Chest and Mediastinum PART V & Abdomen PART VI
1/1428
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
1429 Terms
What is an aberrant right subclavian artery (arteria lusoria)?
An anomaly where the right subclavian artery arises directly from the aortic arch as the 4th branch
What is the correct branching order in arteria lusoria?
Right common carotid, left common carotid, left subclavian, right subclavian
What is the historical term for dysphagia caused by this anomaly?
Dysphagia lusoria
When does arteria lusoria develop during embryologic formation?
Early during embryologic development
What is the incidence of an aberrant right subclavian artery (arteria lusoria)?
Incidence 0.5%–2% of the population
What is the most common aortic arch anomaly?
Left aortic arch with an aberrant right subclavian artery
What symptoms can be caused by an aberrant right subclavian artery (arteria lusoria)?
Dysphagia lusoria, retrosternal pain, chronic cough, difficulty swallowing, weight loss
In what percentage of cases does an aberrant right subclavian artery pass posterior to the esophagus?
80%
In what percentage of cases does an aberrant right subclavian artery pass between the esophagus and the trachea?
15%
In what percentage of cases does an aberrant right subclavian artery pass anterior to the trachea?
5%
What findings can be seen on CT or MRI in patients with an aberrant right subclavian artery (arteria lusoria)?
Aberrant right subclavian artery branching from the aortic arch
What is a Kommerell diverticulum?
Bulbous enlargement of the proximal aberrant subclavian artery at its origin
What key anatomical details can CT or MRI help determine in patients with an aberrant right subclavian artery (arteria lusoria)?
Extrinsic airway compression
What treatment options are available for patients with an aberrant right subclavian artery (arteria lusoria)?
Various surgical procedures may be helpful
What is the prognosis for patients with an aberrant right subclavian artery (arteria lusoria)?
Good
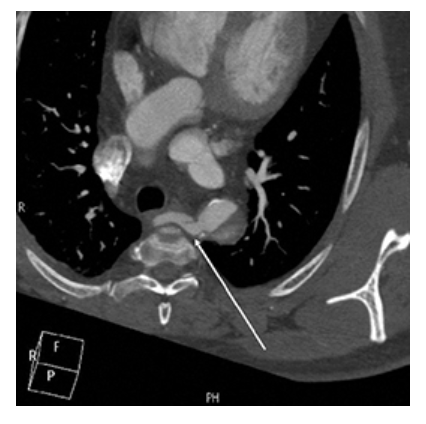
What does the figure show?
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery. Axial contrast-enhanced CT shows aberrant right subclavian artery moving toward the right arm crossing the midline of the body (arrow).
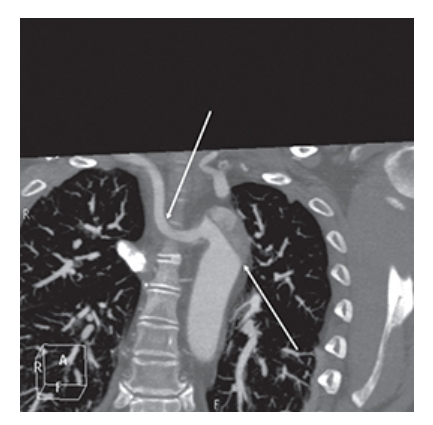
What does the figure show?
Aberrant Right Subclavian Artery. Coronal contrast-enhanced CT shows aberrant right subclavian artery (top arrow). Type B aortic dissection involving the descending thoracic aorta extending up to the left subclavian artery is also seen (bottom arrow).
What is aortic regurgitation (AR)?
Leakage/backward flow of blood from the aorta into the left ventricle through the aortic valve
What are the two most common causes of acute aortic regurgitation (AR)?
Infective endocarditis and prosthetic valve dysfunction
What emerging procedures or devices can lead to aortic regurgitation (AR)?
Post‑TAVR AR and LVAD‑associated complications
What other conditions can cause aortic regurgitation (AR)?
Valvular disease, congenital bicuspid aortic valve, Marfan syndrome
What is the most common cause of aortic regurgitation (AR) worldwide?
