CU 3rd Trimester Study Guide
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
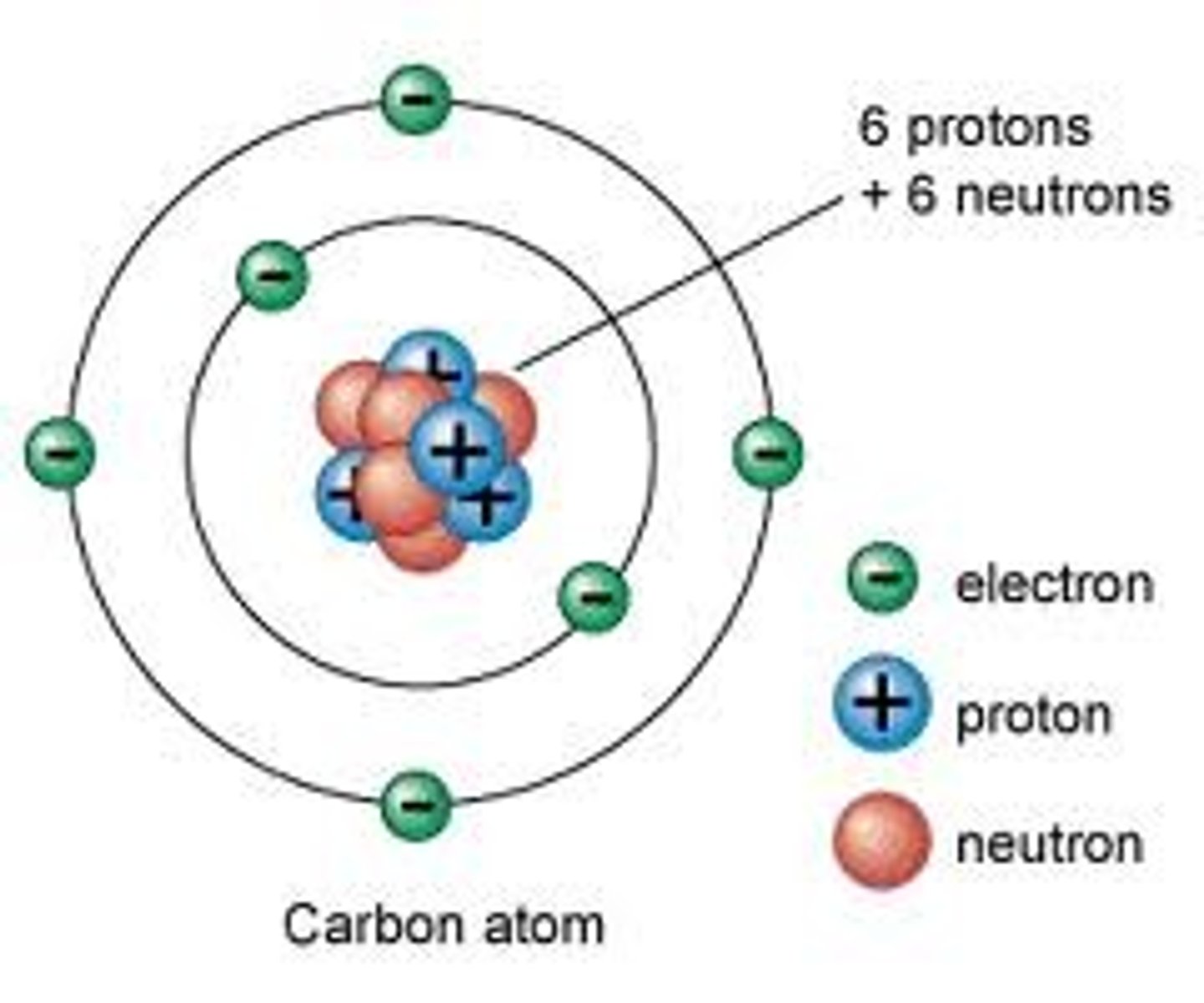
Protons
A positively charged subatomic particle and has a mass of 1 AMU.
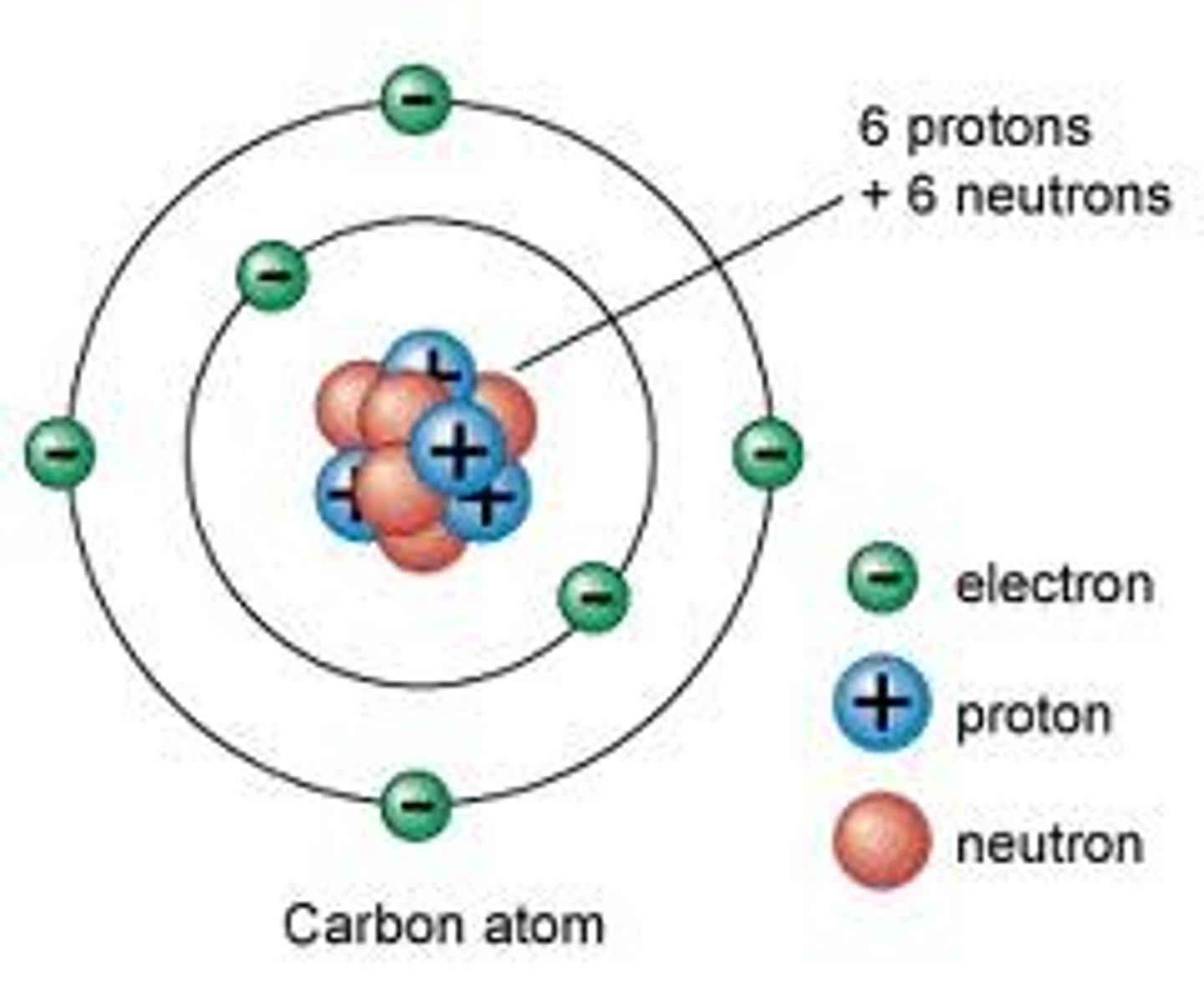
Electron
Negatively charged subatomic particle with no mass.
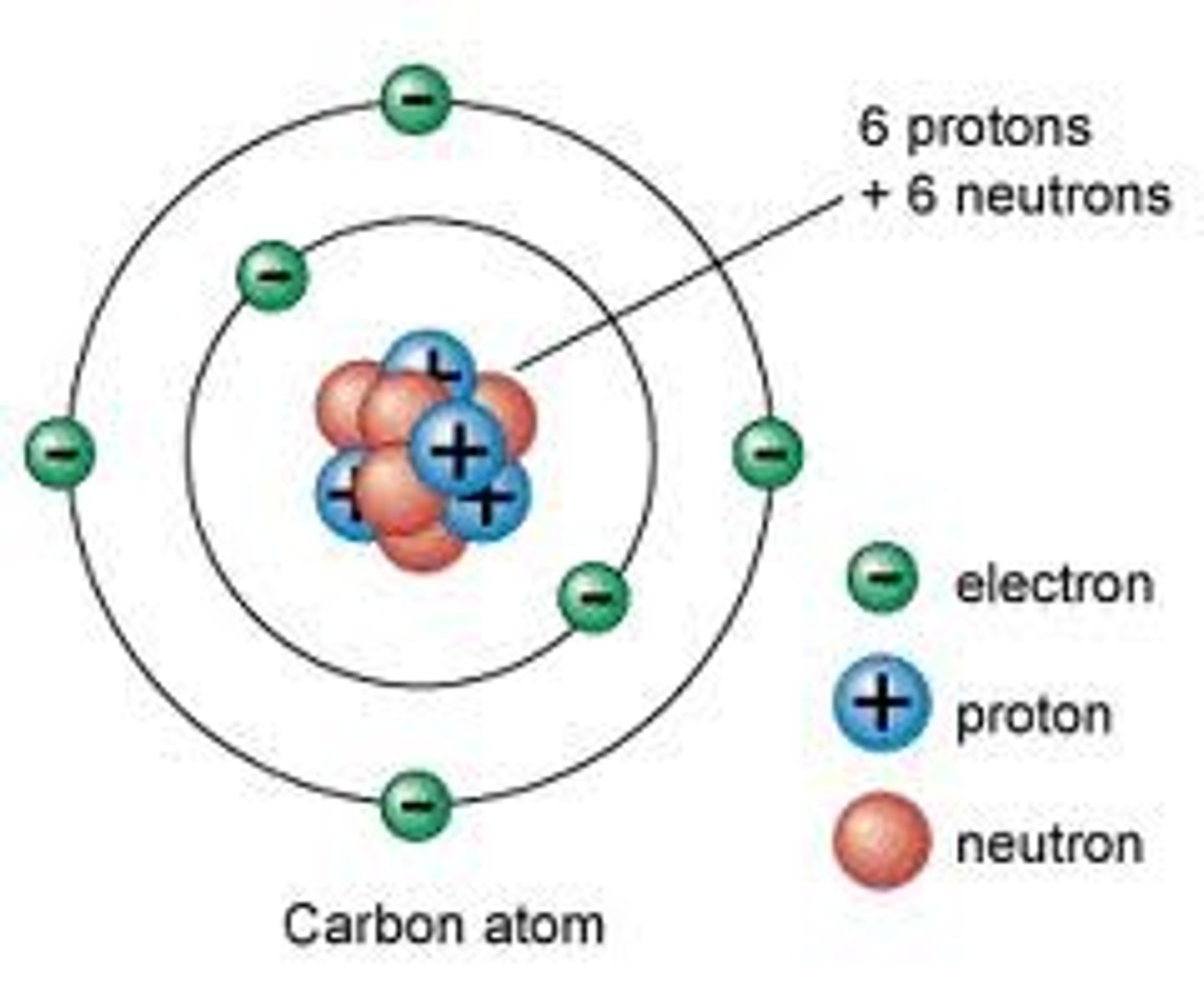
Neutron
Neutrally charged subatomic particle with a mass of 1 AMU.
