UT Austin - UGS 303 Sustaining a Planet
1/189
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
190 Terms
Drivers of consumption
population, affluence, and technology
Gro Brundtland
known as the mother of sustainable development; "sustainable development is development that meets the needs of the present without compromising the ability of future generations to meet their own needs"
Rachel Carson
one of the first people to realize the global dangers of pesticide abuse (DDT). Wrote Silent Spring.
Barry Commoner
an activist scientist who spoke out about environmental hazards emphasized the link between science, technology and society. Wrote Science and Survival
Paul ehrlich
The Population Bomb theory; geometric growth of population
Thomas Malthus
Eighteenth-century English intellectual who warned that population growth threatened future generations because, in his view, population growth would always outstrip increases in agricultural production.
IPAT equation
an equation used to estimate the impact of the human lifestyle on the environment:
impact = population x affluence x technology
At what rate is global population growing?
1 to 2% per year
where is population growing the fastest?
Africa
at what rate is global affluence growing?
3 to 5% per year
where is affluence growing the fastest?
Nigeria, Egypt, and Bangladesh
at what rate is efficiency of resource use changing?
-1 to -2 % per year
3 pillars of sustainable development
economic growth, environmental protection, and social equality
basic trend in global consumption of energy
increasing rapidly due to population and economic growth
pathological science
scientists fool themselves into thinking the NEED to achieve their original hypothesis - too emotionally involved
pseudoscience
does not follow the scientific method
junk science
purported theories with little supporting evidence, crafted to fool lawmakers and the public
carrying capacity
Largest number of individuals of a population that a environment can support
easter island
An island in the eastern Pacific Ocean, part of Polynesia, known for its giant human head statues (Moai)
when was Easter Island discovered?
1722 by Roggeveen who was a European explorer
how was Easter Island reconstructed
1. Lake sediment records (radiocarbon and pollen)
2. Midden records (trash and bones)
3. Oral and recorded histories
4. DNA history
archeological reconstruction/timeline of Easter Island
1. Polynesians blown off course?
2. Many resources
3. Culture and Moai
4.Cycle of growth: population growth
5. Land clearing: more erosion of soil
6. Choices of solutions to growth problem: keep going or control?
7. The real survivors: grass, rats, some people
Modern day examples of tragedy of the commons
Ogallala Aquifer - using it for surrounding farmland
The Gulf of Mexico/Mississippi River - dumping into rivers that lead into the gulf
Carbon Dioxide Atmosphere
tragedy of the commons
situation in which people acting individually and in their own interest use up commonly available but limited resources, creating disaster for the entire community
gulf of mexico tragedy of the commons
Hypoxia is believed to be caused primarily by excess nutrients delivered from the Mississippi River in combination with seasonal stratification of Gulf waters. Excess nutrients promote algal and zooplankton growth.
element
A pure substance made of only one kind of atom
compound
A substance made up of atoms of two or more different elements joined by chemical bonds
minerals
a naturally occurring, inorganic solid that has a crystal structure and a definite chemical composition
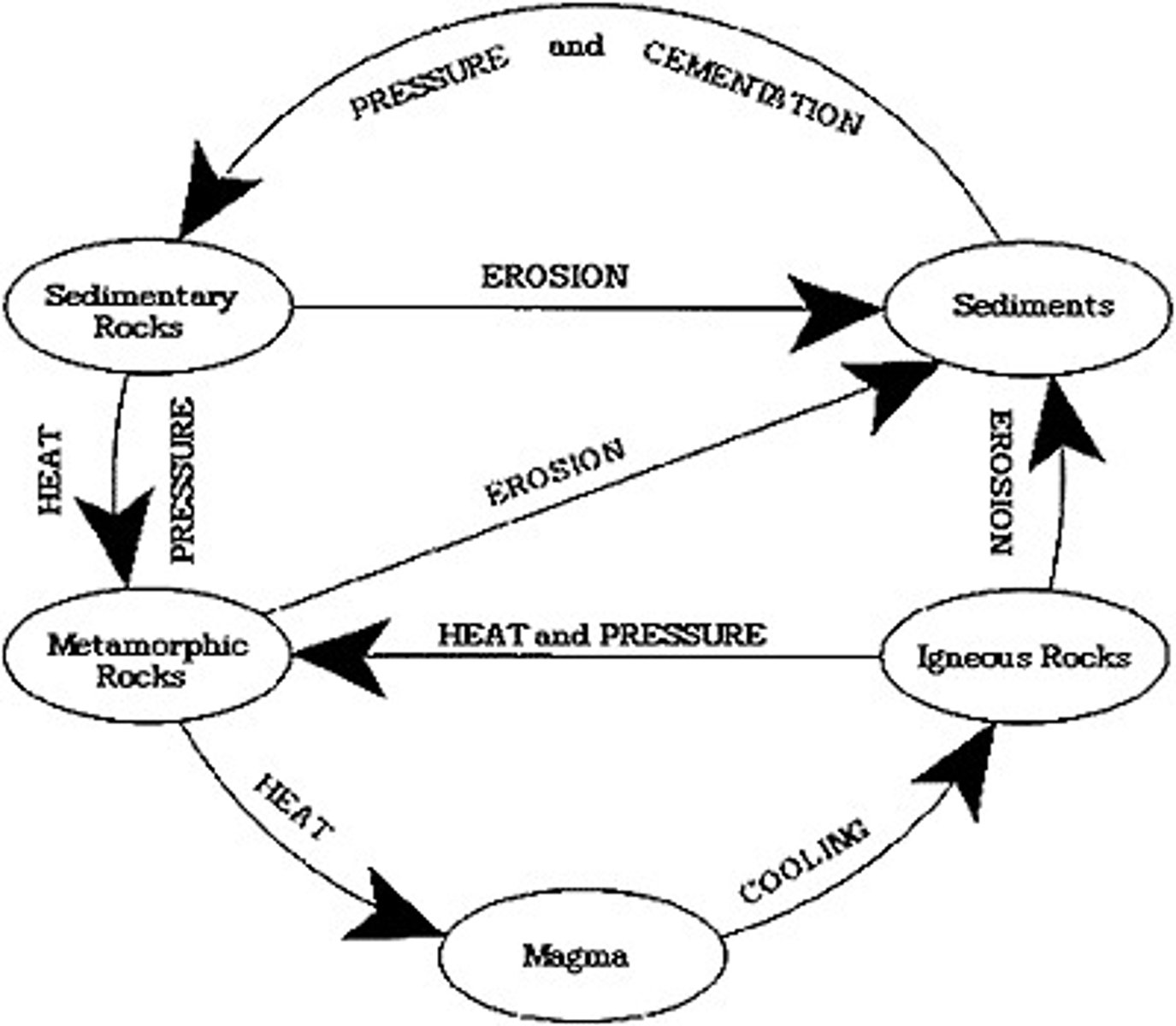
types of rocks
igneous, sedimentary, metamorphic
igneous rock
rock that forms when magma cools and solidifies
sedimentary rock
A type of rock that forms when particles from other rocks or the remains of plants and animals are pressed and cemented together
two ways sedimentary rocks form
1. deposit sediments from erosion of pre-existing rock and then solidify upon burial into rock
2. chemical/water - marine life creates rocks and shells through chemical process
metamorphic rock
A type of rock that forms from an existing rock that is changed by heat, pressure, or chemical reactions.
