Amino Acid Metabolism and Urea Cycle Overview
1/89
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
90 Terms
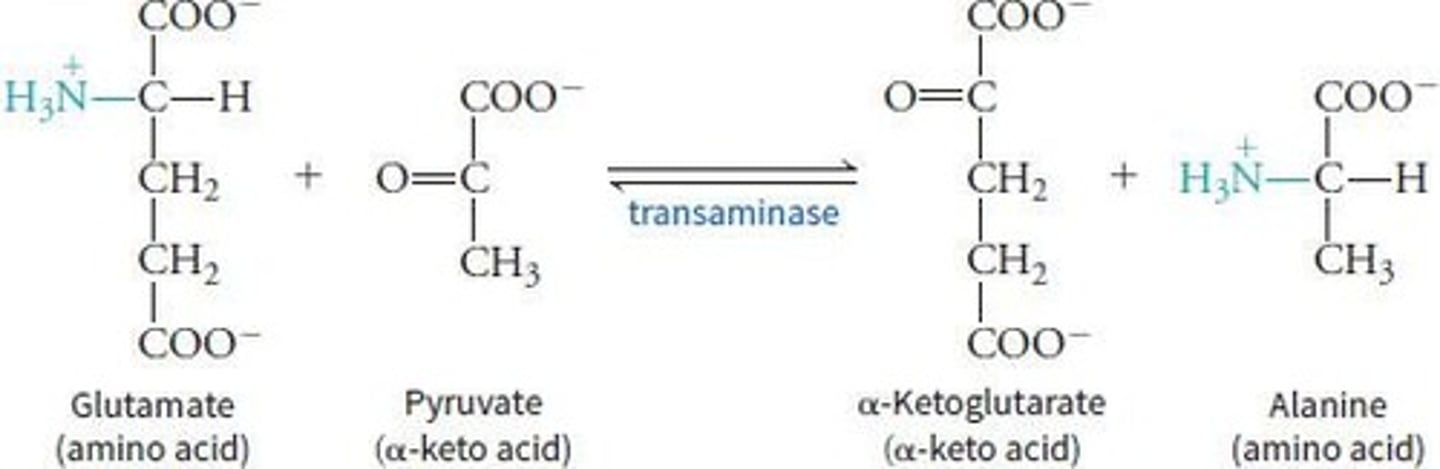
What are the metabolic functions and reactions associated with transaminase (PLP)?
Transaminase (PLP) is involved in the transfer of α-amino groups to α-keto acids, producing corresponding α-keto acids and α-amino acids.
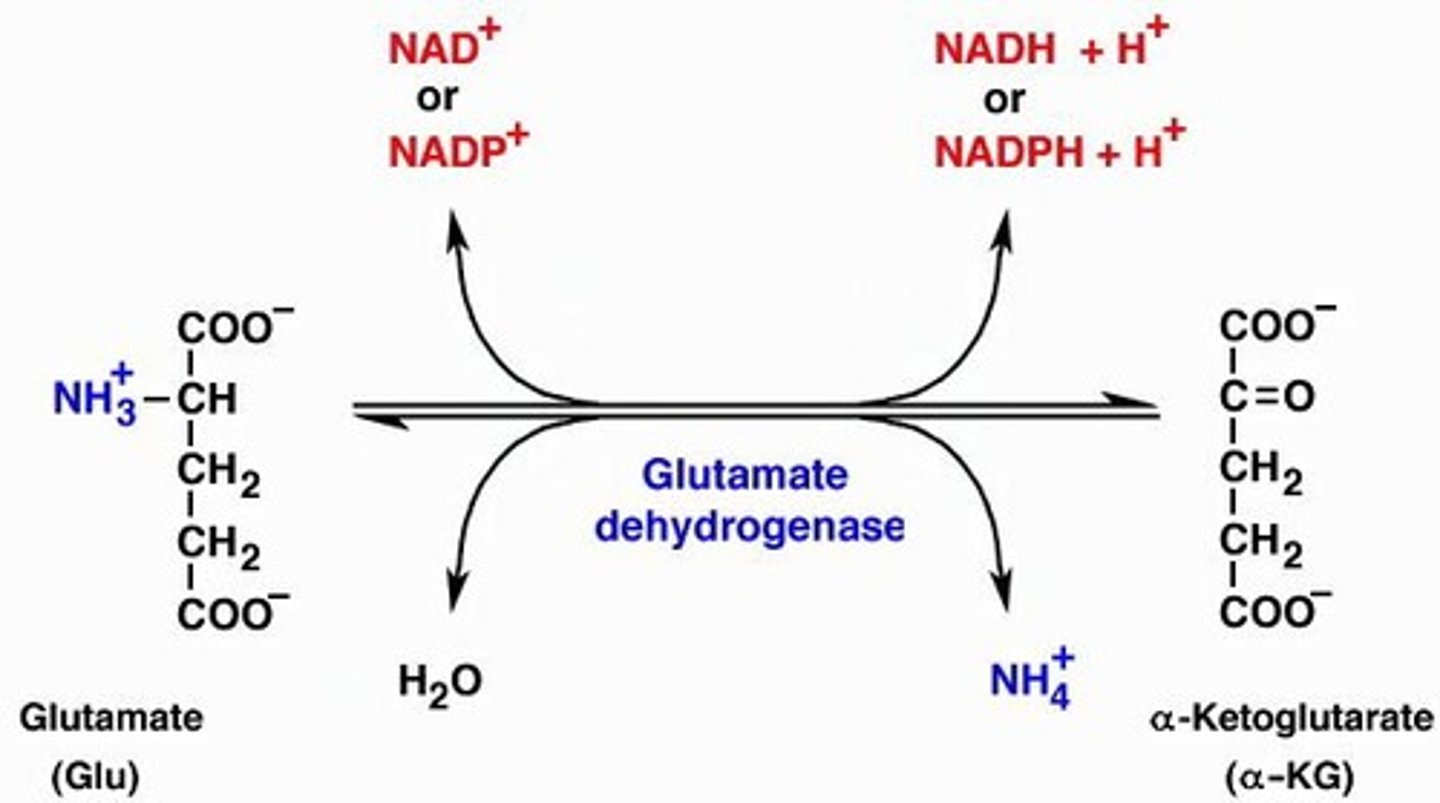
What is the role of glutamate dehydrogenase in amino acid metabolism?
Glutamate dehydrogenase metabolizes glutamate to generate ammonia.
