Water-Soluble Vitamins: Functions, Sources, and Deficiencies in Human Nutrition
1/24
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
25 Terms
What are the two main groups of vitamins?
Water-soluble vitamins and fat-soluble vitamins.
How many water-soluble vitamins are there?
Nine water-soluble vitamins.
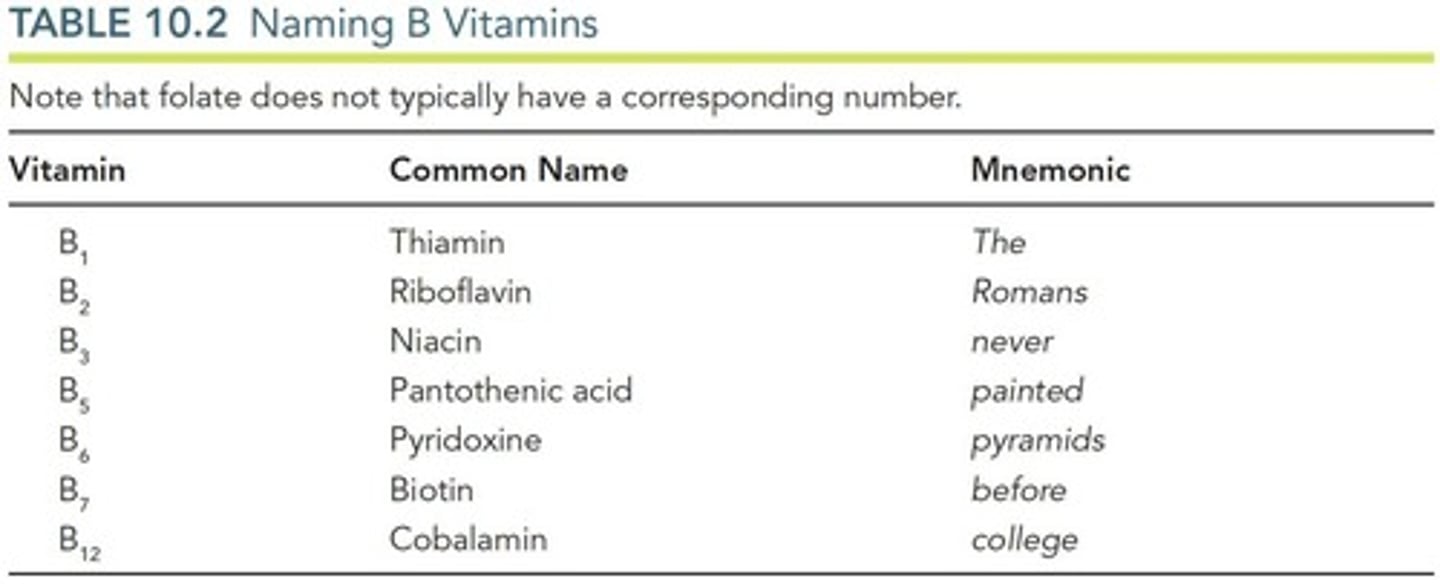
What are the eight B vitamins?
B1 (Thiamin), B2 (Riboflavin), B3 (Niacin), B5 (Pantothenic Acid), B6 (Pyridoxine), B7 (Biotin), B9 (Folate), and B12 (Cobalamin).
What is the primary characteristic of water-soluble vitamins?
They dissolve in water and are easily excreted from the body.
What is the main function of B vitamins?
They are important for energy metabolism.
What is a key property of Vitamin C?
It is a powerful antioxidant.
What factors affect the bioavailability of water-soluble vitamins?
Nutritional status, other nutrients, illness, age, alcohol intake, and medications.
How are water-soluble vitamins absorbed?
Almost all are absorbed in the stomach and small intestines.
What is the difference between 'fortified' and 'enriched' foods?
'Fortified' foods have added nutrients, while 'enriched' foods restore nutrients lost during processing.
What are common sources of Thiamin (B1)?
Pork, fish, legumes, whole grains, and enriched grains.

