Clinical Assessment- Dermatology
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Functions of the integumentary system
-Protection
-Lipid storage
-Coordination of immune response
-Sensory information
-Vitamin D3 synthesis
-Excretion
-Thermoregulation
Parts of the integumentary system
-Epidermis
-Dermis (papillary layer and reticular layer)
-Hair follicles
-Exocrine glands
-Nails
2 layers of the dermis
Papillary Layer and Reticular Layer
Cells in the Epidermis
-Keratinocytes
-Melanocytes
-Langerhan's cells
Layers of the Epidermis (Superficial to Deep)
-Stratum corneum
-Stratum lucidum
-Stratum granulosum
-Stratum spinosum
-Stratum basale
-Basement membrane
How thick is the dermis?
1-4 mm
The ______________ contains blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, nerves, hair follicles, sweat glands, fibroblasts, and mast cells
Dermis
What do fibroblasts do?
Make and break down connective tissue proteins
What do mast cells do?
Involved in immune response to form allergy type symptoms
What is the subcutis (panniculus)?
Adipose layers that separate the dermis from fascia and muscles
What is a pilosebaceous unit?
A hair follicle, sebaceous gland, apocrine sweat gland, and arrector pili muscle
What does decreased skin turgor indicate?
Dehydration
What are examples of alarm symptoms?
-Diffuse erythema
-Fever
-Rapid evolution
-Blistering
-Grey/Purple/Dusky skin
-Sloughing
-S/s of anaphylaxis
Why are Wood's Lamps used?
-Disorders of pigmentation like melasma or vitiligo
-Tinea versicolor
-Tinea capitis
-Scabies or head lice
-Pseudomonas
What does Tinea Versicolor look like under a Woods Lamp?
May emit an orange glow
What does Tinea Capitis reveal under a Woods Lamp?
-Areas of baldness
-Blue-green glow if microsporum species
What does Pseudomonas look like under a Woods Lamp?
Fluorescent green
What is diascopy?
Firmly pressing a microscopic slide/glass spatula over a skin lesion to determine whether the red color of a macule or papule is due to capillary dilation or extravasation of blood that does not blanch
What is a KOH prep?
Potassium hydroxide prep used to microscopically identify fungi or yeast
What is dermoscopy?
Using a hand-held lens with magnification (a dermatoscope) to inspect deeper layers of the epidermis non-invasively
Can be used to distinguish between benign and malignant growth patterns in pigmented lesions
What is confocal microscopy?
A non-invasive imaging technique that enables in vivo visualization of the epidermis down to the papillary dermis in real-time
What patient positioning is best for a full skin examination?
Prone
What is a macule?
A flat, non-palpable lesion less than 1.0 cm in size
What is a papule?
A raised, palpable growth less than 1.0 cm in size
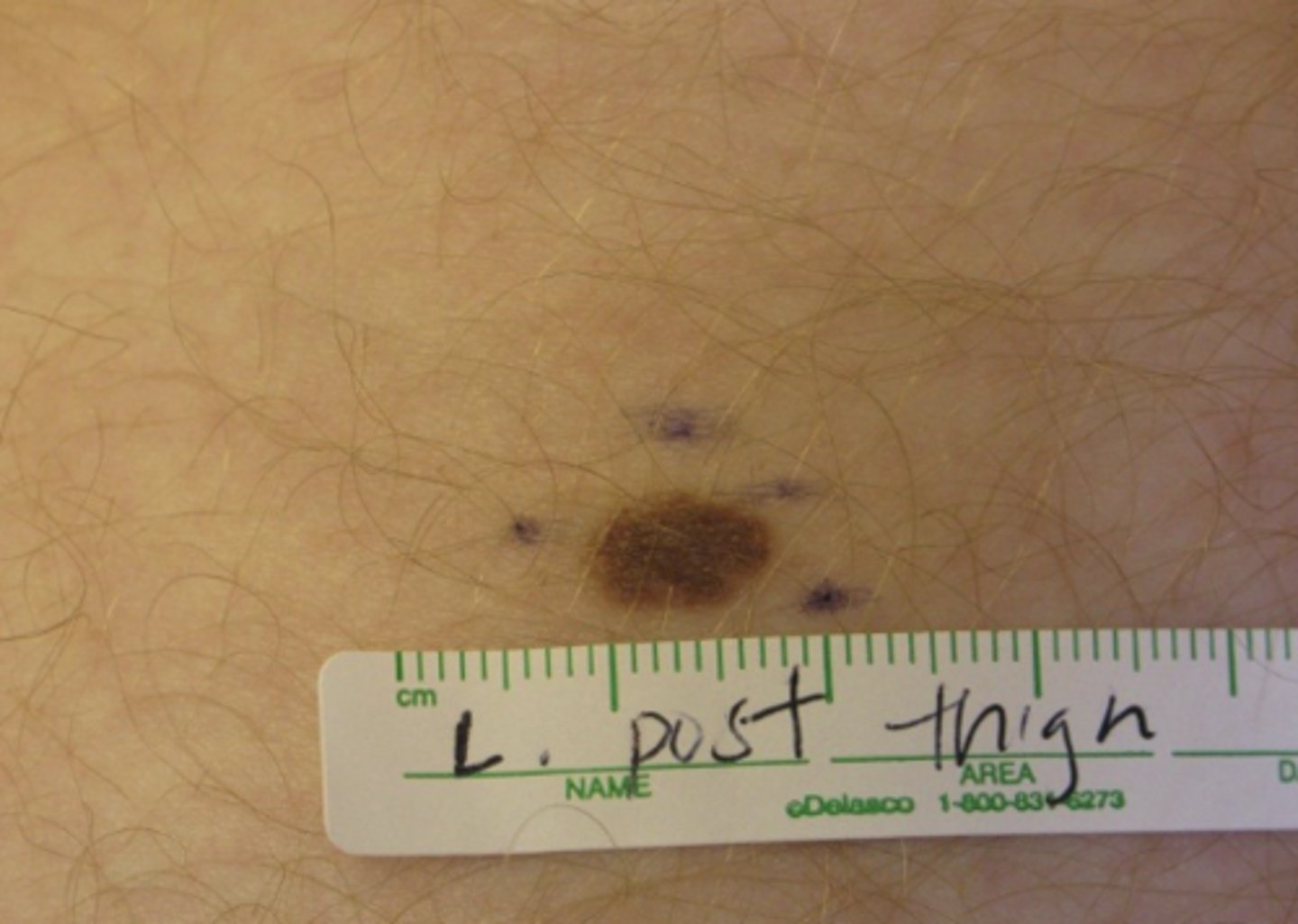
What is a plaque?