rock cycle
A series of processes on the surface and inside Earth that slowly changes rocks from one kind to another
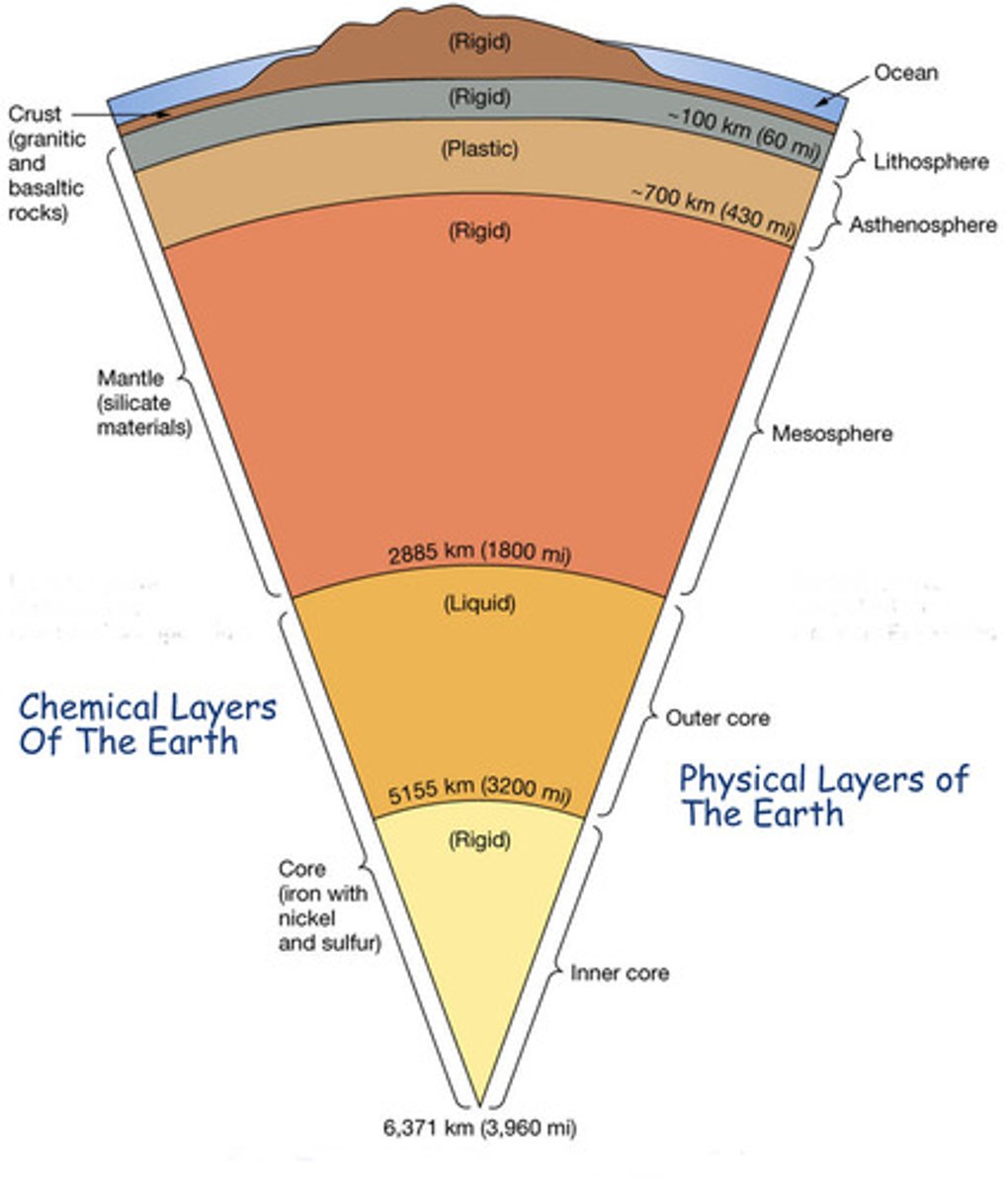
Earth layers
pangea
A supercontinent containing all of Earth's land that existed about 225 million years ago.
Wegener's hypothesis (The Grand Synthesis)
all the continents were once joined together in a single landmass and have since drifted apart
pangea proof points
1. puzzle piece continents
2. fossil and animal distribution
3. earthquakes and volcano distribution
4. differing ages of rocks on the continents and the rocks in ocean basins
evidence of continental drift
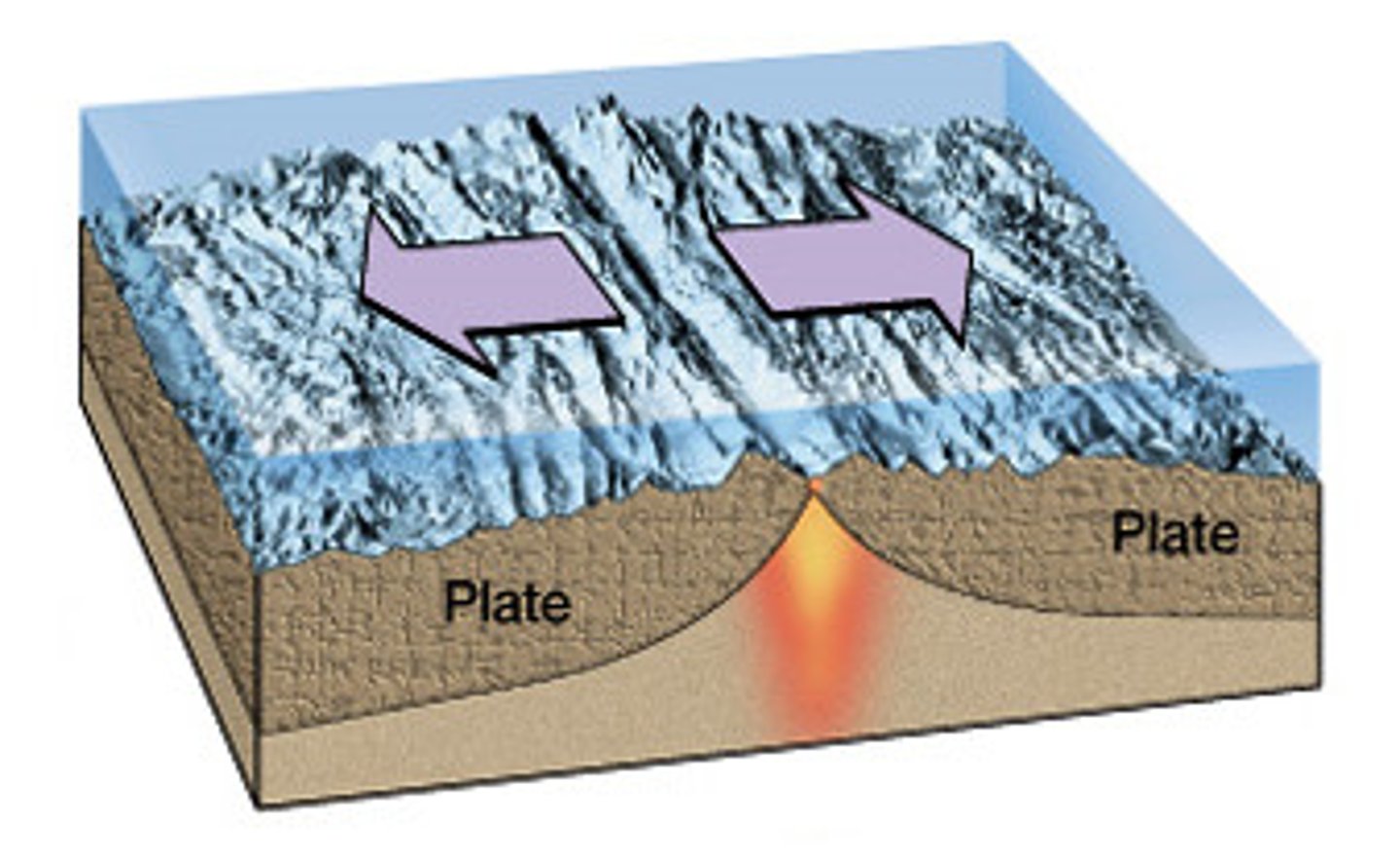
1. seafloor spreading (divergent boundaries)
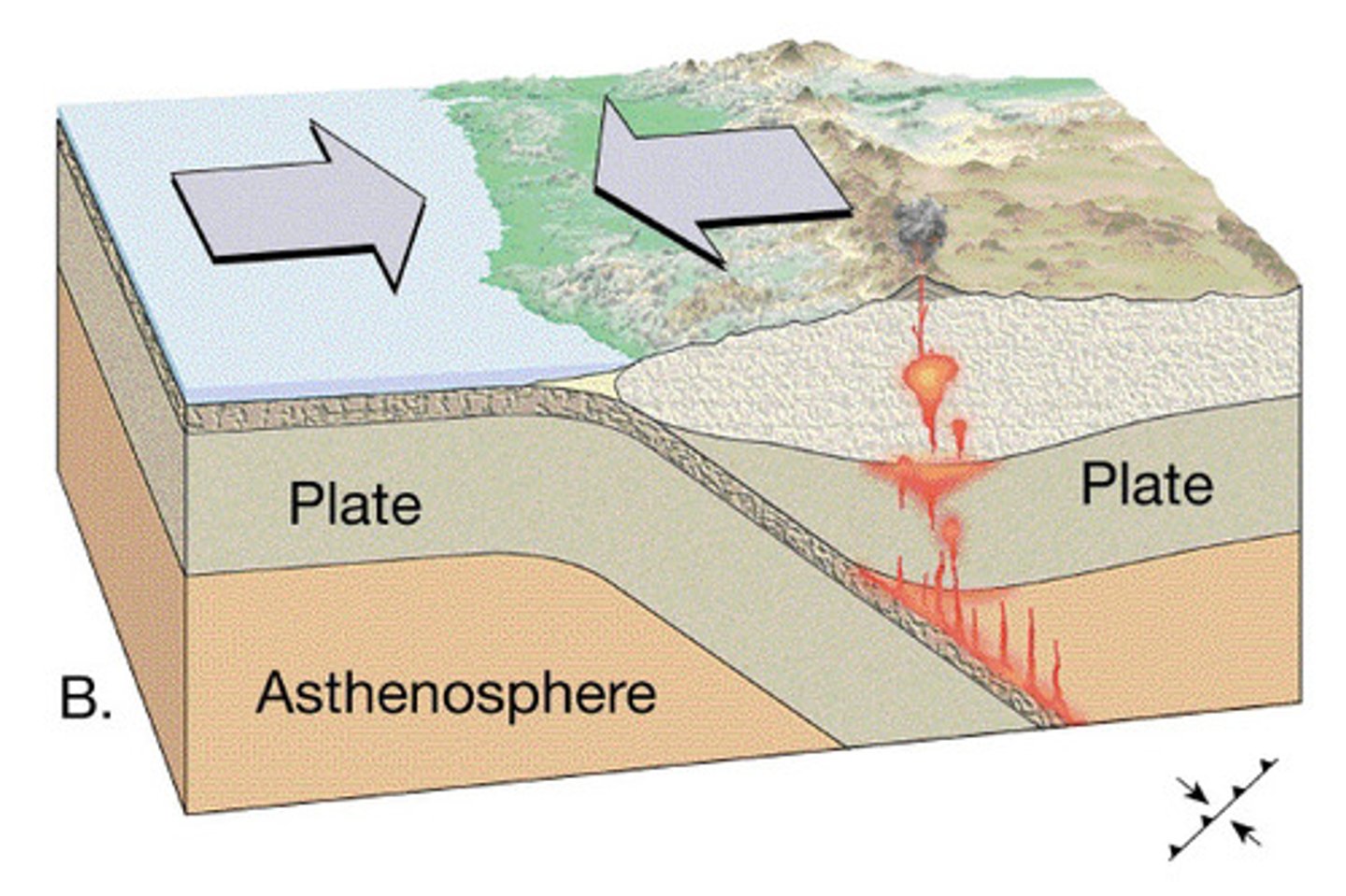
2. mass consumption of seafloor - subduction (convergent boundaries)
lithospheric plate movement rate
1-10 cm/yr
divergent boundary
The boundary between two tectonic plates that are moving away from each other. creates new crust. mild earthquakes and volcanoes. creates ridges and rift valleys
convergent boundary
A tectonic plate boundary where two plates collide, come together, or crash into each other. destroys old crust @ subduction zone. large earthquakes and volcanoes. creates mountains and trenches. the denser plate will subduct under the other plate
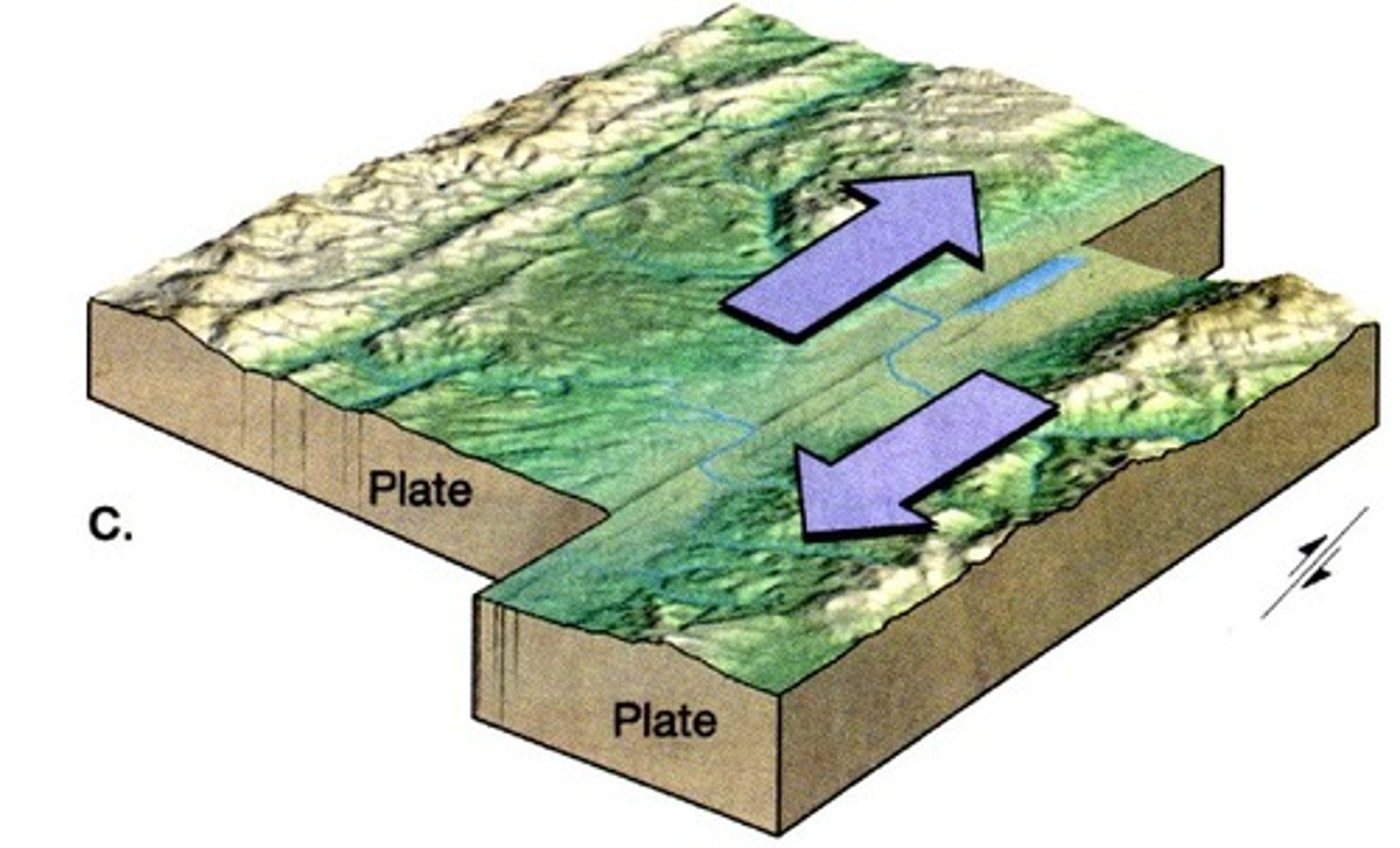
transform boundary
The boundary between tectonic plates that are sliding past each other horizontally. creates major earthquakes
