin cell wall
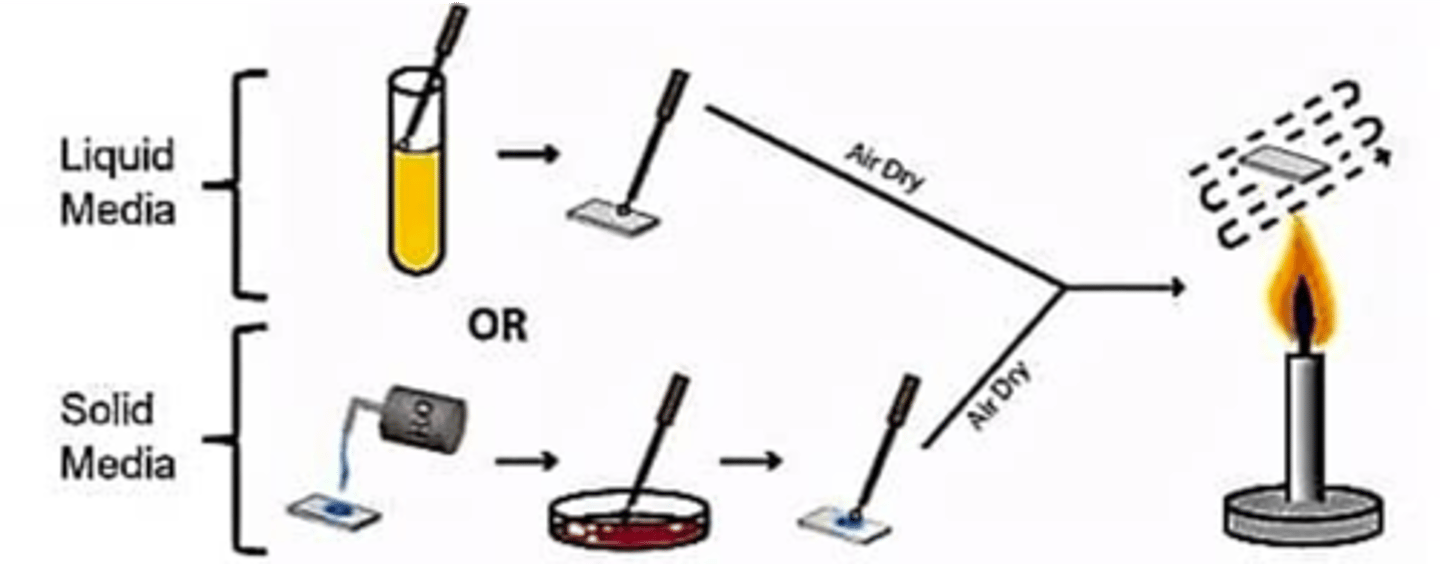
Gram stain steps
1. Heat fix smear
2. Primary Stain (crystal violet)
3. Mordant (iodine)
4. Decolorizer (alcohol)
5. Counter Stain (safranin)
positive- purple to blue
negative- pink or red
Acid Fast Stain
A staining procedure for identifying bacteria that have a waxy cell wall. Used for detection of mycolic acid and mycobacterium spp. Ziehl-Neelsen method (w/ heat), Kinyoun method (w/o heat)
