Ch 9
1/84
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
85 Terms
To fulfill its role, the genetic material must meet several criteria
1. _______: It must contain the ______ (same word) necessary to make an entire organism
Information
To fulfill its role, the genetic material must meet several criteria
2. __________: It must be passed from parent to offspring
transmission
To fulfill its role, the genetic material must meet several criteria
_________: It must be copied
- In order to be passed from parent to offspring
replication
To fulfill its role, the genetic material must meet several criteria
4. _________: It must be capable of changes
- To account for the known phenotypic variation in each species
variation
To fulfill its role, the genetic material must meet several criteria
n 1. ______: It must contain the information necessary to make an entire organism
n 2. _______: It must be passed from parent to offspring
n 3. _______: It must be copied
n In order to be passed from parent to offspring
n 4. _______: It must be capable of changes
n To account for the known phenotypic variation in each species
information; transmission; replication; variation
Griffith studied a bacterium (pneumococci) now known as _______ _______
Streptococcus pneumoniae
S. pneumoniae comes in two strains
S → Smooth
Secretes a _____ capsule
Protects bacterium from the _____ system of animals
Produce smooth colonies on solid media
polysaccharide; immune
S. pneumoniae comes in two strains
R → Rough
_____ to secrete a capsule
Produce colonies with a rough appearance
Unable
In 1928, Griffith conducted experiments using two strains of S. pneumoniae: type IIIS (smooth) and type IIR (rough)
What happens when mouse was injected with live type IIIS bacteria?
Mouse died, type IIIS bacteria recovered from the mouse’s blood
In 1928, Griffith conducted experiments using two strains of S. pneumoniae: type IIIS (smooth) and type IIR (rough)
What happens when mouse was injected with live type IIR bacteria?
Mouse survived, no living bacteria isolated from the mouse’s blood
In 1928, Griffith conducted experiments using two strains of S. pneumoniae: type IIIS (smooth) and type IIR (rough)
What happens when mouse was injected with heat-killed type IIIS bacteria?
