Conduction of Heat
1/21
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
22 Terms
what is thermal conduction?
Thermal conduction is the process where energy is transferred by vibrating particles in a substance
describe how thermal conduction occurs
The vibrating particles transfer energy from their kinetic store to the kinetic store of neighbouring particles
describe the direction of the energy transfer
The direction of energy transfer is always from hot to cold
The higher the thermal conductivity of a material….
the higher the rate of energy transfer by conduction across the material
compare materials with high thermal conductivity to low thermal conductivity materials
Materials with high thermal conductivity heat up faster than materials with low thermal conductivity
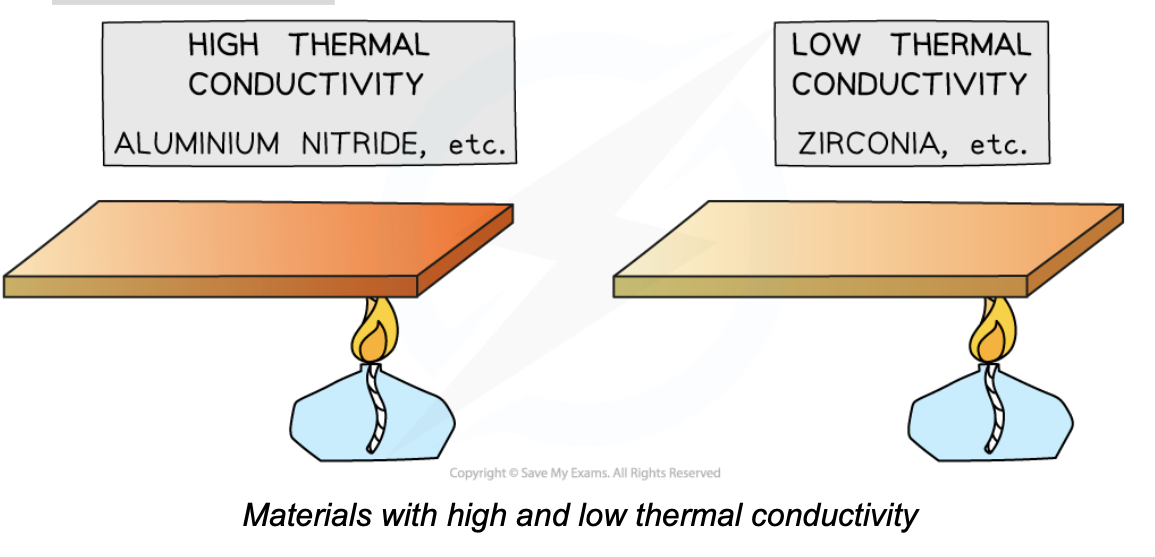
what are 3 examples of substances with a high thermal conductivity
Diamond
Aluminium
Graphite
what are 3 examples of substances with a low thermal conductivity
Air
Steel
Bronze
what is an insulator?
An insulator is a substance that is a poor thermal conductor
give three examples of insulators
wool, plastic, wood
what are insulators used to do?
Insulators are used to reduce energy transfers, for example, to keep a house warm or build a soundproof room
why is a woollen jumper worn in winter?
to retain body heat and keep warm
list three things the energy transfer through a layer of insulating material depends on
temperature difference across a material
thickness of a material
thermal conductivity of a material
how does temperature difference across a material affect the energy transfer through that material?
the greater the temperature difference, the more conduction
how does thickness of a material affect the energy transfer through that material?
the thicker the material, the less energy will be transferred by conduction
how does the thermal conductivity of a material affect the energy transfer through that material?
the higher the thermal conductivity, the more energy will be transferred by conduction
so what do good insulators which keep the energy transfer through them as low as possible have?
A low thermal conductivity
Layers that are as thick as possible
what does loft insulation do?
Insulating the loft of a house lowers its rate of cooling, meaning less energy is lost to the outside
what is loft insulation often made out of?