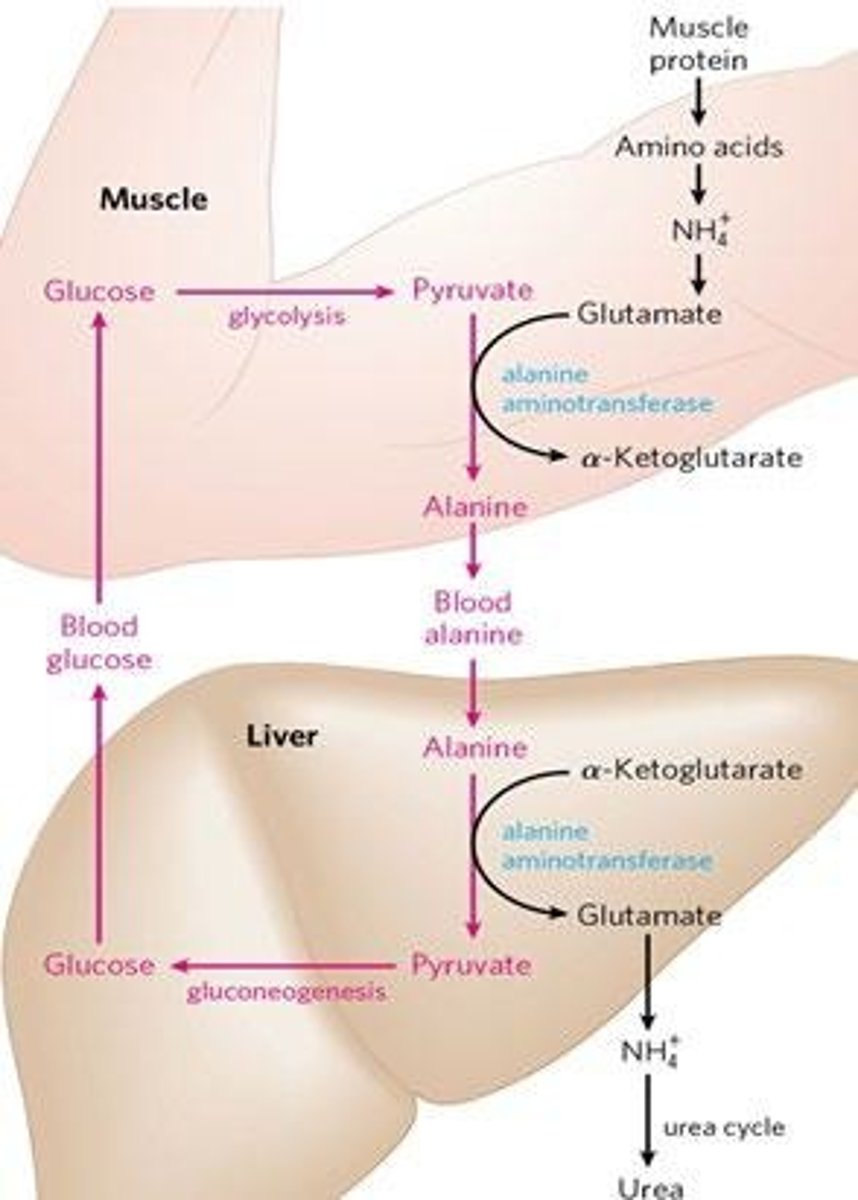
How does the Glucose-Alanine Cycle function in nitrogen transport?
The Glucose-Alanine Cycle moves nitrogen to the liver by converting amino groups from glutamate to pyruvate, producing alanine, which is then used in gluconeogenesis.
What are the deamidation reactions in amino acid metabolism?
Deamidation reactions involve the removal of an amine group from amino acids, often leading to the production of ammonia.
What is the difference between gluconeogenic and ketogenic amino acids?
Gluconeogenic amino acids can be converted into glucose, while ketogenic amino acids can be converted into ketone bodies.
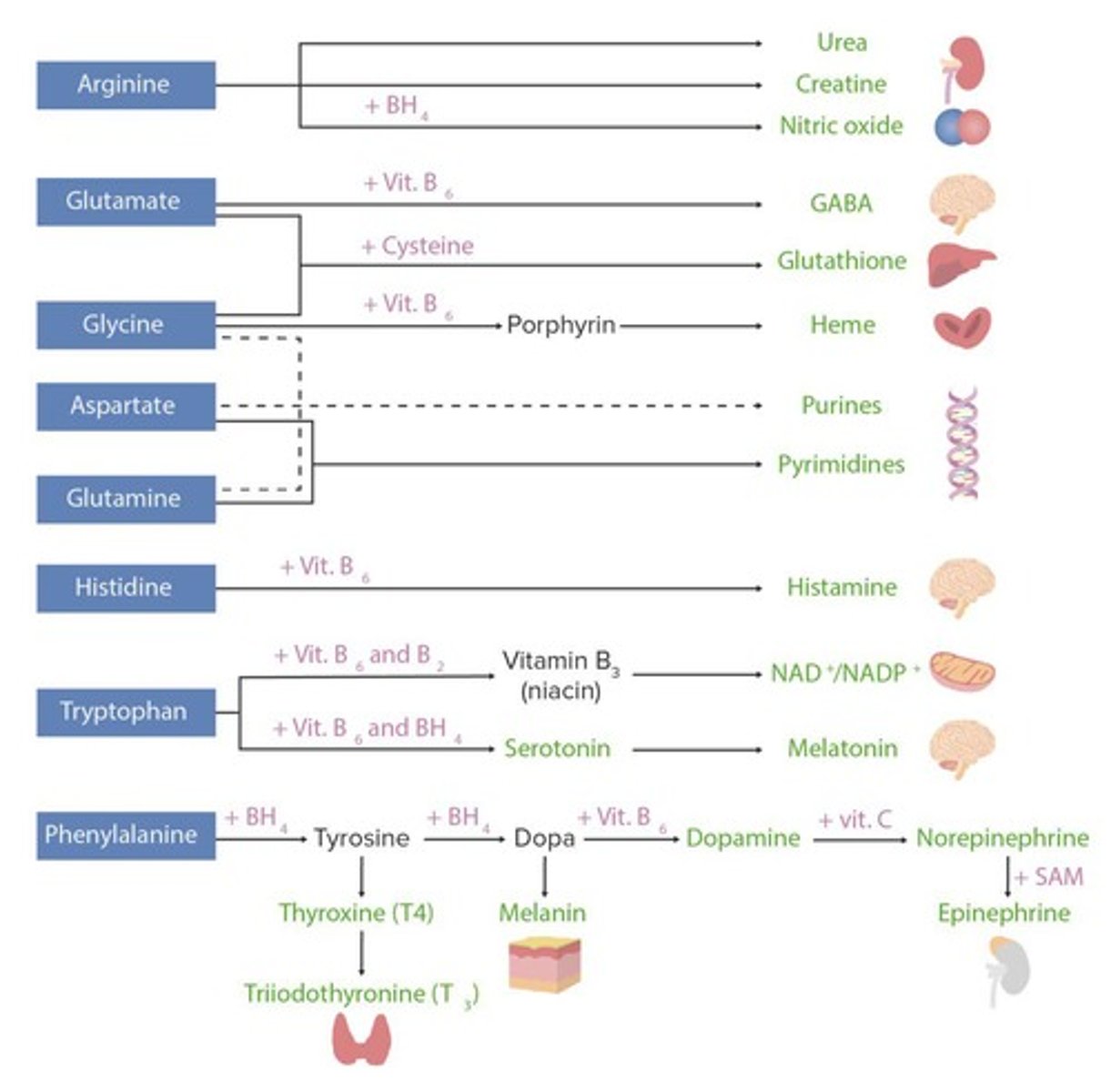
How is nitrogen excreted from the body?