A raised, palpable growth greater than 1.0 cm in size
*Number and location are keys to diagnosis
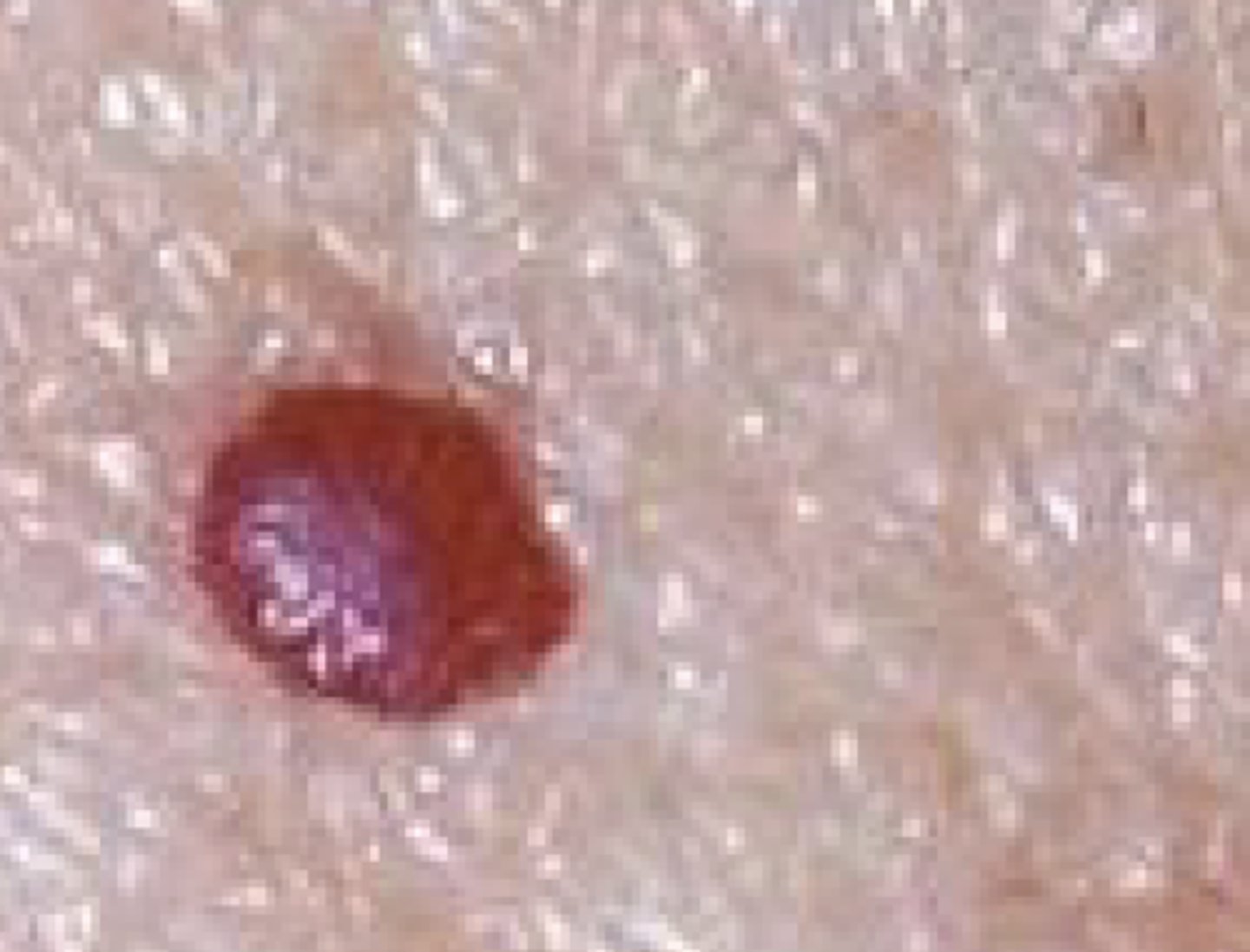
What is a nodule?
A raised, solid lesion greater than 1.0 cm that may occur in the epidermis, dermis, or subcutaneous tissue
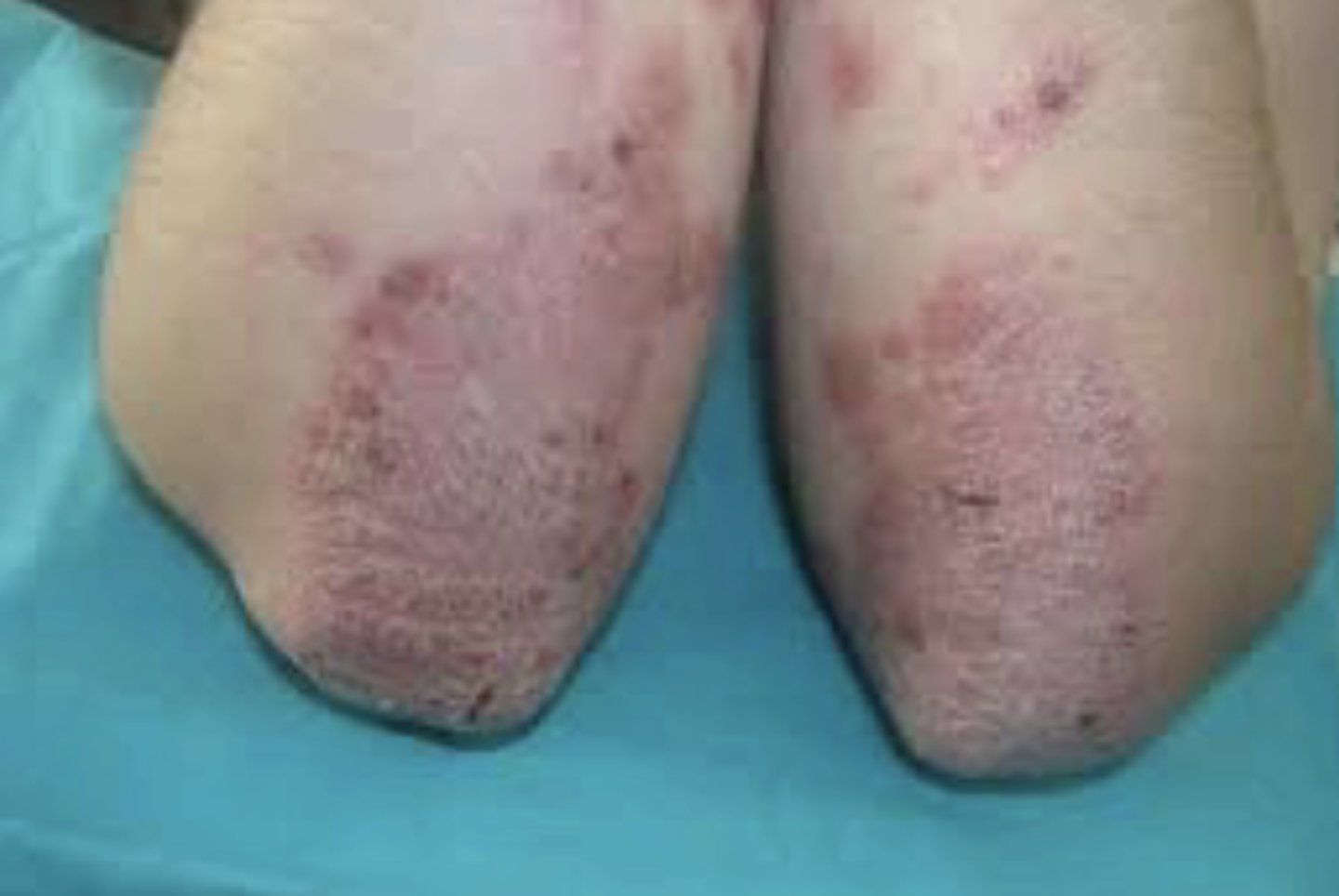
What is a vesicle?