Rheumatic fever
When does aortic regurgitation (AR) incidence peak?
Fourth to sixth decades of life
Which sex is more commonly affected by aortic regurgitation (AR)?
Males
What symptoms may occur in aortic regurgitation (AR)?
Shortness of breath, chest pain, palpitations
What can cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) evaluate in aortic regurgitation (AR)?
AR severity, LV volumes, LV function
What does cardiac magnetic resonance (CMR) quantitative flow measurement calculate?
Regurgitation ejection fraction (EF)
What MRI finding helps diagnose stenosis and regurgitation in aortic regurgitation (AR)?
Signal void “jet” from the valve
What is the treatment for aortic regurgitation (AR)?
Surgical intervention usually indicated; medical therapy may be used
What determines prognosis in aortic regurgitation (AR)?
LV function and overall patient health
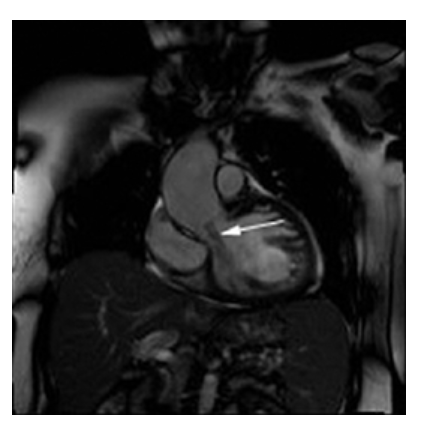
What does the figure show?
Aortic Regurgitation. Coronal oblique view shows moderate jet (dark, signal void) emanating from the aortic value into the left ventricle (arrow). There is also dilatation of the ascending aorta.
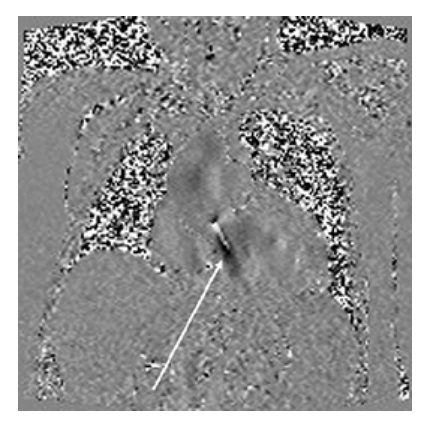
What does the figure show?
Aortic Regurgitation. Velocity encoded coronal image shows aortic regurgitation jet into the left ventricle (arrow).
What is the most common benign tumor of the heart?
Atrial myxoma
Where are most myxomas located?
Left atrium (75%)
What percentage of myxomas occur in the right atrium?
18%
What percentage of myxomas occur in the right ventricle?
4%
What percentage of myxomas occur in the left ventricle?
3%
What is the etiology of cardiac myxoma?
Primary tumor developing mostly in the left atrium
What percentage of myxomas are familial?
5%–10%
What age range most commonly develops myxomas?
30–60 years
Which sex is more affected by myxomas?
Women
Which group has a higher incidence of ventricular myxomas?
Children
What symptoms may occur with atrial myxoma?
Dyspnea on exertion, PND, orthopnea, chest pain, dizziness, fainting, palpitations
Where do myxomas most commonly attach?
Pedunculated attachment to interatrial septum near fossa ovalis
What mechanical complication can occur with cardiac myxoma?
Tumor prolapse through mitral valve causing outflow obstruction
What is the T1 MRI appearance of a myxoma?
Hypointense to myocardium
What is the T2 MRI appearance of a myxoma?
Hyperintense
How does a myxoma appear on SSFP images?
Hyperintense to myocardium, hypointense to blood pool
What is the post‑contrast MRI appearance of a cardiac myxoma?
Heterogeneous enhancement
What is the treatment for atrial myxoma?
Surgical removal of the entire tumor
What is the prognosis for atrial myxoma?