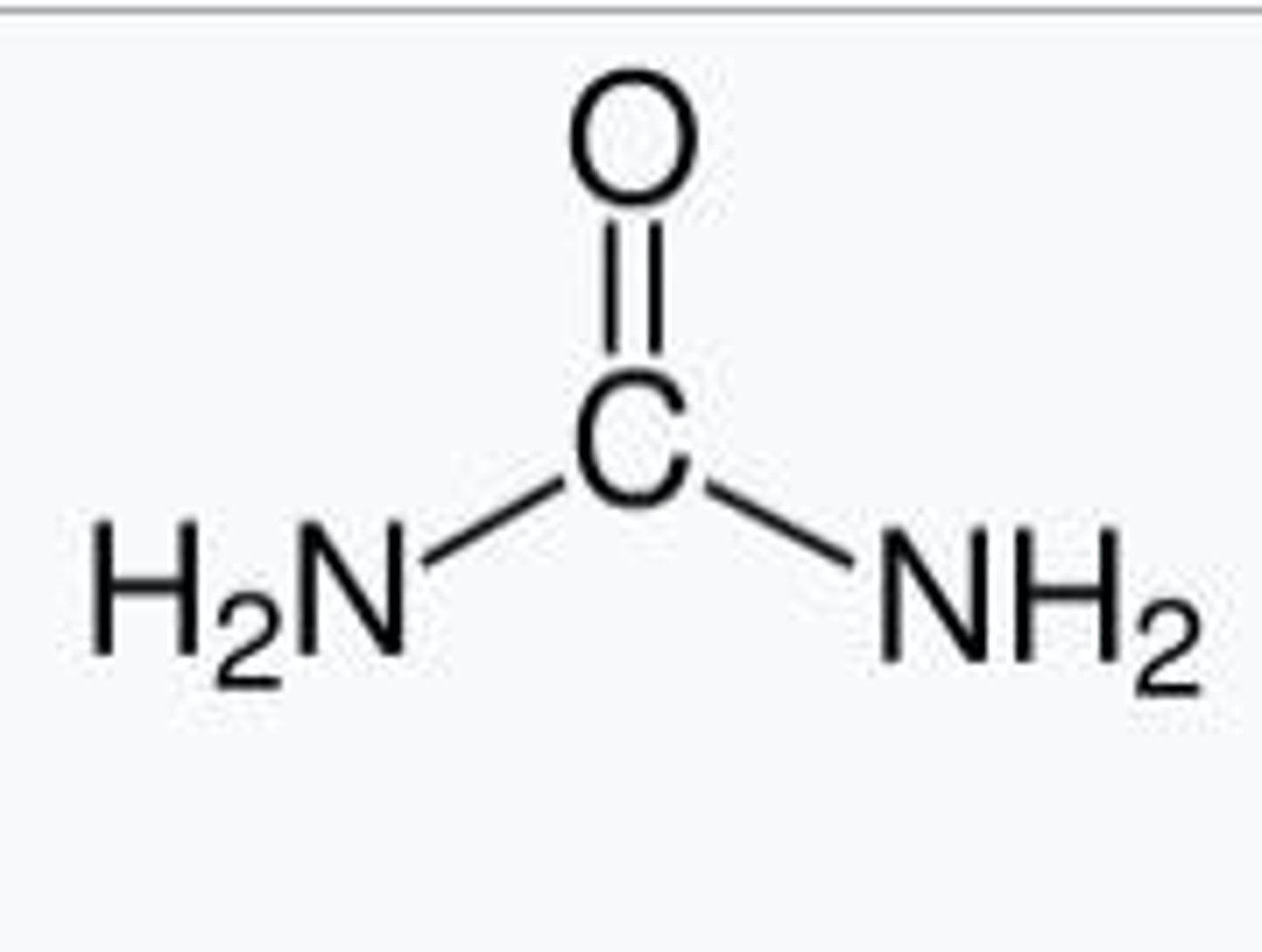
Nitrogen is excreted primarily as urea and uric acid, with urea being produced when nitrogen is in excess.
What are the five starting molecules for amino acid production?
The five starting molecules include pyruvate, oxaloacetate, acetyl CoA, α-ketoglutarate, and other metabolic intermediates.
What are the three major purposes of amino acids in metabolism?
Amino acids serve as substrates for energy generation, protein synthesis, and the synthesis of other products such as heme, purines, and coenzymes.
When are amino acids primarily catabolized?
Amino acids are primarily catabolized during starvation when glucose and fats are low.
What happens to excess nitrogen during amino acid catabolism?
Excess nitrogen is converted into ammonia, which is then transformed into urea for excretion.
How does nutritional stress affect amino acid metabolism?
During nutritional stress, amino acids can be sources of carbon for gluconeogenesis, while excess nitrogen is excreted.
What is the role of α-ketoglutarate in amino acid catabolism?
α-ketoglutarate acts as a recipient of amine groups during amino acid catabolism, forming glutamate.
What is the significance of the urea cycle in nitrogen metabolism?
The urea cycle converts ammonia into urea, allowing for the safe excretion of excess nitrogen from the body.
What is the function of aminotransferases in amino acid metabolism?
Aminotransferases facilitate the transfer of α-amino groups from amino acids to α-keto acids.
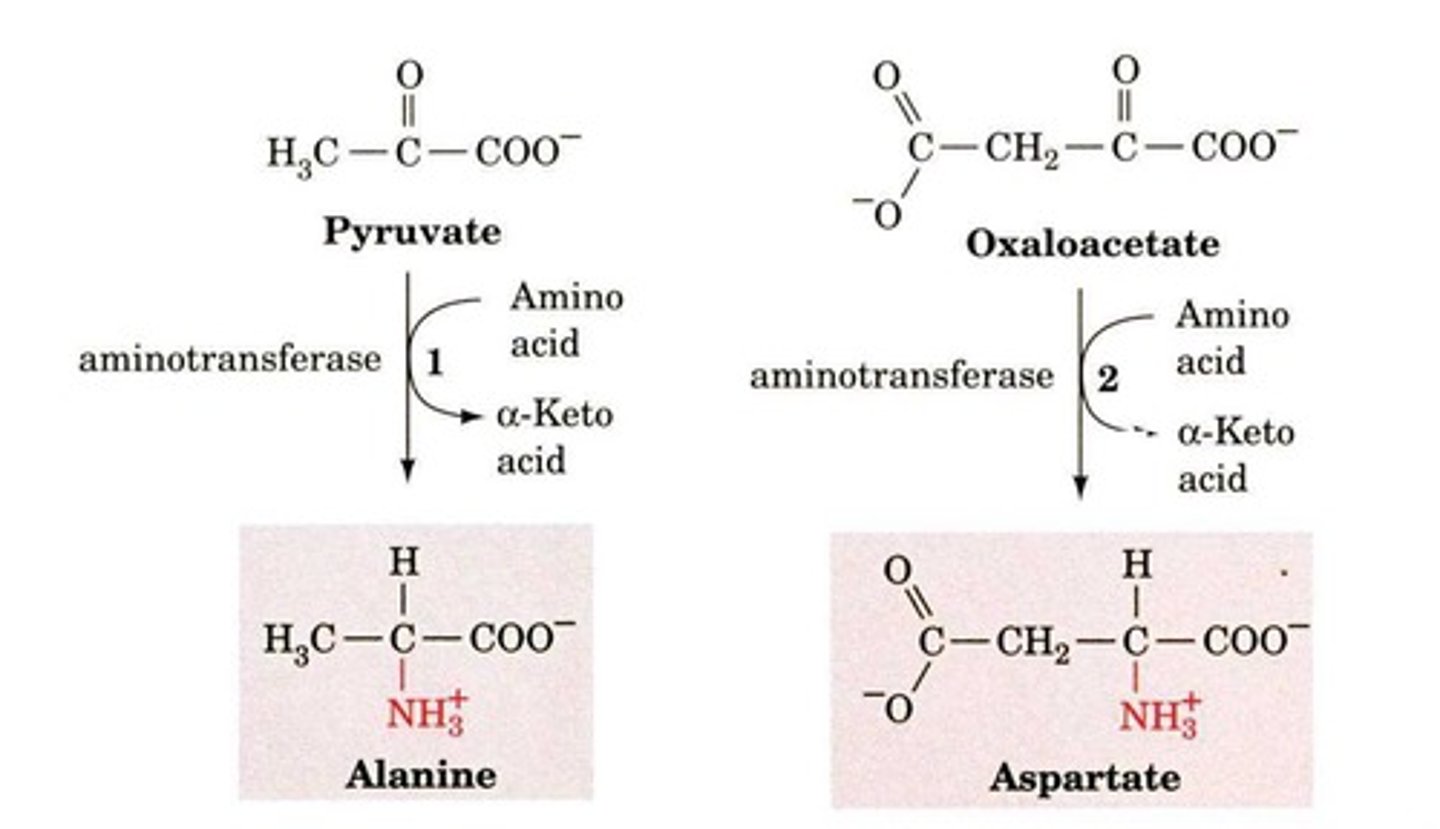
What are the major metabolic pathways for carbohydrates?