A fluid filled, raised growth less than 1.0 cm in size
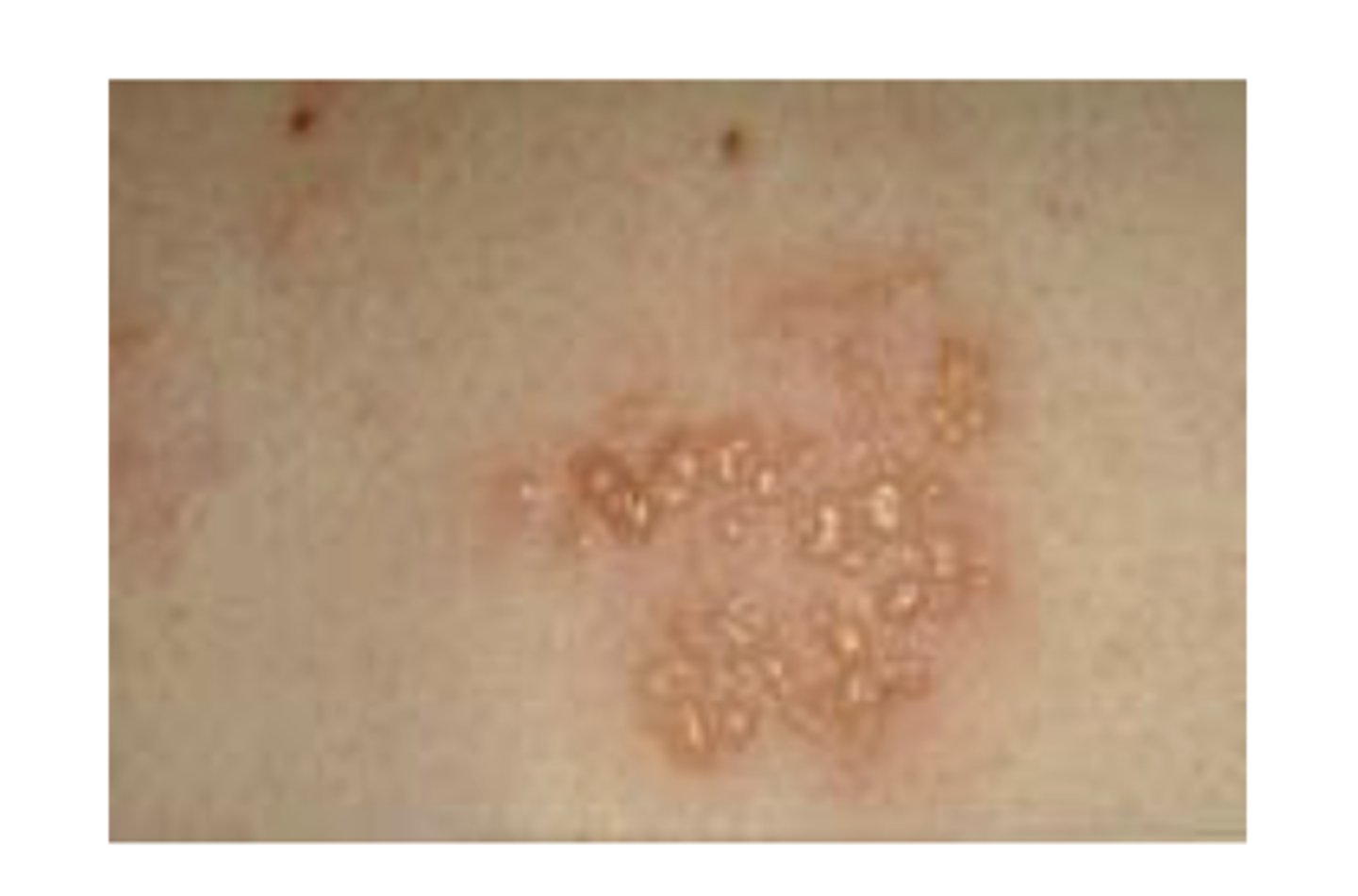
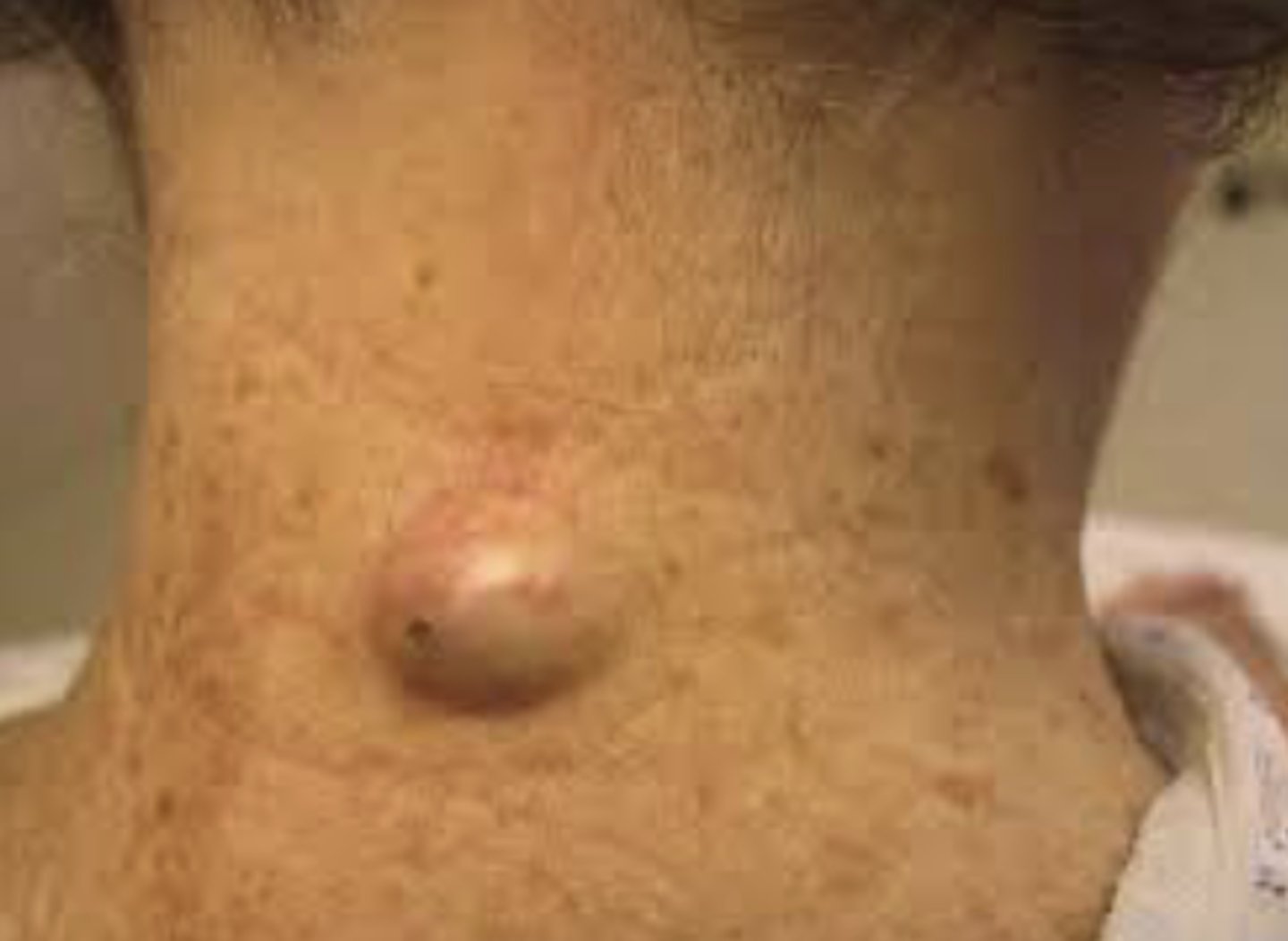
What is a bulla?
A raised, fluid filled growth greater than 1.0 cm
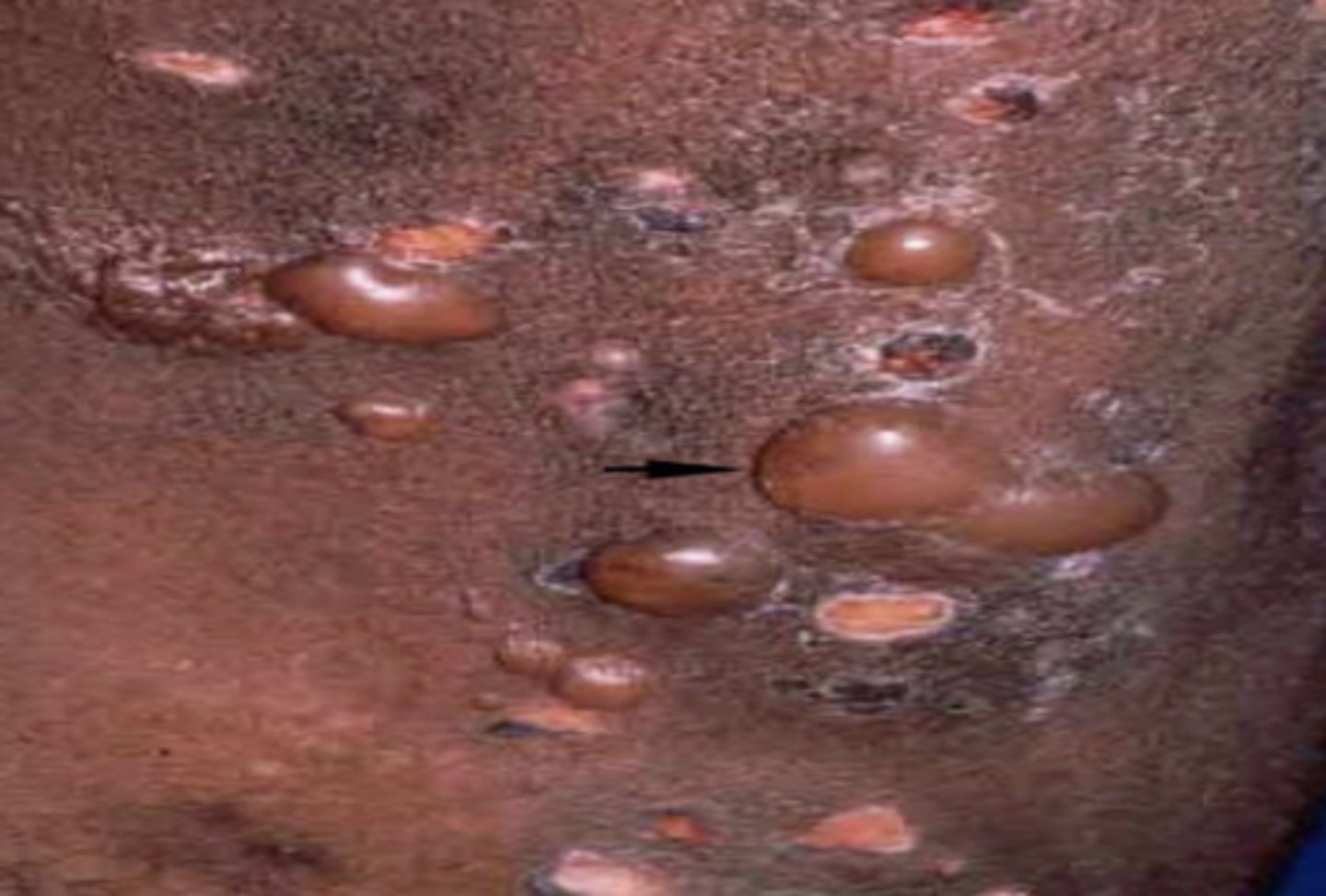
What is a pustule?