Benign, but can cause embolism or obstruct blood flow if untreated
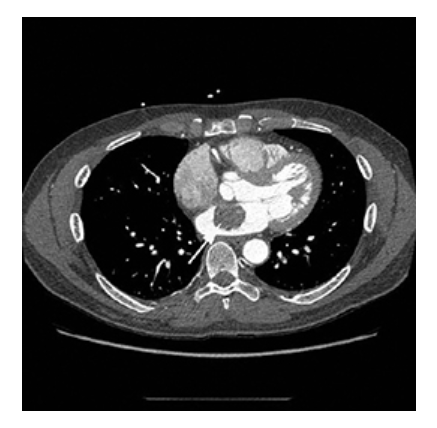
What does the figure show?
Atrial Myxoma. Contrast-enhanced axial CT shows a round filling defect/mass in the left atrium consistent with a myxoma (arrow).
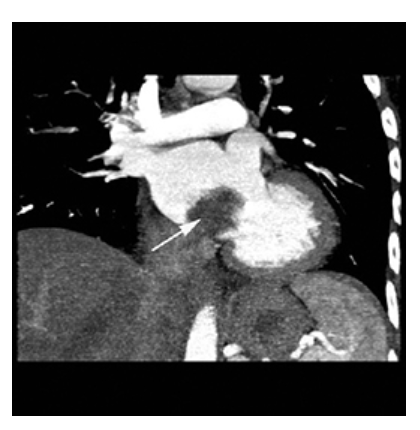
What does the figure show?
Atrial Myxoma. Contrast-enhanced coronal MPR CT shows a round filling defect/mass in the left atrium consistent with a myxoma (arrow).
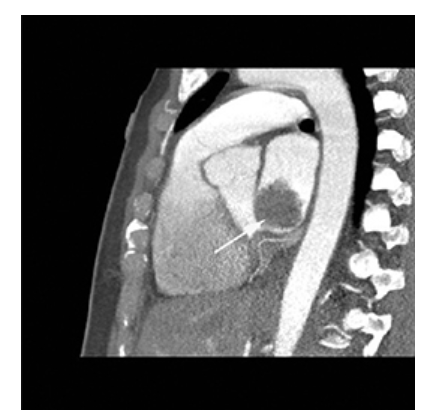
What does the figure show?
Atrial Myxoma. Contrast-enhanced sagittal MPR CT shows a round filling defect/mass in the left atrium consistent with a myxoma (arrow).
What is coronary artery disease (CAD)?
Atherosclerotic plaque buildup in the coronary artery lumen causing reduced or absent blood flow
What are the major risk factors that cause coronary artery disease (CAD)?
Atherosclerotic buildup of fatty deposits (plaques) narrowing the coronary arteries
What is the most common type of heart disease in men and women called?
Coronary artery disease
What is the most common presenting symptom of coronary artery disease (CAD)?
Angina
What other symptoms may occur in coronary artery disease (CAD) besides angina?
Shortness of breath, palpitations, tachycardia, weakness/dizziness, nausea, sweating
What can cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) evaluate in coronary artery disease (CAD)?
Coronary artery patency to determine if a vessel is occluded
What interventional procedures are used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD)?
Balloon angioplasty, atherectomy, laser treatment, stent placement
What surgical procedure may be used to treat coronary artery disease (CAD) in select cases?
Coronary bypass surgery
What factors determine prognosis in coronary artery disease (CAD)?