andes mountains
convergent boundary; nazca plate is subducting under the south american plate
San Andreas Fault
transform boundary; only earthquakes
Iceland
divergent boundary; new crust being formed
Largest carbon reservoir
sedimentary rock
Atmosphere
a gaseous body bound gravitationally to a celestial body
-outermost layer of Earth, formed by outgassing of Earth's interior
-turbulent, rapidly changing
Importance of atmosphere
-makes life that requires respiration possible
-generates climate and weather
-filters a variety of types of electromagnetic radiation
-protects from space debris
-energy transfer
-water cycle
evolution of atmosphere
-CO2 went down due to photosynthesis
-Methane went down due to the chemical reaction with O2 to make CO2 and H2O
-NH3 (ammonia) went down because of the reactions with O2 to produce N
-O2 went up because of photosynthesis
troposphere
lowest layer of the atmosphere; contains the largest percentage of the mass (80%)
-Temperature and water vapor decrease with altitude
-contains 99% of all water vapor in the atmosphere
-contains all weather
-mainly N2 and O2
Stratosphere
2nd layer of the atmosphere
-temperature gradually increases
-contains the ozone layer which helps block UV rays
Mesosphere
3rd layer of the atmosphere
-temperature decreases with altitude
Thermosphere
4th layer of the atmosphere
-temp increases as altitude increases due to the absorption of solar radiation by the limited amount of remaining O2