The major metabolic pathways for carbohydrates include gluconeogenesis, glycogen synthesis (anabolism), and glycolysis, TCA cycle, pentose phosphate pathways, and glycogen breakdown (catabolism).
What are the major metabolic pathways for lipids?
The major metabolic pathways for lipids include fatty acid synthesis (anabolism) and β-oxidation of fatty acids and glycerol catabolism (catabolism).
What are the major metabolic pathways for proteins?
The major metabolic pathways for proteins include catabolism of amino acids and synthesis of nonessential amino acids.
What are the major metabolic pathways for nucleic acids?
The major metabolic pathways for nucleic acids include the synthesis of purine and pyrimidine ribonucleotides and deoxyribonucleotides (anabolism) and nucleotide catabolism and salvage.
What is the significance of the one-carbon system in amino acid synthesis?
The one-carbon system is crucial for the synthesis of amino acids, particularly in the transfer of one-carbon units in various metabolic reactions.
What are the consequences of too much nitrogen in the body?
Excess nitrogen is toxic and must be removed through conversion to urea or uric acid for safe excretion.
How do amino acids contribute to energy production during starvation?
During starvation, amino acids can be catabolized to provide energy and carbon skeletons for gluconeogenesis.
What is the role of the liver in amino acid metabolism?
The liver is central to amino acid metabolism, facilitating gluconeogenesis and processing excess nitrogen.
What is the importance of understanding amino acid metabolism in biochemistry?
Understanding amino acid metabolism is essential for comprehending how the body utilizes proteins and manages nitrogen waste.
What is the purpose of the urea cycle?
To eliminate excess ammonium in the form of urea.
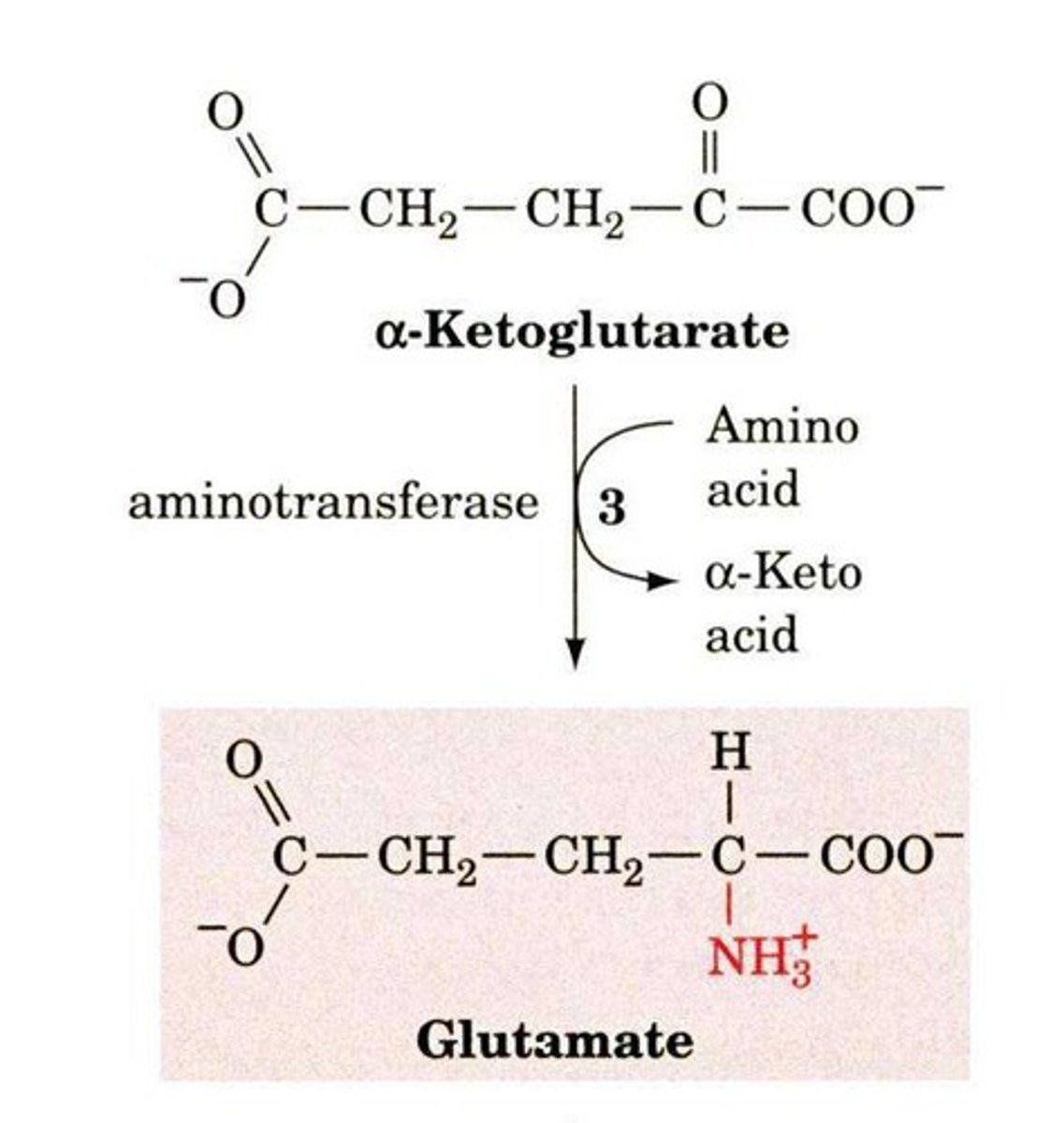
What is transamination?
The transfer of an amino group from an amino acid to an alpha-keto acid, using the vitamin B6 derivative Pyridoxal Phosphate (PLP).
