Introduction to Classification, Evolution, and Plant Biology
1/292
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
293 Terms
Taxonomy
Science of describing, naming, & classifying organisms.
Phylogeny
Evolutionary history of a species or group of related species.

Species
Basic level of classification.
Nested Hierarchy
Groups from Broad to narrow are: Domain to Species.
Taxon
General name for group at any level.
Evolution
Change in ALLELES over time.
Natural Selection
Differential survival and adaptation.

Diversity
Three types of diversity: Genetic, Species, Community and Ecosystem.
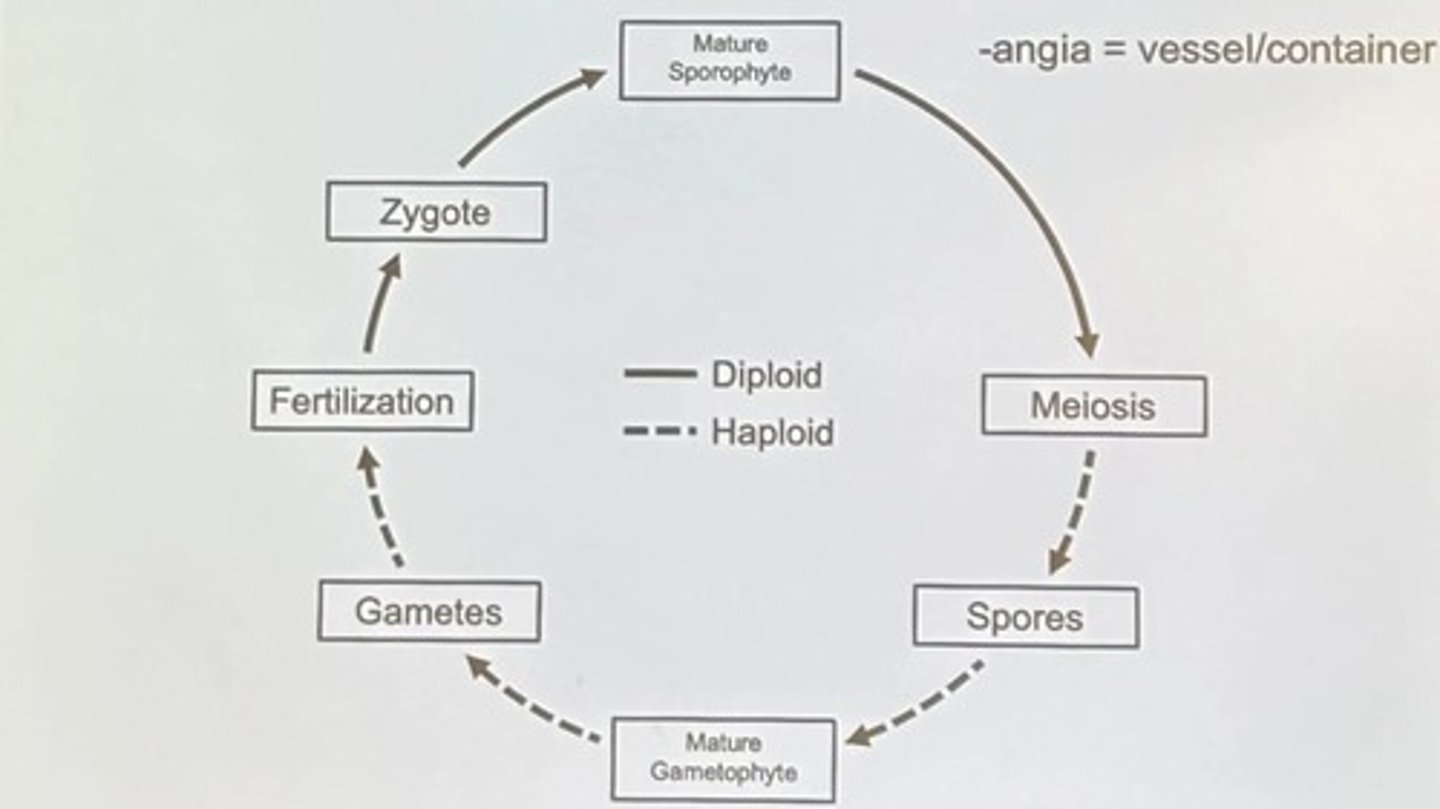
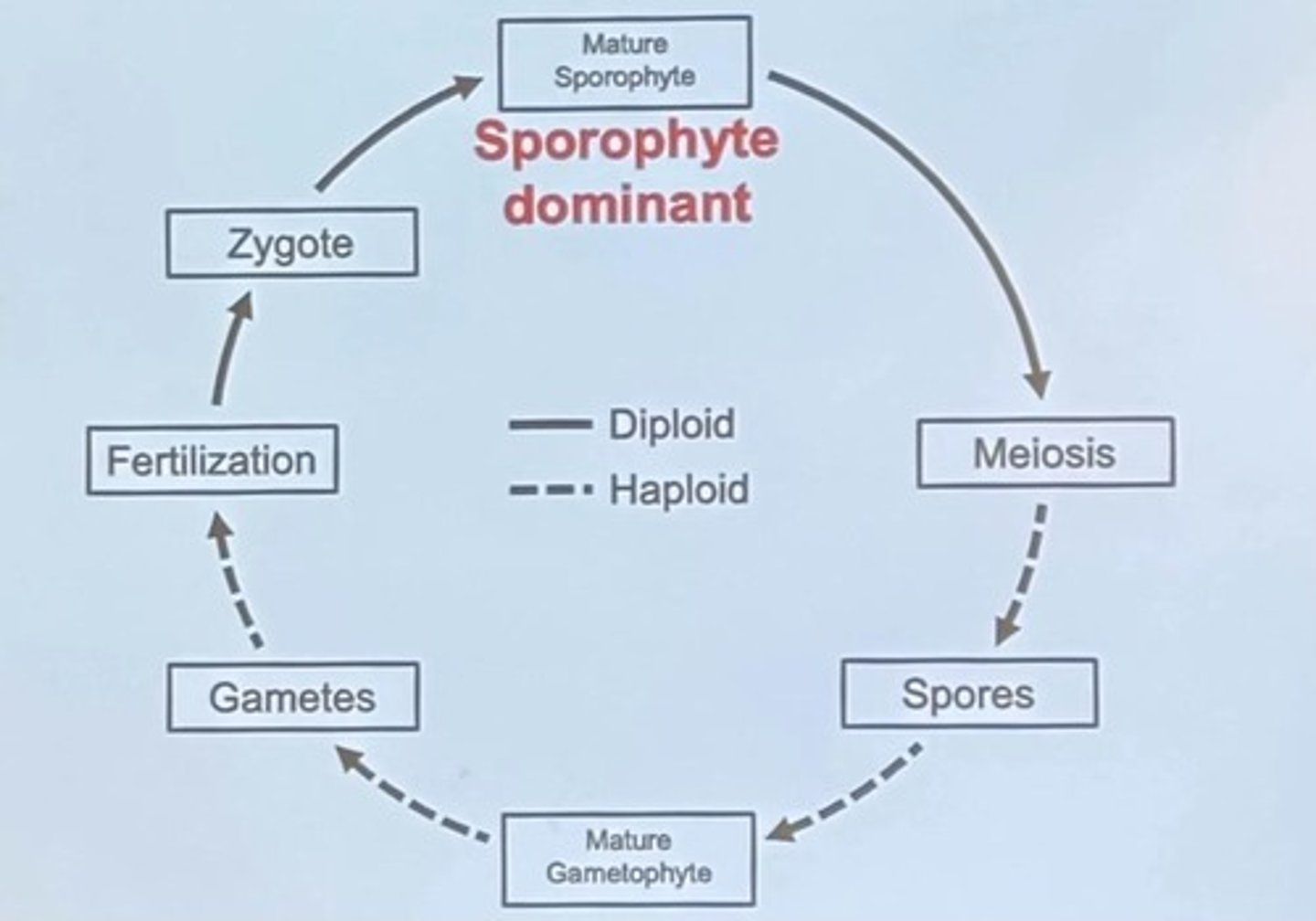
Phylogeny (in context)
Represents an evolutionary hypothesis.