What deficiency is associated with Thiamin (B1) deficiency?
Beriberi, which can cause severe muscle wasting and nerve damage.
What are the main food sources of Riboflavin (B2)?
Meat, dairy products, and enriched foods.
What is a common deficiency associated with Riboflavin (B2)?
Ariboflavinosis, which can cause mouth inflammations.
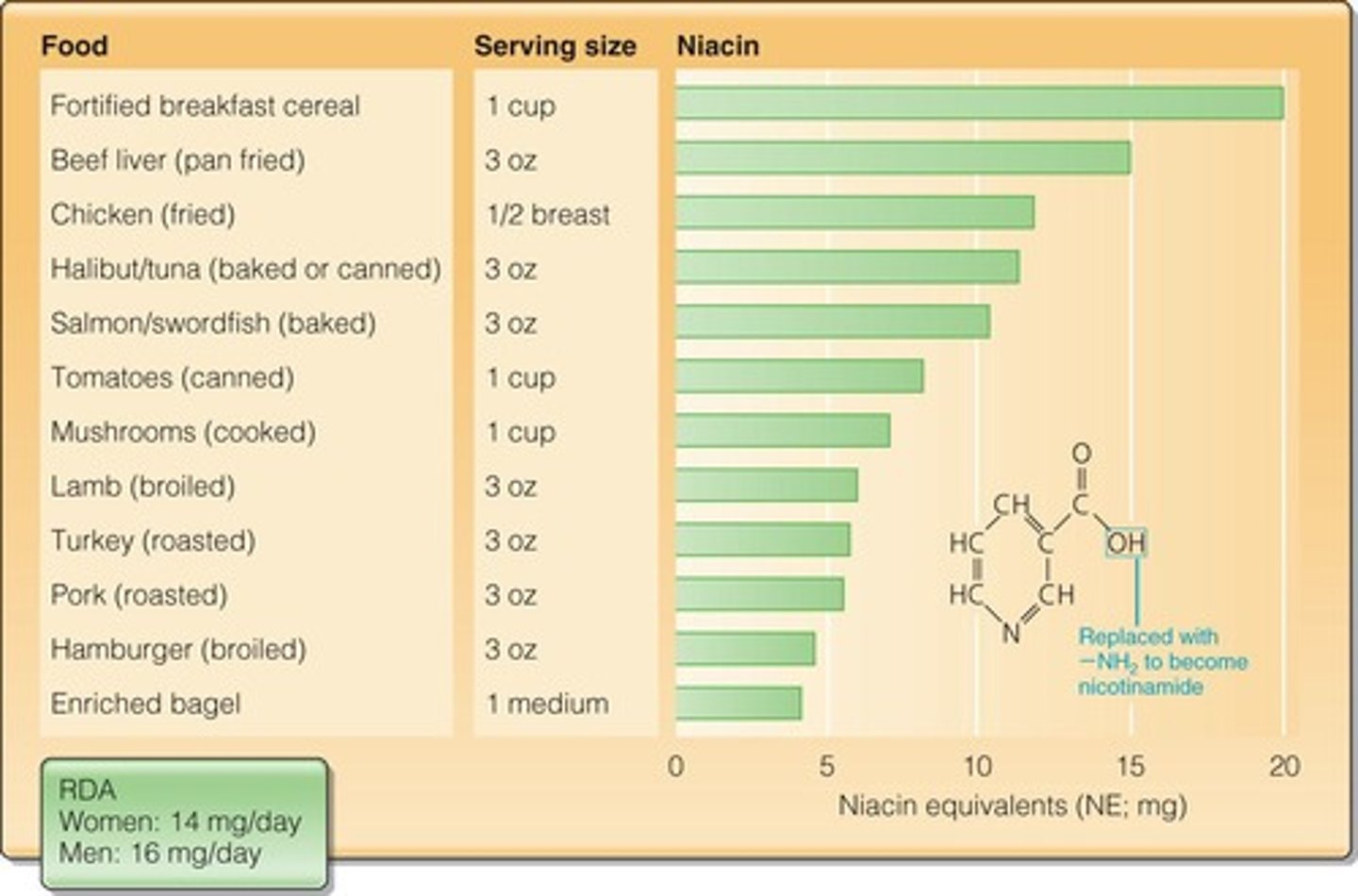
What are the symptoms of Pellagra, associated with Niacin (B3) deficiency?
