Humanities Exam Revision- yr 9
1/45
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Biomes, food security, interconnection
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
46 Terms
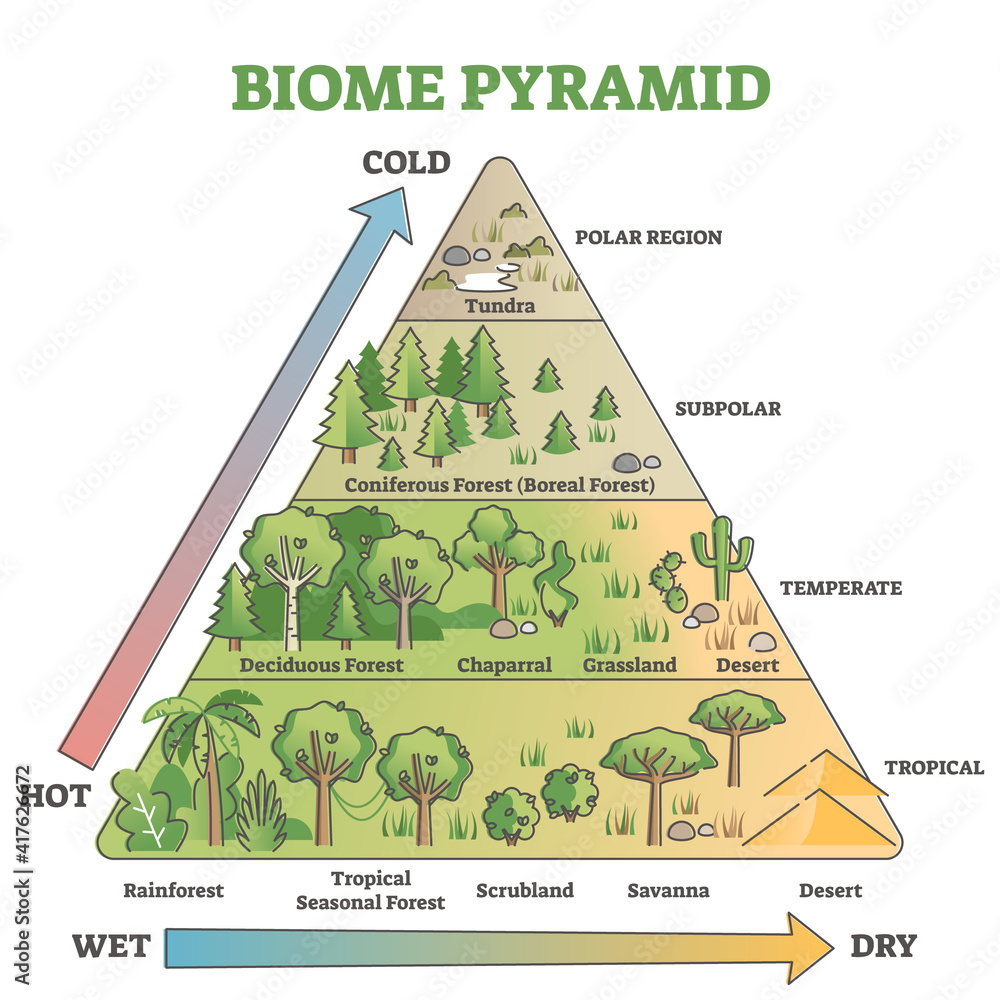
Definition of biomes
A large area of the earth that is home to similar plant and animal communities
How does latitude impact the climate?
Biomes at higher latitudes (further away from the equator) are often cooler and drier
What is latitude and altitude?
Latitude is the measurement North and South from the equator and altitude is the height of an object above a reference point
What are biome characteristics?
Biodiversity, rainfall, locations, temperature/climate
What are the human impacts
Pollution, salinity, fossil fuels, deforestation
What are the 4 things impact a biome’s distribution? Sow carrots, eat lettuce
Soil, climate, elevation, latitude
What is the riparian zone?
The link between terrestrial and aquatic habitats. It is the area where land and water meet. e.g. beach or riverbank
Define food security
A state where people have access to enough safe nutritious food to sustain a healthy life
What are the 3 elements of food security?