A papule with a pus filled center
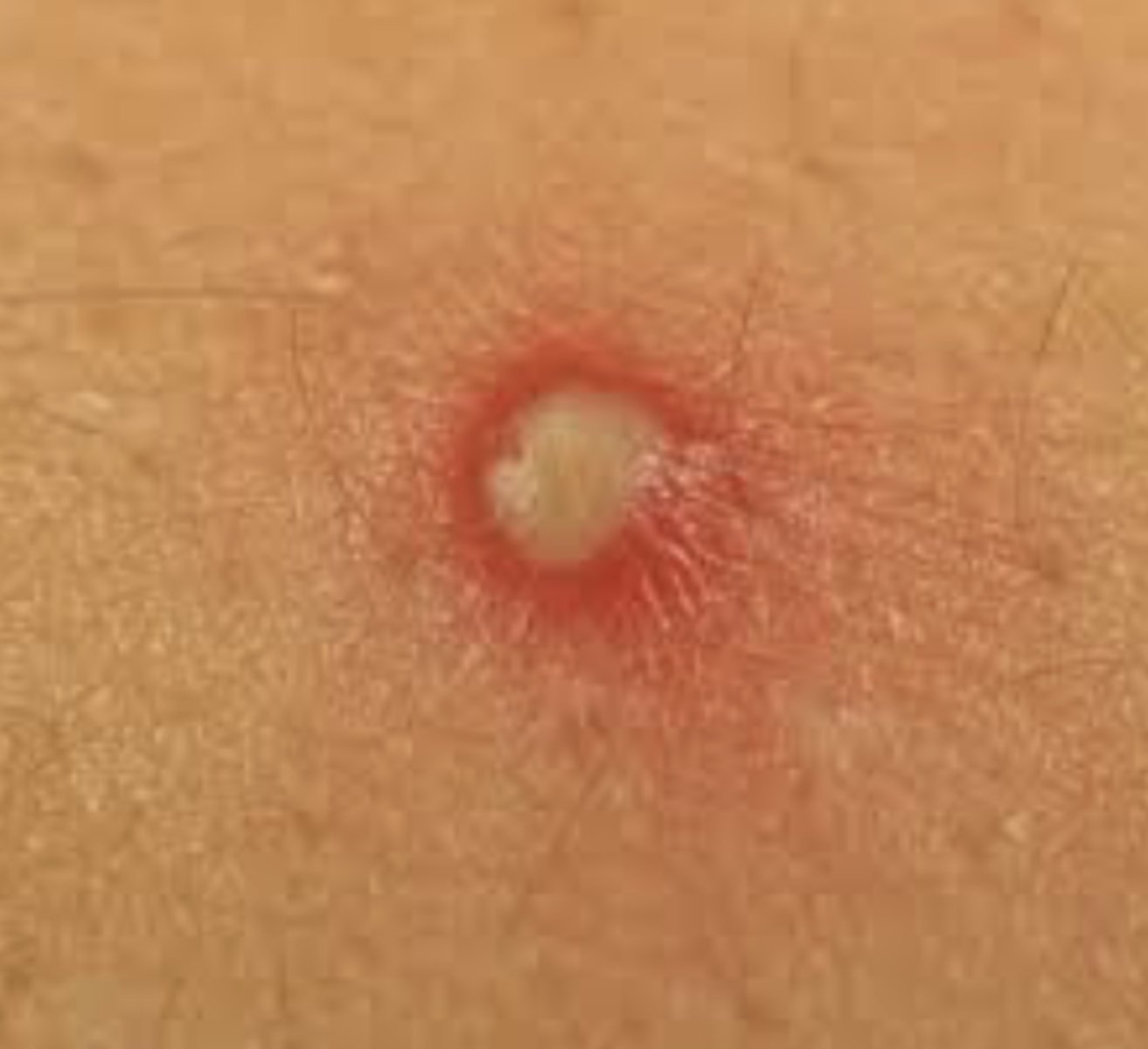
What is a wheal?
Compressible, raised edema that is typically itchy-- hives
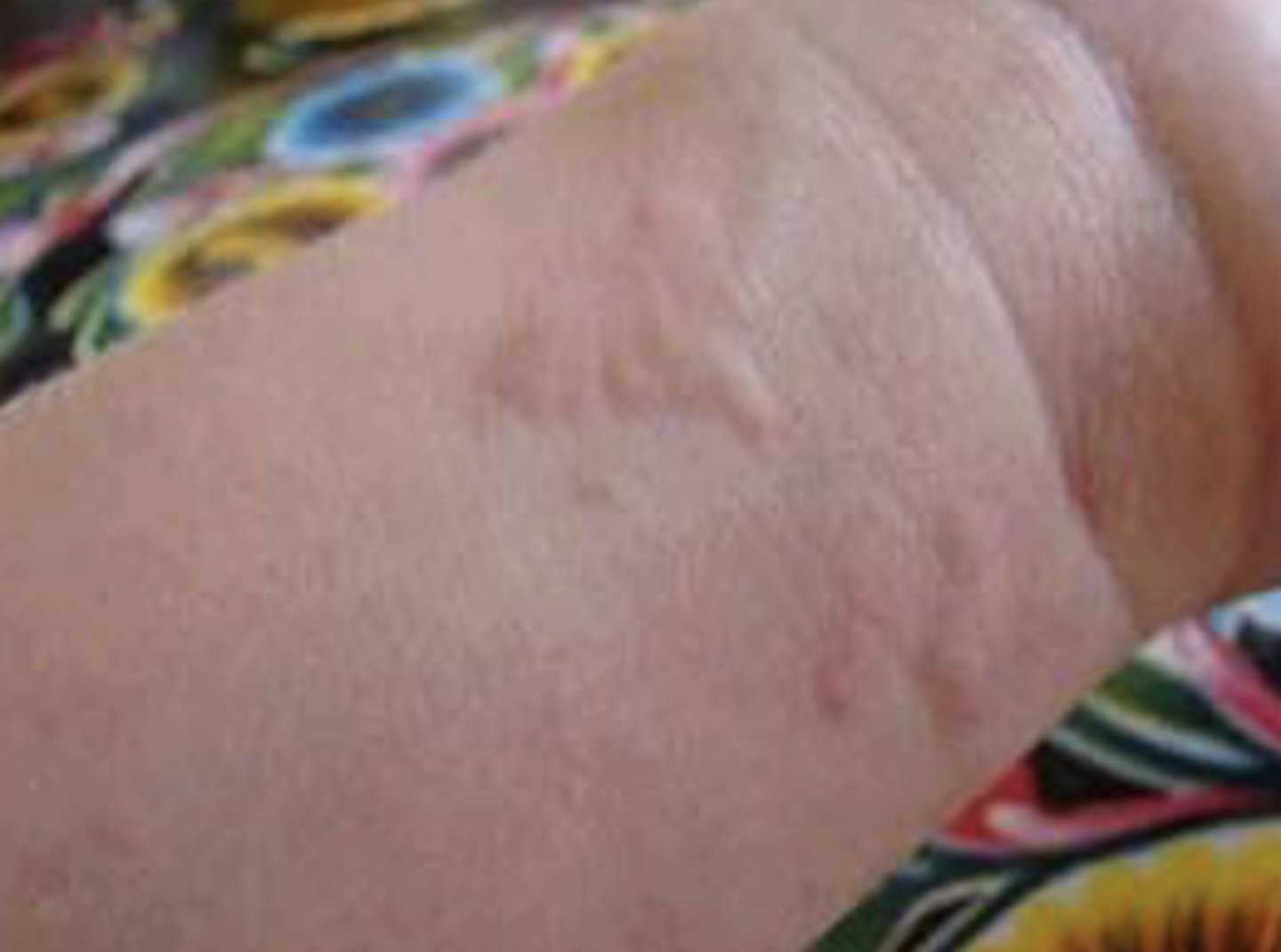
What is a scale?