Exosphere
The outer layer of the atmosphere
-transitional zone between atmosphere and space
benefits of atmosphere and greenhouse gases
without the atmosphere, it would be very very cold
-greenhouse gases help with providing temperate climate
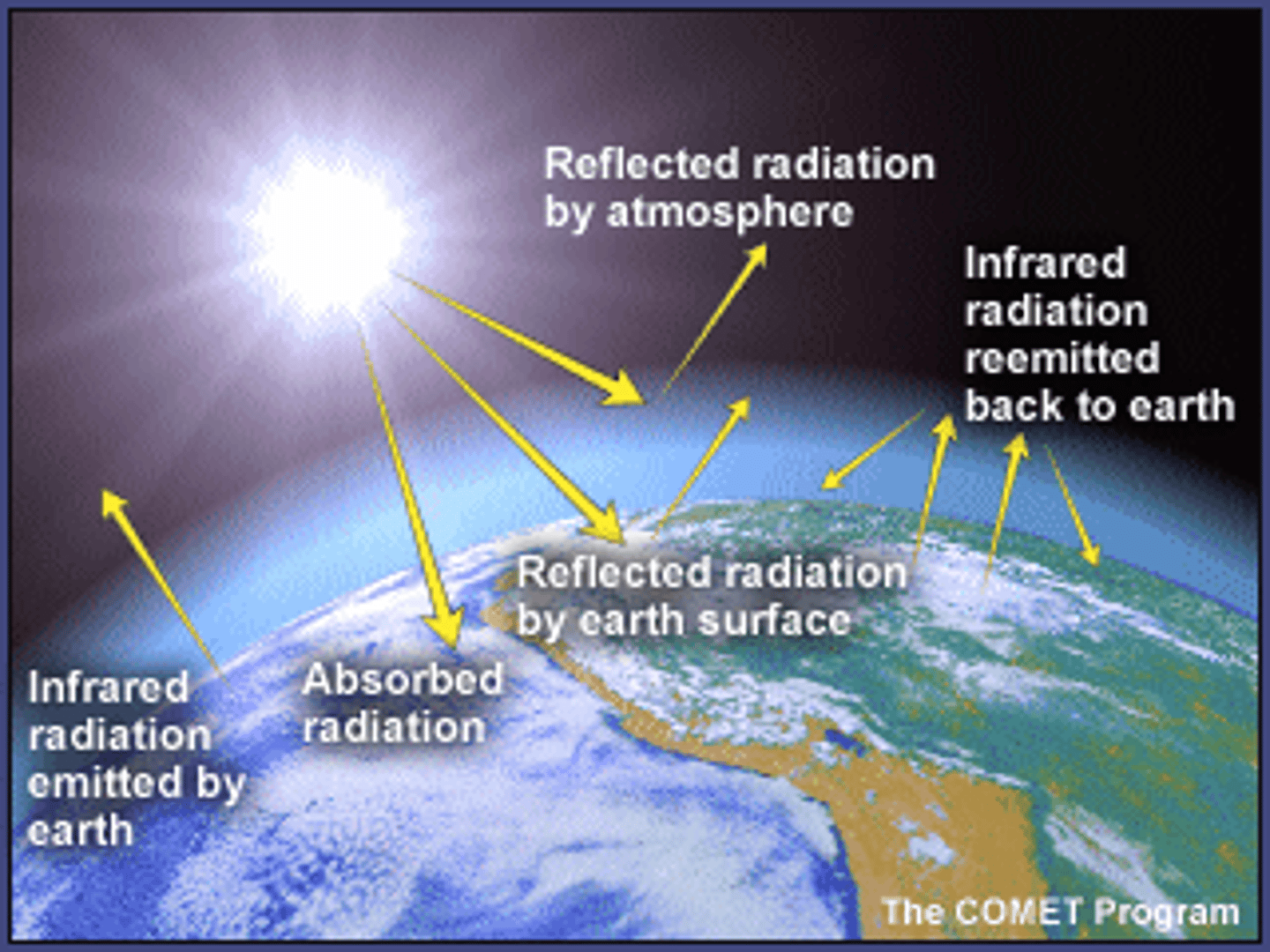
Greenhouse effect
infrared wavelengths cannot escape the atmosphere and heat up the Earth
Greenhouse gases
CO2, CH4 (methane), CFC's, O3, N2O (nitrous oxide)
greenhouse gas functions
-absorb infrared light at key frequencies and warm planet
-must be in the atmosphere for a long time in order to create more greenhouse effects
positive feedback loop
a feedback loop in which change in a system is amplified
negative feedback loop
A feedback loop in which a system responds to a change by returning to its original state, or by decreasing the rate at which the change is occurring.
Equator greenhouse effect
Accepts more solar radiation than the Earth can give off
Polar greenhouse effect
Releases more solar radiation than accepted from the sun
climate change
Change in the statistical properties of the climate system when considered over periods of decades - can be caused by natural sources of anthropogenic sources
global warming
An increase in the average temperature of the earth's atmosphere (especially a sustained increase that causes climatic changes) - due to anthropogenic emissions
Cap and Trade