The 4 D's: dermatitis, dementia, diarrhea, and death.
What is the role of Pantothenic Acid (B5) in the body?
It is involved in energy metabolism and ATP production.
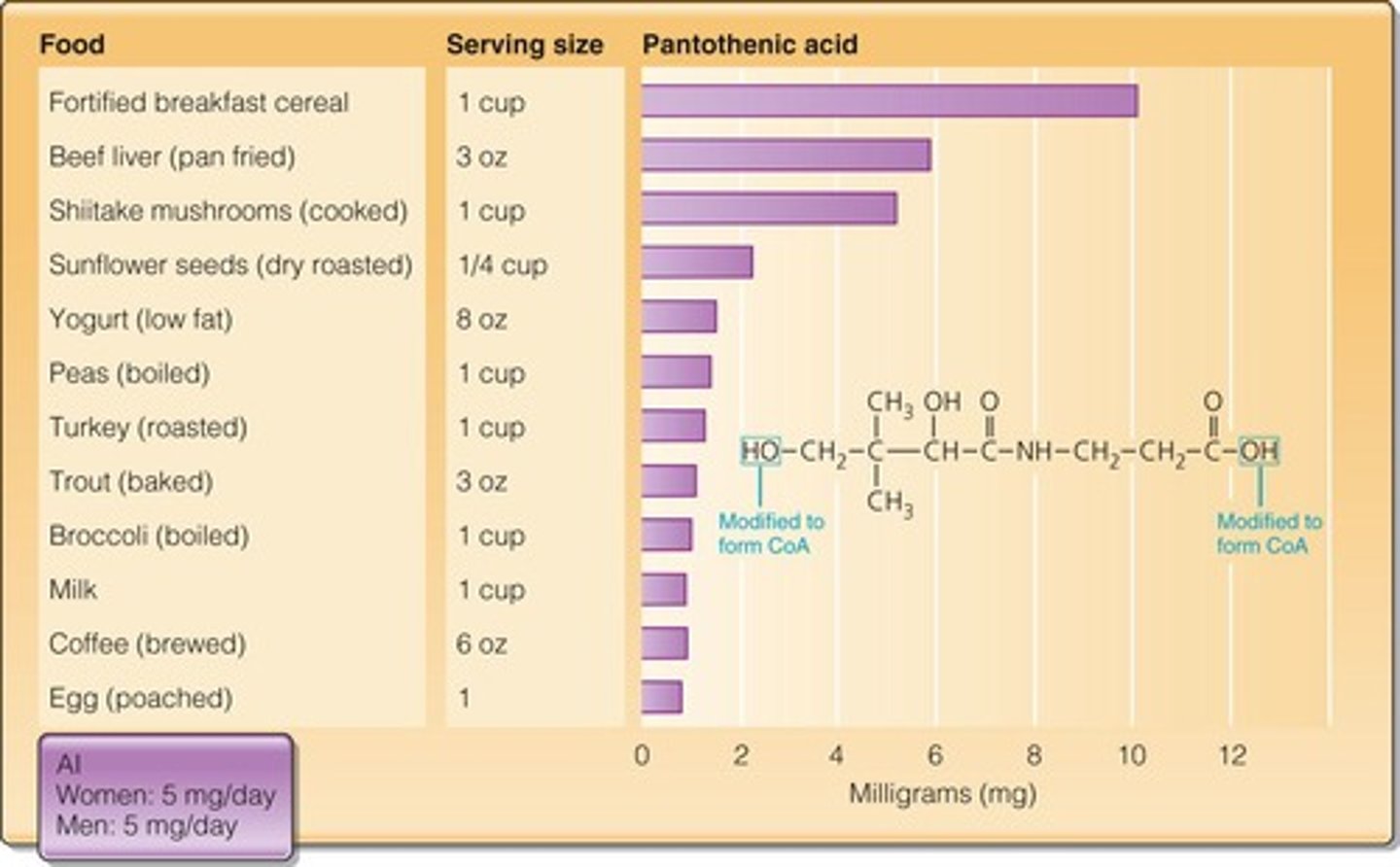
What is a rare deficiency associated with Pantothenic Acid?