Mouse survived, no living bacteria isolated from the mouse’s blood
In 1928, Griffith conducted experiments using two strains of S. pneumoniae: type IIIS (smooth) and type IIR (rough)
What happens when mouse was injected with live type IIR + heat-killed type IIS cells?
Mouse died, type IIIS bacteria recovered from the mouse’s blood
From the mouse experiments, Griffith found out that something from the dead type IIIS was transforming type IIR into type IIIS
He called this process ________
transformation
The substance that allowed this to happen was termed the _____ _____
Griffith did not know what it was
transformation principle
Avery, MacLeod and McCarty identified the transforming principle (genetic material) as ______
DNA
Avery, MacLeod and McCarty identified the transforming principle (genetic material) as DNA
They prepared _____ _____ (DNA, RNA, proteins and carbohydrates) from type IIIS cells containing each of these macromolecules
cell extracts
Only the extract that contained _____ DNA was able to convert type IIR into type IIIS
purified
Treatment of the extract with _____ eliminate transformation
Treatment with RNase or protease did not eliminate transformation
DNAse
In 1952, Alfred Hershey and Marsha Chase provided further evidence that DNA is the genetic material
They studied the bacteriophage T2
It is relatively simple since its composed of only two macromolecules: _____ and _____
DNA; protein
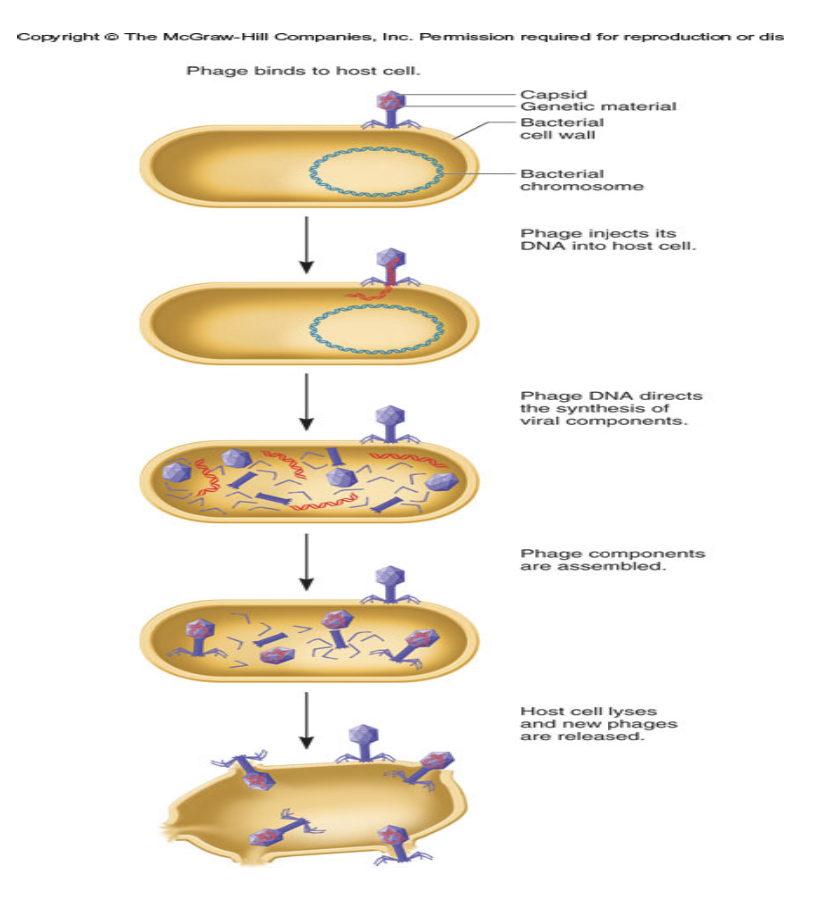
Life cycle of the T2 bacteriophage
-has to inject its “____ ____” into the host cell to direct its propagation
The Hypothesis
Only the genetic material of the phage is injected into the bacterium
Isotope labeling will reveal what is injected into the bacterium (if it is DNA or protein?)
genetic material
The Hershey and Chase experiment can be summarized as such:
Used radioisotopes to distinguish DNA from proteins
32P labels ___ specifically
35S labels ____ specifically
DNA; protein
Radioactively-labeled phages were used to infect nonradioactive Escherichia coli cells
After allowing sufficient time for infection to proceed, the residual phage particles were sheared off the cells
=> Phage ghosts and E. coli cells were separated via centrifugation
Radioactivity was monitored using a ______ ______