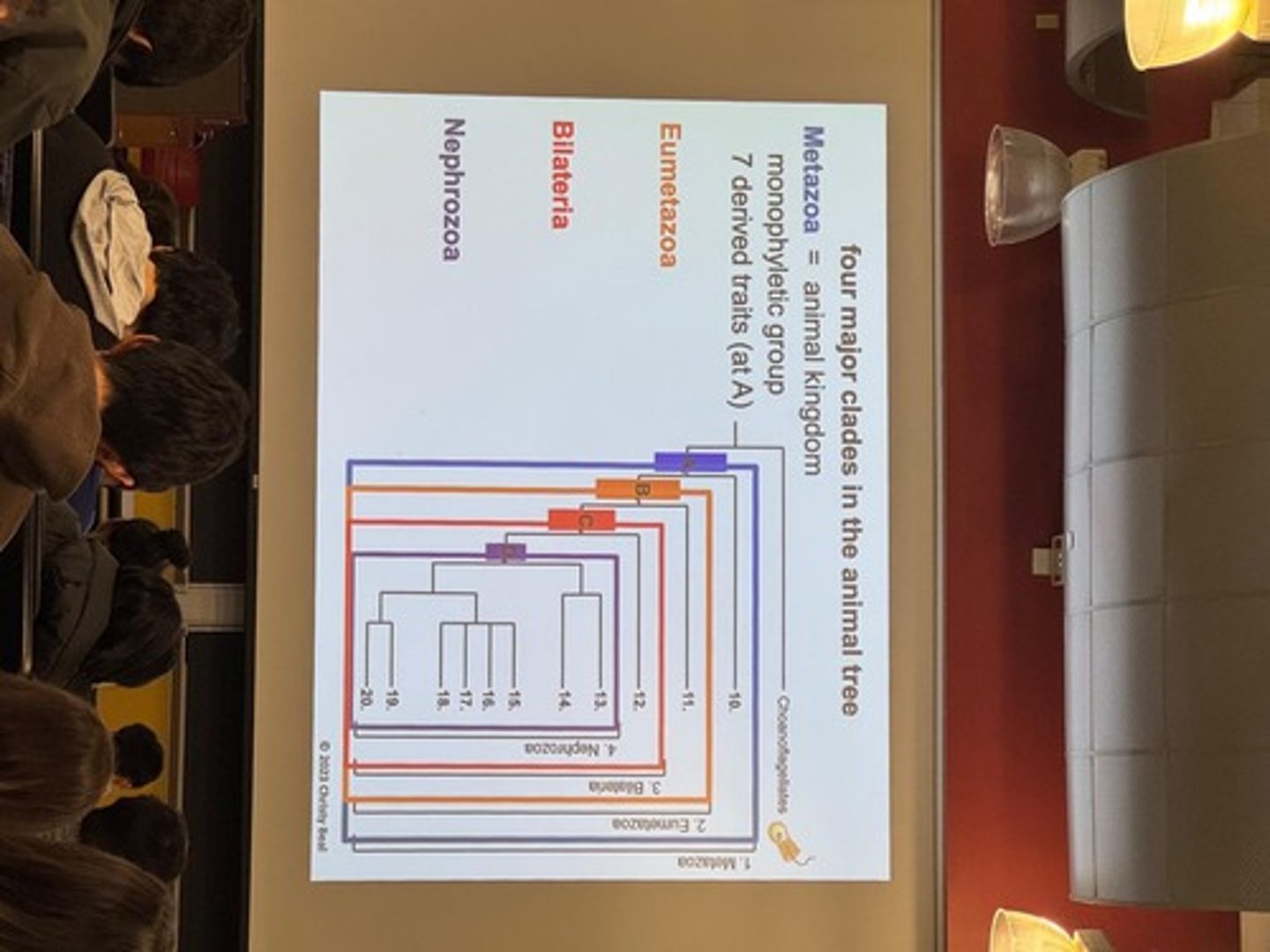
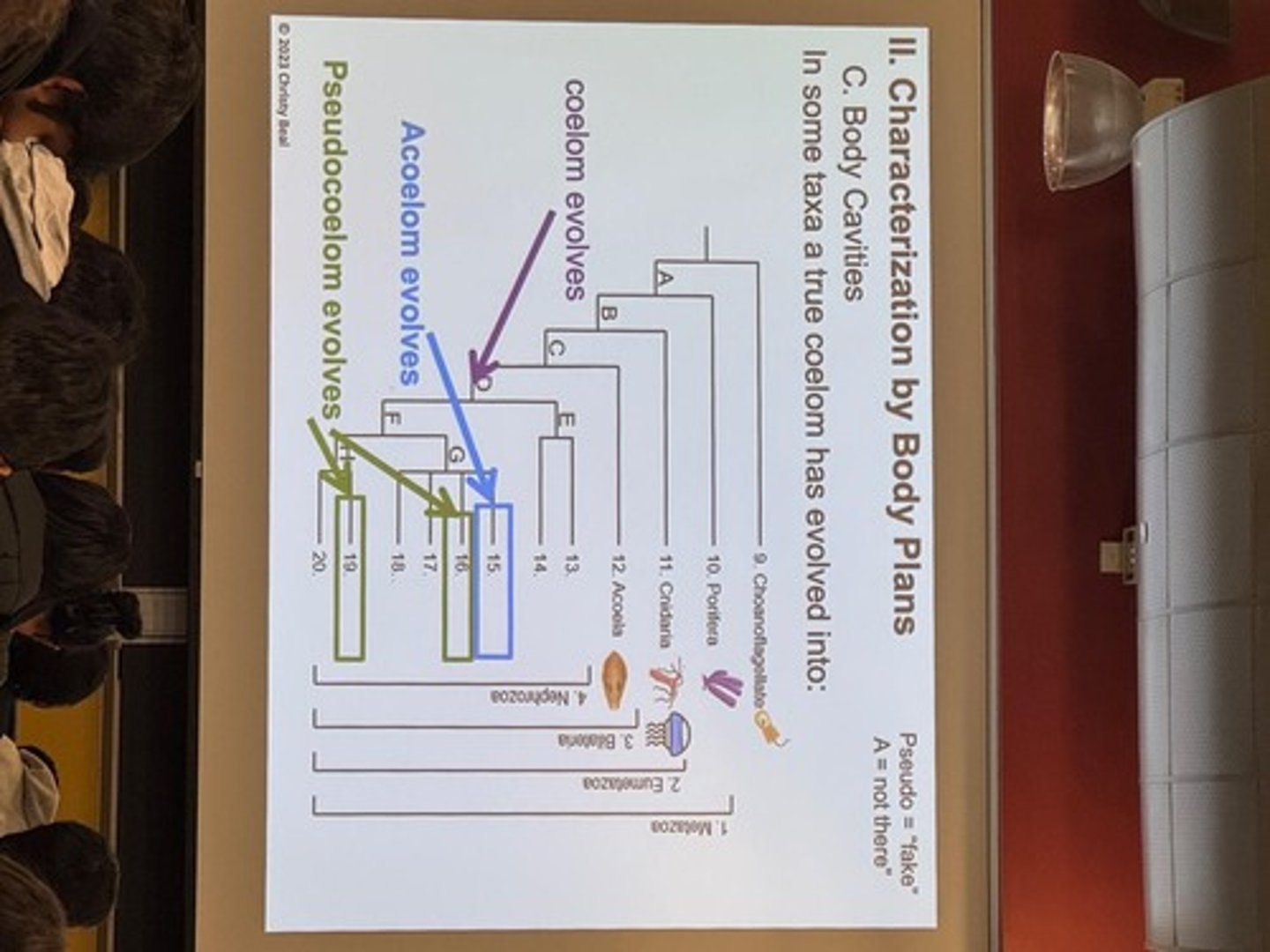
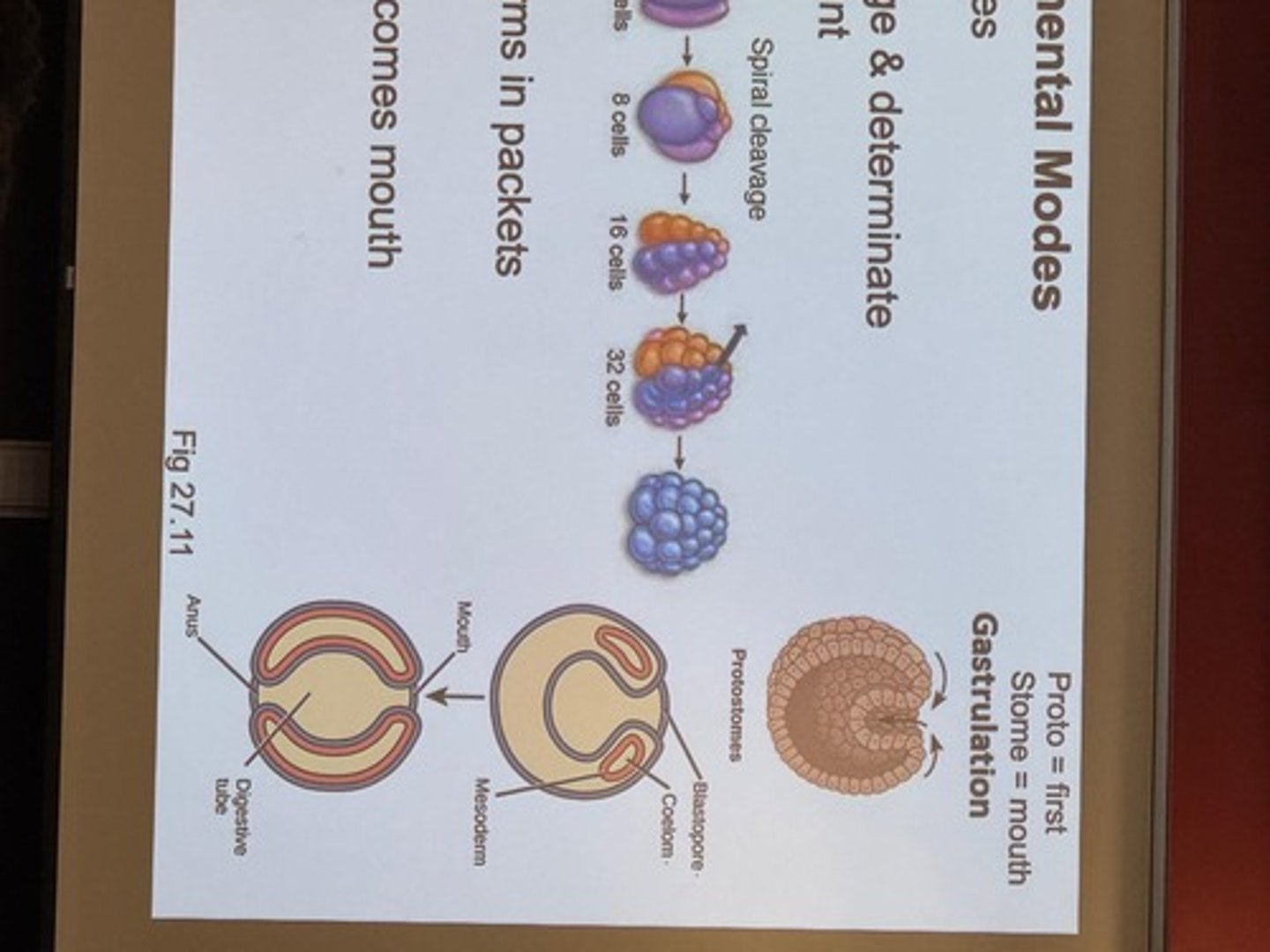
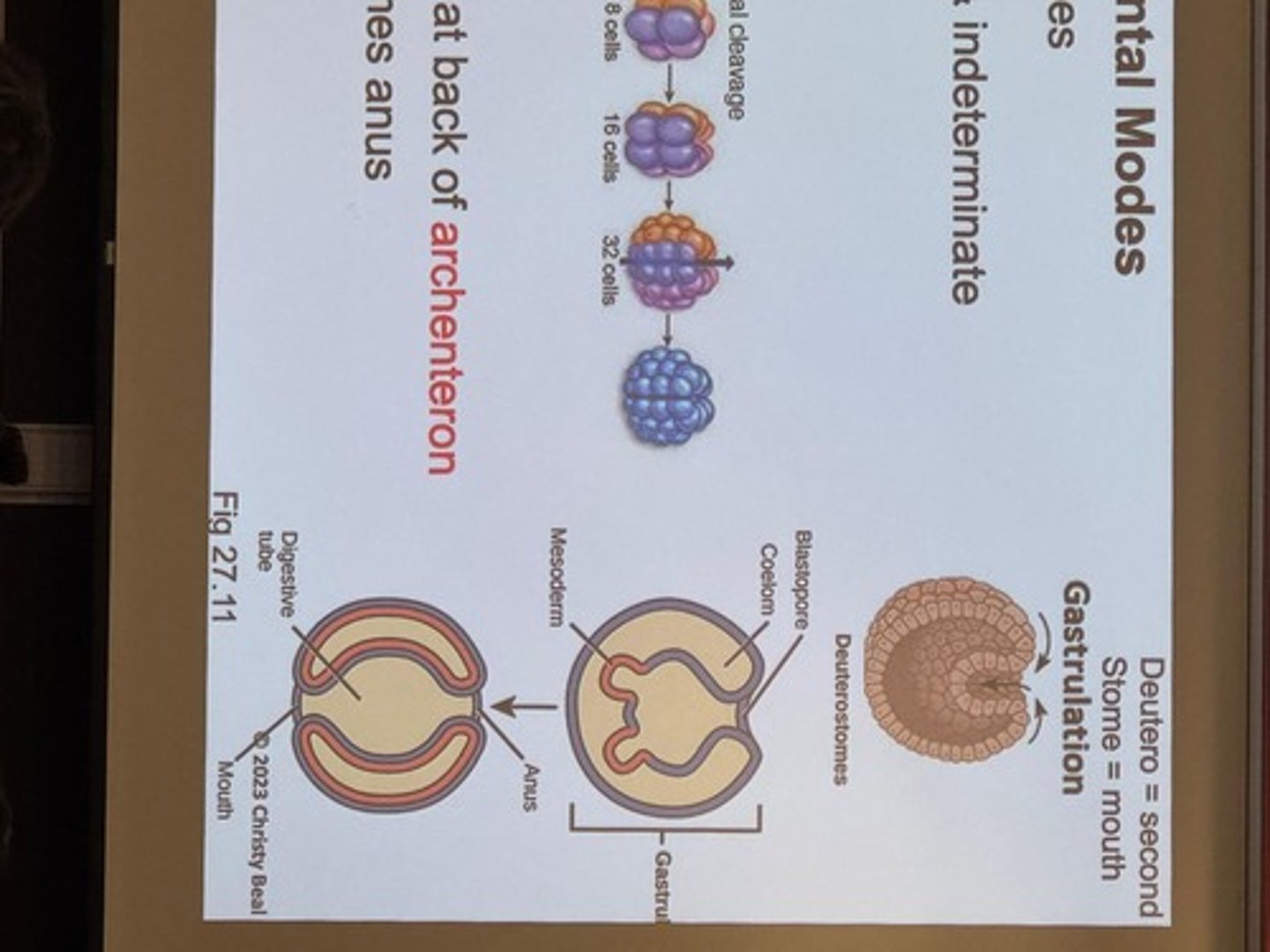
Monophyletic
A group that consists of an ancestor and all its descendants.