Burning feet syndrome.
What is the primary function of Vitamin B6?
It acts as a coenzyme in amino acid metabolism and neurotransmitter synthesis.
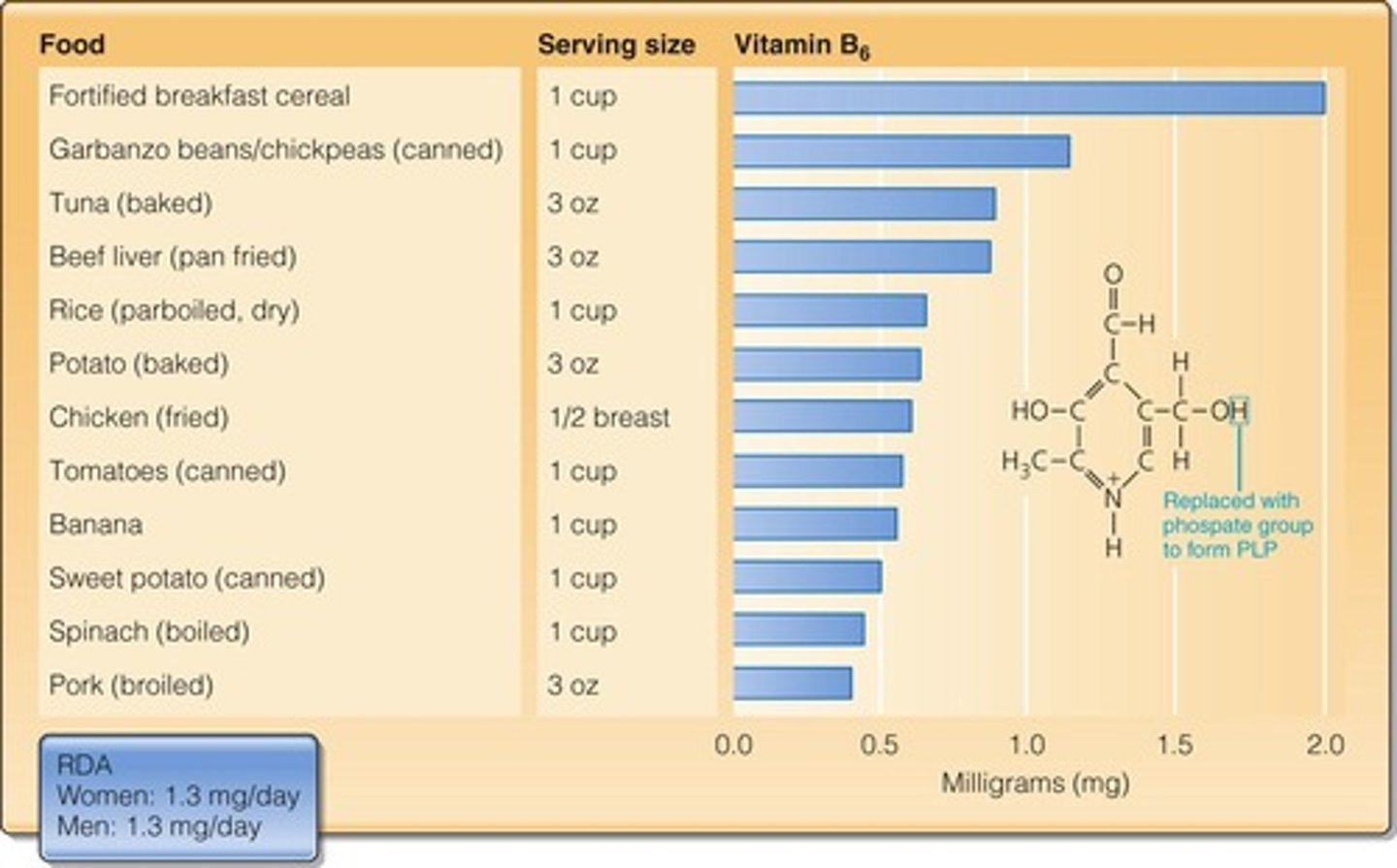
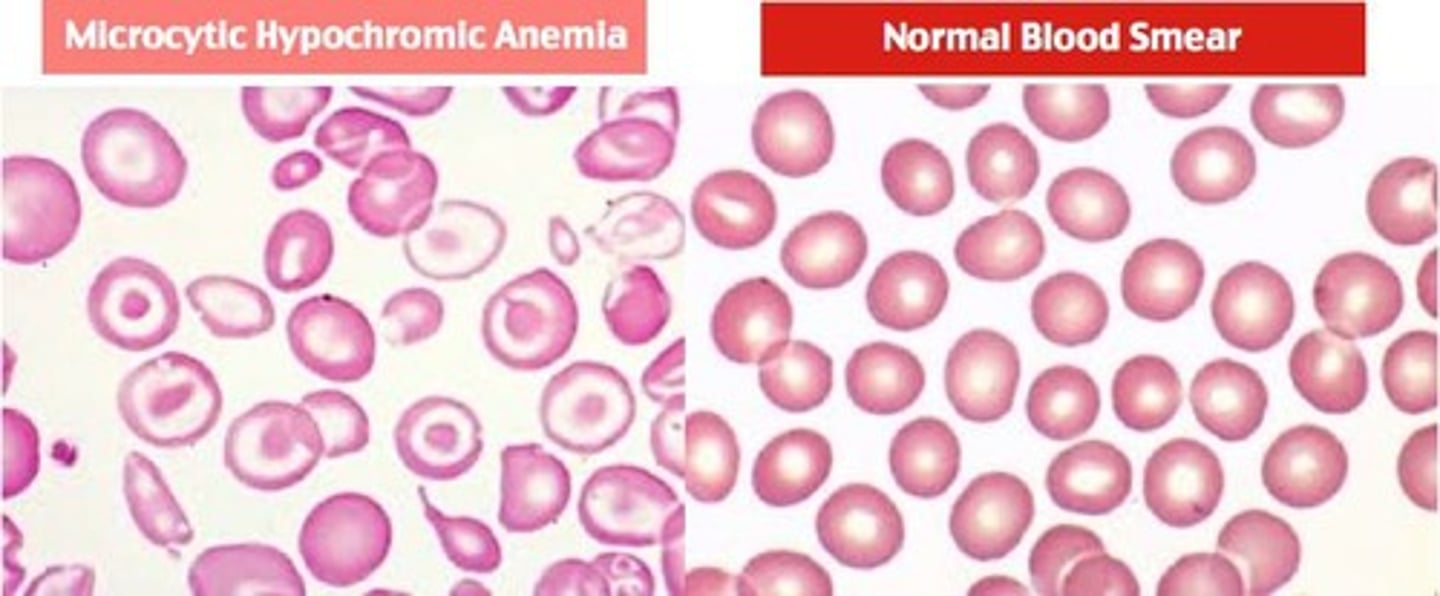
What deficiency is associated with Vitamin B6?
Microcytic hypochromic anemia.