Atomic mass - atomic number
= the number of neutrons in an atom
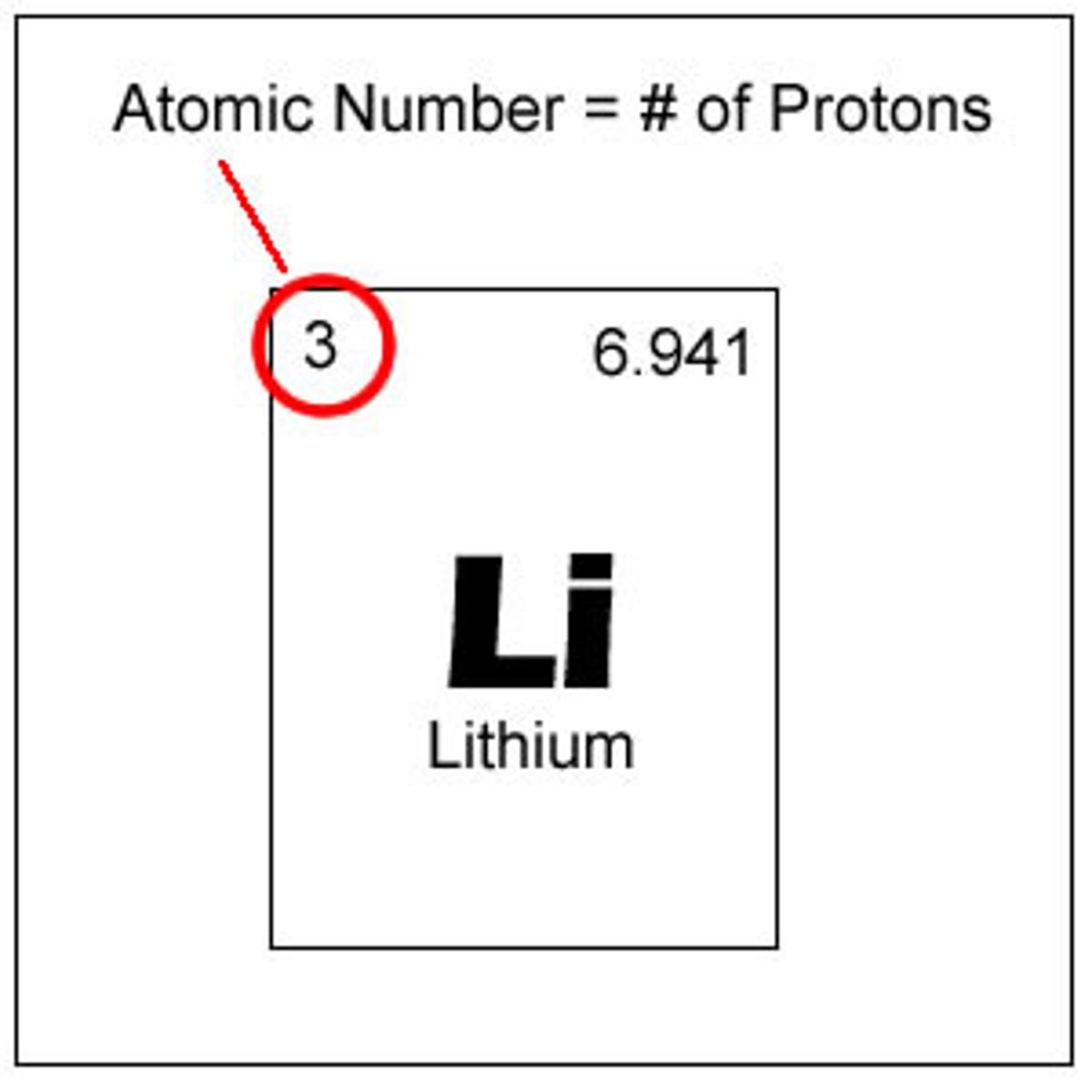
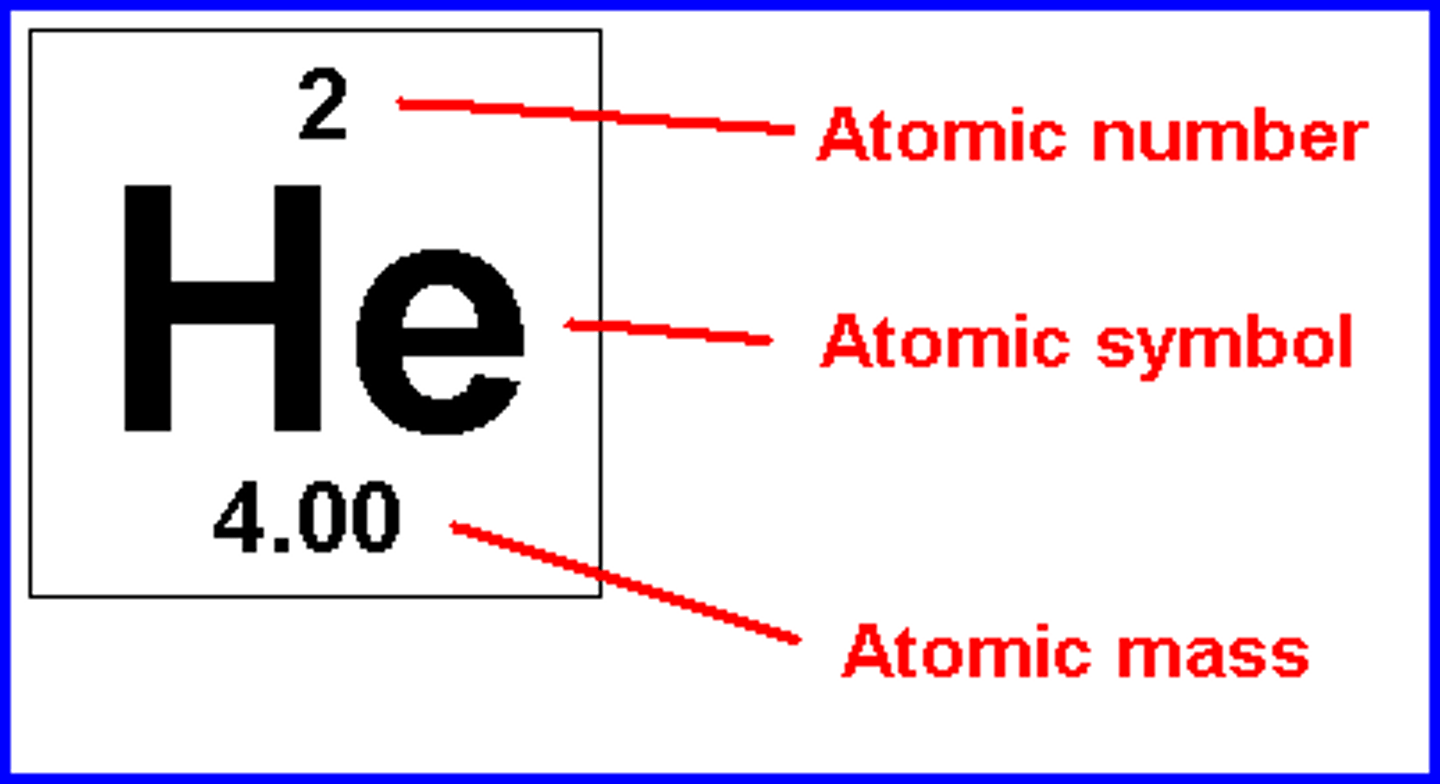
Atomic number
A number assigned to an element that indicates the number of protons in one atom of an element.
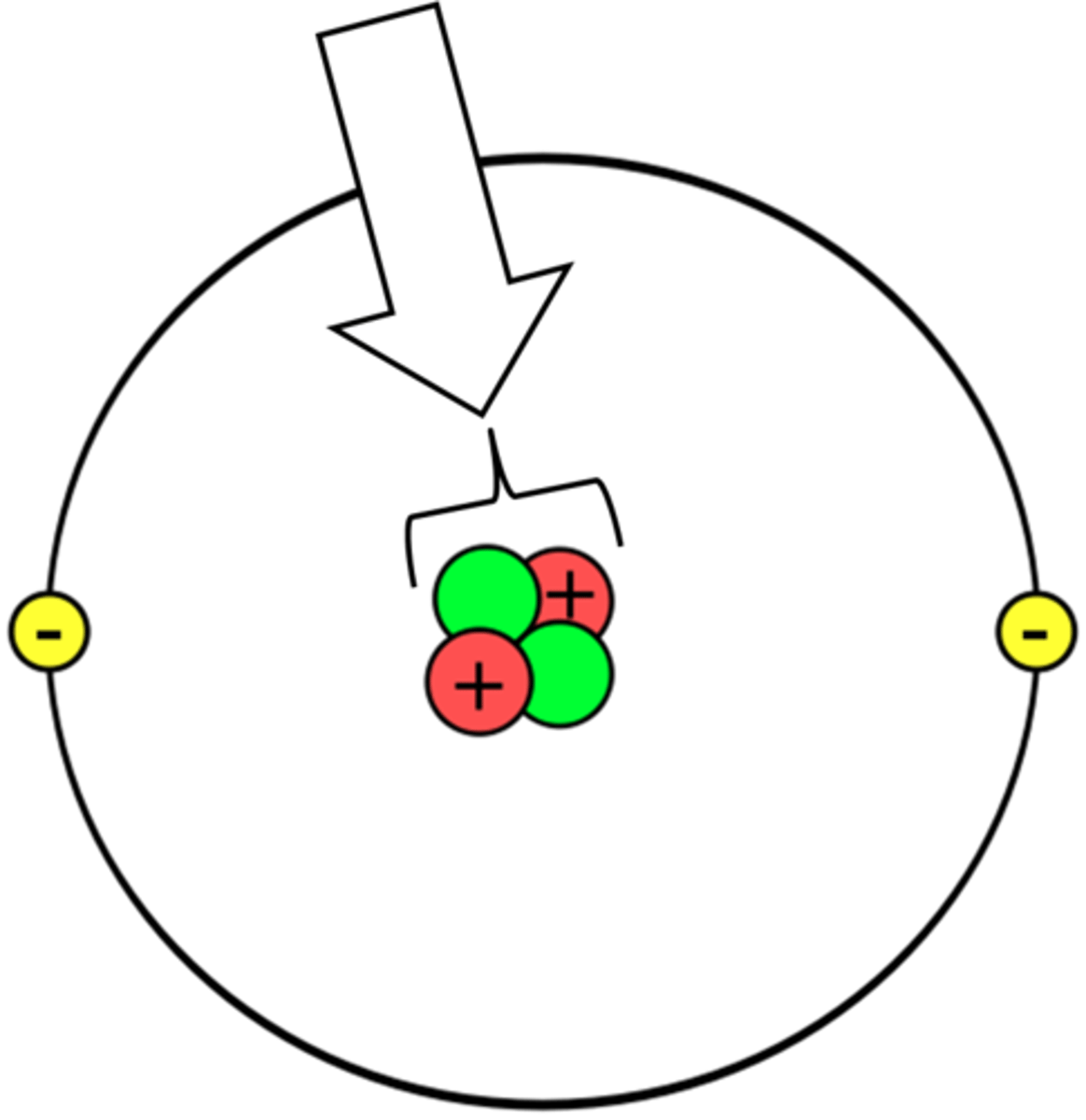
Nucleus
The part of the atom which contains protons and neutrons.