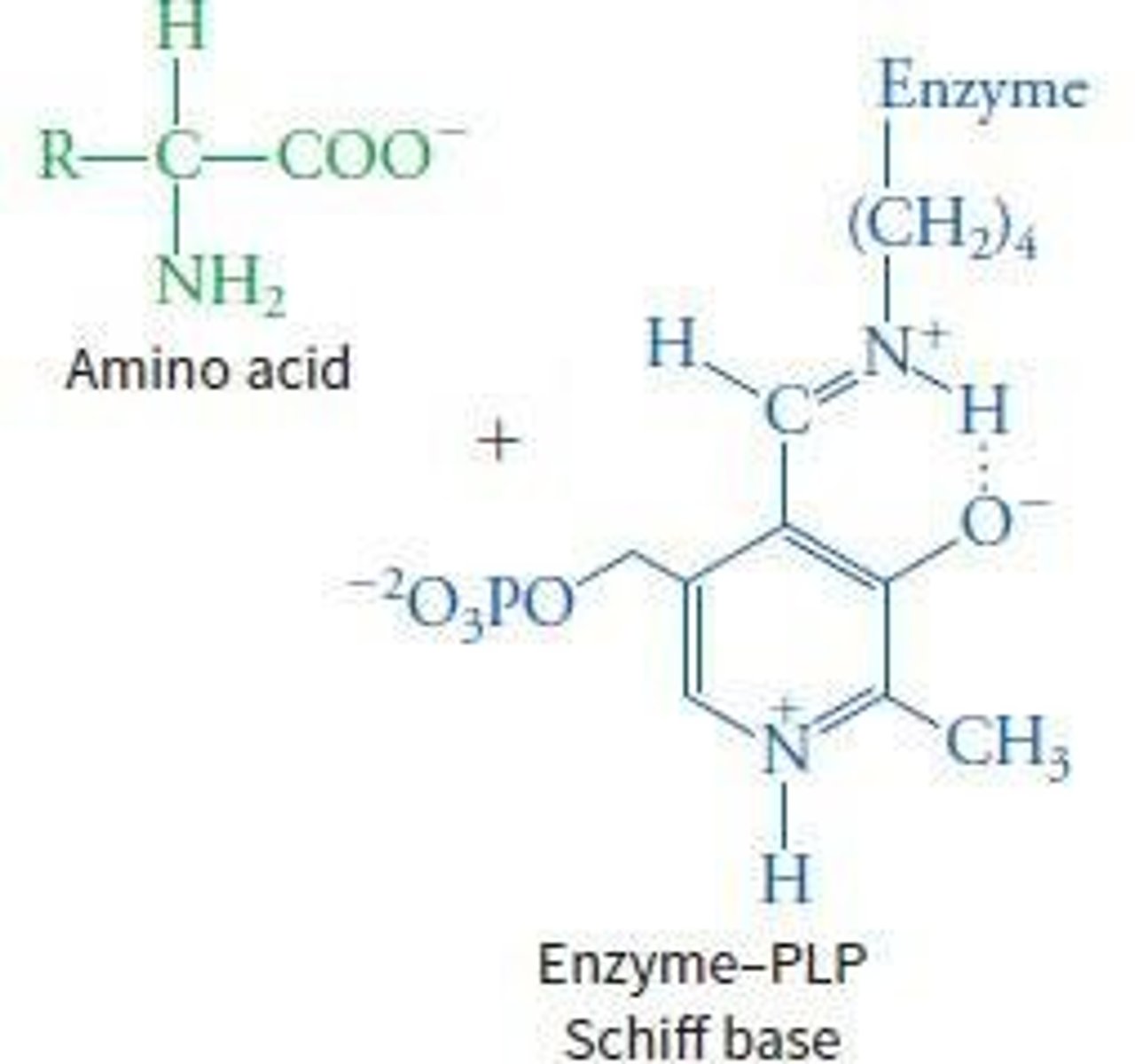
What role does Pyridoxal Phosphate (PLP) play in transamination?
PLP acts as a coenzyme that stabilizes the intermediate and forms a Schiff-base linkage with the ε-amino group of a specific lysine in the aminotransferase enzyme.
What is the net result of the transamination reaction?
The amino group from the first amino acid is transferred to the second amino acid.
What is the role of glutamate dehydrogenase in amino acid metabolism?
It removes the alpha amino group from glutamate to produce free ammonia.
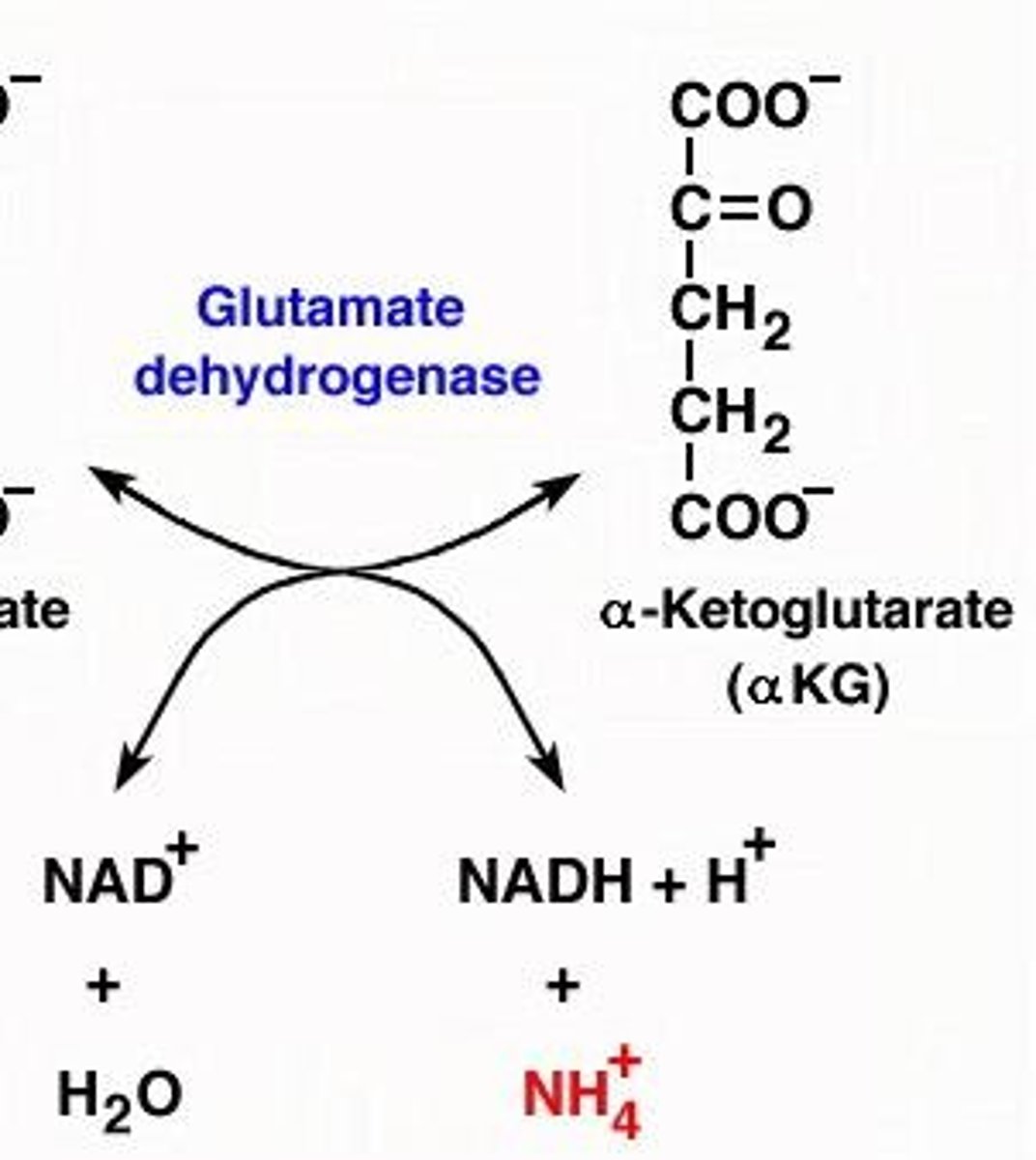
How does oxidative deamination relate to the urea cycle?
Oxidative deamination removes nitrogen from glutamate, which is then processed in the urea cycle.
What is the glucose-alanine cycle?
A mechanism to move nitrogen to the liver, involving the conversion of pyruvate to alanine in muscle and its transport to the liver.