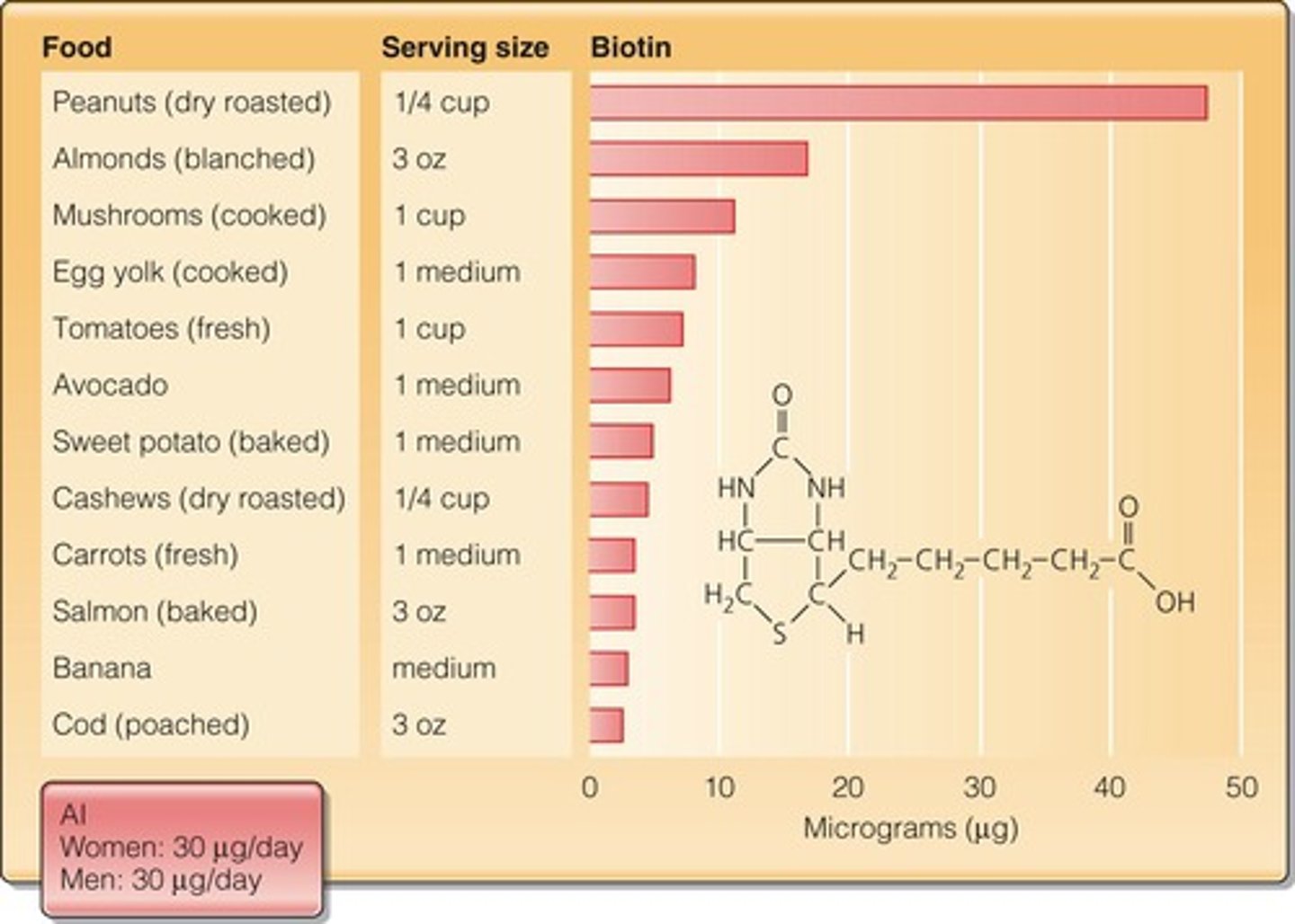
What is a key function of Biotin (B7)?
It is a coenzyme involved in energy metabolism and gluconeogenesis.
What are common sources of Folate (B9)?
Green leafy vegetables, legumes, and enriched foods.
What is a serious consequence of Folate deficiency during pregnancy?
Neural tube defects such as spina bifida.