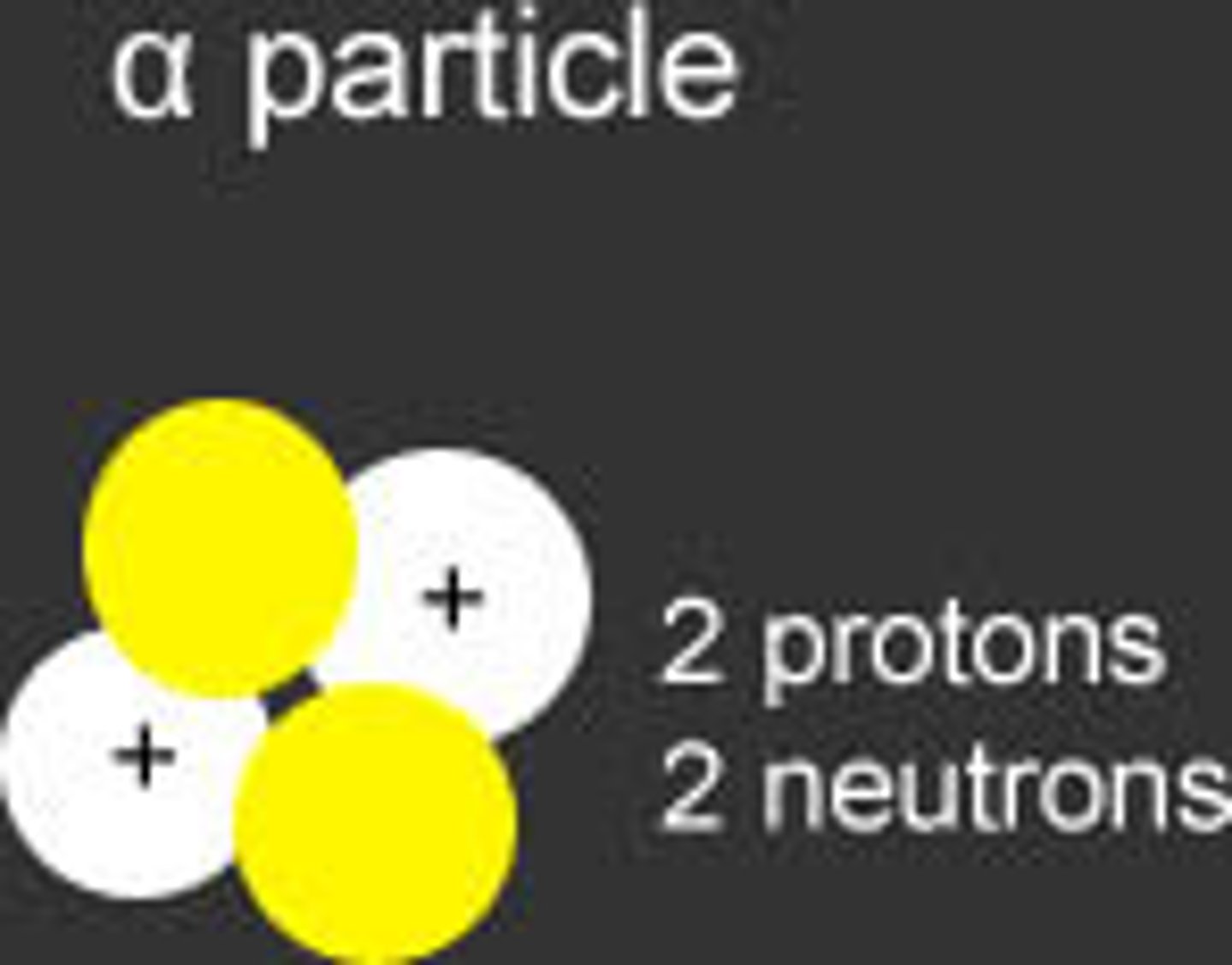
Alpha particle
A particle consisting of 2 protons and 2 neutrons emitted during radioactive decay.
Compounds
When two or more elements are chemically combined.

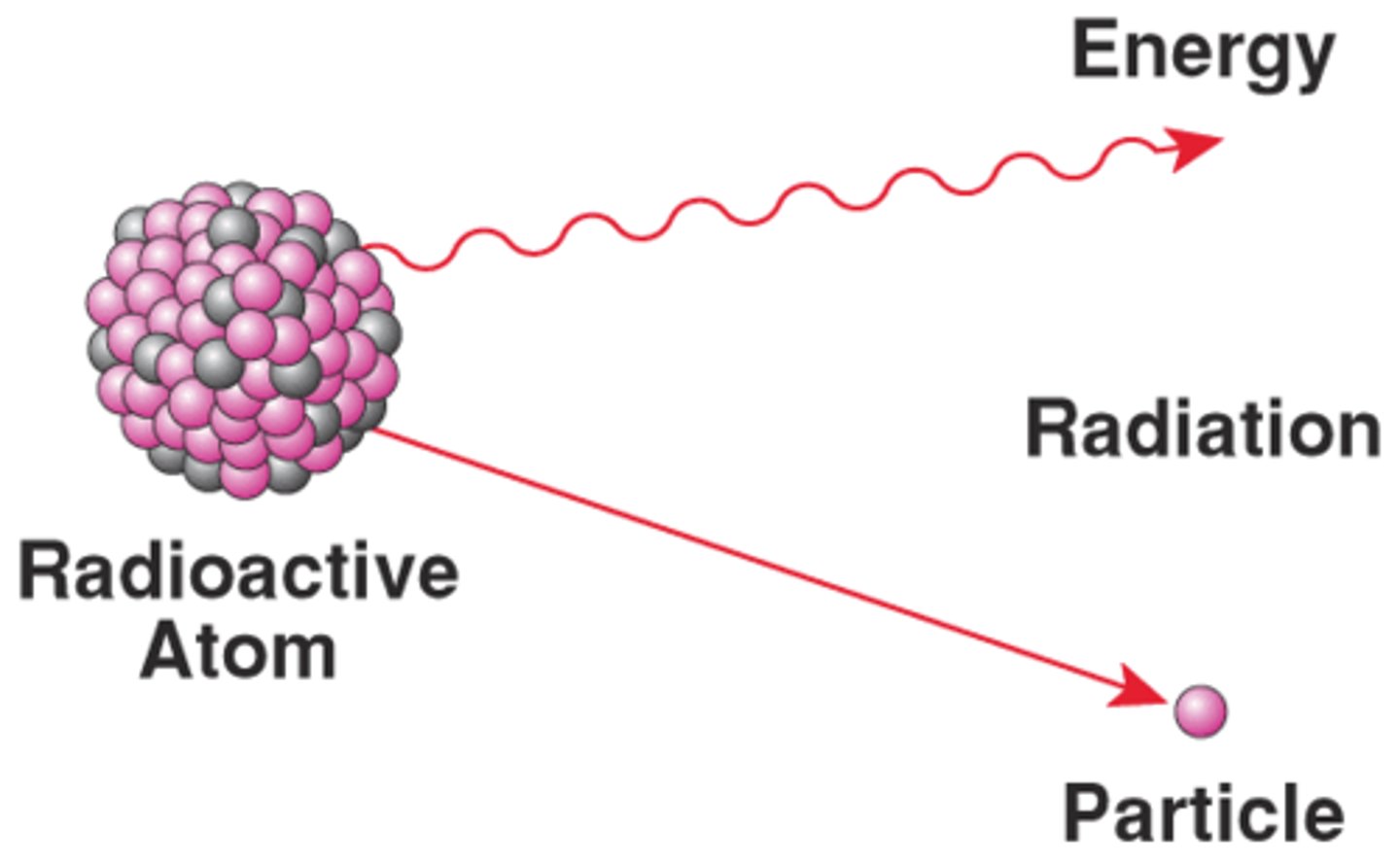
Radioactive Decay
When a radioactive element loses mass and transmutates into another element.
Atomic mass
The mass of one atom of an element.
Mixture
When two or more substances are combined but not chemically bonded.
