EU2 Module 1,2
1/116
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
117 Terms
Surface Water
Is the rain that runs off the surface of the ground into streams, rivers, and lakes
Groundwater
Is water found below the surface of the Earth. It is water that has percolated through porous soil until it reaches an impervious stratum, upon which it collects.
Potable Water
Is clean water that is suitable for human drinking, cooking, and cleaning.
Non-Potable Water
Used for flushing toilets, irrigating, carwash, and for any use other than drinking, cooking, and cleaning.
Surface Water
Readily provides much of the water needed by cities, counties, large industry, and others. However, this source is dependent on recurring rain and treated to provide potable water. During a long period of drought, the flow of water may be significantly reduced.
Reservoirs
Hold surface water during periods of high run-off and release water during periods of low run-off.
Cistern
A storage tank where surface water or rainwater can be collected as it drains from the roof o a building or a more elaborate collection system.
Permeable Stratum
A layer of porous earth that water can pass through such as sands, gravels, or basalt.
Aquifer
Is a saturated permeable stratum that is capable of providing a usable supply of water or an underground reservoir with almost unlimited capacity.
Water Table
It is referred to the level of groundwater.
Groundwater Potability
Groundwater may require treatment to be potable, but often it does not. When treatment is required, it is generally less treatment than is required when making surface water potable.
Types of Water Quality
Chemical, Physical, and Biological
Chemical Quality
Chemical parameters can include pH, acidity, alkalinity, chlorine, hardness, dissolved oxygen, and biological oxygen demand.
Calcium and Magnesium
2 Chemicals in a Hard Water
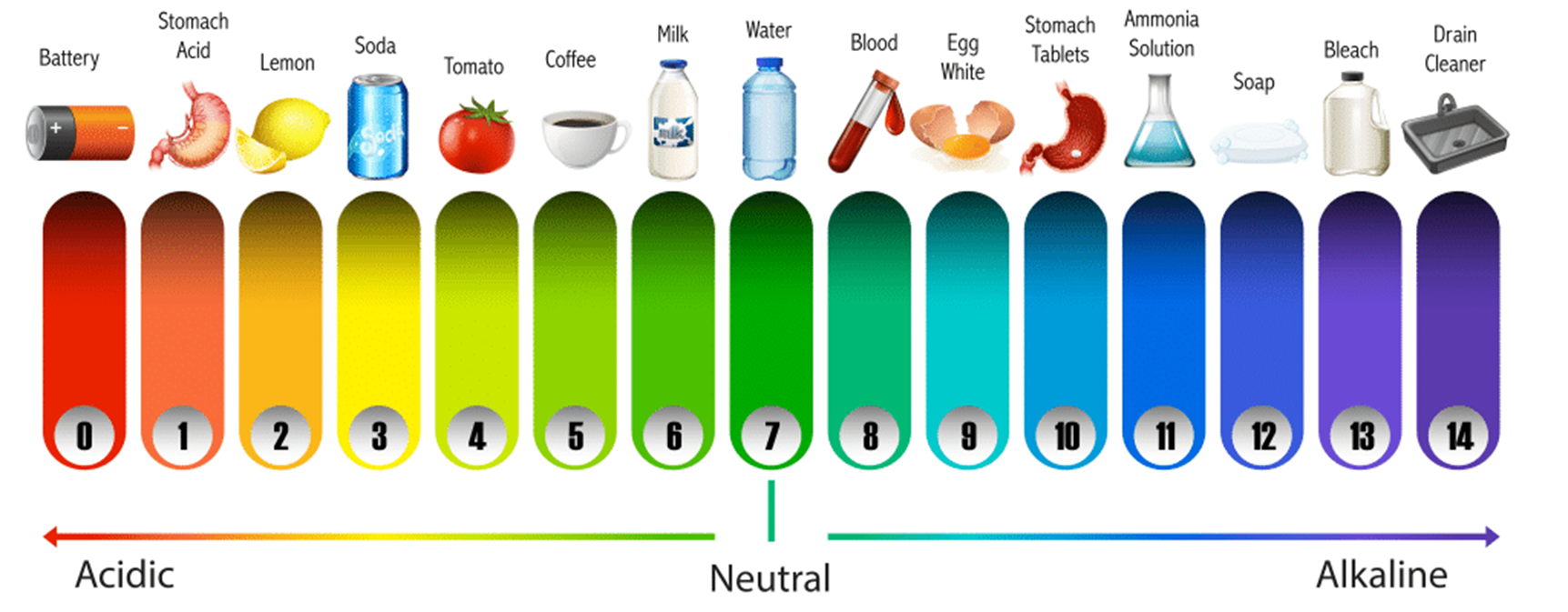
pH
Is a measure of hydrogen ion concentration and an indicator of relative acidity or alkalinity of water.
Biochemical Oxygen Demand (BOD)
The amount of dissolved oxygen that microorganisms need to break down organic materials in water.
pH Scale
Physical Quality
Physical parameters include color, taste, odor, temperature, turbidity, solids, and electrical conductivity.
Biological Quality
Bacteria , Viruses , Protozoans , Phytoplanktons , zooplankton , insects, plants and fish.