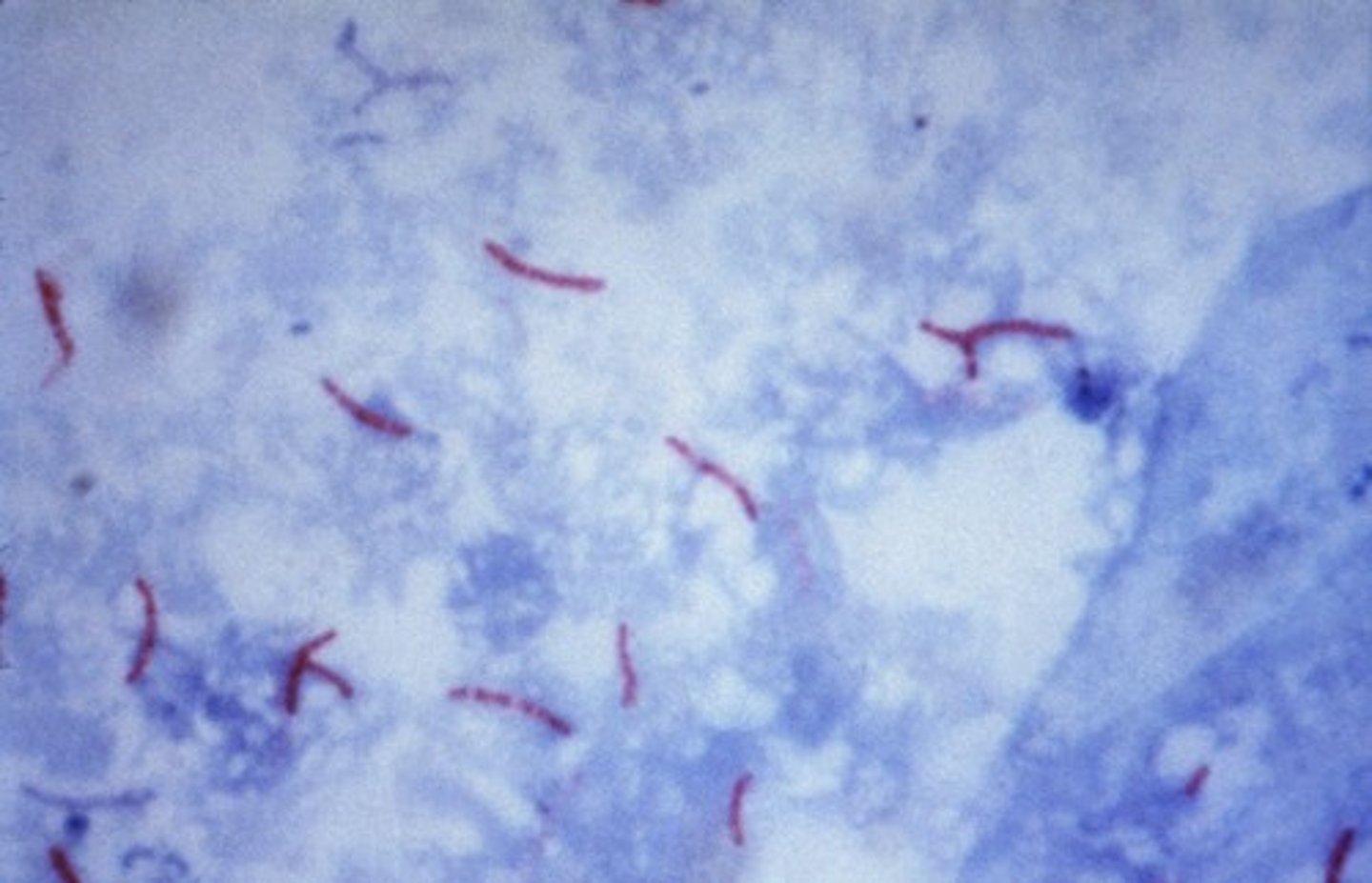
Acid Fast stain steps (Ziehl-Neelsen method)
1. Heat fix smear
2. Primary Stain (carbolfuschin)
3. Decolorizer
4. Counter Stain (methylene blue)
Acid-fast bacteria are-red
Non Acid fast bacteria are- blue
Endospore stain
A differential stain used to detect the presence and location of spores in bacterial cells.