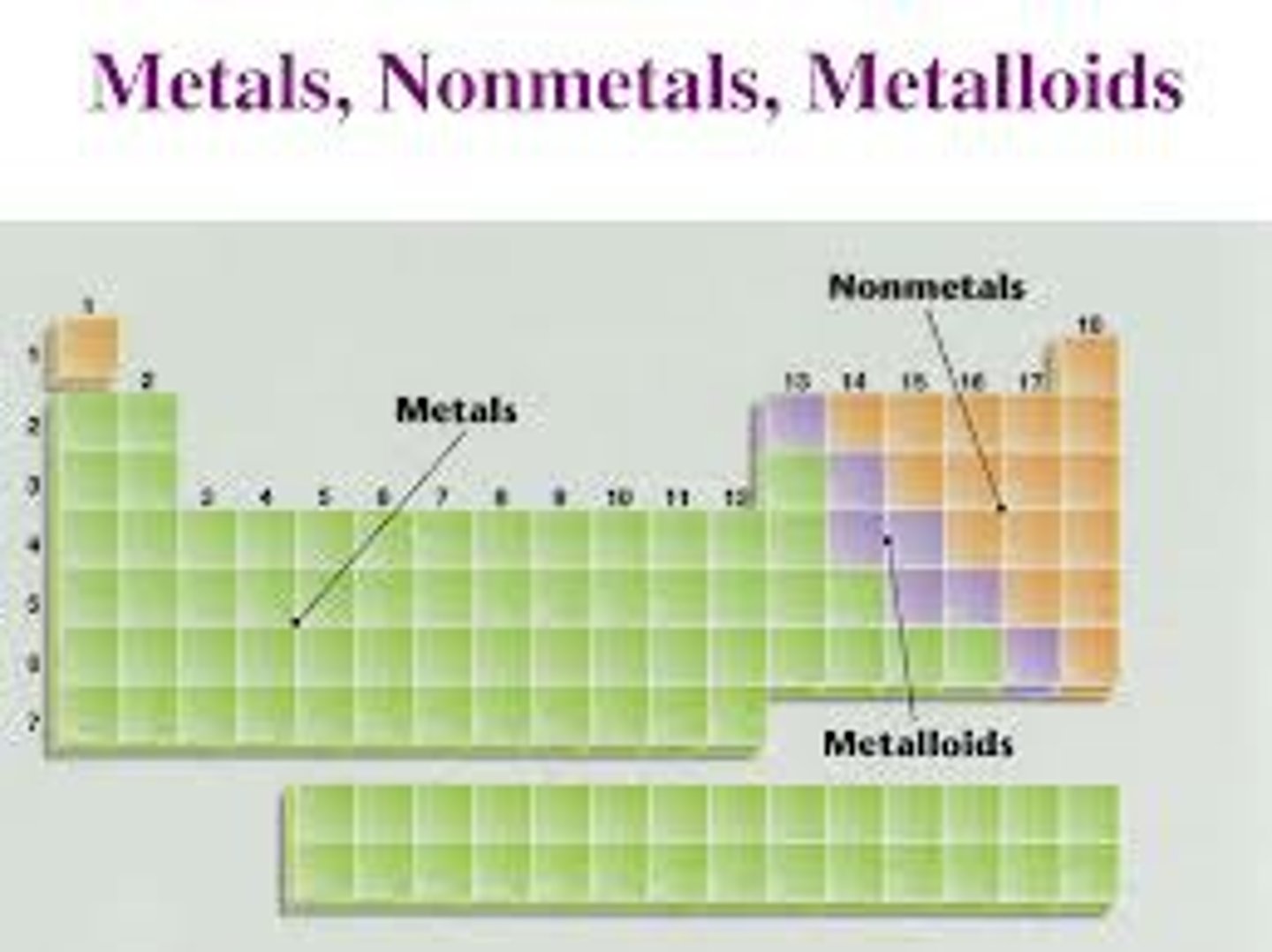
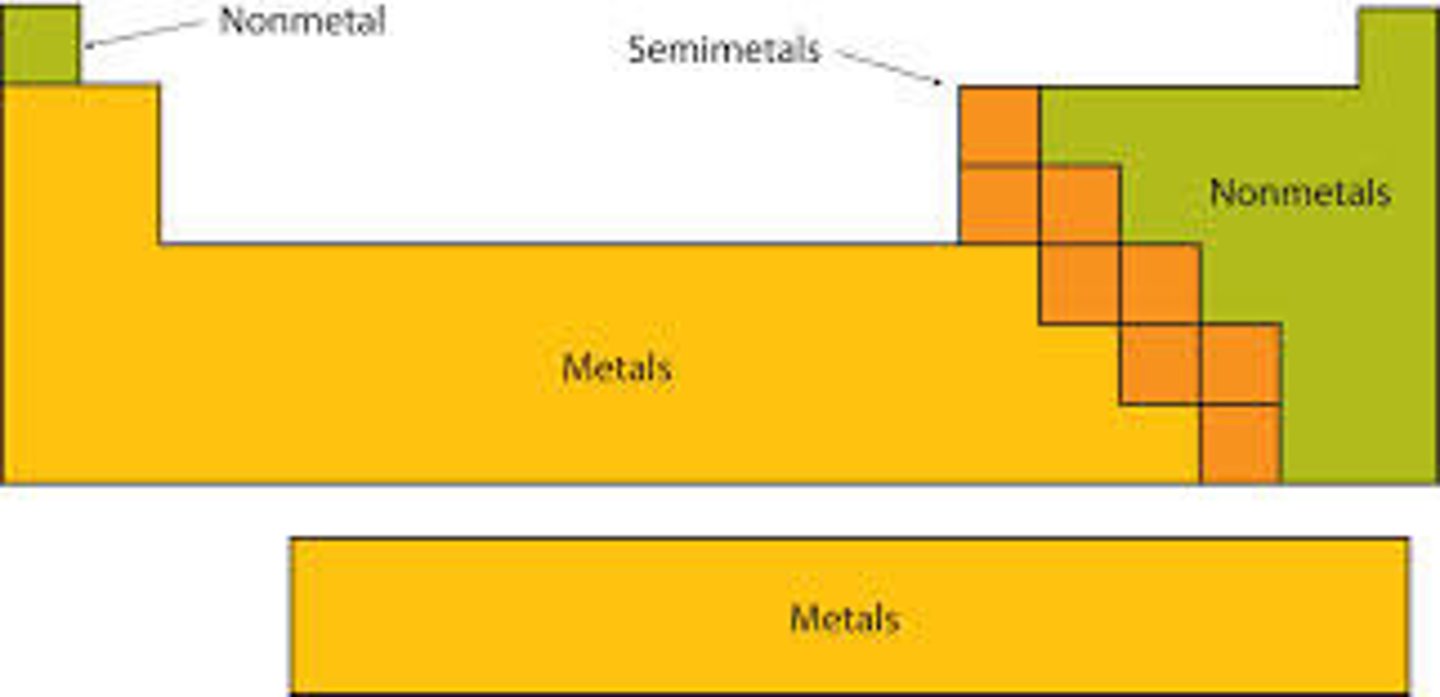
Metals
Elements to the left of the imaginary stair step on the periodic chart that are good at conducting heat and electricity and are malleable.
Non-metals
Elements to the right of the imaginary stair step on the periodic chart that are bad conductors and are not ductile or malleable.
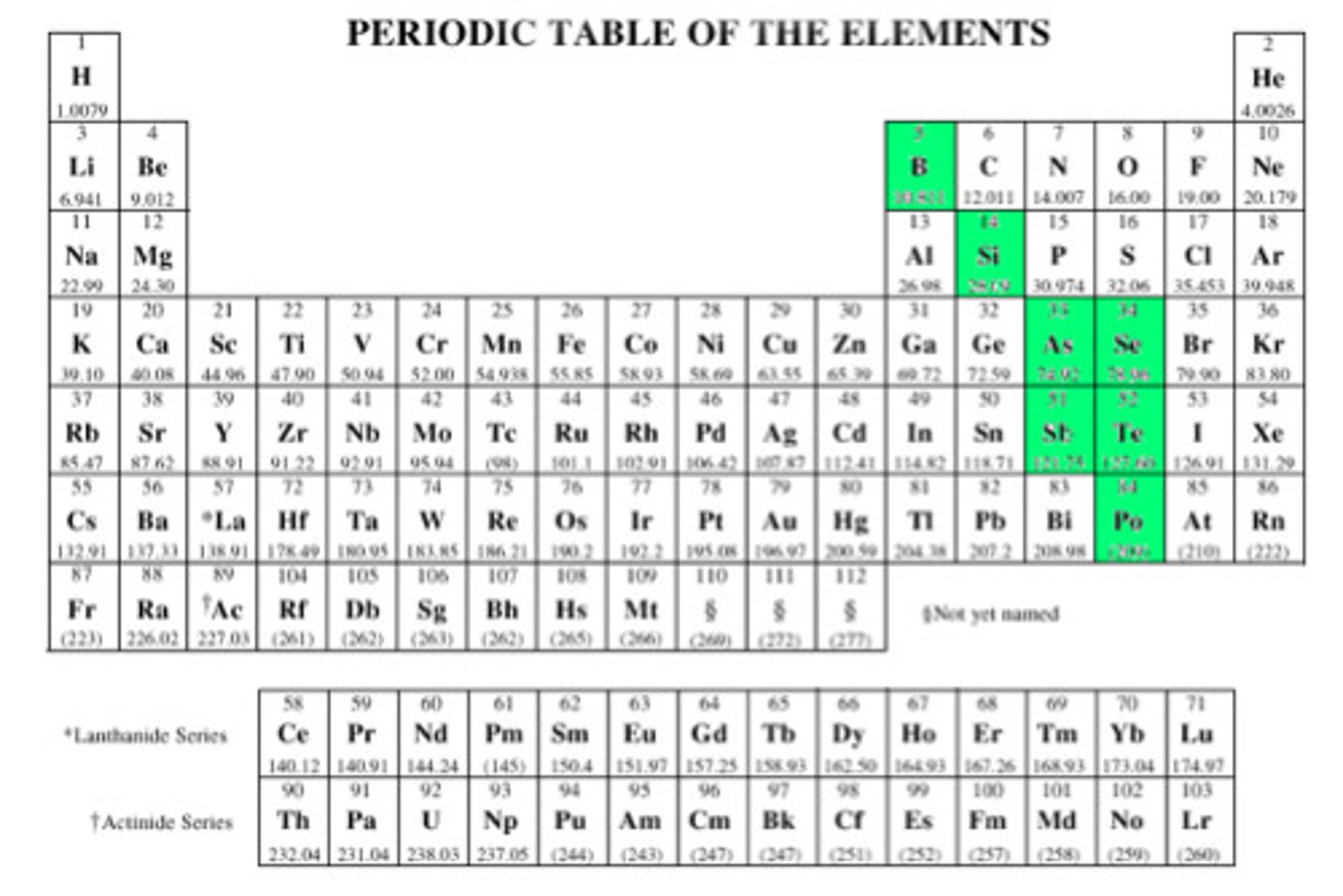
Metalloids
Elements touching the imaginary stair step on the periodic chart (except for aluminum) that share properties of both metals and metalloids.
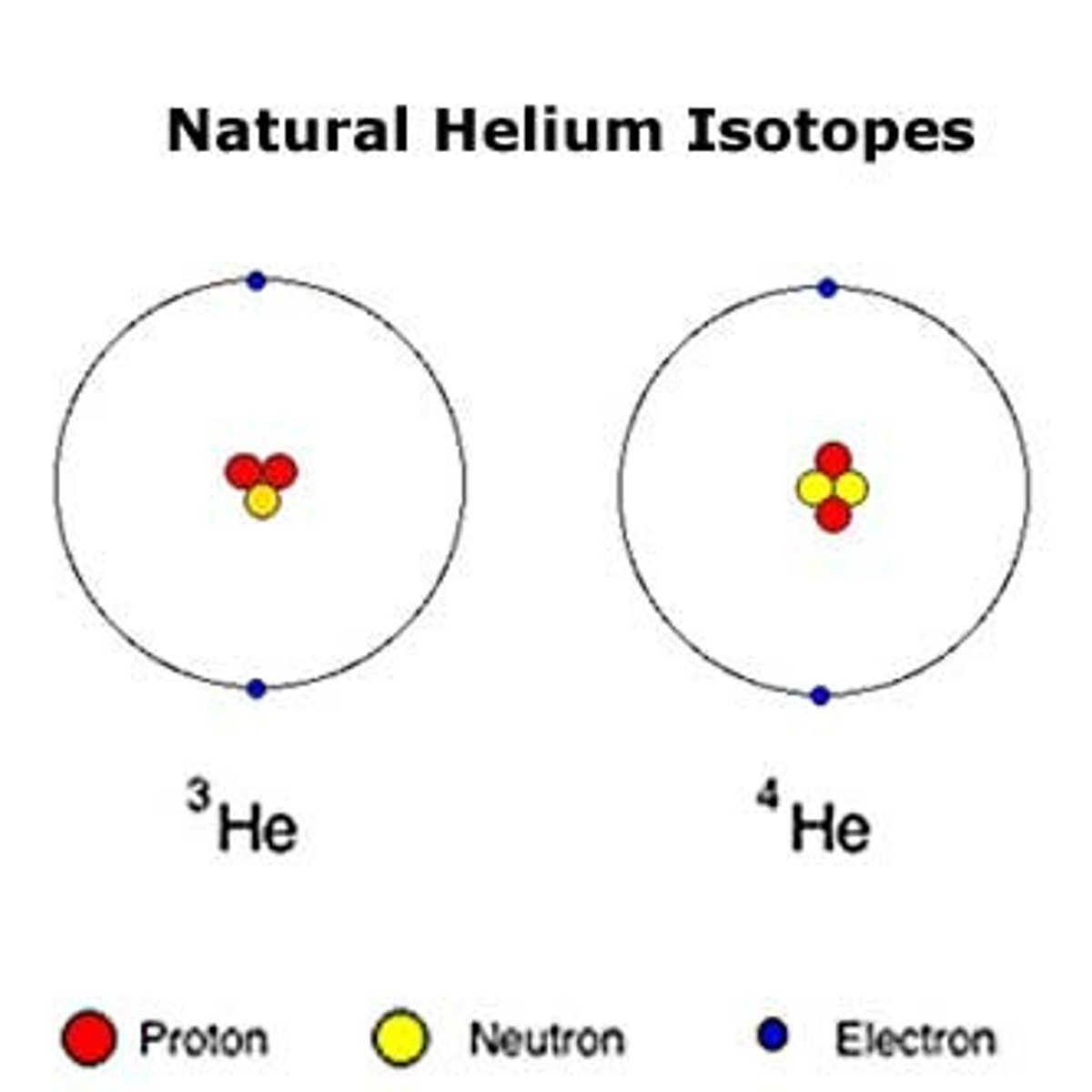
Isotope
Atoms of an element with different number of neutrons.