Flakes of cornified skin layer
What is an erosion?
Loss of superficial epidermis with little to no bleeding
What is an ulcer?
Loss of the epidermis and dermis
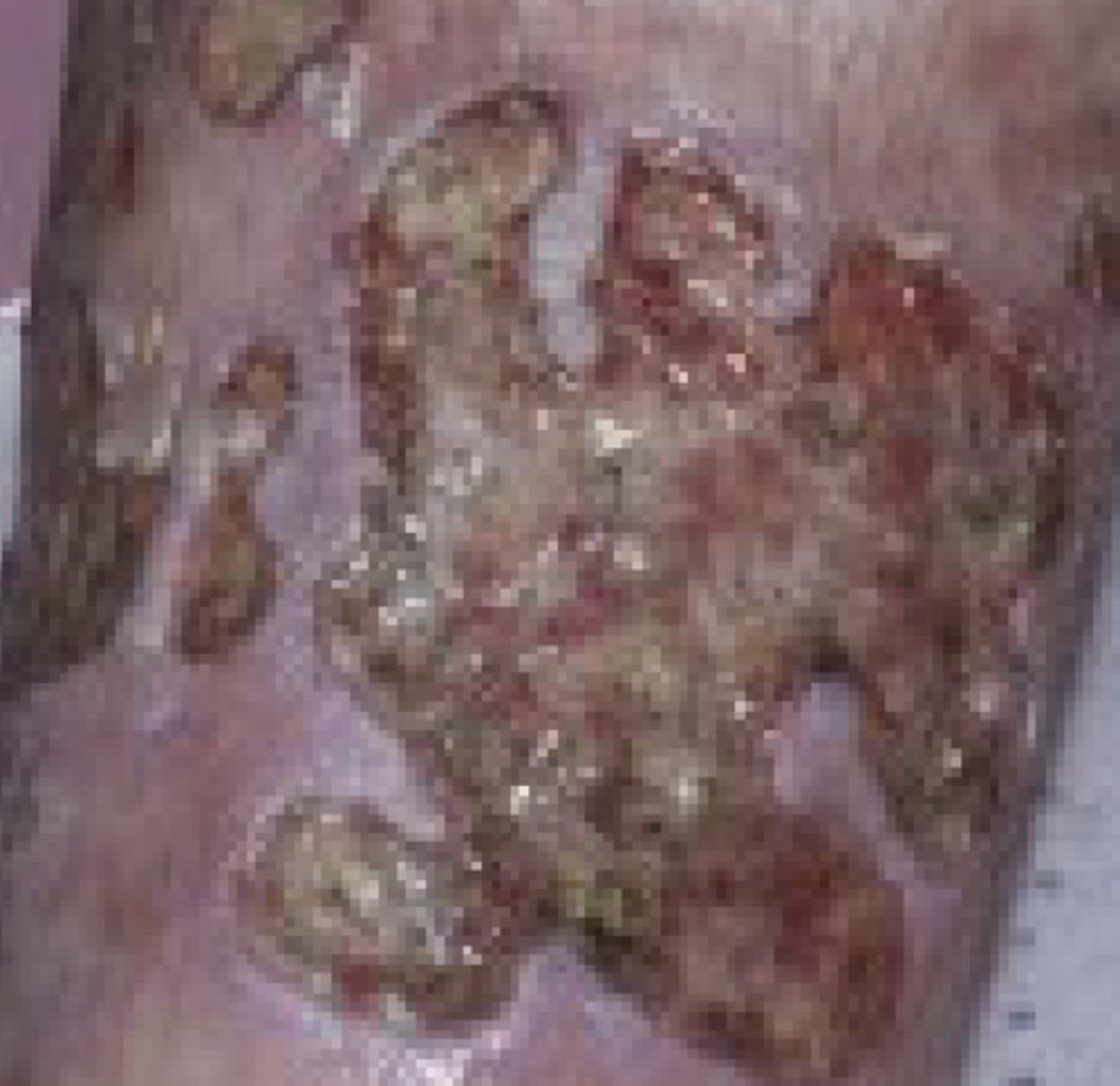
What is a region of excoriation?
A region of ulceration that has been caused by scratching; is often linear
What is a region of lichenification?
An area of thickened, leathery skin that results from chronic rubbing or scratching
What is a fissure?
A crack in the skin
What is a telangiectasia?
An area of prominent blood vessels
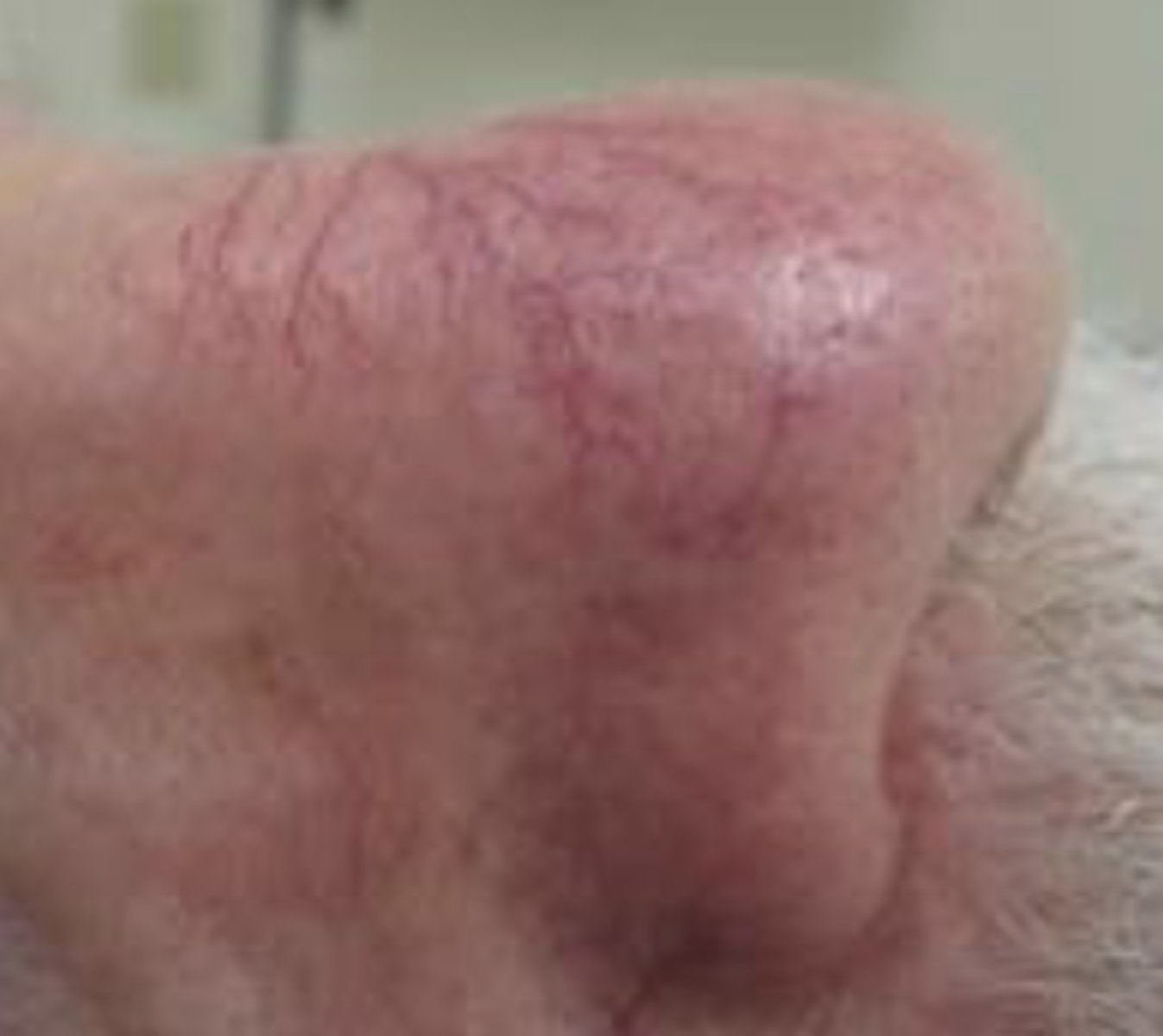
What is a patch?