Sufficient, safe and nutritious food
Threats to food security
Salinity, climate change, water scarcity, competition for land, armed conflict, non-native biodiversity, use of land for fuel
Define globalisation
The increasing connection between countries including economic, political and cultural exchange
What are the 4 different connections to a place?
Spiritual, economic, cultural, historical
What is a spiritual connection to a place?
Factors relating to a person's belief
What is a economic connection to a place?
Factors relating to employment and income
What is a cultural connection to a place?
Factors relating to the shared characteristics of a group or people
What is a historical connection to a place?
Factors related to past experiences, events or memories
What are the 5 different types of industries?
Manufacturing, food, construction, agricultural, entertainment
Impacts of poor transportation systems
It causes an increase to traffic congestion and limits access to essential services
What is a manufacturing industry? Give example
Makes products from raw materials by the use of manual labour or machinery. Example: clothes
What is the food industry? Give example
The production, processing, distribution, and sale of food products. Examples: agriculture and grocery retail.
What is the construction industry? Give example
Involves building, repairing, and renovating structures. Example: residential homes
What is the agricultural industry? Give example
Includes farming crops and raising of livestock. Example: crop farming and livestock ranching.
What is the entertainment industry? Give example
Produces and shares entertainment content such as movies, TV shows, music, sports and games. Example: concerts
What are the social, economical and environmental impacts of tourism?
Social- opportunities to learn about cultures
Economical- Provides jobs and support
Environmental- Investment in water quality, pollution reduction and infrastructure
How has technology assisted the tourism industry?
Allows people to find places to go, places to stay and things to do in certain places
What is one advantage of trade?
You can get products from other countries without having to travel there
What is one disadvantage of trade?
Supports larger companies that neglect wages, workers, and materials on a global scale.
Define monoculture, polyculture and subsistence farming
Monoculture farms grow a single type of crop over a field. Polyculture farms plant several kinds of crops on the same piece of land at the same time. Subsistence farming is when a farmer grows food for themselves and their family on a small plot of land.
What are the pros and cons (can be risky) of monoculture farming?
Pros: It is easier to take one kind of crop and grow it because of less specific needs.
Cons: Impacts the environment and increases pests and diseases
What are the pros and cons of polyculture farming?
Pros: Promotes biodiversity, reduces crop failure (Reduces pests, improves soil health)
Cons: Hard to manage various crops with different requirements and growth patterns.
Define seed domestication
When humans choose to collect seeds to save and replant the following year.
Define urbanisation and link to food security
The growth of cities as people move from rural areas. It increases food demand, strains supply systems, and reduces agricultural production.
Examples of raw materials
Water, vegetables, cotton, wood, oil, coal and metals.
What is salinity, and how does it impact food security?
When soil or water has too much salt, which harms crops. This affects food security by reducing food production and making it harder to grow enough food.
What are indigenous hunting methods, and how do they contribute to sustainable farming?
Fish traps assist sustainability by allowing access to food using non-invasive hunting that doesn’t hurt the environment. Fire assists sustainability by regenerating the land and encouraging the growth of helpful and non-invasive species of plants.
What is the difference between place and space?
Space is an area made up of connections. Place is somewhere made up of subjective features, human experiences, and cultural significance.
Name the continents
Asia, Africa, North America, South America, Antarctica, Europe, and Australia
What does GDP stand for and what is it?
Gross domestic product and the measurement of a nations overall economic activity
Sustainability definition and example
Ability to maintain or support a process over time eg using paper bags
Fossil fuels definition
Non-renewable energy sources
How soil impacts a biomes distribution
All plants rely on soil for energy and nutrients to survive
How climate impacts a biomes distribution
Determines the temperature and precipitation of a biome, which influences which types of biodiversity can thrive there
How elevation impacts a biomes distribution
Higher elevations experience colder temperatures. The atmosphere is thinner at higher elevations and cannot trap heat as easily.
How Latitude impacts a biomes distribution
Affects temperature and sunlight, with low latitudes supporting tropical biomes and high latitudes supporting colder biomes
Pros and cons of subsistence farming
Pros: provides food security and low environmental impact
Cons: limited income and vulnerability to climate change
Differences between food availability and food accessibility
Food availability means having enough good-quality food consistently and reliably. Food accessibility is with enough available and within peoples’ reach so they are able to get what is needed