Exothermic
Chemical reactions in which energy is given off.

Endothermic
Chemical reactions in which energy is taken in.

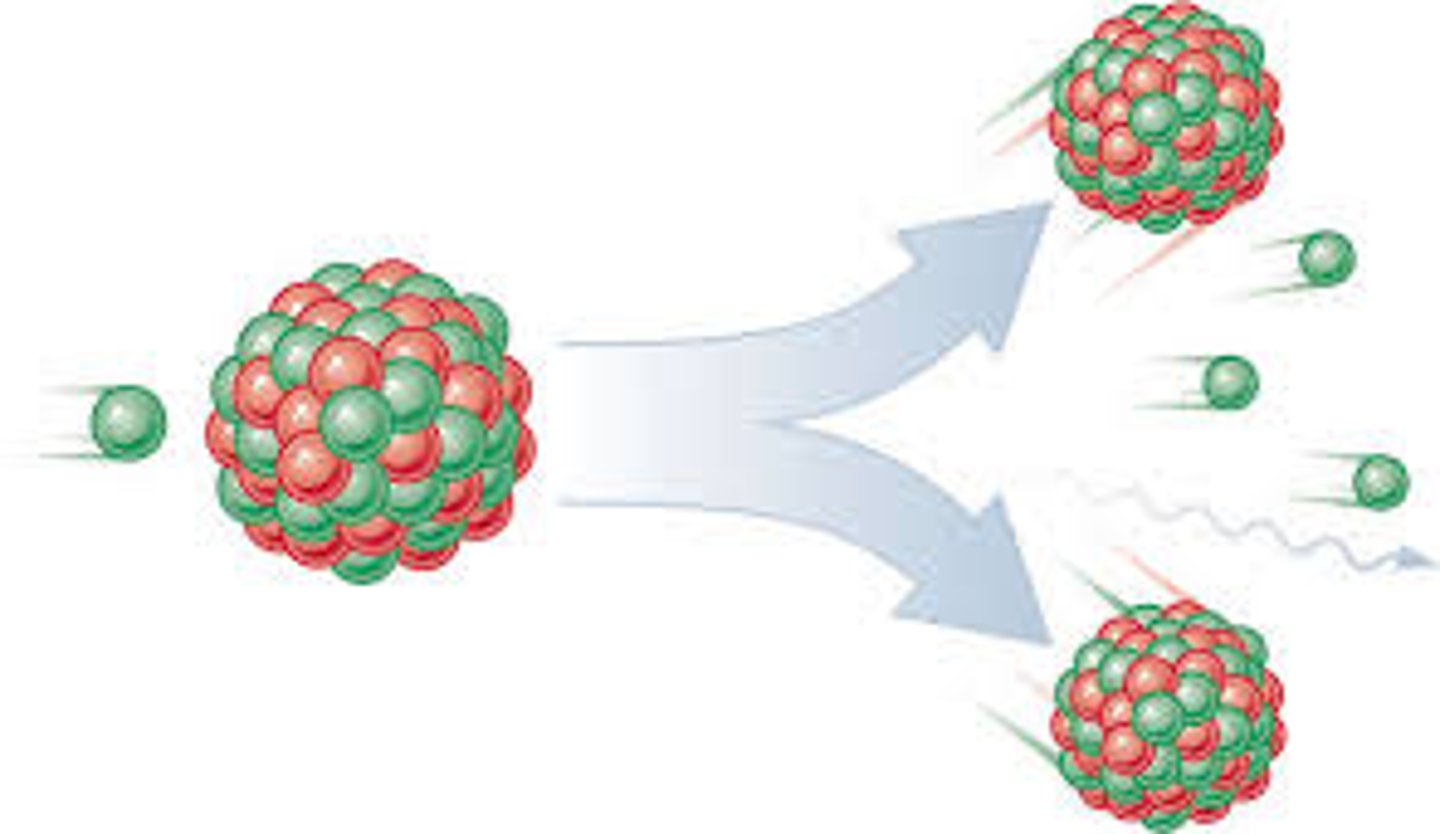
Nuclear fission
A nuclear reaction in which the nucleus of one atom is split into two.
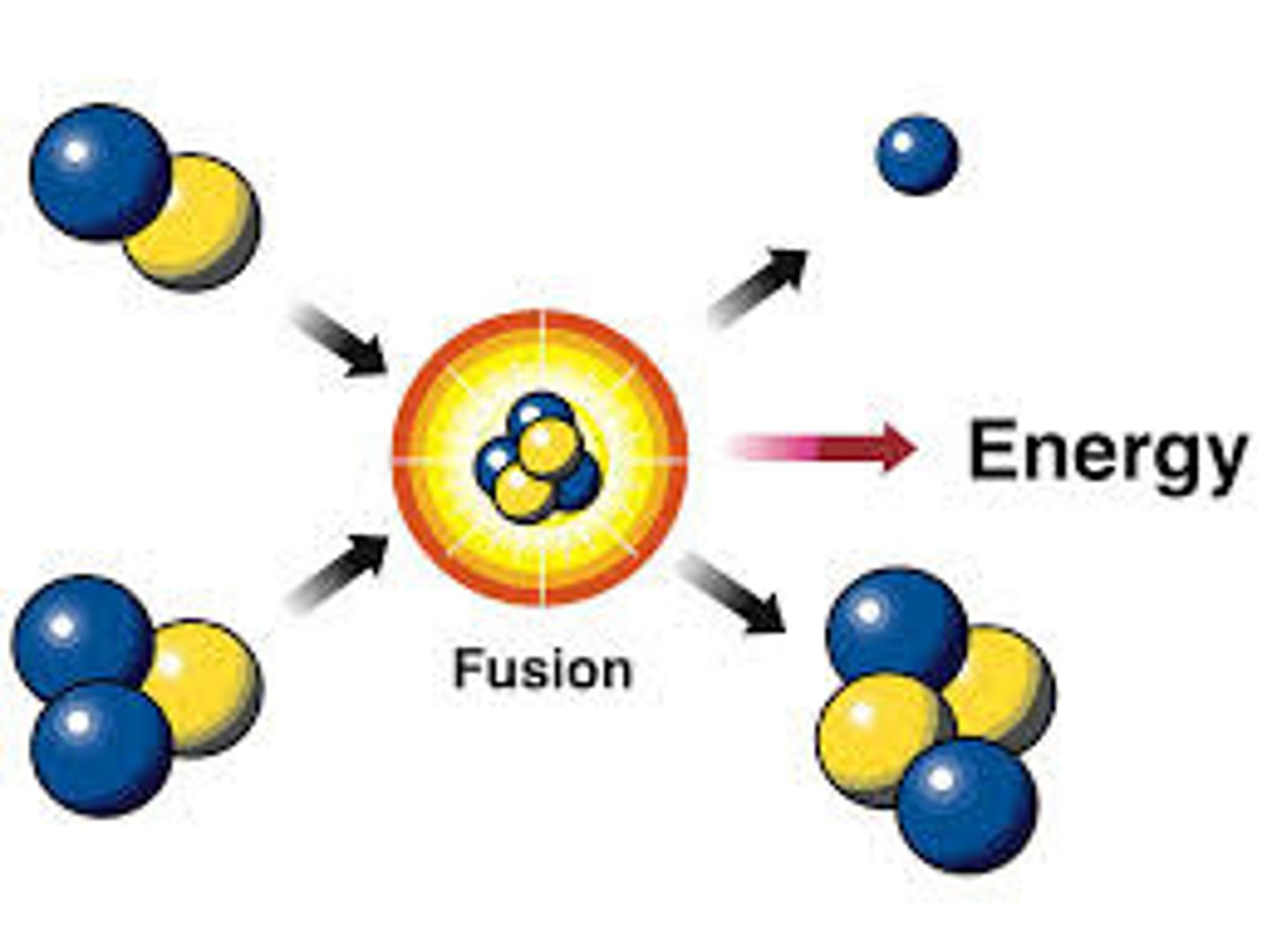
Nuclear fusion
A nuclear reaction in which the nuclei of two atoms combine to form one nuclei.