A flat, non-palpable lesion > 1.0 cm in size
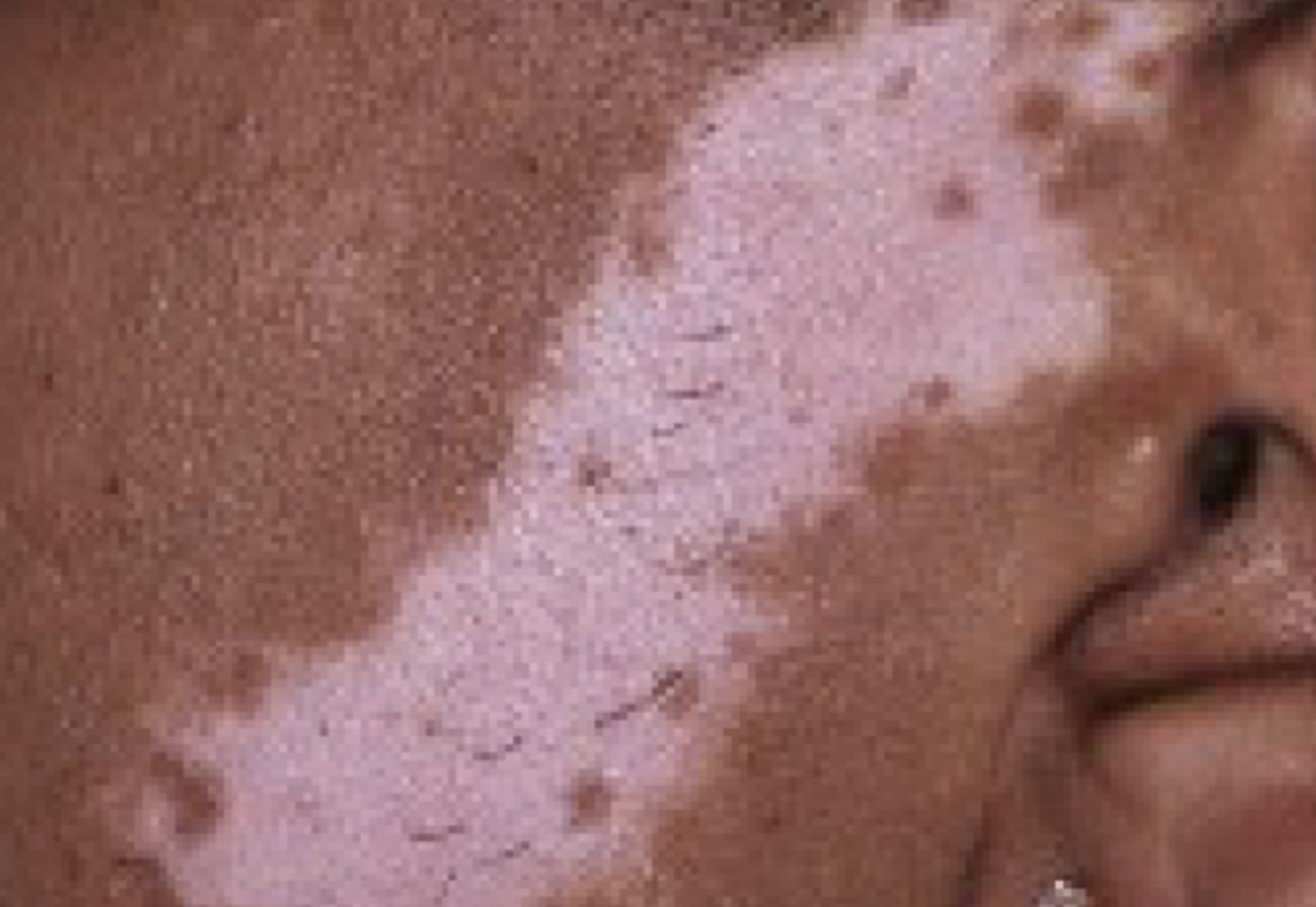
What is a cherry angioma?
A benign, tiny, vascular growth that occurs with aging
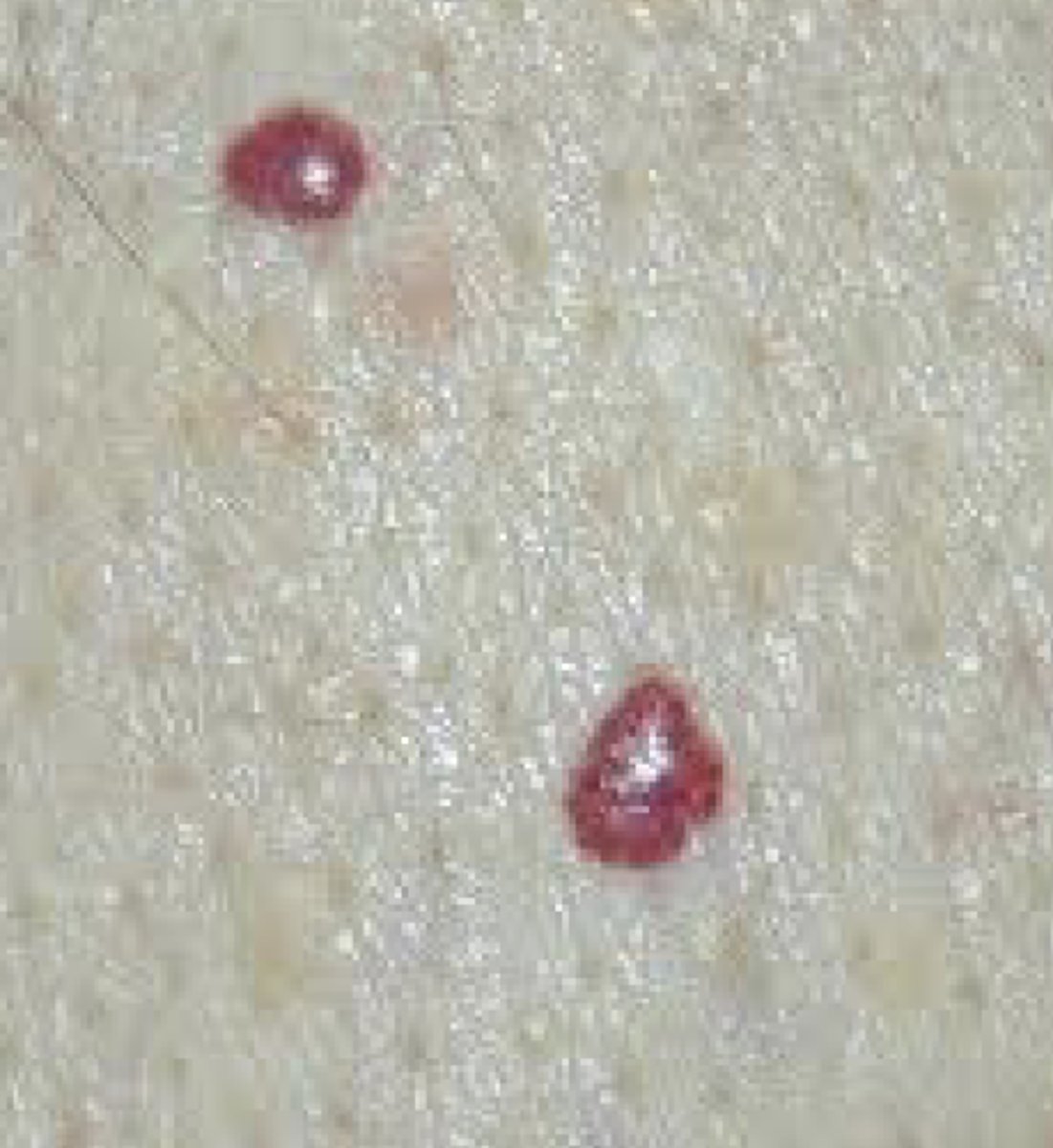
What are petechiae?