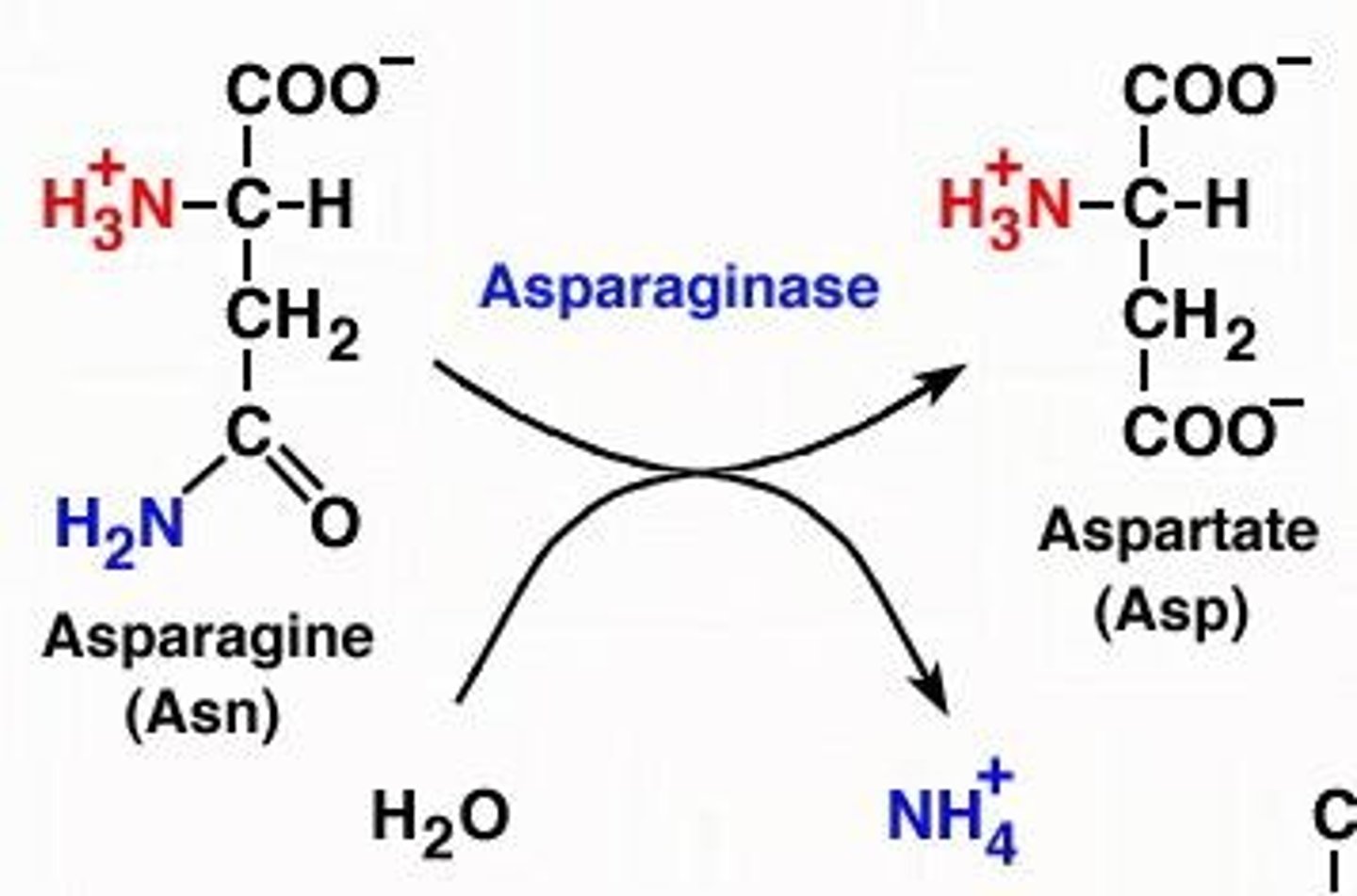
What are the two possible reactions to generate glutamate from asparagine or glutamine?
1. Glutamine is converted to glutamate by glutaminase. 2. Asparagine is converted to aspartate by asparaginase, which can then be converted to glutamate.
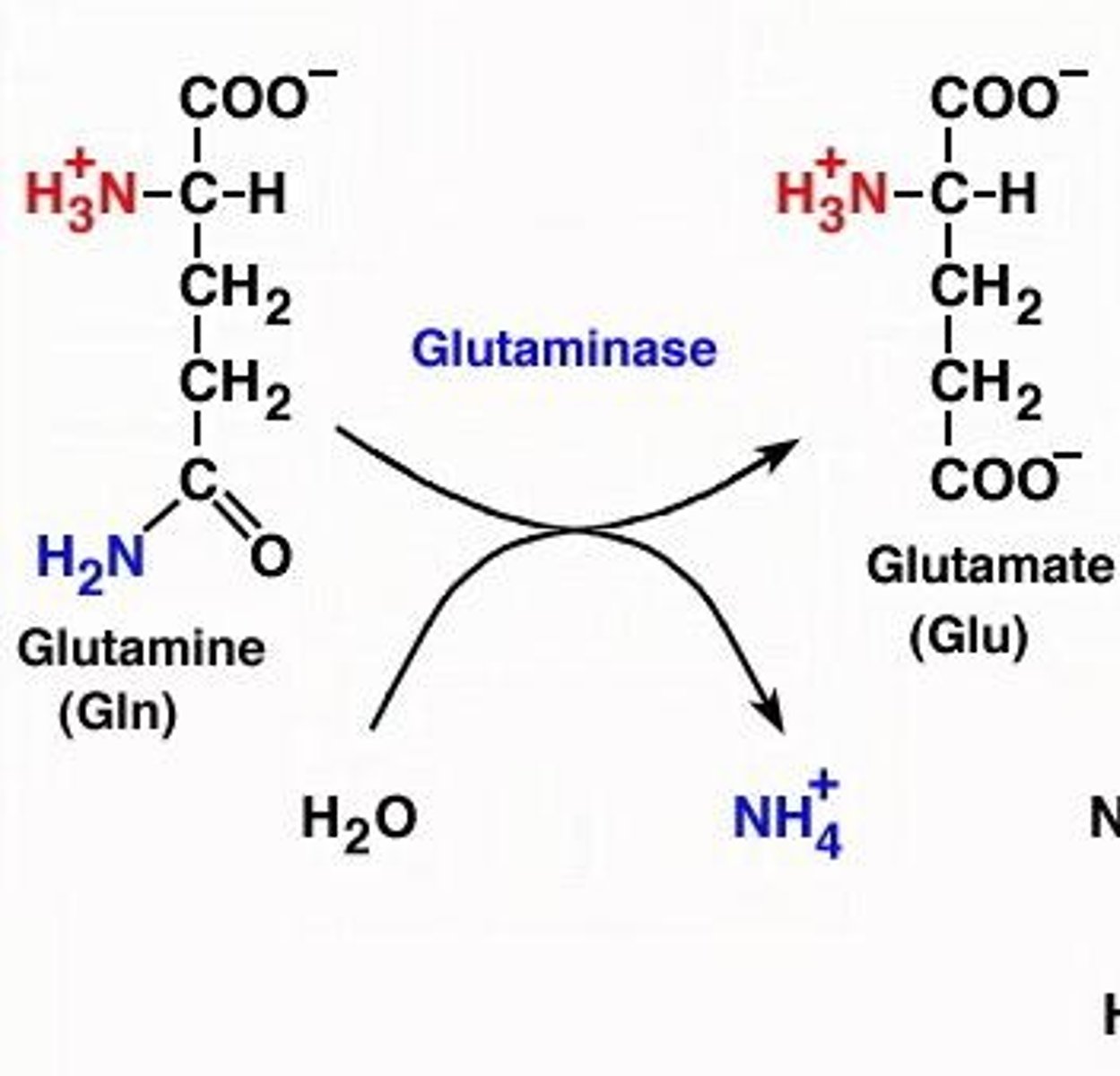
What is the role of α-ketoglutarate in transamination?