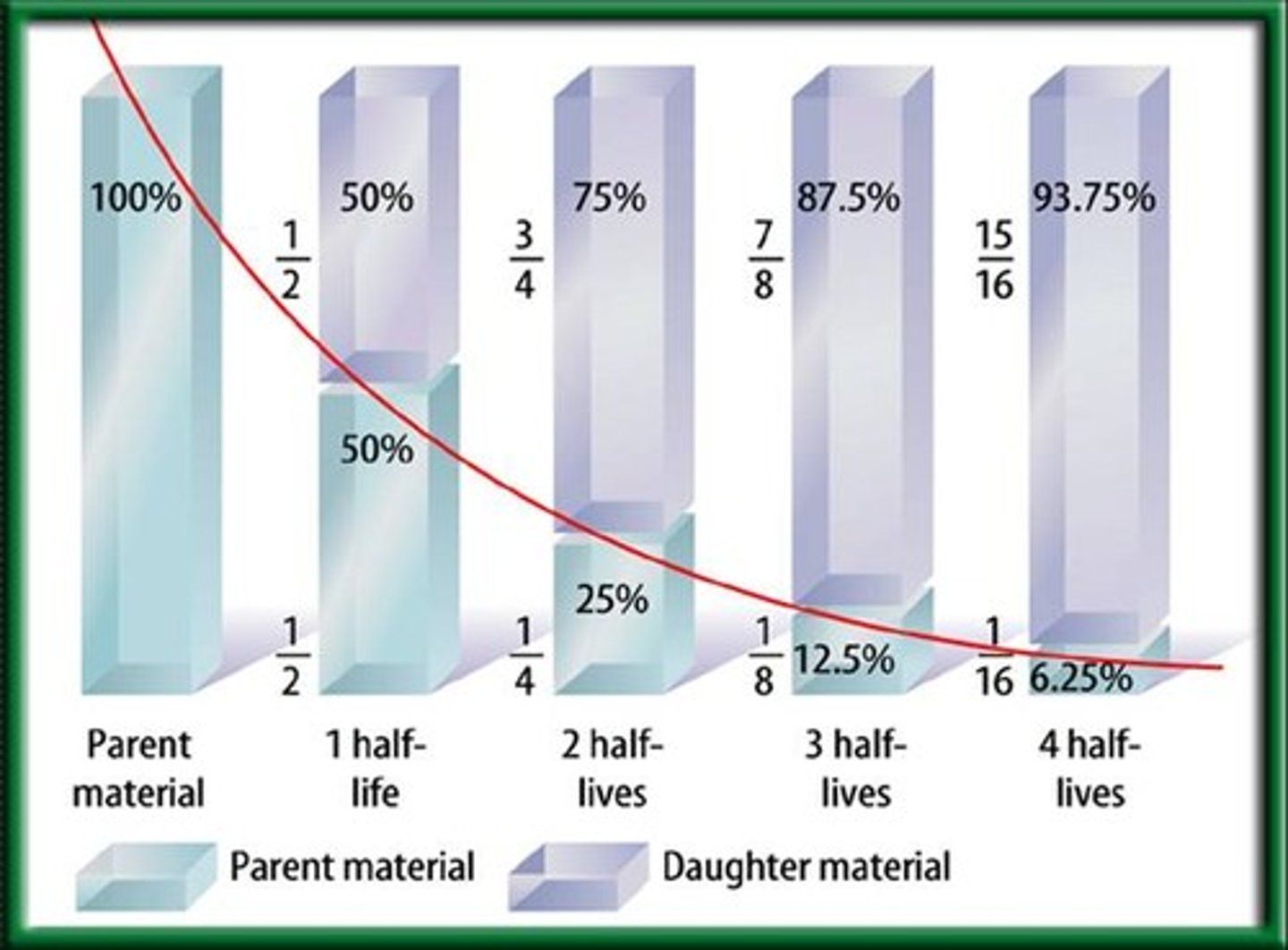
Half life
The amount of time it takes for half of a radioactive isotope to transmutate into another element.
Actinides
The bottom most period of elements which are all radioactive and most are synthetic.
Lanthanides
Elements towards the bottom of the periodic chart that are soft metals that can be cut with a knife.
Product
The result of a chemical reaction.
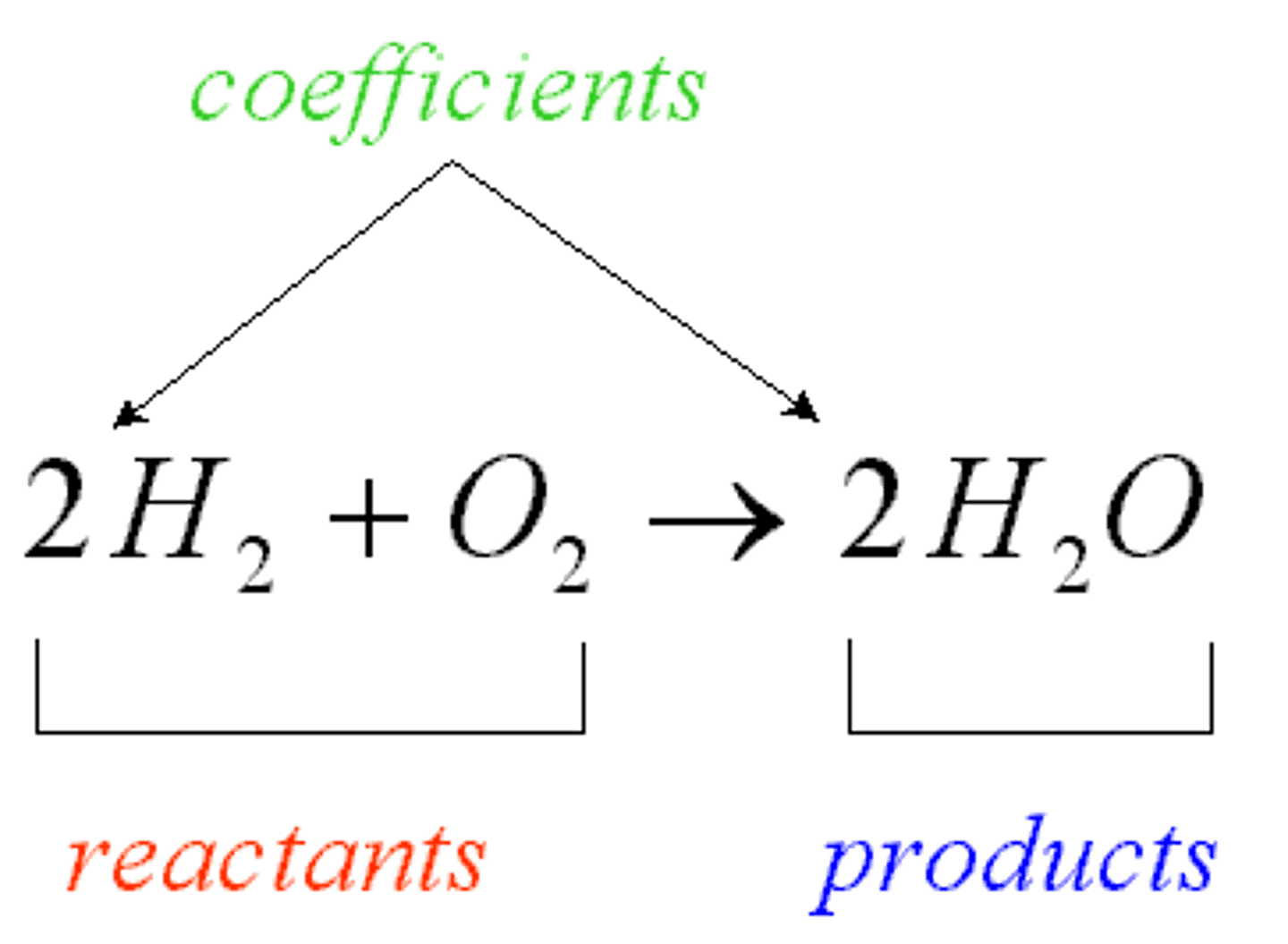
Reactants
The two substances involved in forming a chemical reaction.
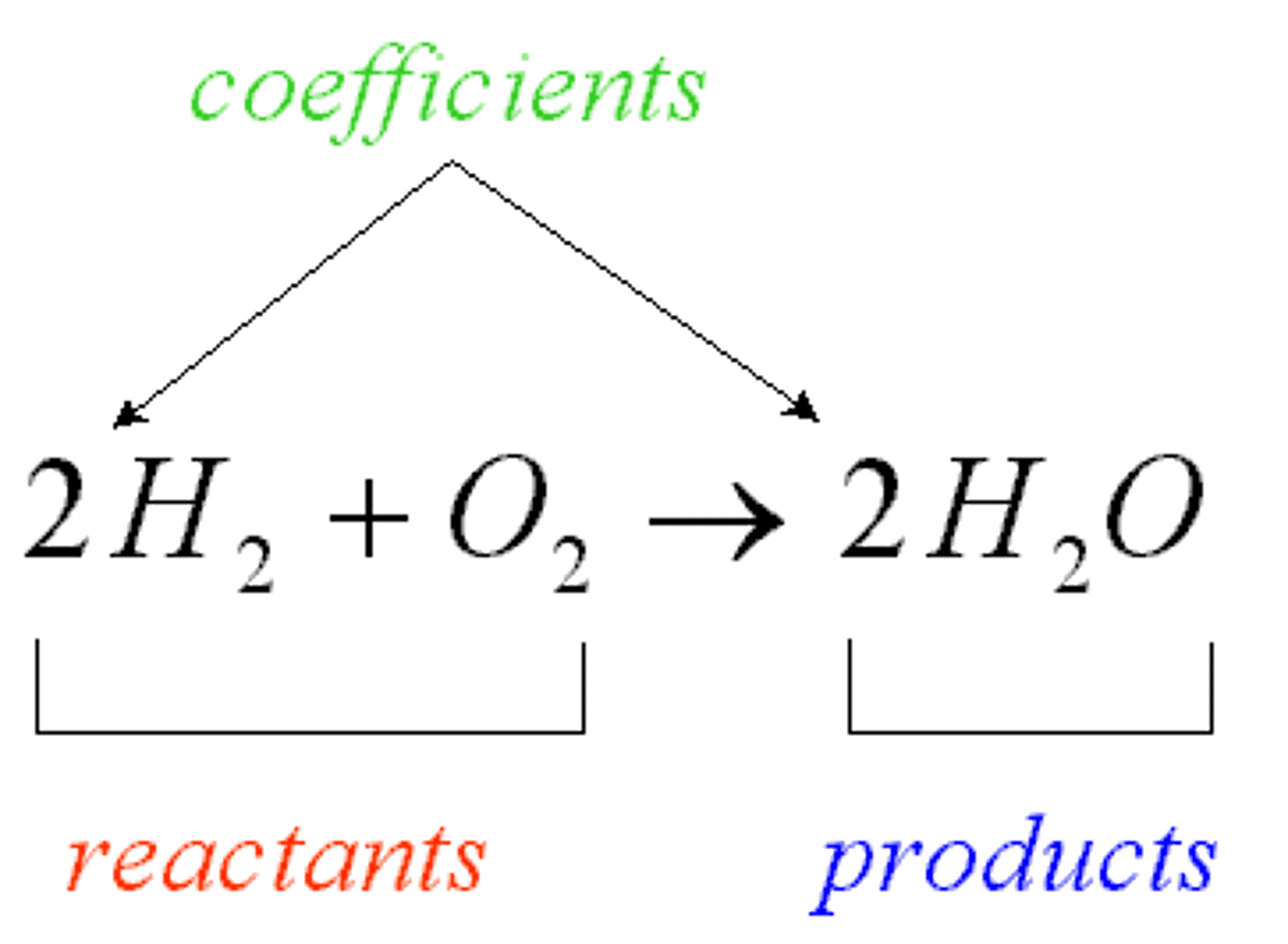
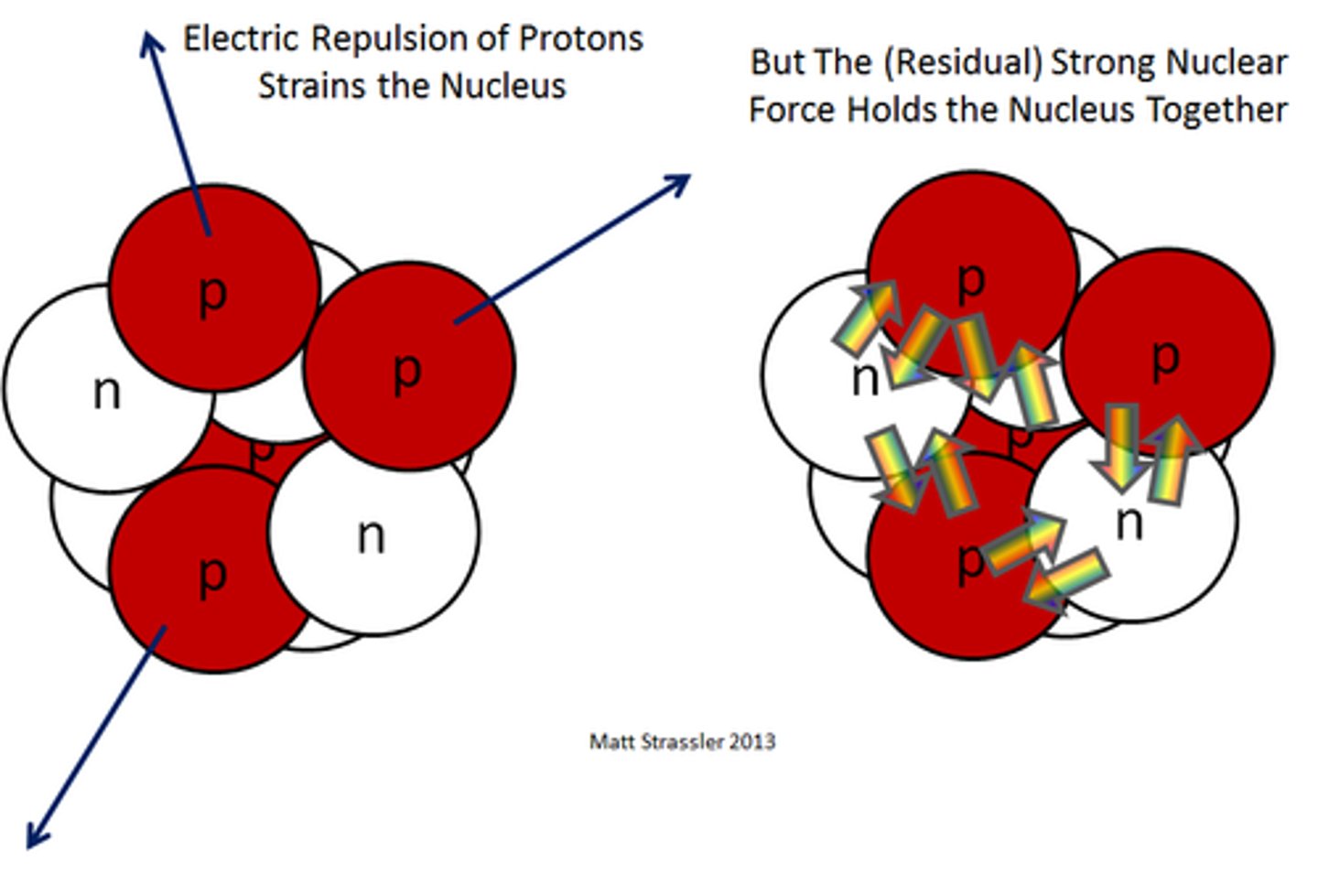
Strong nuclear force
A fundamental force responsible for holding the nuclei of atoms together.
Catalyst
A substance that starts a chemical reaction but is not changed in the chemical reaction.