scintillation counter
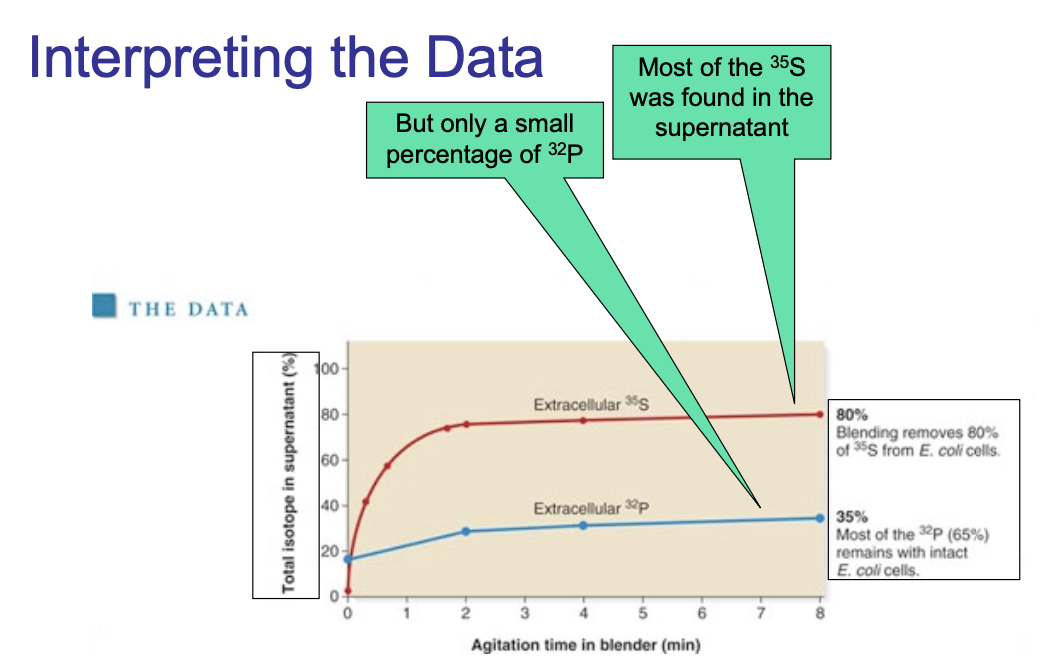
The results suggest that DNA is injected into the bacterial ____ during infection
This is the expected result if DNA is the genetic material
cytoplasm
Is it true that RNA functions as the genetic material in some viruses?
Yes
In 1956, A. Gierer and G. Schramm isolated RNA from the tobacco mosaic virus (TMV, a plant virus) which infects and causes lesions in plants
____ _____ caused the same lesions as intact TMV viruses
Therefore, the viral genome is composed of RNA
purified RNA
DNA and RNA are large _____ with several levels of complexity
macromolecules
1. ______ form the repeating units
nucleotides
Nucleotides are linked to form a ______
strand
Nucleotides form the repeating units
Nucleotides are linked to form a strand
Two strands can interact to form a _____ _____ (DNA) –remember RNA molecules are primarily single stranded
double helix
Is DNA double-stranded or single-stranded?
double-stranded
Is RNA double-stranded or single-stranded?
single-stranded
The double helix DNA folds, bends and interacts with proteins resulting in 3-D structures in the form of _______
chromosomes
The _______ is the repeating structural unit of DNA and RNA
nucleotide
The nucleotide is the repeating structural unit of DNA and RNA.
It has three components. What are they?
a phosphate group, a pentose sugar, a nitrogenous base
What is the sugar found in DNA?
deoxyribose
What is the sugar found in RNA?
ribose
What are the purines?
Adenine and Guanine
What are the Pyrimidines?
Thymine and Uracil and Cytosine?
Is uracil found in DNA?
No
Do purines have a double ring or single ring?
double ring
Do pyrimidines have a double ring or a single ring?
single ring
Is Thymine found in RNA?
No
Base + sugar + phosphate → ?
Example
Adenosine monophosphate (AMP)
Adenosine diphosphate (ADP)
Adenosine triphosphate (ATP)
nucleotide
Phosphate is always attached to the __’ side of the ribose
5’
Base is always attached to the ___’ side of the ribose
1’
The difference between ribose and deoxyribose is that ribose has an extra OH on the __’ side
2’
Nucleotides are ____ linked together by ____ bonds
covalently; phosphodiester
A phosphate connects the __’ carbon of one nucleotide to the _’ carbon of another.