Amoebiasis
is a cause of diarrhoea among travellers with poor sanitation
Entamoeba Histolytica
A parasite that is the cause of Amoebiasis.
Agricultural Runoff
Pesticides and Herbicides
Industrial Runoff
Metals and Mine Tailings
Turbidity(cloudiness) and bacteria
Impurities in Surface water
Higher concentration of Dissolved Chemicals
Impurities in Groundwater
Dissolved Chemicals and microorganisms
Impurities in Seawater
Chemical Analysis of the water
indicates the parts per million of each chemical found in the water
Bacteriological Quality of the water
provides an estimate of the density of bacteria in the water supply. The presence of any coliform organisms indicates that the water supply may be contaminated with human or animal wastes (perhaps seepage from a nearby septic tank field or animal pasture).
Surface Water
Contains larger quantities of turbidity (cloudiness) and bacteria
Groundwater
Contains higher concentrations of dissolved chemicals
Seawater
Contains high concentrations of dissolved chemicals and microscopic organisms
Filtration Equipment (taste and odor)
Removal of bacteria using chlorine
Addition of flocculating and precipitating agent
Ion exchange process to remove excessive hardness
Methods to Improve Water Quality
Sodium Sulfite
Used to remove the taste of chlorine
Coagulation and Flocculation
Settling and solids removal
Flouridation of public water
method of reducing tooth decay in children
Desalination process
Saline or salt is removed from water. Used in countries like Kuwait, UAE, and Qatar
Alum
Example of Flocculating and Precipitating Agent
Flow Restrictors
it can reduce the amount of water used by 50% depending on the type installed
Water Saving Toilets
Toilets that are mounted high on the wall so the water would gain velocity to flush. This could be accomplished between 1 and 1 ½ gal
Gray Water System
processing of household wastewater for reuse. In the design of the gray-water system, the water from the bathtub or shower and the washing machine is run into a collection tank instead of going into the sewer lines. From the collection tank, the water is filtered and chlorinated and then reused as water to flush the toilets. This water reuse system cuts water consumption by about one-half.
Building Supply or Water Service
Is a large water supply pipe that carries potable water from the district or city water system or other water source to the building.
Water Meter
Is required by most district water supply systems to measure and record the amount of water used. It may be placed in a meter box located in the ground near the street or inside the building.
Building Main
Is a large pipe that serves as the principal artery of the water supply system. It carries water through the building to the furthest riser. It is typically run (located) in a basement, in a ceiling, in a crawl space, or below the concrete floor slab.
Riser
Is a water supply pipe that extends vertically in the building at least one story and carries water to fixture branches. It is typically connected to the building main and runs vertically in the walls or pipe chases.
Fixture Branch
Is a water supply pipe that runs from the riser or main to the fixture being connected. In a water supply system, it is any part of a piping system other than a riser or main pipe. Fixture branch pipes supply the individual plumbing fixtures. A fixture branch is usually run in the floor or in the wall behind the fixtures.
Fixture Connection
It runs from the fixture branch to the fixture, the terminal point of use in a plumbing system. A shut-off valve is typically located in the hot and cold water supply.
Water Tower
must be tall enough to deliver adequate pressure to all of the houses and businesses in the area of the tower.
100 to 200 ft (30 to 60 m)
Water in a water tower tank must be _______ above the highest plumbing fixture being served.
0.433 psi
Each foot of water height provides ____ of pressure.
Lateral
The water service pipe in an underground pipe
Rigid Pipe Distribution Configuration
the hot and cold water distribution pipes are installed parallel to one another as they convey hot and cold water to risers and branch pipes
6 in or 150 mm
required spacing of hot and cold pipe to prevent heat interchange
Zone
A branch supplying water to two or more fixtures. It can supply one or many fixtures on one floor or on a few floors.
Groups
Fixtures are typically located in clusters. For example, in a commercial building or school, restrooms for men and women are grouped together with fixtures arranged against a common plumbing chase.
Plumbing Wall
There are times when the width of a wall needs to be increased to allow for pipes running horizontally to pass by drainage pipes (or other pipes) running vertically.
Chase
It is a vertical opening through a floor or several floors that is enclosed with walls between floors. It can enclose piping only or it can enclose electrical wiring and/or mechanical system ducting and/or pipes that run vertically from floor to floor through the building.
Pipe Tunnels
may be used on large projects to provide concealed space for the passage of mechanicals at ground level and from building to building. Hangers from the top or side of the tunnel are used to support the pipes. Access may be from either end of the tunnel, or access floors may be provided.
Shut off Valve
Readily accessible valves used to close off the water supply to a fixture, appliance, or system
Homerun (Manifold) Distribution Configuration
consists of a plastic or metal plumbing manifold and flexible plastic piping
Cross-linked Polyethylene (PEX)
piping that is typically used in Homerun Configuration
Upfeed System
water pressure from the water supply main is relied on to drive water flow through the system (40 to 80 psi)
Pumped Upfeed Distribution System
water enters one or more pumps where its pressure is boosted to pressures of 150 to 250 psi (1000 to 1700 kPa) or more. A vertical riser carries this high-pressure water to fixtures at the top of the building
Pressure Reducing Stations
are placed on every 10th floors to decrease any excessive pressure before the water enters the fixture
Down Feed System
water is pumped to elevated storage tanks in, or on, the building, and the water is fed down into the building by gravity. This gravity system, fed from the upper stories to the lower, is called a downfeed distribution system. Water entering the building flows through pumps that develop sufficient water pressure to drive water to storage tanks serving zones of about 10 floors each.