a method for managing pollution in which a limit is placed on emissions and businesses or countries can buy and sell emissions allowances
Carbon tax
a fee that the government charges polluters for each unit of greenhouse gas they emit
Drivers of atmospheric circulation
1. solar radiation
2. gravity
3. Earth's rotation and orbit
Principles of atmospheric circulation
1. Hot air rises
2. Wind is movement of air in response to pressure gradients
3. Hot air can hold more moisture than cold air
4. Winds are deflected by Earth's rotation
5. Sun's rays hit Earth more directly at low latitude
6. Differential heating of land and oceans
seasons
Caused by the tilt of Earth on its axis as it revolves around the Sun
temperature
1. solar insolation: intensity varies with latitude due to changing footprint of energy flux
2. intensity and duration of insolation determined by tilt of the Earth
Aphelion
point in a planet's orbit that is farthest from the sun
Perihelion
orbital point nearest the sun
Angle of Tilt of Earth
23.5 degrees
How fast does the equator move?
1000 mi/hr
How fast do the poles move?
0 mi/hr
convection cells
circular patterns caused by the rising and sinking of air
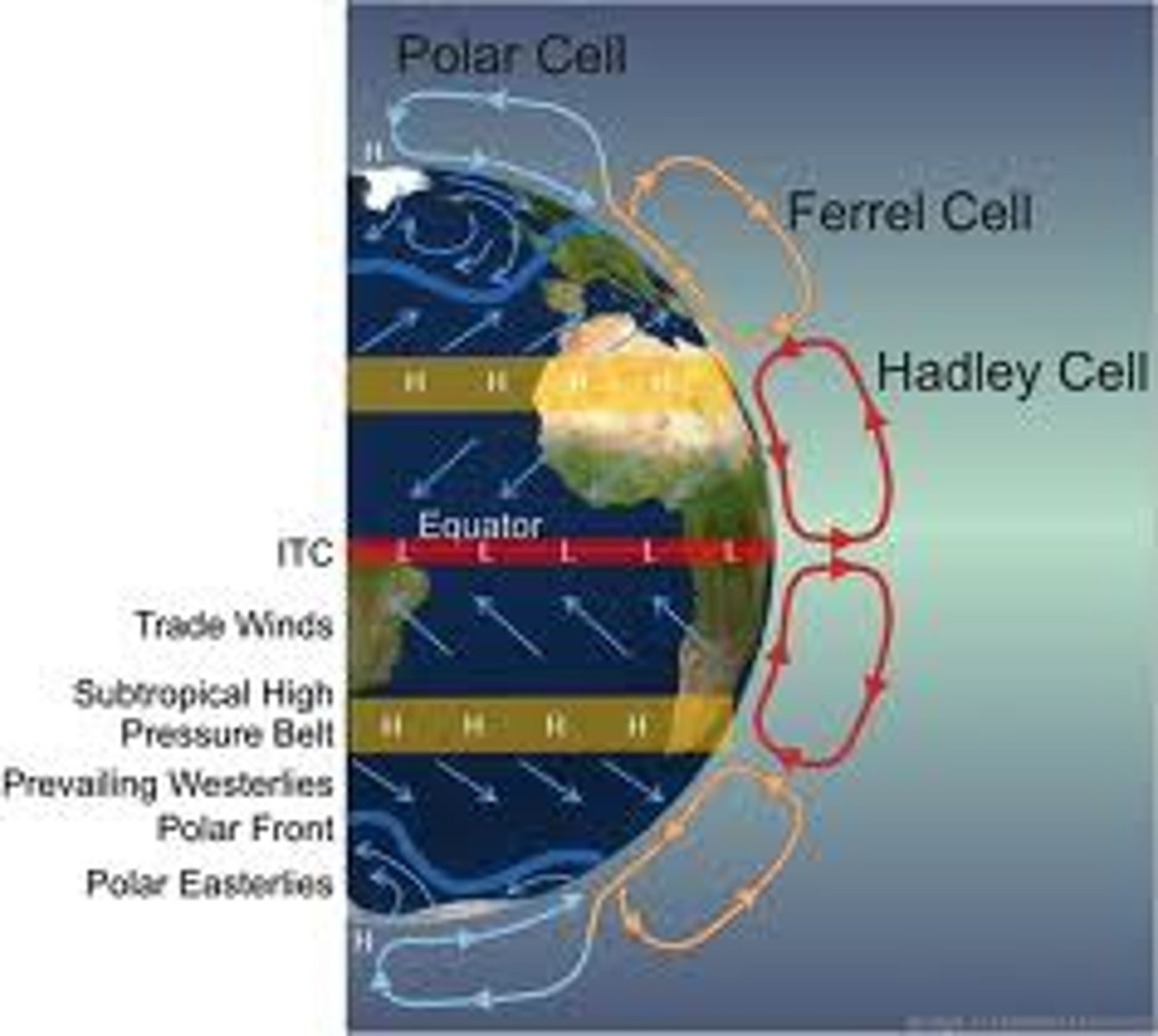
High pressure areas are caused by
converging air
low pressure areas are caused by
diverging air
Coriolis effect
Causes moving air and water to turn left in the southern hemisphere and turn right in the northern hemisphere due to Earth's hemisphere.