5'; 3’
A strand has directionality ____’ to ___’
5’; 3’
A Few Key Events Led to the Discovery of the Structure of DNA
In 1953, James Watson and Francis Crick discovered the ____ _____ structure of DNA
The scientific framework for their breakthrough was provided by other scientists including:
Rosalind Franklin and Maurice Wilkins
Erwin Chargaff
double helical
Rosalind Franklin
She made marked advances in __-____ _____ techniques with DNA
x-ray diffraction
The _____ _____ Rosalind Franklin obtained suggested several structural features of DNA
Helical
More than one strand
10 base pairs per complete turn
diffraction pattern
Erwin Chargaff’s Experiment
Chargaff pioneered many of the biochemical techniques for the isolation, purification and measurement of nucleic acids from living cells
It was already known then that DNA contained the four bases: A, G, C and T
Chargaff analyze the _____ _____ of DNA in different species
base composition
The compelling observation was that
Percent of _____ = percent of ____
Percent of _____ = percent of _____
adenine; thymine, guanine; cytosine
Percent of adenine = percent of thymine
Percent of guanine = percent of cytosine
This observation became known as _____ _____
It was crucial evidence that Watson and Crick used to elucidate the structure of DNA
Chargaff’s rule
The DNA Double Helix
General structural features (Figures 9.17 & 9.18)
Two strands are twisted together around a common axis
There are __ bases and 3.4 nm per complete twist
10
The two strands are _________
One runs in the 5’ to 3’ direction and the other 3’ to 5’
antiparallel
The helix is ____-___
As it spirals away from you, the helix turns in a clockwise direction
right-handed
The DNA Double Helix
The double helix structure is stabilized by
1.) ______ bonding between _____ ____
n A bonded to T by two hydrogen bonds
n G bonded to C by three hydrogen bonds
hydrogen; complementary bases
The DNA Double Helix
The double helix structure is stabilized by
2. ______ interaction between bases
(Base stacking)
Within the DNA, the bases are oriented so that the flattened regions are facing each other
The planar surface of bases are hydrophobic (water insoluble
Hydrophobic
A bonded to T by ___ hydrogen bonds
2
G bonded to C by ____ hydrogen bonds
3
There are two asymmetrical grooves on the outside of the helix
1. ____ groove
2. ____ groove
major; minor
There are two asymmetrical grooves on the outside of the helix
1. Major groove
2. Minor groove
Certain proteins can bind within these grooves
They can thus interact with a particular sequence of ____
These proteins binding to the groves may alter DNA structure and regulate gene expression
bases
The DNA double helix can form different types of secondary structure
The predominant form found in living cells is ___-____
B-DNA
The DNA double helix can form different types of secondary structure
The predominant form found in living cells is B-DNA
However, under certain in vitro conditions, ___-DNA and __-DNA double helices can form
A; Z
Is A-DNA right-handed helix or left-handed helix?
right-handed
How many bp per turn does A-DNA have?
11 bp
A-DNA occurs under conditions of ____ ____
low humidity
Is A-DNA biologically important?
no, there is little evidence suggesting this
Is Z-DNA right-handed or left-handed?
left-handed
How many bp per turn does Z-DNA have?
12 bp
For Z-DNA, evidence from yeast suggests it may play a role in _____ and _____
transcription; recombination
In A-DNA, bases substantially ____ relative to the central axis
titled
In B-DNA, bases relatively ____ to the central axis
perpendicular
In Z-DNA, bases substantially ____ relative to the central axis
tilted
The Three-Dimensional Structure of DNA
To fit within a living cell, the DNA double helix must be extensively compacted into a 3-D conformation
This is aided by ____-____ _____
DNA-binding proteins
DNA double helix is compacted into a 3-D conformation by what?
DNA-binding proteins
DNA is wound around ____ proteins
histone
The primary structure of an RNA strand is much like that of a DNA strand
Compare Figures 9.16 & 9.7
RNA uses ____ as a base
uracil
RNA uses ____ (what sugar?) with ___’ ___ (what chemical)
ribose; 2’; OH
RNA strands are typically several hundred to several thousand nucleotides in length
In RNA synthesis, only ___ of the two strands of DNA is used as a template
one
Although usually ____-____, RNA molecules can form short double- stranded regions
single-stranded
Although usually single-stranded, RNA molecules can form short double- stranded regions
• This secondary structure is due to _____ ____-____
A to U and C to G
Allows short regions to form a double helix
complementary base-pairing