Pin point (1-2 mm) red or purple papule or macule caused by hemorrhage
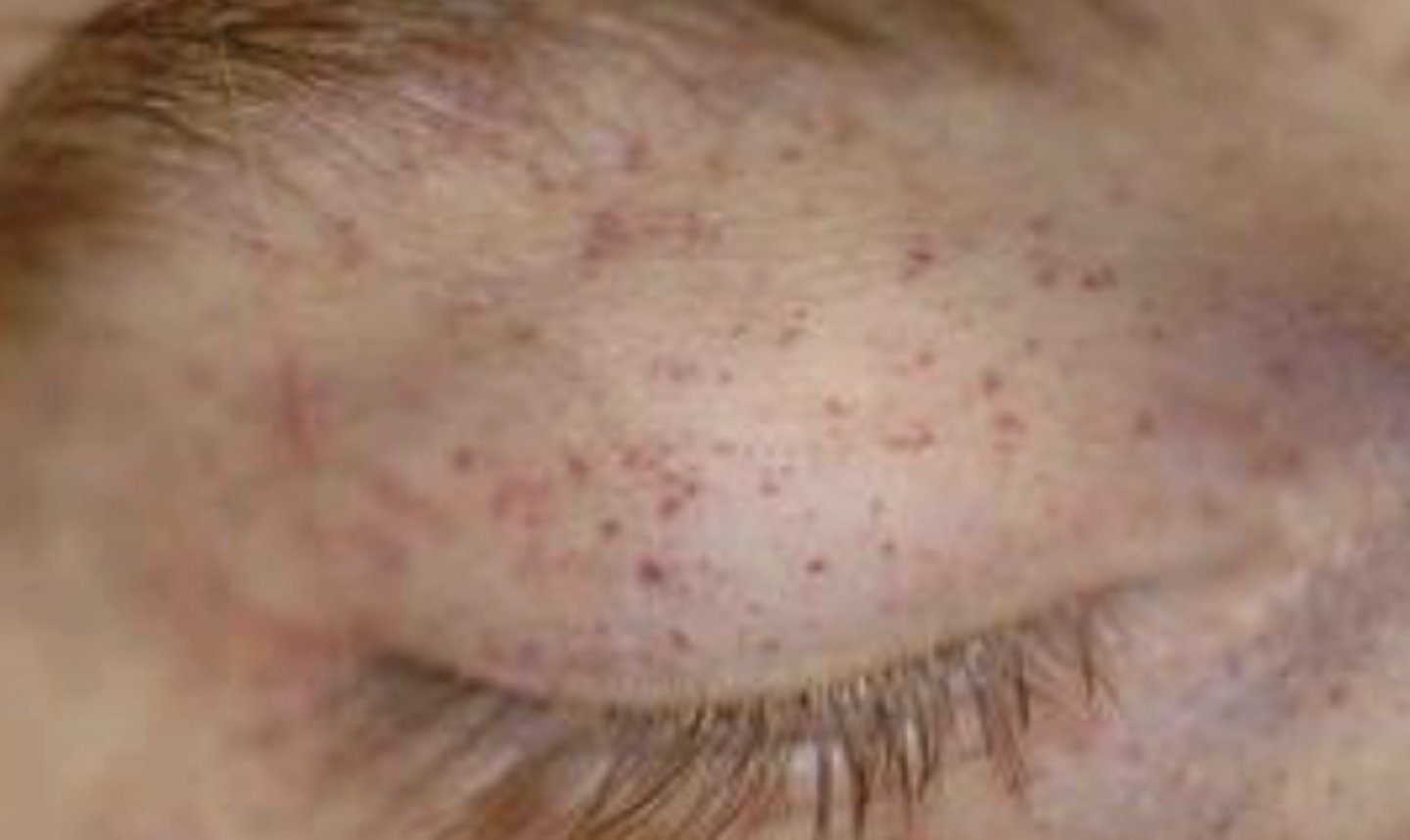
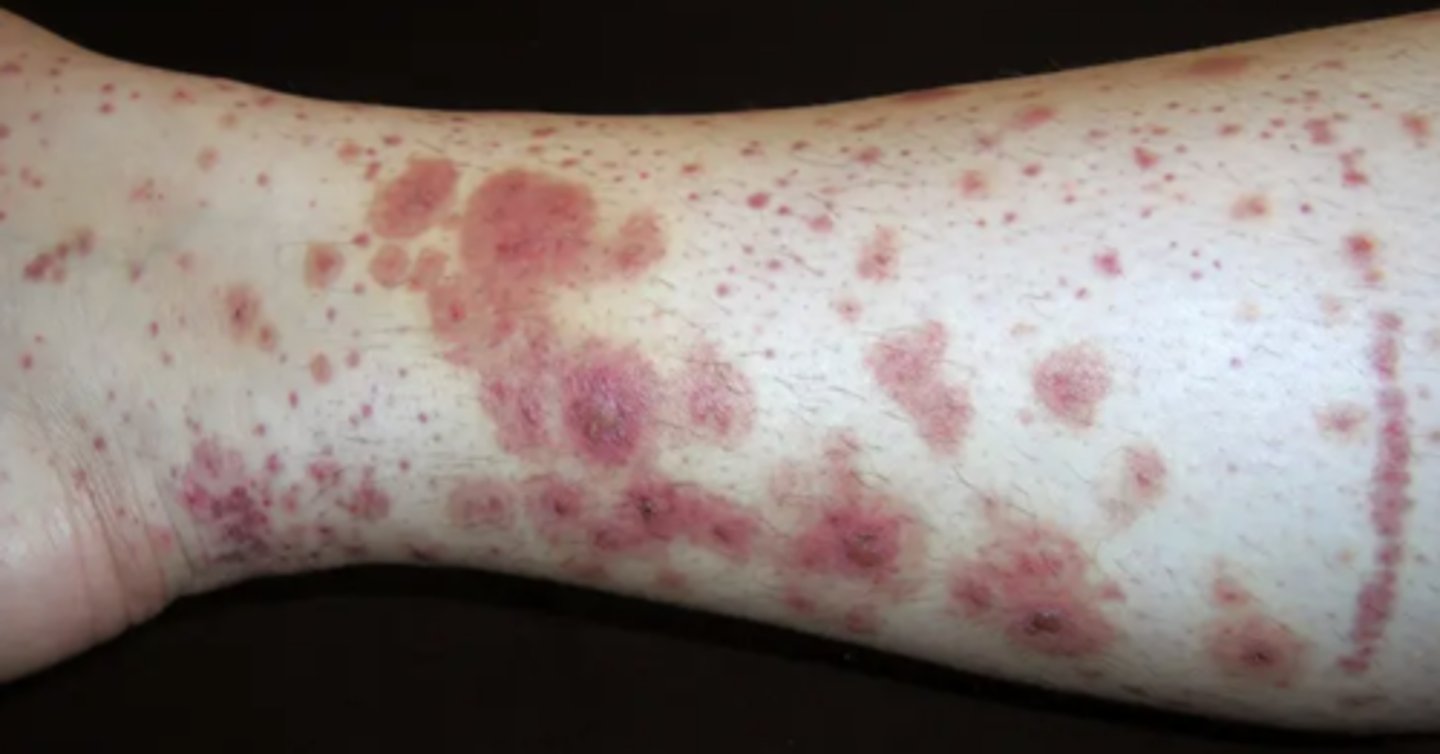
What are purpura?
