restorative procedures for primary dentition 1
1/46
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
47 Terms
what are the important reasons to restore primary teeth
quality of life (child/carer)
space maintenance (hold onto C and E)
unpredictable rate of caries progression/arrest
prevent extractions - MH (medical contraindications e.g. delayed healing, endocarditis)
why is the rate of caries faster in primary teeth
enamel is thinner therefore caries reaches dentine faster
from dentine = faster spread of caries
what are less important reasons to restore primary teeth
patient education/acclimatisation
aesthetics
parent wishes
what are the effects to the quality of life
may lead to pain, infection
affects child’s ability to speak, eat, play, learn, socialise, sleep
affects confidence
time away from school = fall behind with learning
parent/carer need to take time of work = financial impact
impact greater amongst socially/economically disadvantaged
what are the financial implications
march 2019 = almost 90% hospital tooth extractions in 0-5 yrs was due to decay
commonest reason for hospital admission in 6-10 yrs
cost to NHS = £50.9 million due to decay
what was the fiction trial
began in 2008
multi centre RCT
7 locations across UK, 72 dental practices
1058 children, 3-7 yrs
atleast 1 primary molar with caries into dentine
what did the fiction trial test for and what was the conclusion
testing 3 approaches to caries management:
conventional restoration and prevention (inc LA)
biological management and prevention (no LA)
prevention alone
conclusion = no evidence of difference in outcomes
what to consider when deciding whether to restore or remove a primary tooth
the child (cooperative?)
the tooth
the disease (extent? pulp involvement?)
what other thing should be considered when deciding to restore/remove tooth
time of exfoliation (check radiographs)
site and extent of lesion (restorability/remaining sound tooth tissue = saucer shaped tooth = not restorable)
risk or presence of pain/infection
number of teeth affected
childs cooperation /access /moisture control
parents wishes/ demands
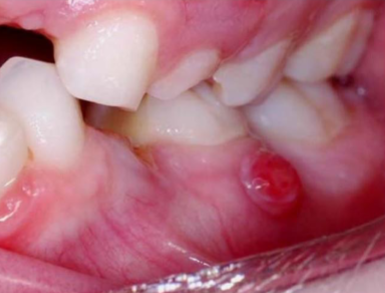
what to do if a patient presents with this
need to extract tooth or else infections wont heal
what is the worst case of keeping a tooth with infection
sepsis = infection travels to the blood stream
what to do at each appointment for caries recognition
check prescription from dentist
check history (clinical symptoms)
extra-oral (facial swelling)
intra-oral (visual, radiographs)
how to do a visual exam
consider position of child (baby pts = knee-to-knee, or pts head on parents arm)
teeth must be dry and clean
good lighting
know what is normal
posterior bitewings radiographs
essential adjunct to clinical examination
should be considered even for pre-school children
necessary for detection of approximal caries
risk assessment required first
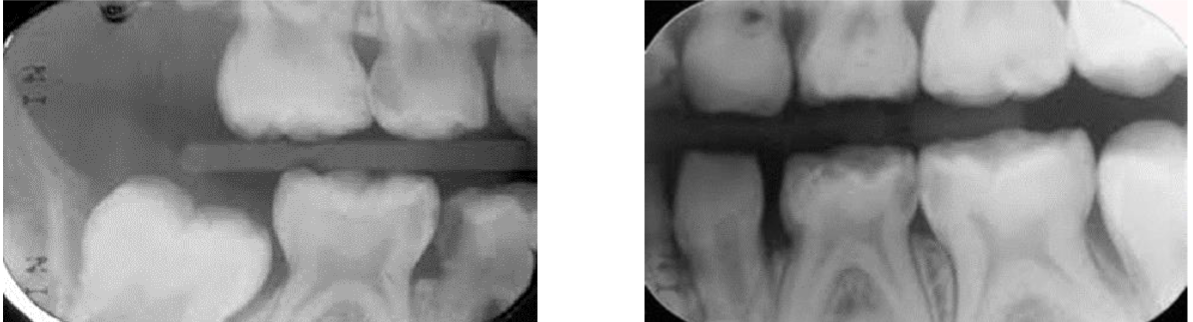
how many lesion are there
patient 6 yrs ? = 6 not fully erupted
if theres a cavity on distal of D = do radiographs as might find cavity in mesial of E
what are some other methods of caries detection
fibre optic transillumination
electrical caries detection tools
laser fluorescence device
what are the non restorative options for carious primary teeth
site specific prevention
non-restorative cavity control
extraction
what are the restorative options for carious primary teeth
no caries removal restorations (preferred method for primary teeth)
selective caries removal and restoration
complete caries removal and restoration
what is the aim of site specific prevention
to stop progression of caries and promote remineralisation
its non-invasive so acceptable to children
relies on behaviour change (parents need to be on board)
what is site specific prevention suitable for
early carious lesion on occlusal or proximal surfaces (in enamel)
early carious lesion on an anterior tooth
arrested lesions
teeth close to exfoliation (+ asymptomatic = leave tooth alone)
what is the process of site specific prevention
highlight lesion
agree process (parent accepts responsibility)
apply preventative measures (TBI, diet advice, fluoride varnish 3 monthly, silver diammine fluoride 6 monthly)
record
review (every 3 months)
what is silver diamine fluoride
non-AGP
non-invasive (MID)
used ‘off-label’ (used for somethings its not designed for)
duraphat = fluoride varnish = used for caries prevention