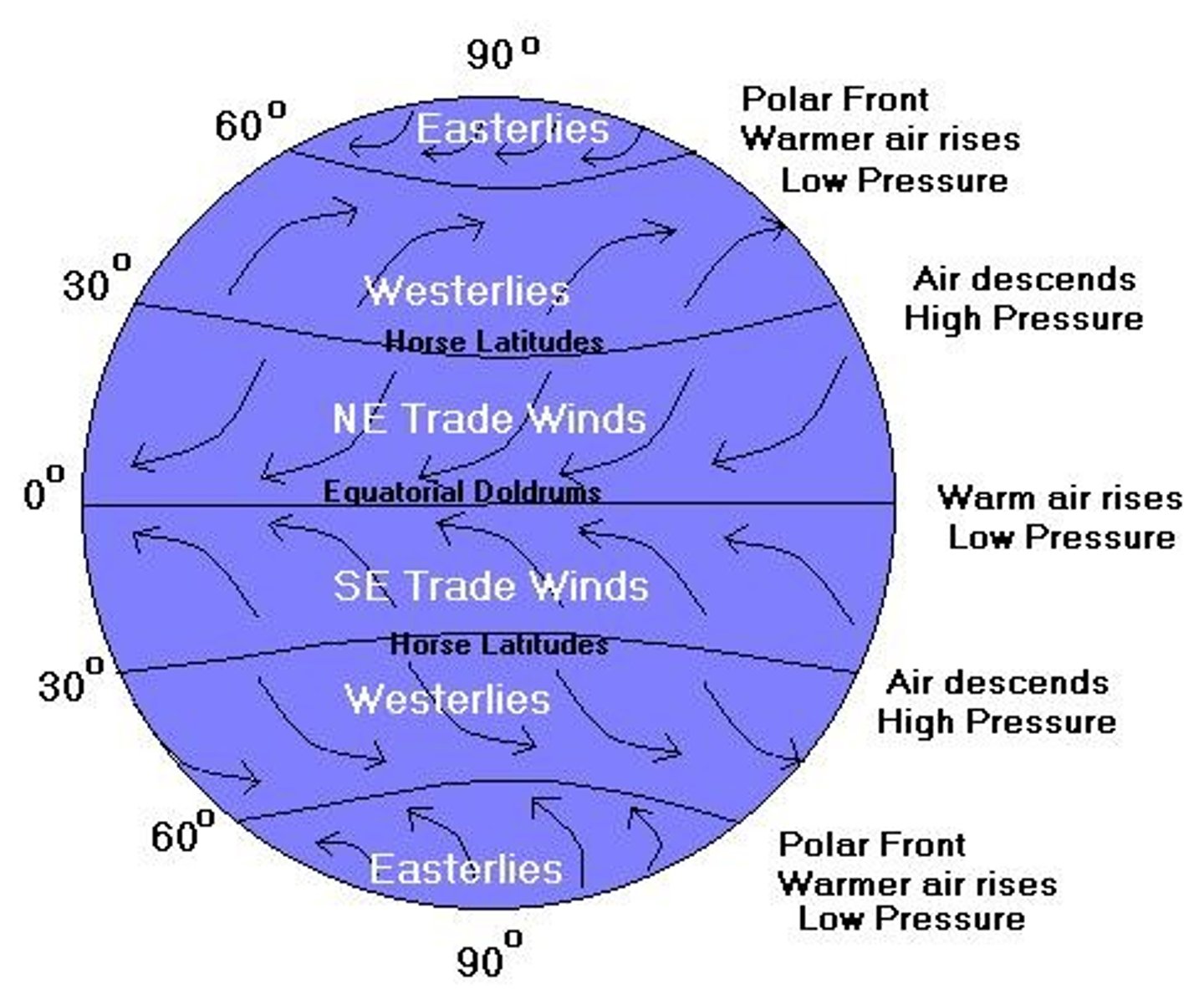
Low pressure system
a large body of circulating air with low pressure at its center and higher pressure outside of the system - cyclone
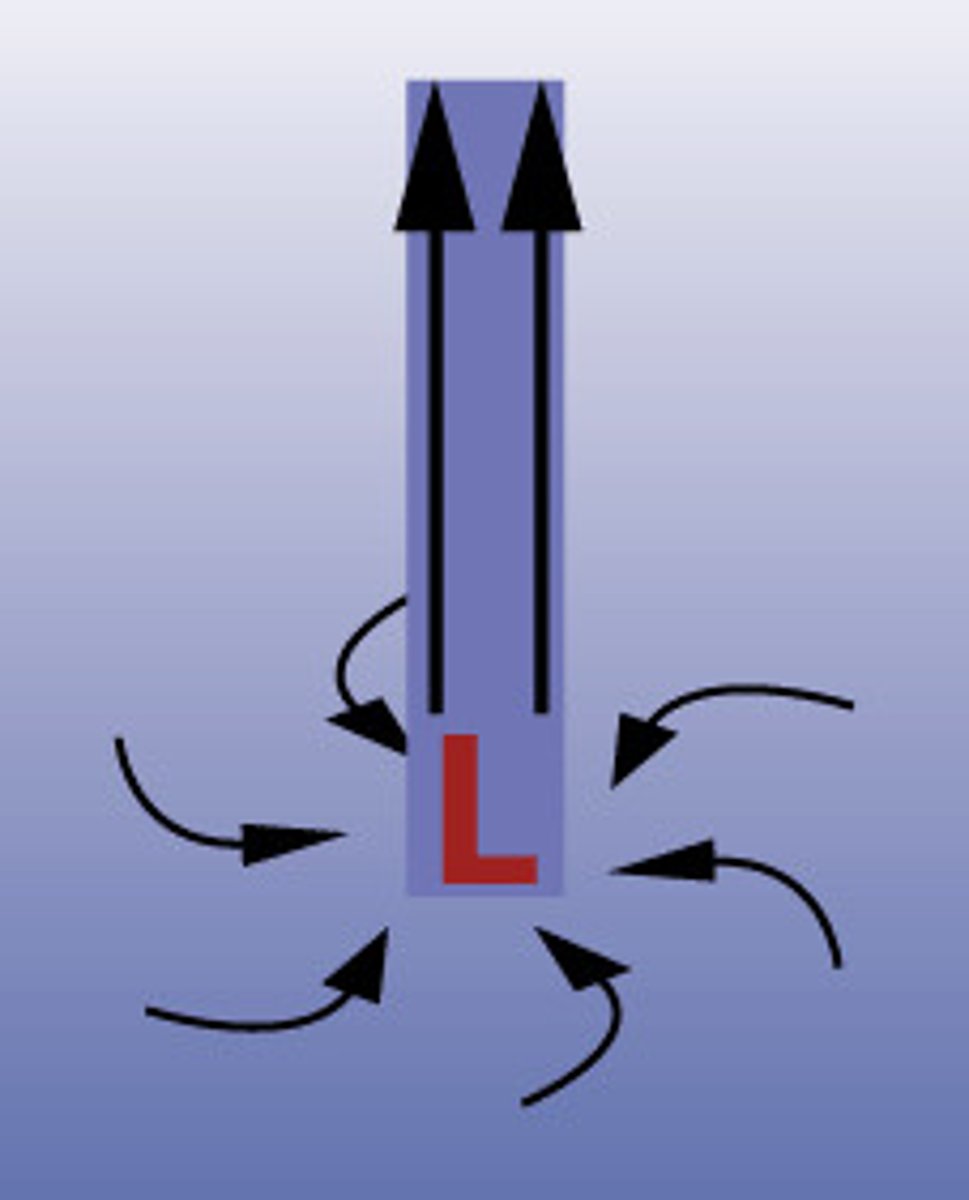