Patient recovery; lifestyle changes improve outcomes
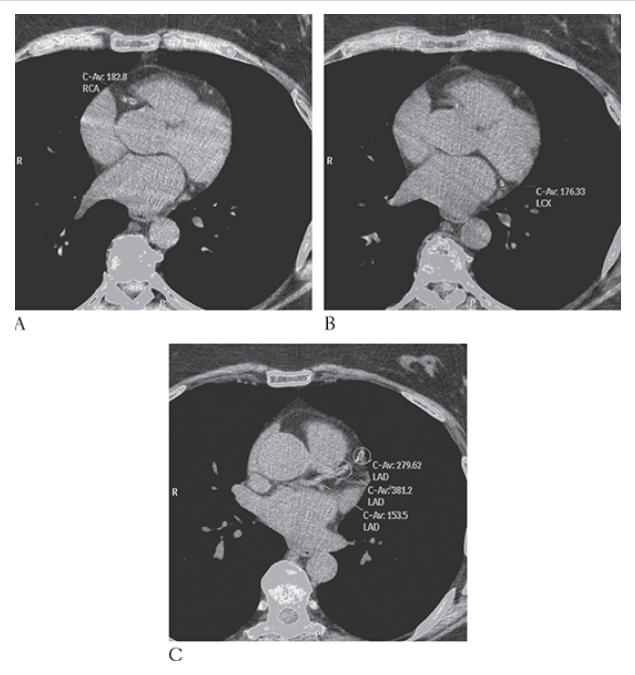
What is A
Coronary Artery Disease. Nonenhanced CT (NECT) shows computer-aided detection and calculation of coronary artery calcification in the right coronary artery
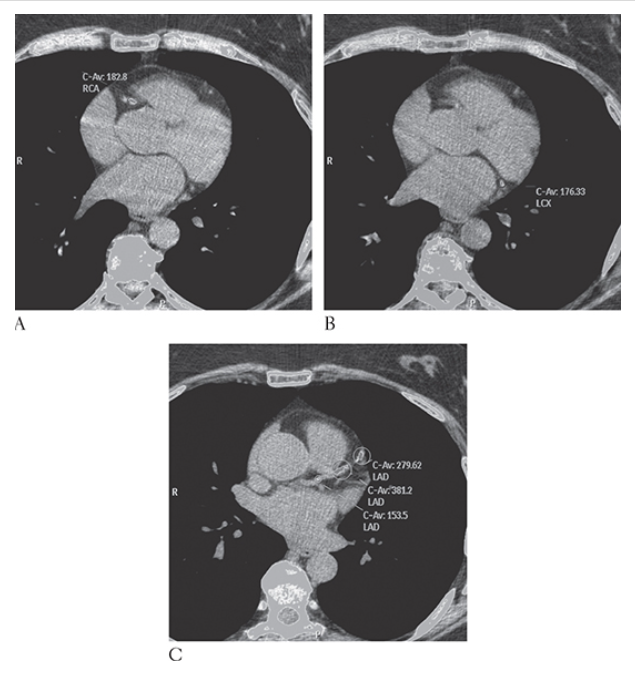
What is B
Coronary Artery Disease. Nonenhanced CT (NECT) shows computer-aided detection and calculation of coronary artery calcification in the left circumflex artery
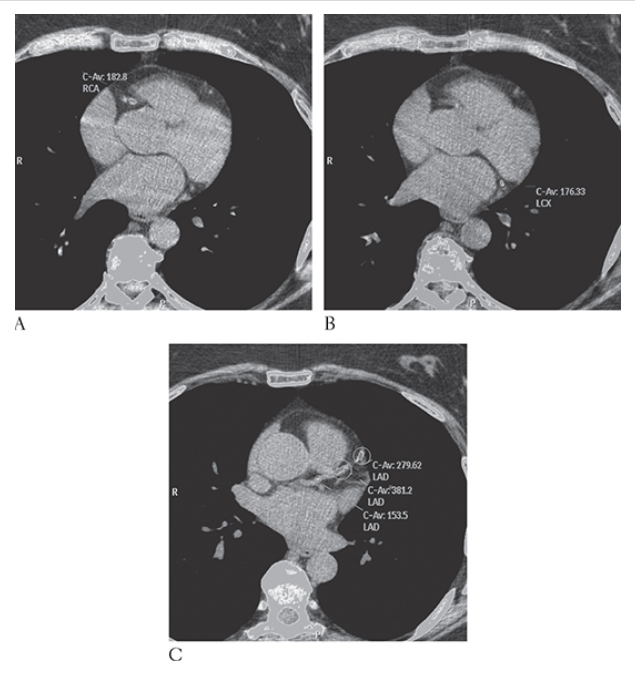
What is C
Coronary Artery Disease. Nonenhanced CT (NECT) shows computer-aided detection and calculation of coronary artery calcification and left anterior descending coronary artery
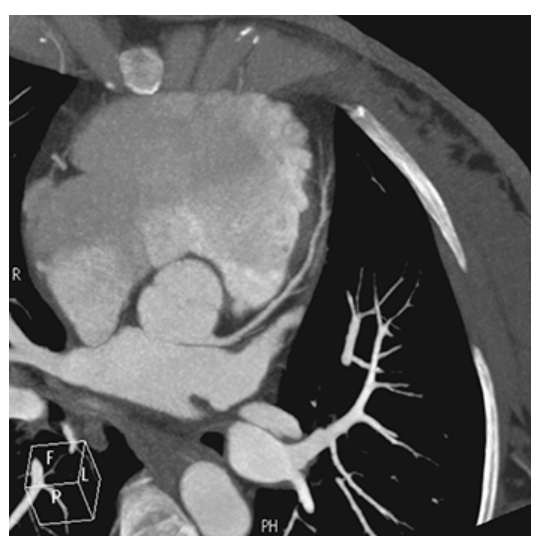
What does the figure show?