Physical change
A change in which the chemical identity of a substance is not changed.

Chemical change
A change in which the chemical makeup of a substance is altered.

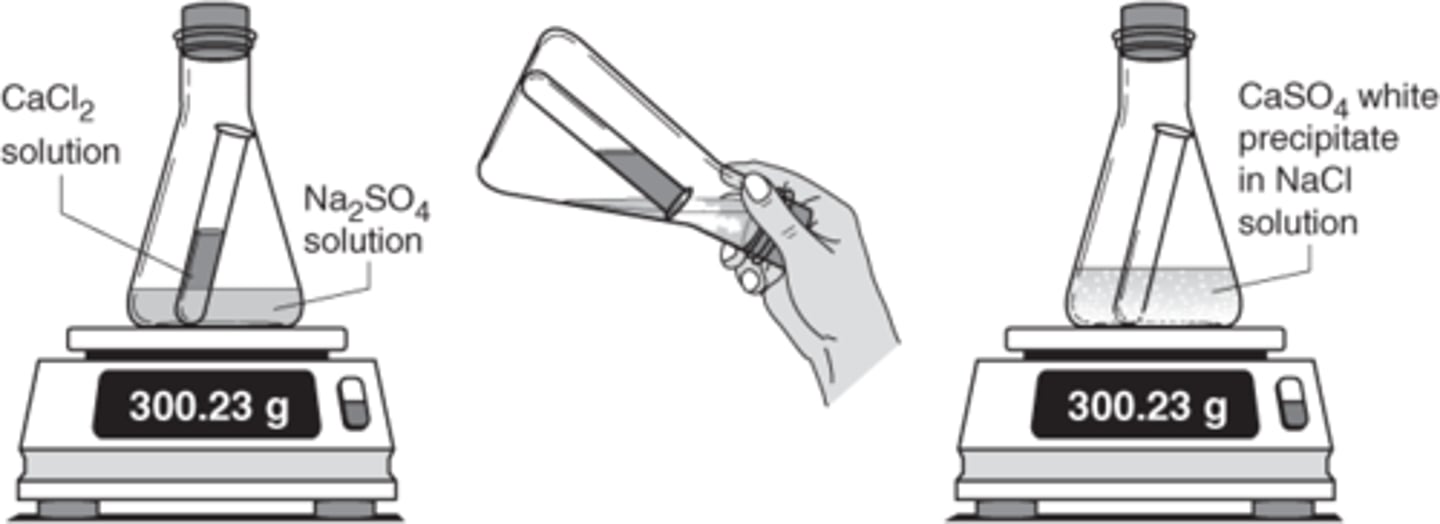
Law of conservation of mass
A law that states that no matter is lost or gained during a chemical reaction.
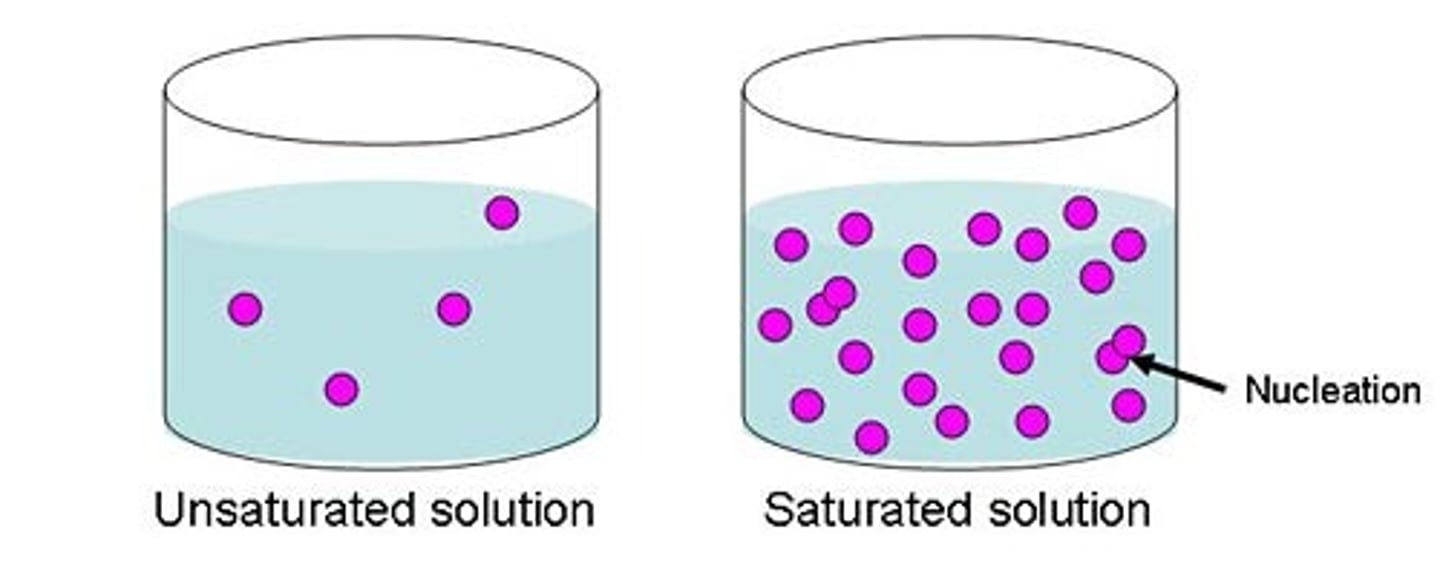
Saturated
A solution in which no more solute can dissolve.
Things that speed up chemical reactions
Catalysts
Increased surface area
Increased concentrations
Increased temperature
Acid
A solution that has a positive hydrogen ion, is corrosive to metal, and has a sour taste, and a pH less than 7.
Base
A solution that has a negative hydroxyl (OH-), is slippery when wet, tastes bitter, and is usually a good cleaner, and has a pH greater than 7.