high pressure system
a large body of circulating air with high pressure at its center and lower pressure outside of the system - anticyclone
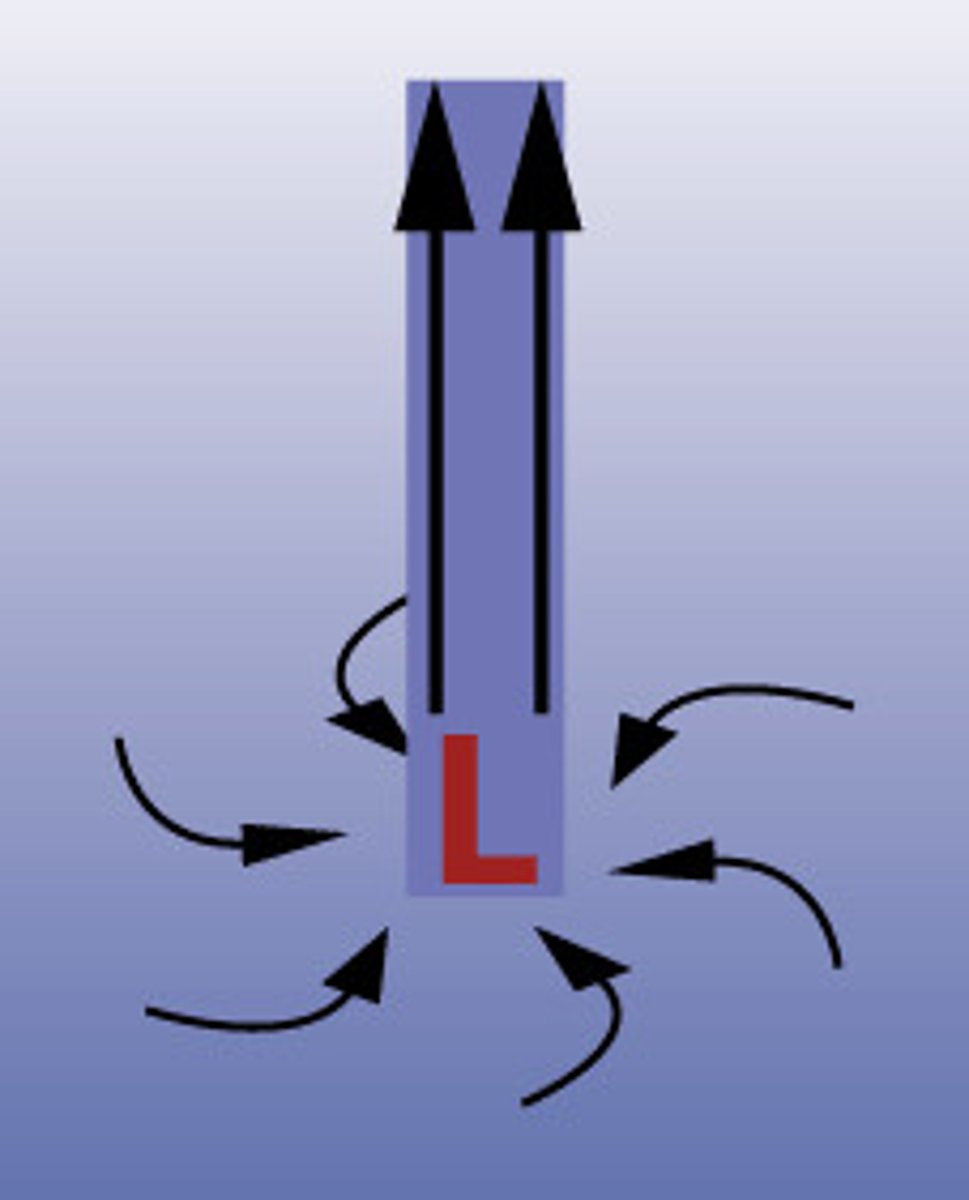
Northern Hemisphere high pressure system