Coronary Artery Disease. Maximum intensity projection CT coronary angiogram showing near-complete occlusion of the right coronary artery.
What is a pericardial effusion?
Collection of fluid in the pericardial sac
What are possible causes of pericardial effusion?
Infection, inflammation, immunologic, traumatic, uremic, neoplastic, hypothyroidism, chylopericarditis, CHF
Most cases of pericardial effusion are related to what underlying processes?
Secondary diseases with known or suspected underlying processes
What symptoms may occur in patients with pericardial effusion?
Chest pain, dyspnea, lightheadedness
What is the imaging modality of choice for diagnosing pericardial effusion?
Ultrasound
What is the normal thickness of the pericardium?
3 mm
What pericardial thickness suggests pericardial thickening?
>4 mm
What can cardiovascular magnetic resonance (CMR) assess in pericardial effusion?
Ventricular filling patterns
What treatment is often required for pericardial effusion?
Pericardiocentesis to treat or prevent tamponade
When is surgery needed for pericardial effusion?
When pericardiocentesis is insufficient or complications occur
What is the prognosis for pericardial effusion?
Serious condition; hospitalization required until treatment or improvement
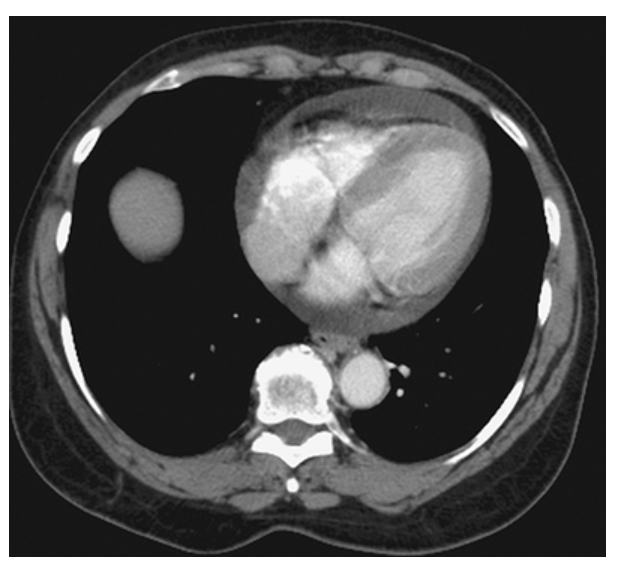
What does the figure show?
Pericardial Effusion. Contrast-enhanced CT (CECT) shows increased fluid density around the heart consistent with a pericardial effusion.
What does the figure show?
Pericardial Effusion. Normal for comparison.
What is situs inversus?
Right‑to‑left reversal of thoracic and abdominal organs; includes dextrocardia (cardiac apex to the right)
What is situs inversus totalis?
Complete right‑to‑left transposition of thoracic and abdominal organs
What is the etiology of situs inversus?
Congenital
How common is situs inversus?
Occurs in ~0.1% of the population
Which form of situs inversus is more common?
Situs inversus with dextrocardia
What percentage of patients with situs inversus + dextrocardia have congenital heart disease?
3%–5%
What vascular finding is common in situs inversus with dextrocardia?
Right‑sided aortic arch
Which form of situs inversus is rare and usually associated with congenital heart disease?