Paraphyletic
A group that includes an ancestor but not all its descendants.
Polyphyletic
A group that does not include the most recent common ancestor.
Branch point
Where lineages diverge in a phylogenetic tree.

Sister taxa
Groups that share a most recent common ancestor.

Basal taxon
A lineage that diverges early in the history of a group.
Polytomy
A branch point from which more than two descendant groups emerge.

Extant species
Species that are not extinct.

Obligate intracellular parasites
Viruses that require a host cell to replicate.
Capsid
Protein coat that surrounds DNA/RNA in viruses.
Host range
The specific species that a virus can infect.
Lytic Cycle
Viral replication cycle that kills the host at the end.
Lysogenic Cycle
Viral replication cycle where virus DNA hides in hosts as a prophage.
Virulent phage
Phage that kills the host at the end of the cycle.
Temperate phage
Phage that can use either the lytic or lysogenic cycle.
Prophage
Virus DNA that hides in hosts during the lysogenic cycle.
Prokaryotes
Organisms that lack a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles.
Probiotic Soup
Hypothesis about how life first originated.
Iron-sulfur
Another hypothesis about the origin of life.
DNA location in prokaryotes
Prokaryotes put their DNA in the nucleoid region.
Nucleoid
Single haploid chromosome found in prokaryotes.
Prokaryotes
Organisms that lack a membrane-bound nucleus and have a simpler internal organization.
Cell Wall Functions
Protection, maintain cell shape, and prevents bursting in hypotonic solution.
Peptidoglycan
A component found in the cell wall of bacteria, varying in amounts between species.
Gram Staining
A two-step process using crystal violet and safranin to identify bacteria.
Gram Positive
Bacteria that appear purple due to thick cell walls that hold the violet stain.
Gram Negative
Bacteria that appear pink due to a thin peptidoglycan layer that does not hold the violet stain.
Motility
The ability of some prokaryotes to move.
Taxis
Movement of an organism in response to a stimulus, can be positive or negative.
Flagella
A structure used for movement, found in all domains but analogous in structure due to convergent evolution.
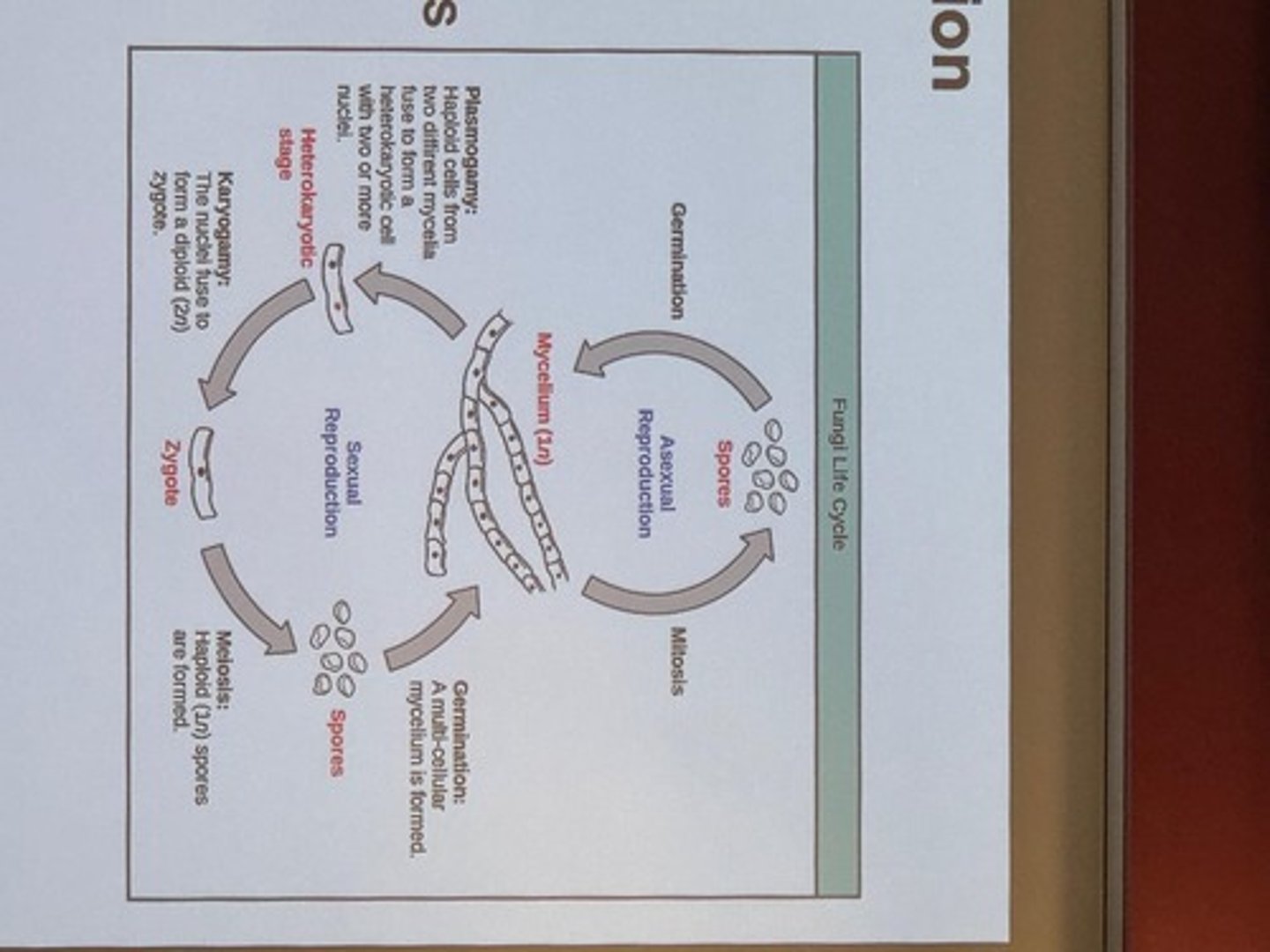
Binary Fission
A method of asexual reproduction in prokaryotes that produces identical copies.