in UK prescribed silver diamine fluoride = used for dentine sensitivity NOT caries prevention
decribe what silver diamine fluoride is
clear, odourless liquid
silver = antibacterial
fluoride = remineralisation of enamel
NOT licensed in the UK for caries prevention
commonly 38%
44,800 ppm
pH 13 (protect soft tissues with vaseline)
how is silver diamine fluoride used
applied similar way to fluoride varnish
review after 2-4 weeks (if caries not arrested then reapply and then review in 6 months)
applied 6 monthly
what are the issues with using silver diamine fluoride
bad taste = apply toothpaste to child tongue
turns teeth/decay black (aesthetics and warn patient/carer beforehand)
need written consent (consent form 2)
temporary staining of clothes and soft tissues
what is the aim of the non restorative cavity control
to reduce the cariogenic potential of the lesion
non-invasive
relies on behaviour change
lesion needs to be cleansable
what is the process of the non restorative cavity control
highlight lesion
agree process (parent accepts responsibility)
make lesion cleansable
apply preventative measures (TBI, diet advice, fluoride varnish 3 monthly, SDF 6 monthly)
record
review
how is the lesion made cleansable
open cavity
remove overhang enamel
show parent how to get toothbrush to clean
make the cavity a dish shape
what are the different restorative materials
preformed metal crowns *
amalgam
composite *
glass ionomer
compomers
fissure sealants *
*for paediatric patients
is amalgam used in paediatric patients
not used in primary teeth
minimata treaty = phasing down of using amalgam due to environmental pollution from mercury
caveat = can use amalgam but unless deemed necessary by practitioner on the ground of specific medical needs
which patients are not allowed to have amalgam
pregnant and breastfeeding
<16 years old
what is the aim of no caries removal
to completely seal the lesion from the oral environment to slow/ arrest progression
what are the 2 different options for no caries removal
hall technique
fissure sealants
what is the hall technique suitable for
suitable for advanced occlusal or proximal lesions (cavitated lesions?)
what are fissure sealants suitable for
suitable for non-cavitated occlusal or proximal lesions (caries only in enamel)
what is the aim of selective caries removal
to remove sufficient carious tissue to enable an effective marginal seal with a bonded adhesive material
which patients is the selective caries removal suitable for
suitable for advanced occlusal lesions
reduced risk of pulpal exposure
reduced time for cavity prep
may not require LA
what are the 2 techniques for selective caries removal
conventional or ART (MID)
what is the conventional technique for caries removal
access caries using highspeed hand speed (LA needed)
remove superficial caries until ADJ is clear (slow speed bur)
clear cavity wall until hard and scratchy
ensure efficient depth for restoration placement
remove undermined enamel
place adhesive, bonded restoration
fissure seal over top (stops ingress of bacteria)
what is the atraumatic restorative technique (ART)
removal of carious tissue ONLY using hand instruments
no need for LA
can be used for stabilisation
conserves sound tooth tissue
restored with GIC
which lesions is the ART technique suitable for
only for occlusal lesion (NOT MO/DO)
can be used to treat rampant caries to stabilise it before proper treatment
describe the ART technique
ensure instruments are sharp
isolate with CWR
enlarge access if required
scoop out soft caries (excavator)
clean and dry cavity with CWP
restore with GIC using finger pressure
cover with vaseline (waterproof it)
avoid eating for 1 hour
what is the aim of complete caries removal
to remove all infected carious tissue and restore function
which patients is complete caries removal suitable for
suitable for advanced occlusal or proximal lesions
is the complete caries removal technique preferred
there’s higher risk of pulpal exposure
requires LA, high speed handpiece and good moisture control
more demanding for child and clinician
hence other techniques preferred (Hall technique)
when is the Hall technique used
no pulp involvement
no infection
early lesion (only in enamel)
describe the complete caries removal process
deliver LA
apply rubber dam
access cavity
remove caries (careful of pulp)
apply matrix if needed
line cavity if close to pulp
restore with composite