It acts as a universal amino group recipient during transamination reactions.
What happens during the deamidation of asparagine?
The amide group is removed, producing aspartate, which can then be converted to glutamate.
What is the significance of the Schiff base formation in transamination?
It facilitates the transfer of the amino group from the amino acid to the alpha-keto acid.
What cofactors are required for oxidative deamination?
NAD+ / NADP+ or NADH / NADPH.
How does ammonia produced in oxidative deamination get utilized?
It is used in the carbamoyl synthase reaction.
What is the function of transaminases?
They transfer α-amino groups onto α-keto acids to form corresponding α-keto acids and α-amino acids.
What is the result of hydrolysis of the Schiff base during transamination?
The release of the alpha-keto acid and regeneration of enzyme-bound PLP.
What is the role of glutamate in nitrogen metabolism?
Glutamate can undergo oxidative deamination to remove nitrogen, contributing to the urea cycle.
What is the significance of the α-carbon removal in transamination?
It allows for the transfer of the amino group to form glutamate.
What is the result of deamidation of glutamine?
It releases ammonium and produces glutamate.
What is the outcome of deamidation of asparagine?
It produces aspartate, which can be further converted to glutamate.
What is the relationship between transamination and amino acid synthesis?
Transamination reactions are reversible and can also be used to synthesize new amino acids.
What is the primary function of the urea cycle?
To convert excess ammonia into urea for excretion.
How does the body move nitrogen?
Through deamidation or aminotransferase reactions that produce glutamate.
What is the role of transaminases in amino acid metabolism?
Transaminases transfer α-amino groups onto α-keto acids, producing corresponding α-keto acids and α-amino acids.
What does glutamate dehydrogenase do?
Glutamate dehydrogenase removes the alpha amino group from glutamate, producing free ammonia.
What is the purpose of the urea cycle?
The urea cycle converts ammonia into urea for excretion, particularly during high levels of ammonia production from amino acid catabolism.
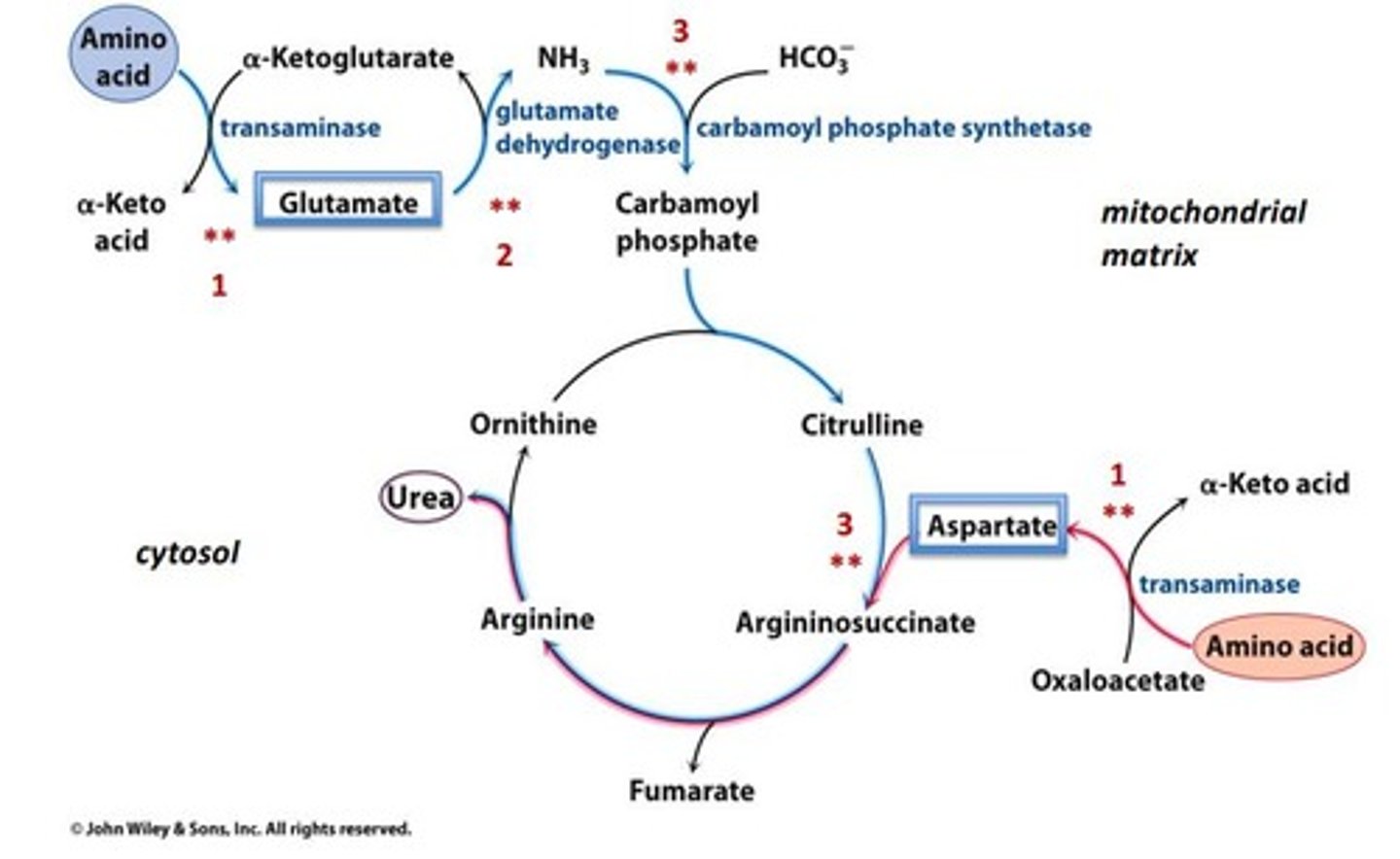
What are the substrates required for the urea cycle?
The urea cycle requires CO2, ammonium ion, and arginine, and it consumes 3 ATP.
Where does urea go after it is produced in the urea cycle?
Urea is excreted into the bloodstream, cleared by the kidneys, and dumped into the urine.
How many reactions occur in the urea cycle, and where do they take place?
The urea cycle consists of 5 reactions: 2 occur in the mitochondria and 3 in the cytosol.
From where does the first nitrogen atom in urea originate?
The first nitrogen atom in urea is derived from glutamate, which generates ammonia for the carbamoyl phosphate reaction.
What is carbamoyl phosphate, and how is it formed?
Carbamoyl phosphate is synthesized from ammonia, ATP, and bicarbonate.
What does carbamoyl phosphate combine with to form citrulline?
Carbamoyl phosphate combines with ornithine to form citrulline.
Where does the second nitrogen atom in urea come from?
The second nitrogen atom in urea is derived from aspartate after a transamination reaction from oxaloacetate.
What is the role of argininosuccinate in the urea cycle?
Argininosuccinate is formed by the combination of citrulline and aspartate and is then cleaved into arginine and fumarate.
What enzyme cleaves argininosuccinate?
Argininosuccinate is cleaved by argininosuccinate lyase.
What is the final step of the urea cycle?
The final step is the cleavage of arginine by arginase to form urea.
How is nitrogen removed from the body during normal times?
During normal times, nitrogen is removed via uric acid synthesis and secretion, primarily from purine metabolism.
What is the starting point for purine metabolism?