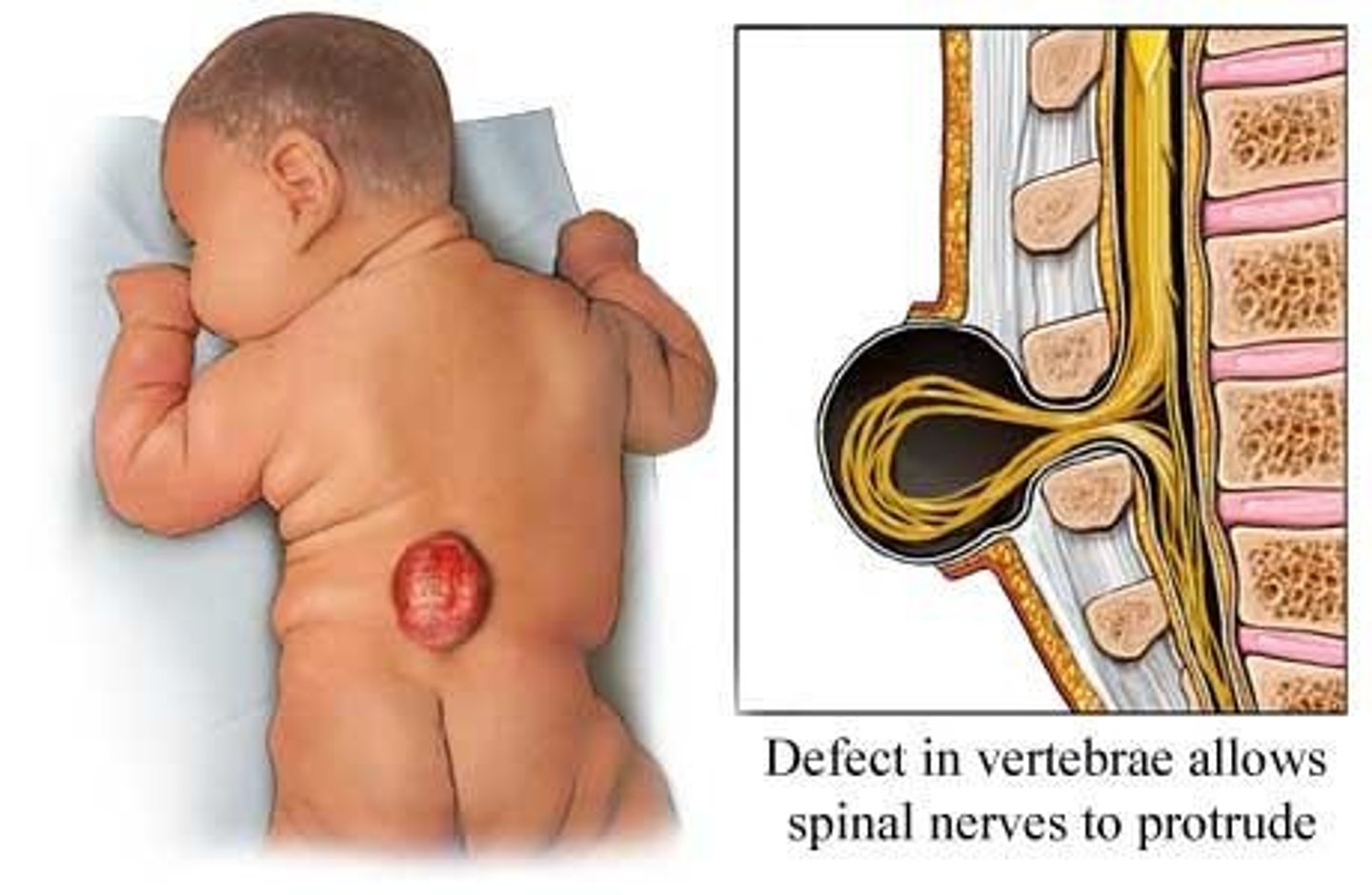
What is the primary source of Vitamin B12?
Animal products, as it is made only by microorganisms.
What deficiency is associated with Vitamin B12?
Pernicious anemia, which can cause severe neurological damage.

What is a critical role of Vitamin C?