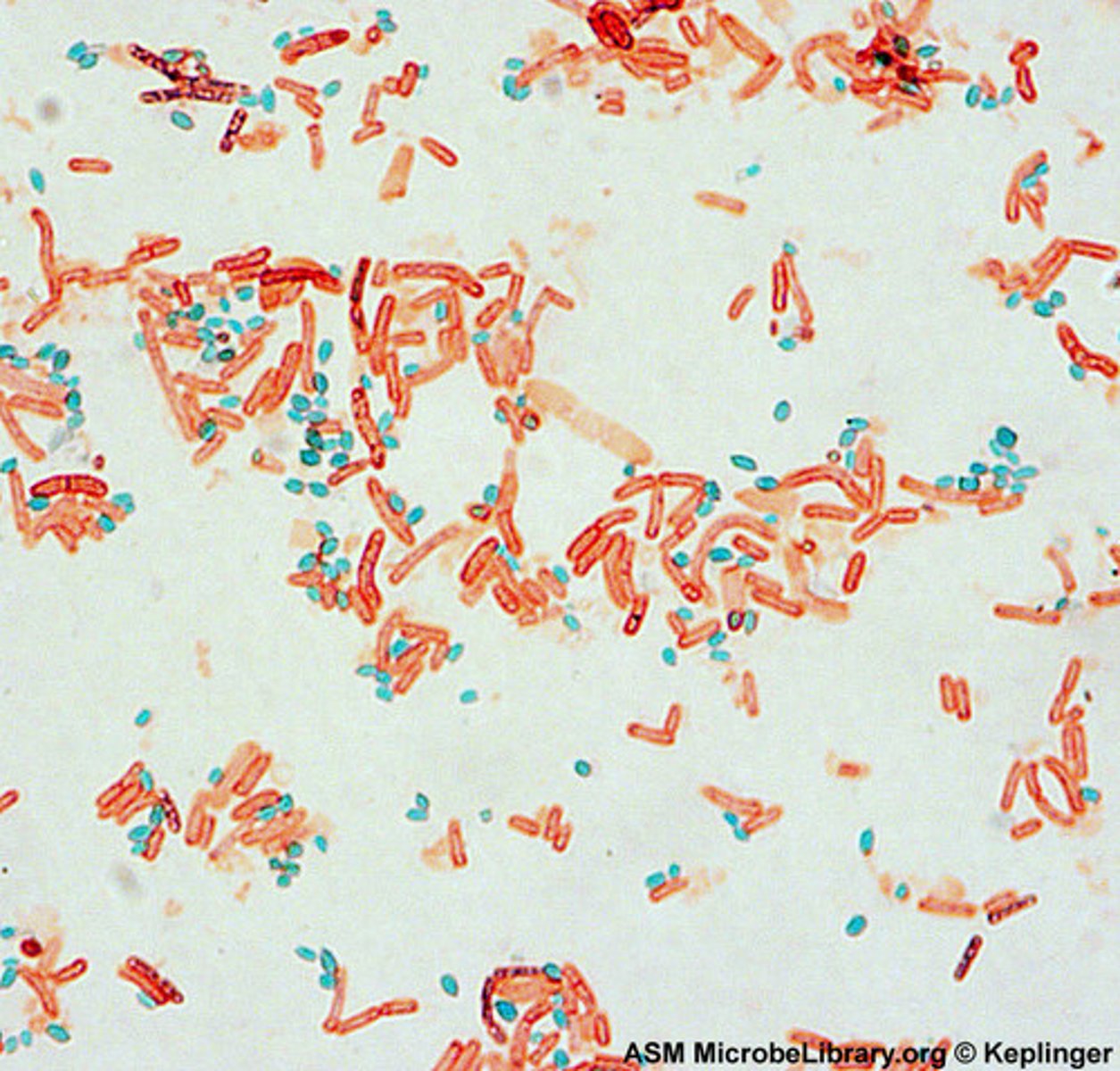
Endospore stain steps (Schaeffer-Fulton method)
1. heat fix smear
2. primary stain (malachite green)
3. decolorizer (water)
4. counter stain (safranin)
endospore- green
other structures-pink
Flagella stain
The staining agent adheres to and coats the otherwise thin flagella, making them visible with the light microscope.