Purine metabolism starts with ribose-5-phosphate as the sugar backbone.
What is the key nitrogen donor in purine metabolism?
Glutamine is the key nitrogen donor in purine metabolism.
What are the products of purine breakdown?
Purines are broken down into xanthine and hypoxanthine.
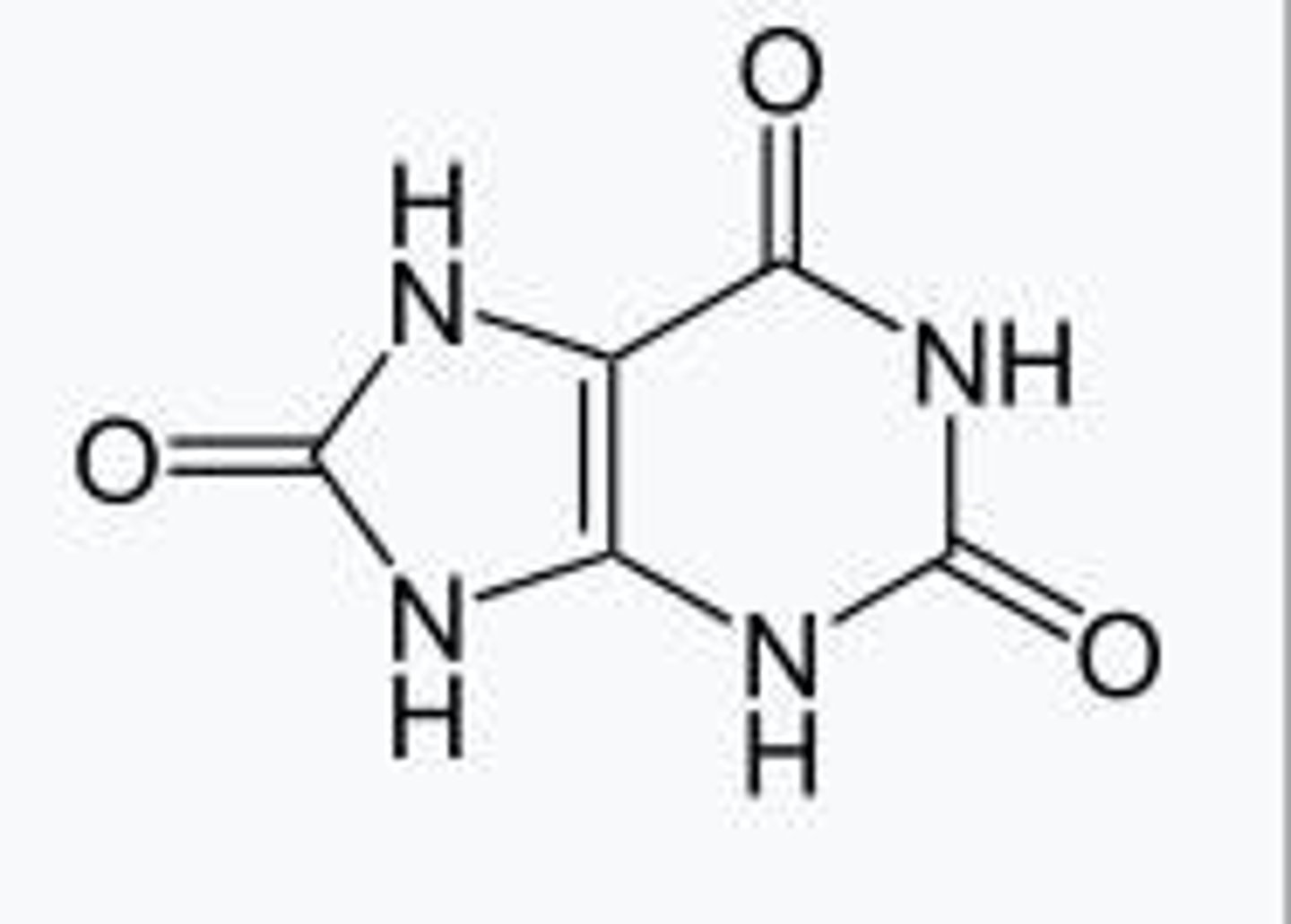
What enzyme converts xanthine and hypoxanthine into uric acid?
Xanthine oxidase converts xanthine and hypoxanthine into uric acid.
What is a consequence of uric acid excretion?
The excretion of uric acid produces reactive oxygen species (ROS).
What is the glucose-alanine cycle?
The glucose-alanine cycle moves nitrogen to the liver.
What are deamidation reactions?
Deamidation reactions involve the removal of an amide group from an amino acid, contributing to nitrogen metabolism.
What is the significance of purine metabolism in nitrogen removal?
Purine metabolism leads to the production of uric acid, which helps in the excretion of nitrogen.
How is nitrogen removed from the body?
Through the excretion of uric acid via purine metabolism.
What are the five starting molecules for amino acid synthesis?
Aromatic acids, Glycine, Serine, Proline, and intermediates from the Urea Cycle.
What is the role of serine in amino acid metabolism?
Serine is a precursor for glycine and cysteine and donates methyl groups to the one-carbon pool.
What is one-carbon metabolism?
It refers to the movement of one-carbon units in various biological pathways, crucial for synthetic and degradative processes.
What are transamination reactions?
Reactions that involve the addition or removal of an amino group, often using enzymes like transaminases.
What is the purpose of the Urea Cycle?
To remove excess nitrogen from the body by converting ammonia into urea for excretion.
What is the significance of glutamate in amino acid metabolism?
Glutamate serves as a nitrogen donor in transamination reactions.
What are gluconeogenic amino acids?
Amino acids that can be converted into glucose through gluconeogenesis.
What are ketogenic amino acids?
Amino acids that can be converted into ketone bodies.
How does the Glucose-Alanine Cycle function?
It moves nitrogen to the liver by converting alanine to pyruvate, facilitating gluconeogenesis.
What is the role of Tetrahydrofolate in metabolism?
It carries one-carbon units to nucleotide synthesis, particularly for purines.
What is the relationship between serine and one-carbon metabolism?
Serine donates carbon units to the one-carbon pool, essential for various metabolic processes.
What is produced from the deamidation reactions?
Deamidation reactions lead to the generation of glutamate.
What is the significance of the Urea Cycle's five reactions?
They are essential for converting ammonia into urea, facilitating nitrogen excretion.
What is the source of nitrogen in urea?
Nitrogen in urea comes from the amino acid aspartate and ammonia.
What is the role of asparagine synthetase?
It catalyzes the conversion of aspartate to asparagine, utilizing glutamine as a nitrogen source.
How is uric acid produced?
Uric acid is produced through the breakdown of purines during nucleotide metabolism.
What is the significance of phosphoenolpyruvate in amino acid biosynthesis?
It is part of the aromatic amino acid biosynthesis pathway, utilizing intermediates from glycolysis.
What are the two reactions involved in serine production?
Serine is produced through two reactions involving glycolytic intermediates and nitrogen from glutamate.
What is the importance of the one-carbon system in amino acid synthesis?
It is critical for the synthesis of nucleotides and amino acids, facilitating various metabolic pathways.
What are the intermediates used in aromatic amino acid biosynthesis?
Chorismate is a key intermediate in the biosynthesis of aromatic amino acids.
What is the relationship between serine, glycine, and cysteine?
Serine is a precursor for both glycine and cysteine, which are important for various metabolic functions.
What is the significance of the 3-phosphoglycerate family in amino acid synthesis?
It is a glycolytic intermediate that contributes to the production of serine.