Situs inversus with levocardia
Are most patients with situs inversus symptomatic?
Usually asymptomatic
What condition occurs in ~25% of patients with situs inversus?
Primary ciliary dyskinesia (Kartagener syndrome)
What triad defines Kartagener syndrome?
Situs inversus, bronchiectasis, chronic sinus infections
What is MRI useful for in situs inversus?
Difficult cases and associated cardiac anomalies
What is the treatment for situs inversus?
No treatment
What is the prognosis for situs inversus?
Good
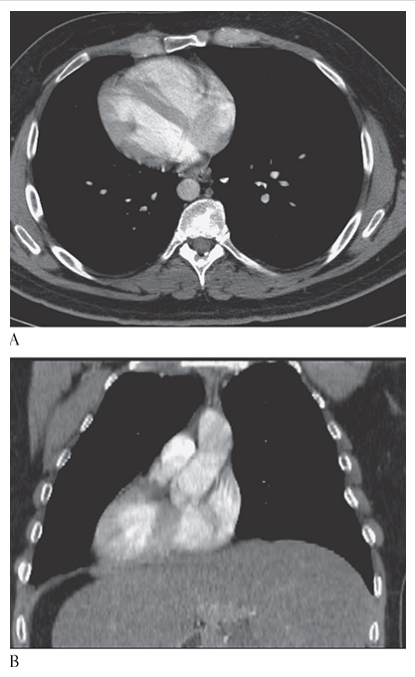
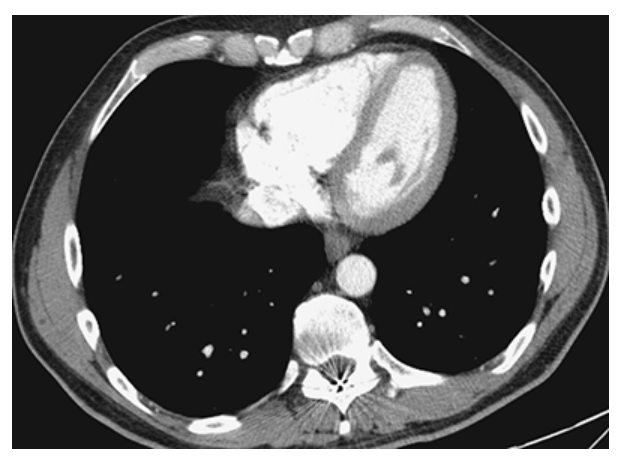
What is A
Situs Inversus. CT axial show the heart apex on the right.
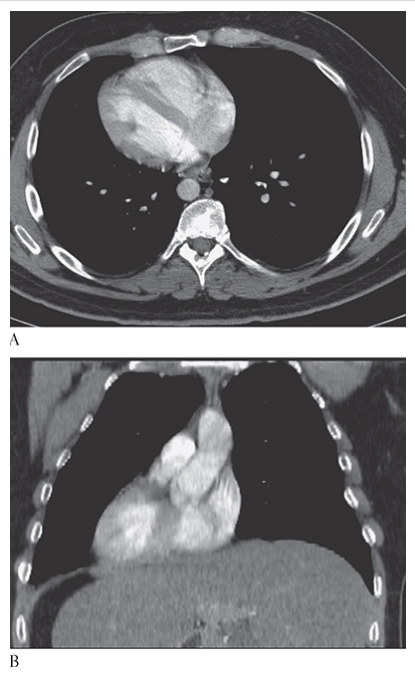
What is B
Situs Inversus. CT coronal multiplanar reconstruction (MPR) show the heart apex on the right.
What is Superior Vena Cava (SVC) Syndrome?
Obstruction of blood flow through the superior vena cava
What are common causes of Superior Vena Cava (SVC) syndrome?
Radiation, central venous catheter cannulation, tumor bulk, adenopathy, fibrosing mediastinitis
What is the most common underlying category of causes of Superior Vena Cava (SVC) syndrome?
Malignant mediastinal tumors
What is the most common symptom of Superior Vena Cava (SVC) syndrome?
Dyspnea