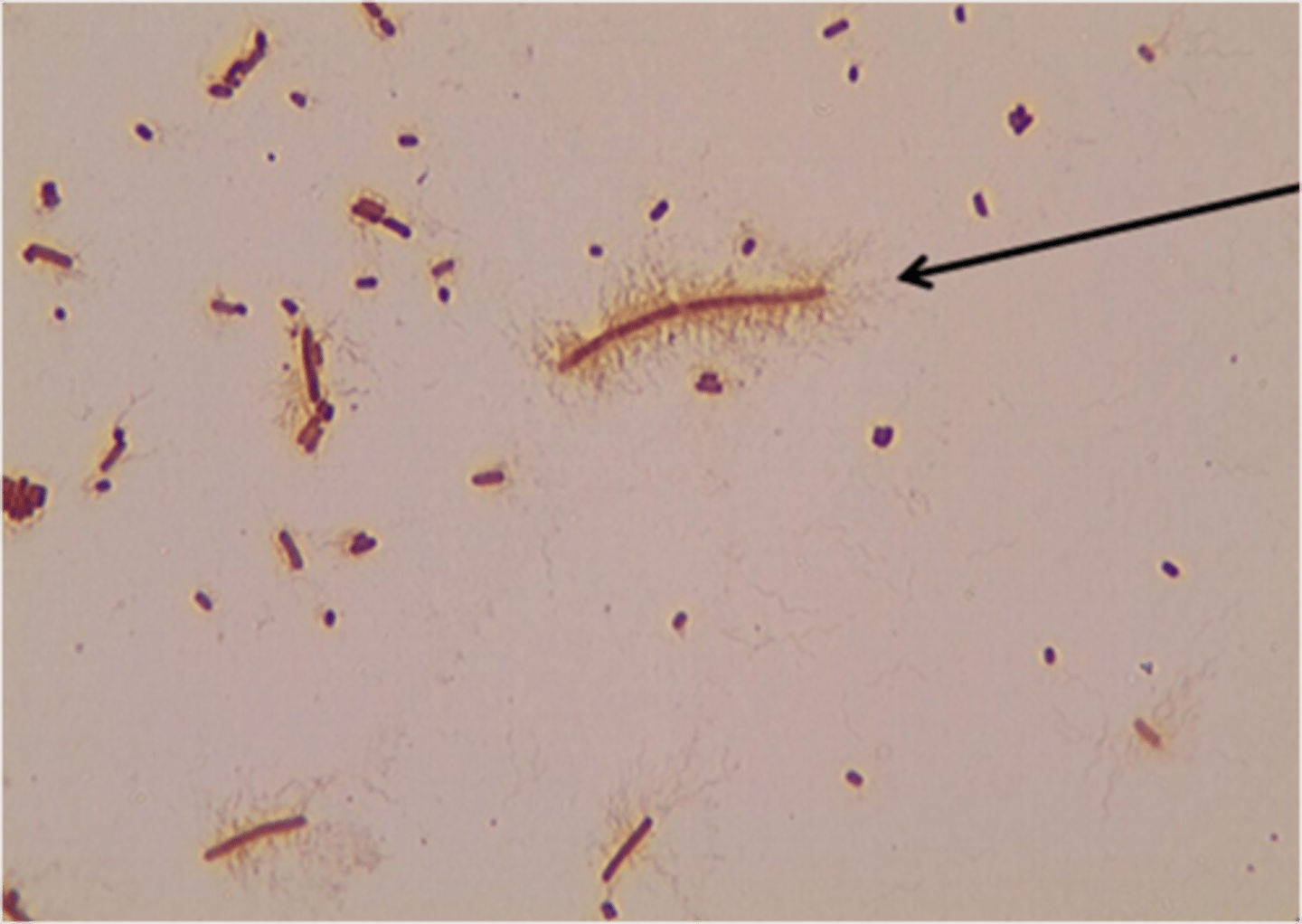
Flagella stain steps
1. No heat smear
2. Primary stain (specialized)
3. Decolorizer (water)
4. Counter stain (carbol fuschin)
Capsule stain
Diagnostic tool for detecting protective coatings. Dyes do not penetrate the capsule.