It acts as an antioxidant and is essential for collagen production.
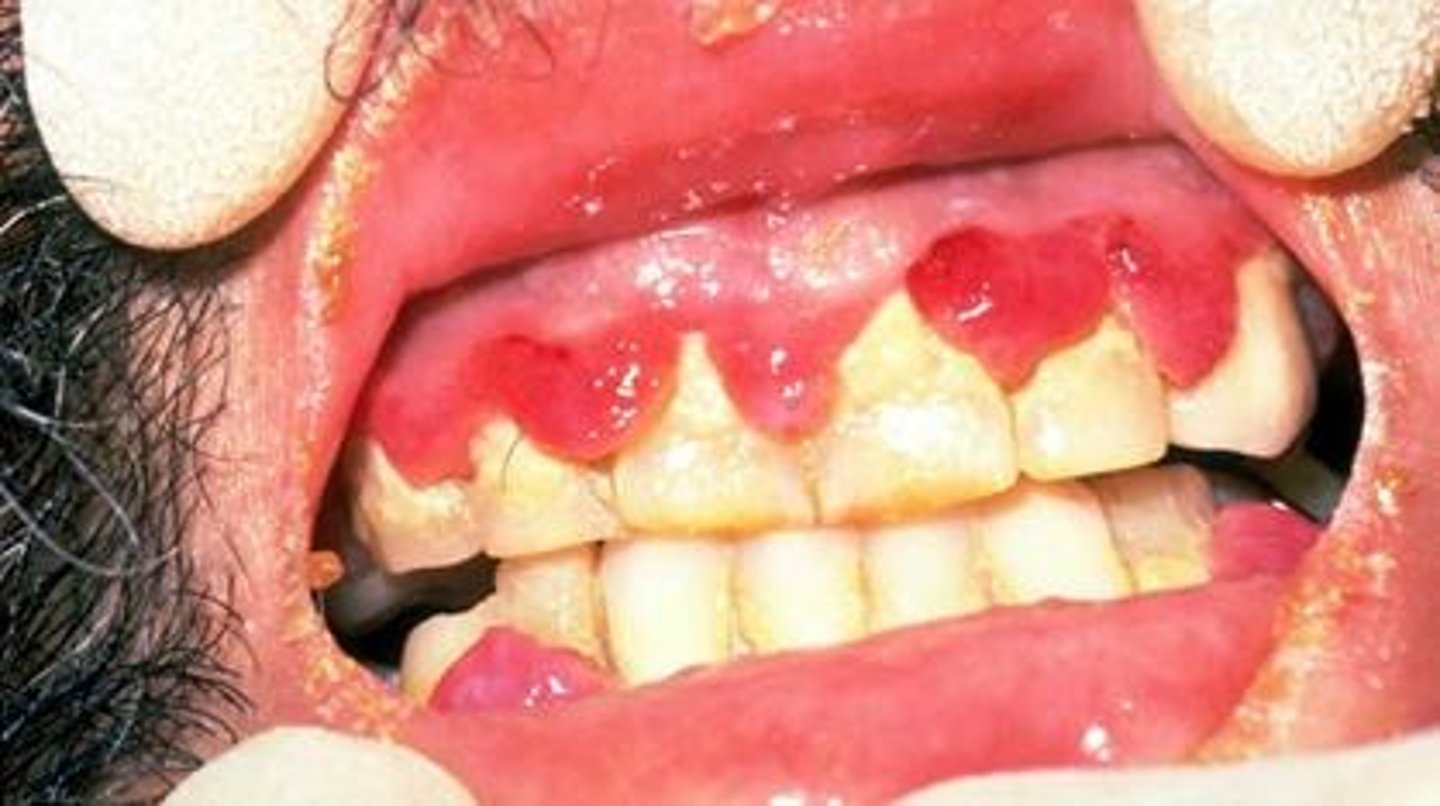
What deficiency is associated with Vitamin C?
Scurvy, which can lead to symptoms like fatigue and bleeding gums.