Things that affect the solubility of a solute in a solvent
Pressure
Temperature
Type of solute
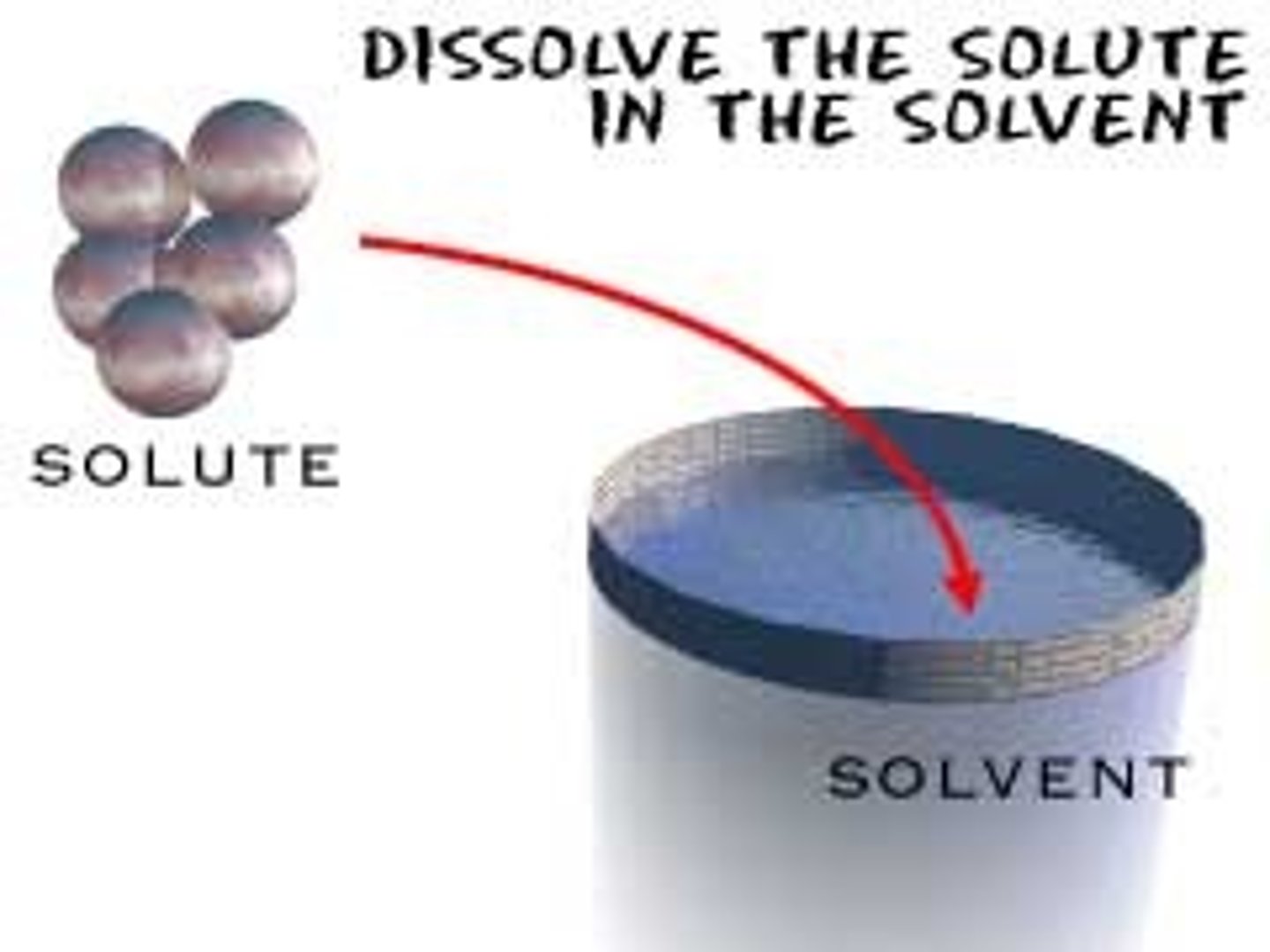
Solute
The substance in a solution that is present in a lesser quantity and gets dissolved.
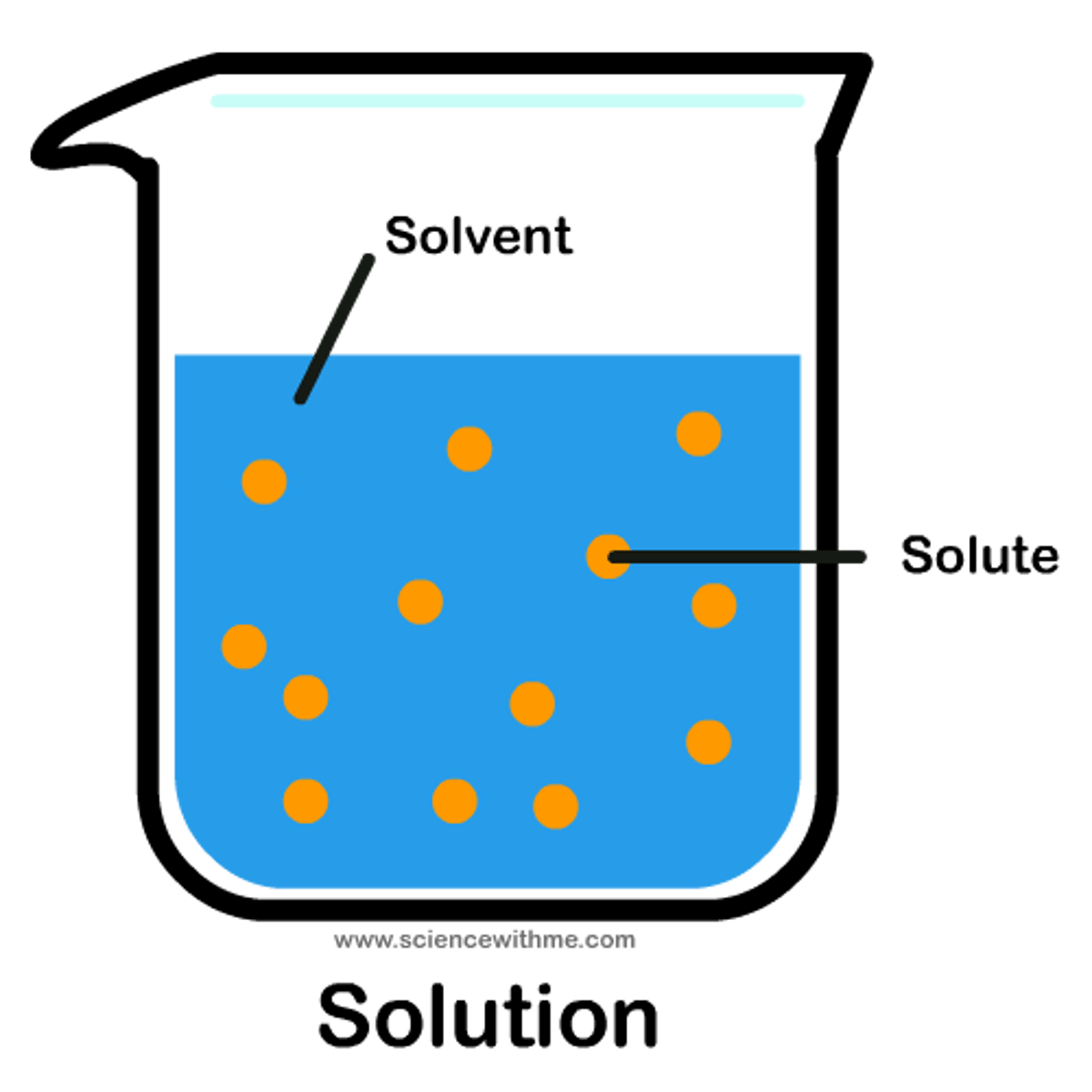
Solvent
A substance in a solution that is present in a greater quantity and does the dissolving.
Neutralization
The reaction that occurs when an acid and a base are mixed with each other which results in water and a salt.
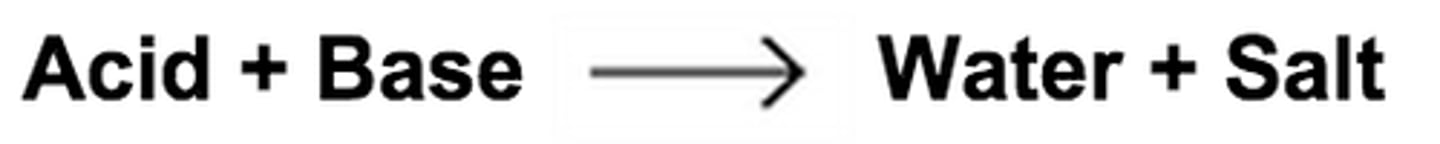
Indicator
A substance that helps determine the presence of an acid or base.

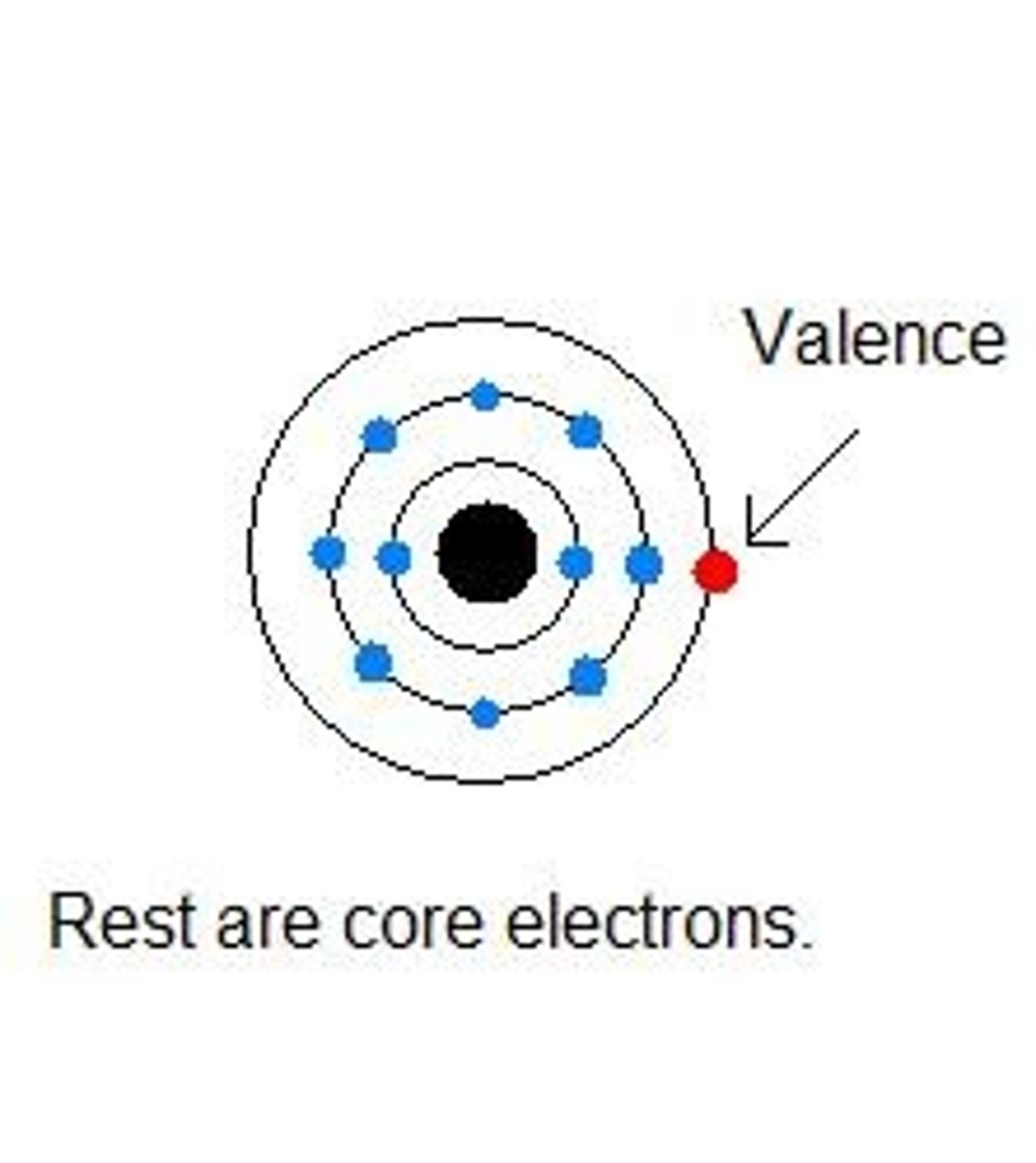
Valence electrons
Electrons on the outermost electron orbital or an atom. (Can be determined by which family the element is found in).