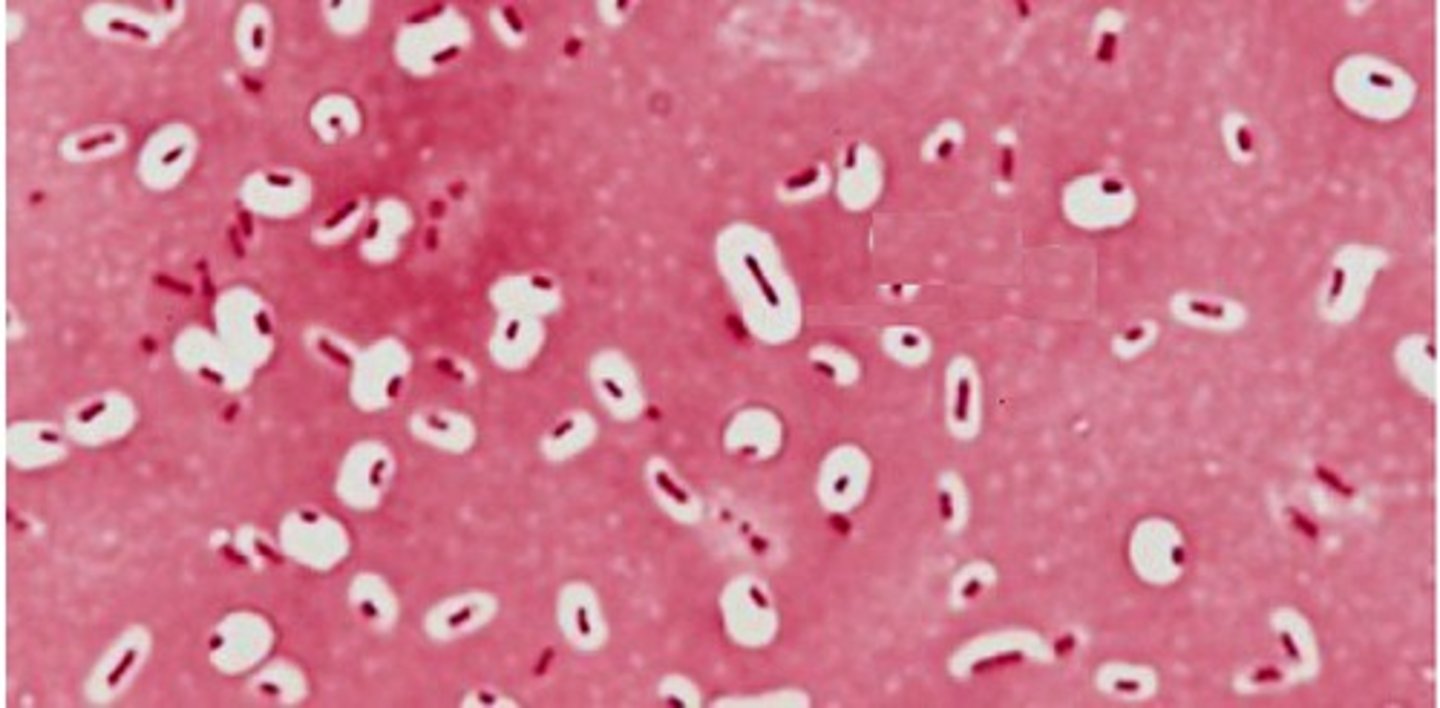
Capsule stain steps
1. no heat smear
2. primary stain (india ink)
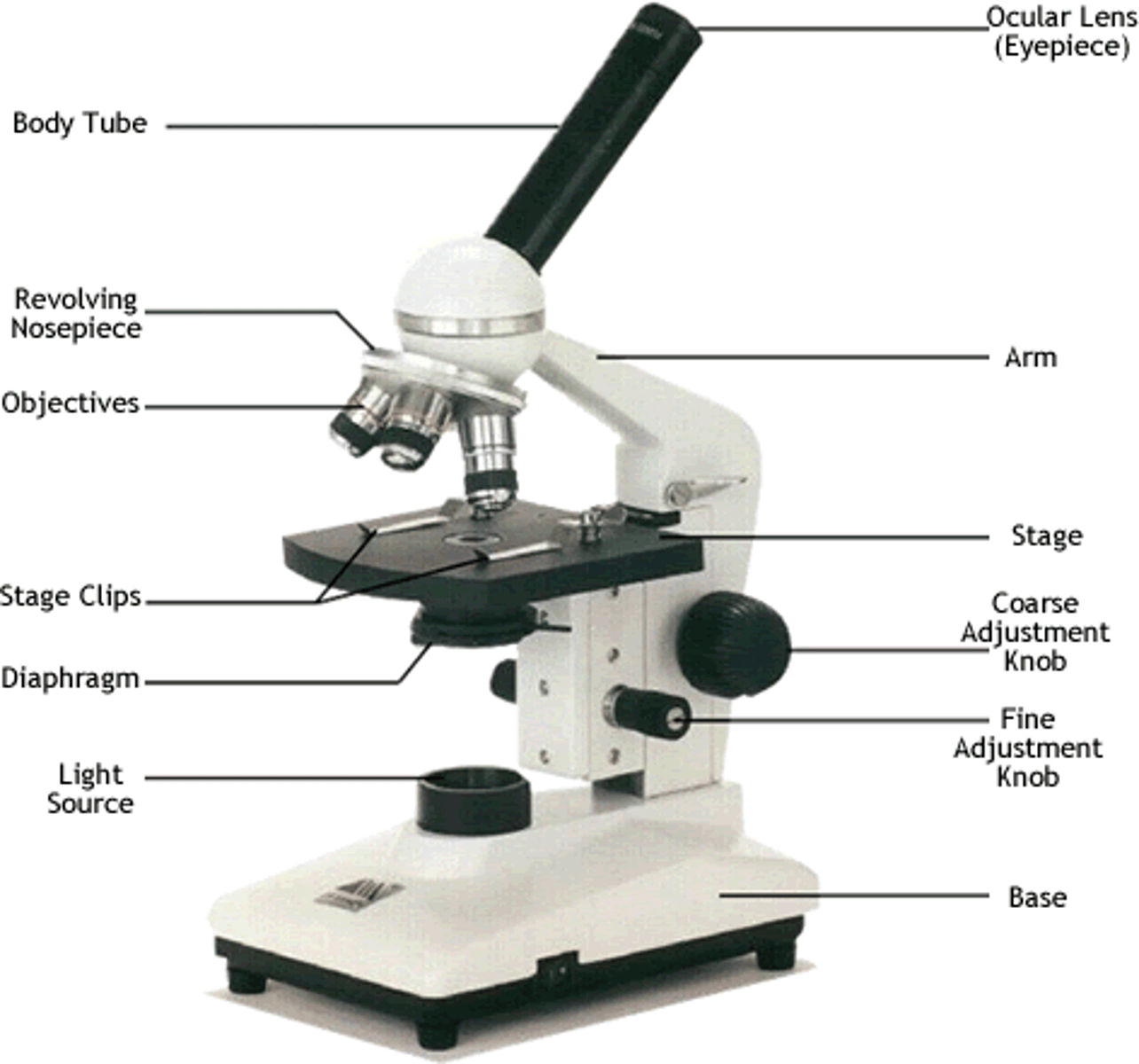
Eye piece (ocular lens)
10x magnification
Objective lenses
4-100x
Total Magnification
ocular lens x objective lens
Direct immunofluorescence
fluorophore is conjugated directly to the antibody molecule that recognizes and binds the molecule of interest
indirect immunofluorescence
An immunofluorescent diagnostic technique in which the fluorochrome is not attached to the primary antibody that recognises the target antigen, but to a secondary antibody that binds the primary antibody. Causes a higher intensity fluorescence.