The insulation is often made from fibreglass (or glass fibre)
what is fibreglass/glass fibre made out of and why is it a good insulator?
a reinforced plastic material composed of woven material with glass fibres laid across and held together
The air trapped between the fibres makes it a goodinsulator
compare the loft insulation to the roof material
loft insulation has a much lower thermal conductivity than the roof material
how is loft insulation built to make it a good insulator
Several layers of insulation make it very thick and therefore decrease the rate of cooling
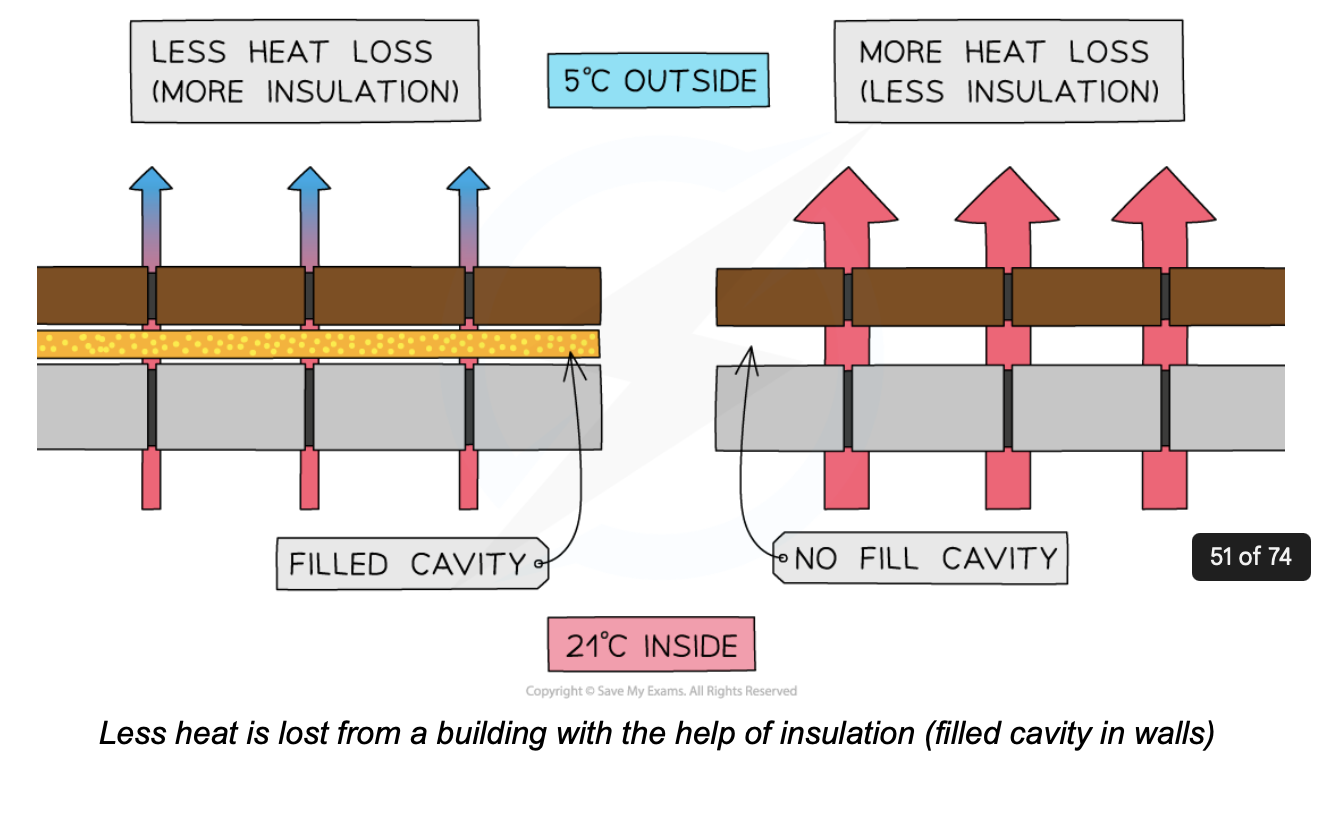
explain how are houses in cold countries adapted to the weather (2)
Houses in cold countries are fitted with cavity wall insulation which is made from blown mineral fibre filled with gas
This lowers the conduction of heat through the walls from the inside to the outside