Non-palpable, non-blanching violaceous discoloration of the skin
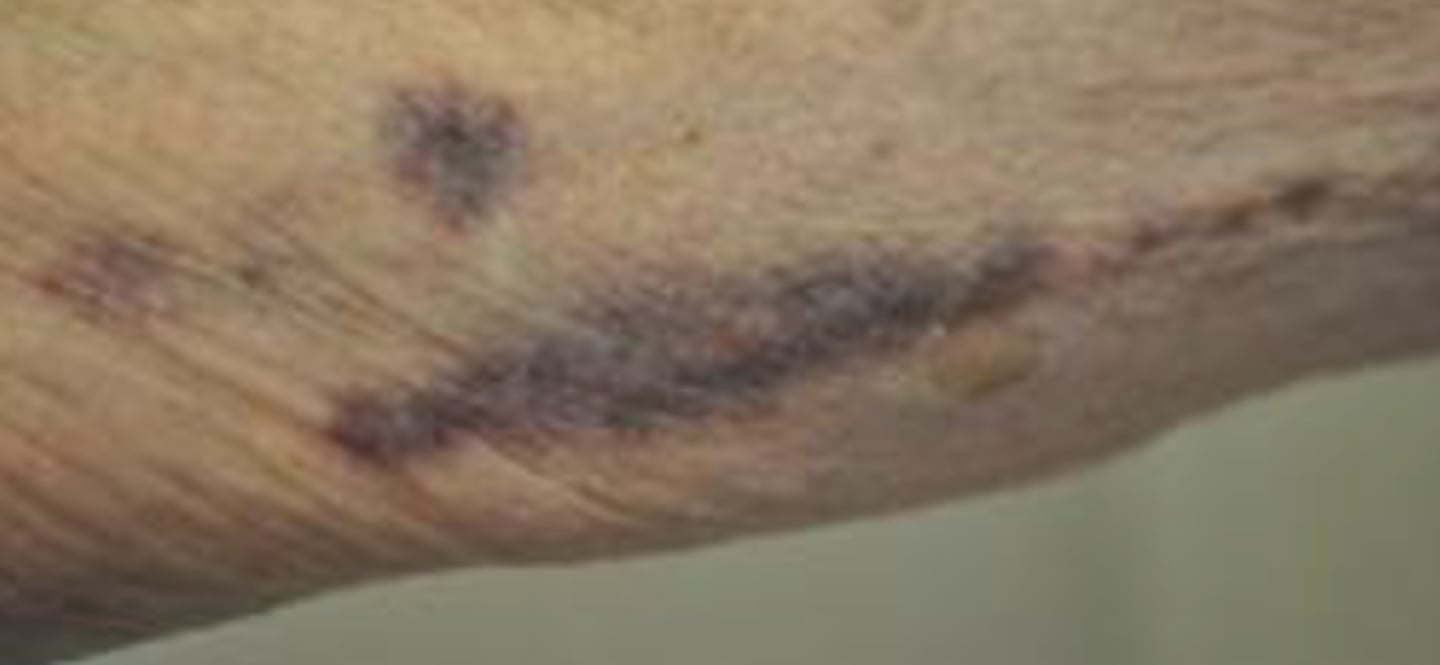
What is ecchymosis?
Individual bruising
What is a tumor?
A solid mass, larger than 1.0 cm
What is atrophy?
Loss of some portion of the skin
What does serpiginous mean?
Snake-like
What does annular mean?
Circular with central clearing
What does umbilicated mean?
Having a central dimple
What does morbilliform mean?
Rosy, maculopapular
What are examples of macules?
-Nevi
-Melanomas
-Superficial basal cell carcinomas
-Freckles
-Lentigines
What are examples of patches?
-Melanoma
-Cage au lait spots
-Vitiligo
-Superficial basal cell carcinomas
What are examples of papules?
-Nevi
-Neurofibromas
-Cherry angiomas
-Seborrheic keratoses
-NMSCs
-Nodular melanomas
-Actinic keratoses
-Dermatofibromas
What are examples of plaques?
-Non-melanoma skin cancers
-Psoriasis
-Eczema
-Lichen simplex chronicus
-Granuloma annulare
What are examples of pustules?
-White heads
What are examples of vesicles?
-Herpes
-Chicken pox
-Contact dermatitis
What are examples of nodules?
-Cysts
-Lipomas
What are examples of bulla(e)?
-Blisters
What are spider angiomas?
A telangectasia with a central red circle and small vessels branching from it
What are the 4 phases of the hair growth cycle?
1. Anagen--> growth phase
2. Catalan--> transition phase
3. Telogen--> exogenous shedding phase
4. Hair falls out and new anagen forms
90% of hairs on the scalp are in what growth phase?
Anagen phase
What is the male androgenetic hair loss pattern?
Frontal receeding, hair loss around the temples, formation of an "M" shape
What is the female androgenetic hair loss pattern?
Gradual thinning from the crown down
What is areata?
Sudden onset of well defined, localized round or oval patches of hair loss without scarring
What is the most common infection of the hand?
Paronychia
What is clubbing?
Bulbous swelling of the soft tissue at the nail base with loss of the normal angle between the nail and the proximal nail fold
What is melanonychia?
Pigmented streaks in the nail plate
What is onycholysis?
A painless separation of the whitened opaque nail plate from the pinker translucent nail bed
What is onychomycosis?
Most common fungal infection of the nail plate that causes nail thickening and subungual debris
What is Hutchinson's sign?
Pigment changes in the eponychium seen with subungual melanoma
What is the best prevention of Onychonycosis?
Treat and prevent tinea pedis
What are risk factors for melanoma?
-Red or blonde hair
-Light (blue/green) eyes
-Easily burnt/history of sunburns
-Family history of skin cancer
-History of pre-cancers or actinic keratoses
-History of UV exposure
-High number of nevi
What is the biggest cause of skin cancers?
UV radiation
What are the ABCDEs of melanoma?
-Asymmetry
-Borders, irregular
-Color, dark black/multicolored/red and pigmented
-Diameter, > 5 mm
-Evolving
What is the EFG criteria for nodular melanomas?
-Elevated
-Firm
-Growing/continuous growth for 1 month
What are the ABCDs of pediatric melanoma?
-Amelanotic
-Bleeding bump
-Color uniformity
-Any diameter
Why and when is local anesthesia used during dermatology procedures?
Provides reversible blockade of nerves leading to loss of pain sensation
Used in repair of lacerations, skin surgery, treatment of painful oral or genital lesions, and in removal of superficial lesions
Are amides long or short acting?
Long acting
Are esters long or short acting?
Short acting
Where are amides metabolized?
Liver
Where are esters metabolized?
Plasma and tissue fluids
Where are amides excreted?
In the urine
Where are esters excreted?
Urine
What are examples of amides?
-Lidocaine
-Bupivacaine
-Mepivacaine
-Prilocaine
What are examples of esters?
-Benzocaine
-Procaine
-Cocaine
-Tetracaine
Why is epinephrine added to lidocaine?
Increases lidocaines duration of action by 60-180 minutes
What does epinephrine do?
Aids with vasoconstriction, reduces systemic absorption of the amide/ester it is combined with, and shortens the onset of action
What are absolute contraindications to epinephrine use?
-Untreated hyperthyroidism or pheochromocytoma
-Severe hypertension and CAD
-Periorbital infiltration in patients with narrow angle glaucoma
-Patients taking ergot-containing medications
What are side effects of epinephrine use?
-Cardiac dysrhythmia
-Increased blood pressure
-Anxiety
-Ischemia
*Mainly occur due to injection directly into a vessel
What can be used as a buffer to prevent burning with local anesthetic use?
Sodium chloride
*Can degrade epinephrine
What are common side effects of allergies/sensitivities to local anesthetics?
-Bruising
-Edema
-Prolonged nerve damage
-Temporary motor nerve paralysis
Why are skin biopsies done?
To determine the cause of a lesion or condition, to remove a lesion, or both
What are the types of skin biopsies?
-Shave
-Saucerization (deep shave)
-Punch
-Incisional
-Excisional
What is a shave biopsy?
The horizontal shave of a skin lesion that can be superficial or deep
What conditions indicate a shave biopsy?
*Good for elevated lesions
-Skin tags
-Papillomatous nevi
-SKs
-Areas of tension
-Areas where hypertrophic scars are common
When should shave biopsies not be used?
When a patient is on a blood thinner, has a defibrillator, or pacemaker
What is saucerization?
A "scoop shave"; tangentially removing a lesion in its entirety by extending more deeply into the dermis and providing clinically clear 1-2 mm margins
Saucerization is considered a _____________ biopsy
Excisional
What is the gold standard for biopsy of melanomas?
Excisional biopsy; allows the entire lesion to be examined
Punch biopsy is considered a _____________ biopsy
Incisional
When are sutures indicated?
-Hemostasis
-Reduce likelihood of infection
-Decrease amount of scar tissue
-Repair loss of structure, function, or both
-Improve cosmetic appearance
To minimize infection and scar potential, wounds should be closed within _____________ of the injury
8 hours