Genetic Diversity
Variability in genetic characteristics within a population, promoted by rapid reproduction and mutation.
Mutation Rate
The chance of a mutation occurring in a gene is 1 in 10 million.
E. coli Mutations
E. coli populations can have about 9 million mutations per day in a human host.
Vertical Gene Transfer
Transfer of genetic material from parent to offspring.
Horizontal Gene Transfer
Transfer of genetic material not from parent to offspring.
Transformation
A form of horizontal gene transfer where DNA from the surroundings is incorporated into a bacterium.
Transduction
A process where phages transfer bacterial DNA between bacteria.
Conjugation
A process where DNA is shared between two individuals, involving a pilus.
Phototrophs
Organisms that obtain energy from light.
Chemotrophs
Organisms that obtain energy from chemical reactions.
Cyanobacteria
Photoautotrophs that obtain energy from sunlight.
Autotroph
An organism that uses CO2 as a carbon source.
Heterotroph
An organism that obtains carbon from food.
Clostridium botulinum
A chemoheterotroph that gets energy from chemical reactions and carbon from food.
Obligate Aerobe
needs oxygen (like you!)
Obligate Anaerobe
oxygen will kill, must have none
Facultative Anaerobe
can live with or without oxygen
Obligate
required
Facultative
helps but not needed
Aer
Greek for air
An
as prefix means none
Prokaryotic Diversity
Divides prokaryotes into 2 domains
Bacterial Diversity
Includes mitochondria & other mutualistic bacteria
Cyanobacteria
Photoautotrophs
Cyanobacteria
Most gram negative
Cyanobacteria
Phytoplankton
Cyanobacteria
Ancestors of chloroplasts
Archaea Diversity
Prokaryotes
Extremophiles
Organisms that thrive in extreme environments
Cell walls but No peptidoglycan
Characteristic of Archaea
Halophiles
high salt environments
Thermophiles
very hot environments
Methanogens
unique to Archaea
Marsh gas
methane from Archaea
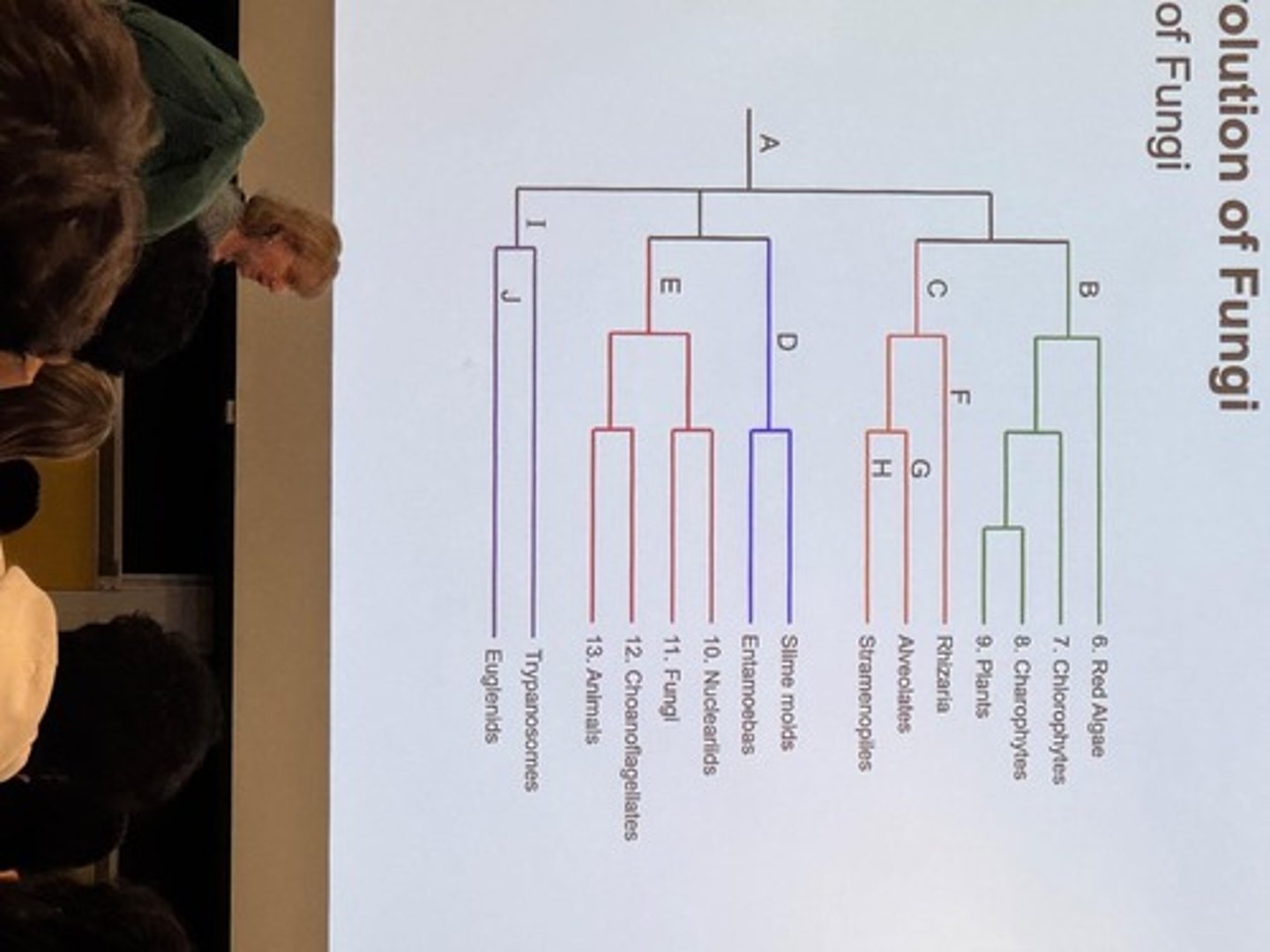
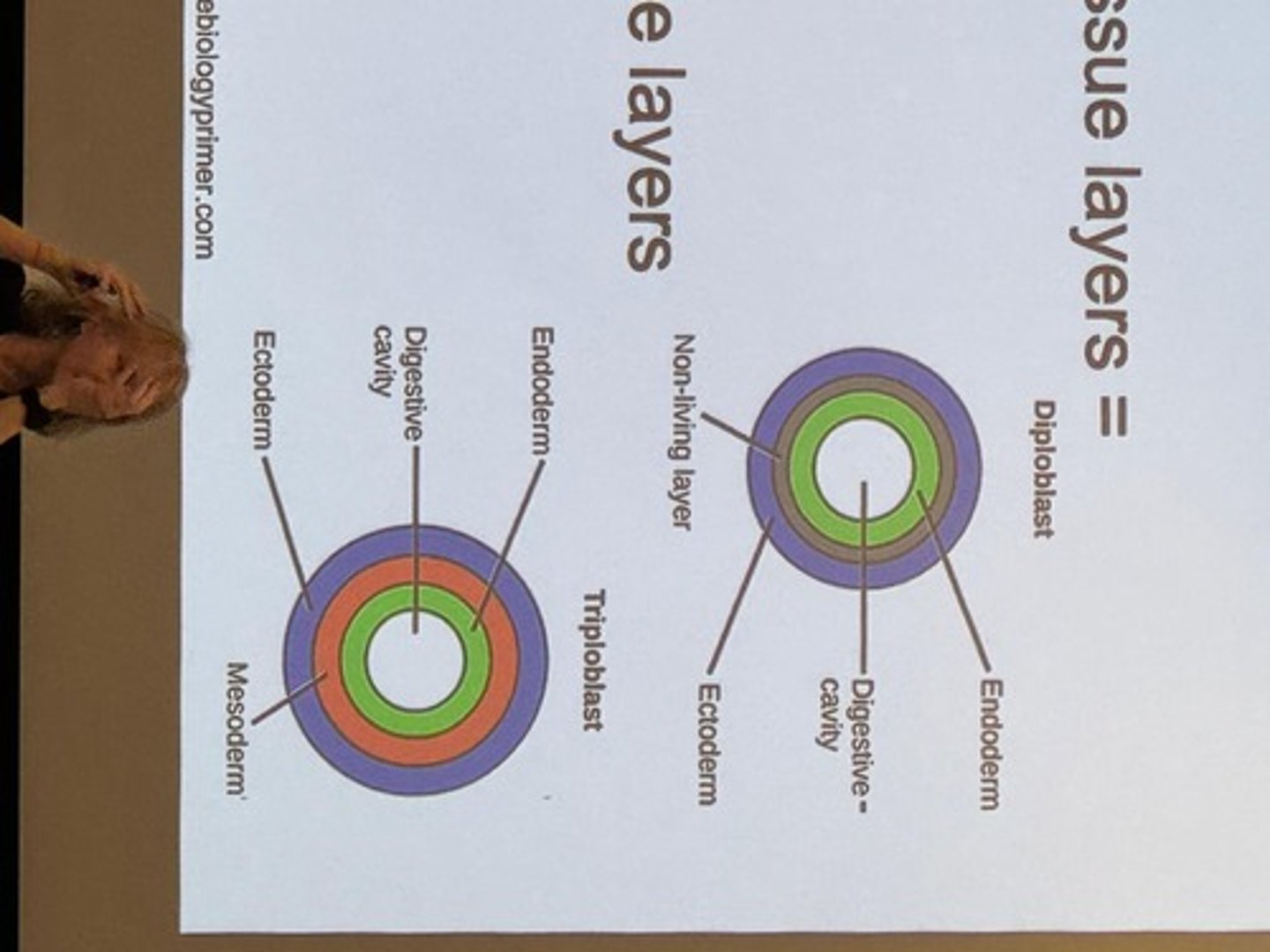
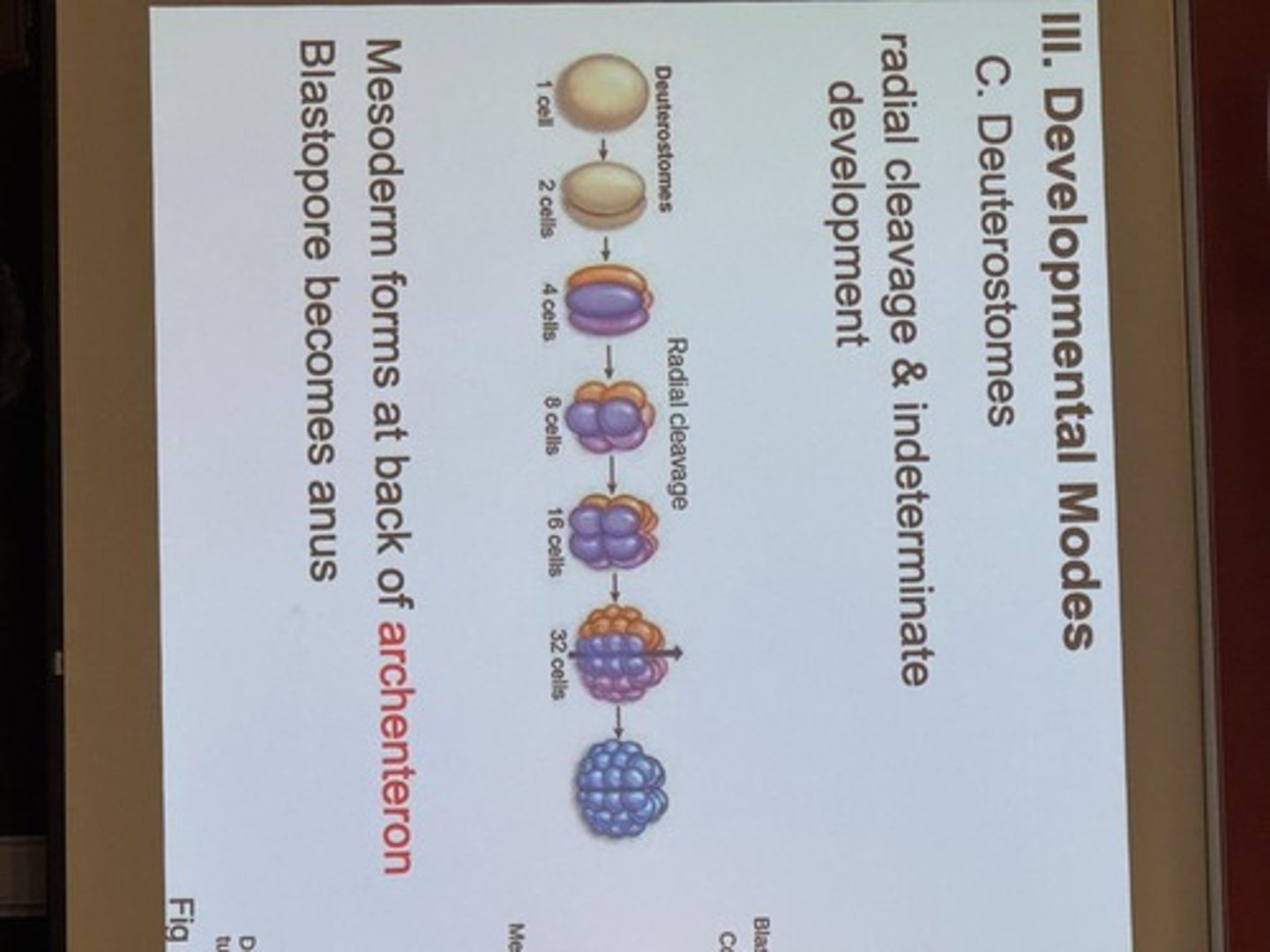
Eukaryotic Cell Structures
The root of Eukarya is not known
Polytomy
We are not sure who is the ancestor of whom
Endosymbiosis
a cell was engulfed by another cell and they now live together
Endosymbiont theory
Mitochondria and Chloroplasts were bacteria
Primary Endosymbiosis
a bacteria is engulfed
Serial Endosymbiosis
is when this happens in series
Plastids
organelles that result from Secondary endosymbiosis
Protists
A general word for all Eukaryotes but traditionally does not include the Plants, Animals, or Fungus
Archaeplastida
Ancient Plastids
Red Algae
Red color pigment phycoerythrin
Green Algae
Closely related to land plants
Chlorophytes
One of the two main groups of green algae.
Charophytes
The second main group of green algae.
SAR
A clade that includes Stramenopiles, Alveolates, and Rhizarians.
Shared derived traits
Characteristics that are unique to a particular clade.
Stramenopiles
A group characterized by long 'hairy' flagella and shorter 'smooth' flagella.
Photosynthetic algae
Algae that have chloroplasts and can perform photosynthesis.
Diatoms
A type of algae that contributed to the potato famine.
Brown Algae
Multicellular algae, such as kelp.
Alveoli
Flattened vesicles just inside the plasma membrane that support it.
Apicomplexans
A group of mostly parasitic organisms.
Malaria
A disease that killed over 384,000 people in 2019.
Rhizarians
A group characterized by a skeletal structure of calcium or silica.
Foraminiferans
A group of Rhizarians known as forams.
Tests
Porous shells made of calcium carbonate.
Amoebozoa
A group characterized by derived characteristics and genetic similarities.