Hydrostatic Pressure
hydrostatic force per unit area, is perpendicular to the interior walls at every point or force exerted on any molecule within the fluid is the same in all directions.
Hydrostatic Force
force exerted by the weight of the fluid against the walls of a vessel containing the fluid.
Water Pressure Difference
is the driving force behind fluid flow
Residual Water Pressure
is the pressure available at the outlet, just before a fixture. It affects water output of a fixture
Minimum and Maximum Water Velocity
Noise, erosion of inner pipe walls and valves, and economy of installation, operation, and maintenance dictate the _____
Cavitation
is a physical phenomenon that occurs in a liquid when it experiences a drastic drop in pressure that causes the liquid to vaporize into small vapor bubbles and can cause undesirable vibration that can lead to erosion or leaking.
Cross-Connection
is an unsatisfactory connection or arrangement of piping that can cause non potable water to enter the potable water system.
Gap
It exists between the faucet and the rim of the bowl in lavatories, sinks, and tubs to create a separation and avert a cross-connection.
Backflow
is a type of cross-connection that occurs when contaminated water or some other liquid or substance unintentionally flows backwards into distribution pipes containing potable water
Atmospheric Vacuum Breaker (AVB)
the most common type, consists of a body, a check valve-like member (to prevent backflow), and an atmospheric opening. The AVB is not a testable device.
Pressure Vacuum Breaker (PVB)
is a type of backflow prevention device used to keep non potable (or contaminated) water from entering the water supply
Double Check Assembly (DCA) or Double Check Valve
is a backflow prevention device assembly that consists of two check valves assembled in series usually with a ball valve or gate valve installed at each end for isolation and testing.
Water Hammer
A large pressure develops when fluid moving through a pipe is suddenly stopped. In a plumbing supply system, the sudden closing of a valve will cause fast-flowing water to stop quickly, resulting in a large increase in pressure that makes pipes rattle
Air Chamber
The trapped air is compressible, which cushions the pressure surge as the valve is closed and absorbs the hydraulic shock.
Water Hammer Arrestor
are patented devices that absorb Hydraulic shock.
Thermal Expansion
In a residence, the upper limit for hot water pipes is usually 125°F (52°C). Cold water piping will be subjected to a much smaller temperature range, usually with a low of 35°F (2°C) and a high of about 80°F (27°C).
Expansion Bends
make use of pipe fabricated with U-shaped or circular bends. The increase in the length of pipe from thermal expansion is accommodated by flexing or springing of the bends or loops
Viscosity
As water flows through a pipe, its _____ (thickness) increases with temperature decrease. Water at 40°F (4°C) is twice as viscous as water at 90°F (32°C) and four times as much at 170°F (77°C). As a result, pumping energy and cost are higher when water temperatures are lower.
Volume Change with Temperature Change
Water is the only substance that can exist as a solid, liquid, and gas at ordinary temperatures. Like most substances, water expands when it is heated.
Aging
As pipes in a plumbing system are used, their inner walls become increasingly rough
Pipe Insulation
is applied to the outer walls of piping to reduce heat loss from the pipe or prevent condensation on the outside pipe walls. Foam and covered fiberglass insulation are common pipe insulation materials
Testing
The water supply system should be tested for leaks before it is covered with finish materials to determine if it is watertight.
12.7%, 2700 gal (10 200 L)
Leaks account for about ____ of household per capita water use in a typical U.S. home (AWWA). A leak of just one drop per second will waste about ______ of water a year.
Galvanic corrosion
Changes in water chemistry
Improper addition of chemicals
Agressive Water
Excessive water velocity
Cause of Potential Leaks
Cold Water
Water from shallow underground water service lines enters the building at a temperature that fluctuates with climate, season, and location of the water service line.
2°C in midwinter
21°C or more in midsummer
50° to 55°F
constant temperature from deep wells year-round
Chilled Water
Is desired, such as from a drinking fountain
used to cool water to a temperature of about 10°C before its used
is a vapor compression refrigiration system
Heated Water
used in bathing, cleaning, washing, and other associated purposes
potable water that is heated to 120°F
Domestic Hot Water
hot water that is used for bathing, dishwashing, and clothes washing is reffered to
Tempered water
heated water below 120°F is called
105
115
140
160
180
180
Typical Temperatures

Legionella Pneumophilia
it was a concern that requires hot water distribution temperature to be higher than 120°F
above 110°F
Water temperature that can be painfully hot to touch
120°F and above
exposure to this temperature will cause scalding(burning) of the skin
105°F
temperature limited by health regulations at lavatories, baths, and showers
125
130
135
140
145
150
155