Anticyclone
-non-visible
-clockwise
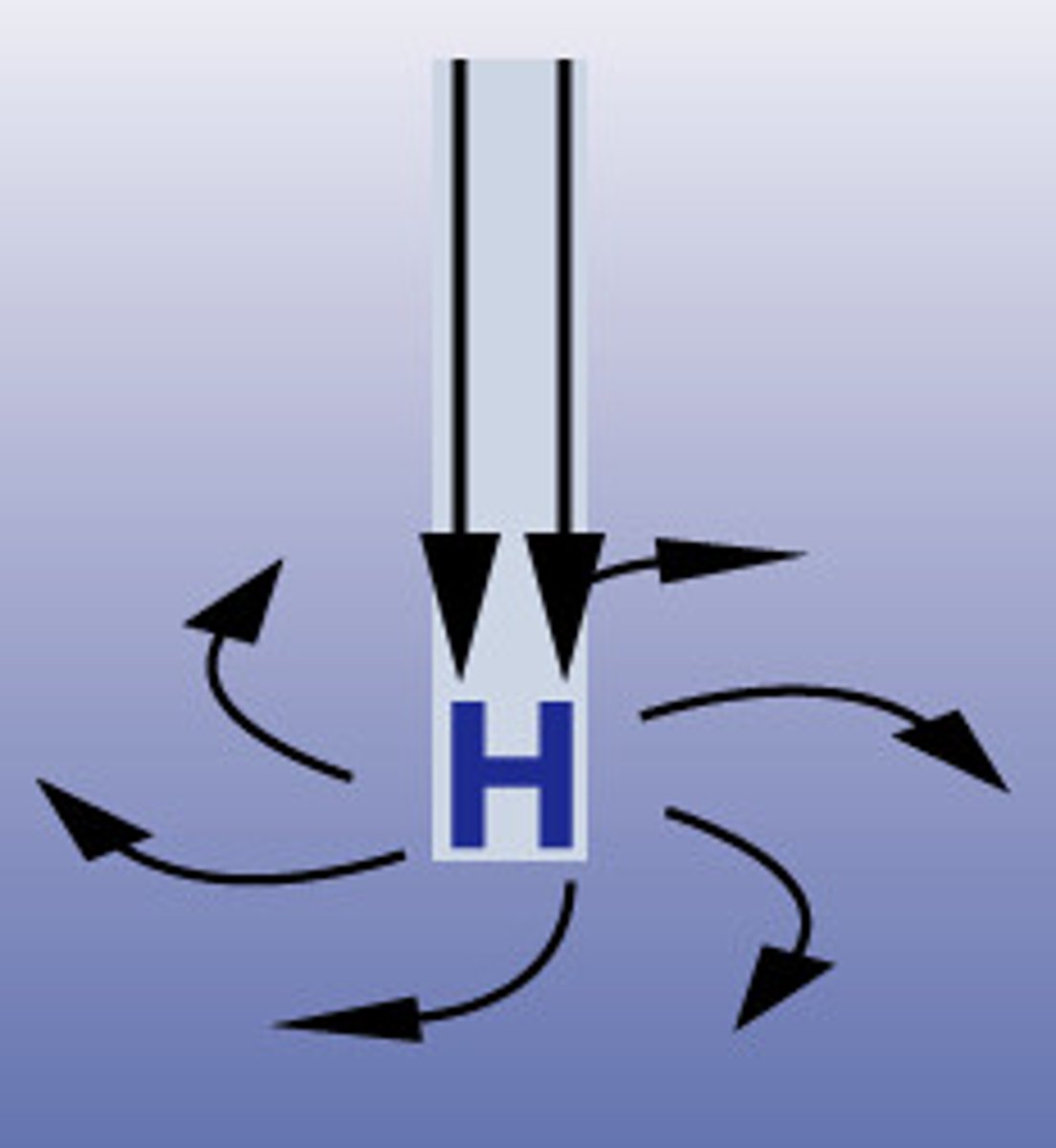
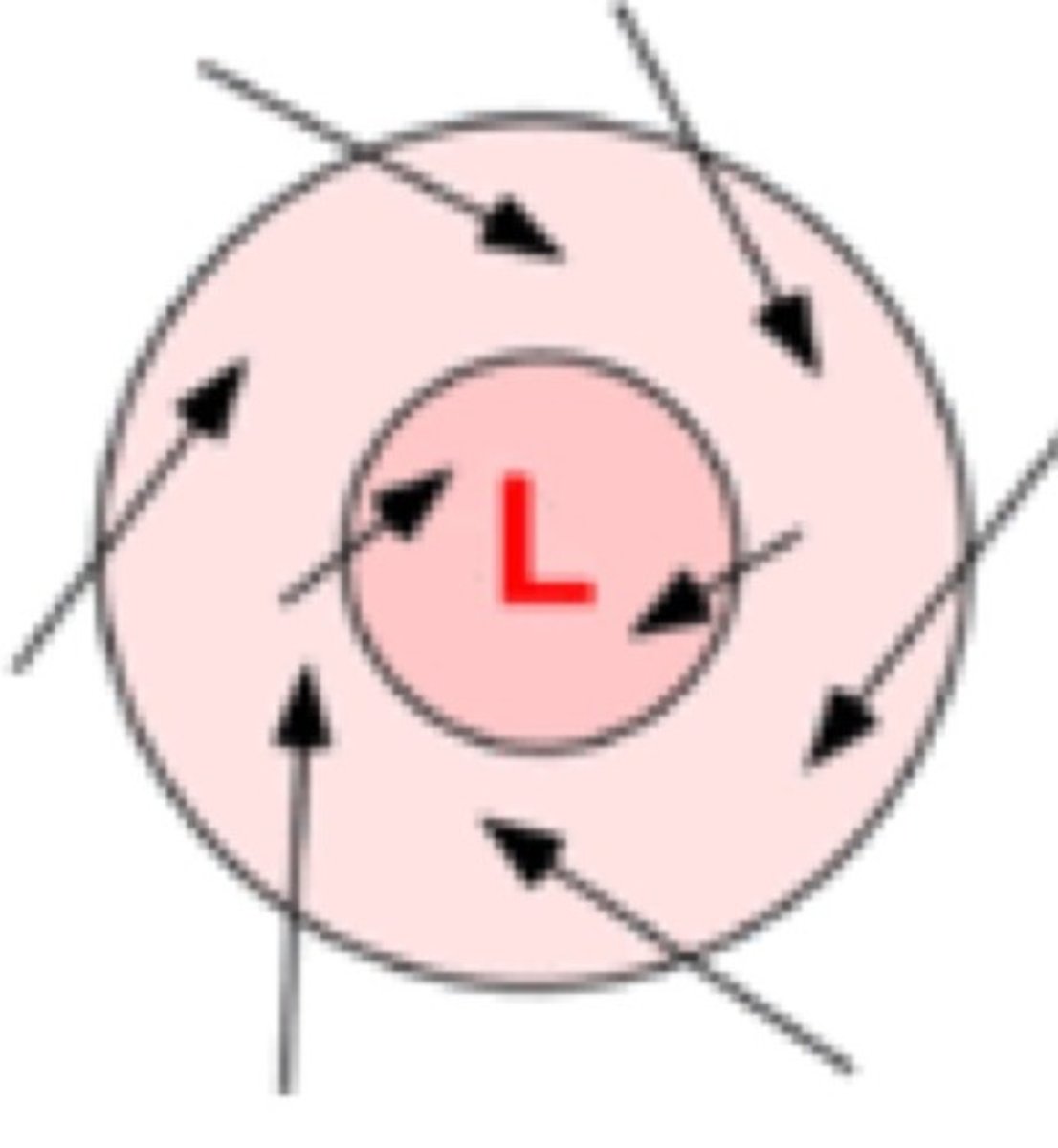
Northern Hemisphere low pressure system
Hurricane/Cyclone
-visible
-counterclockwise
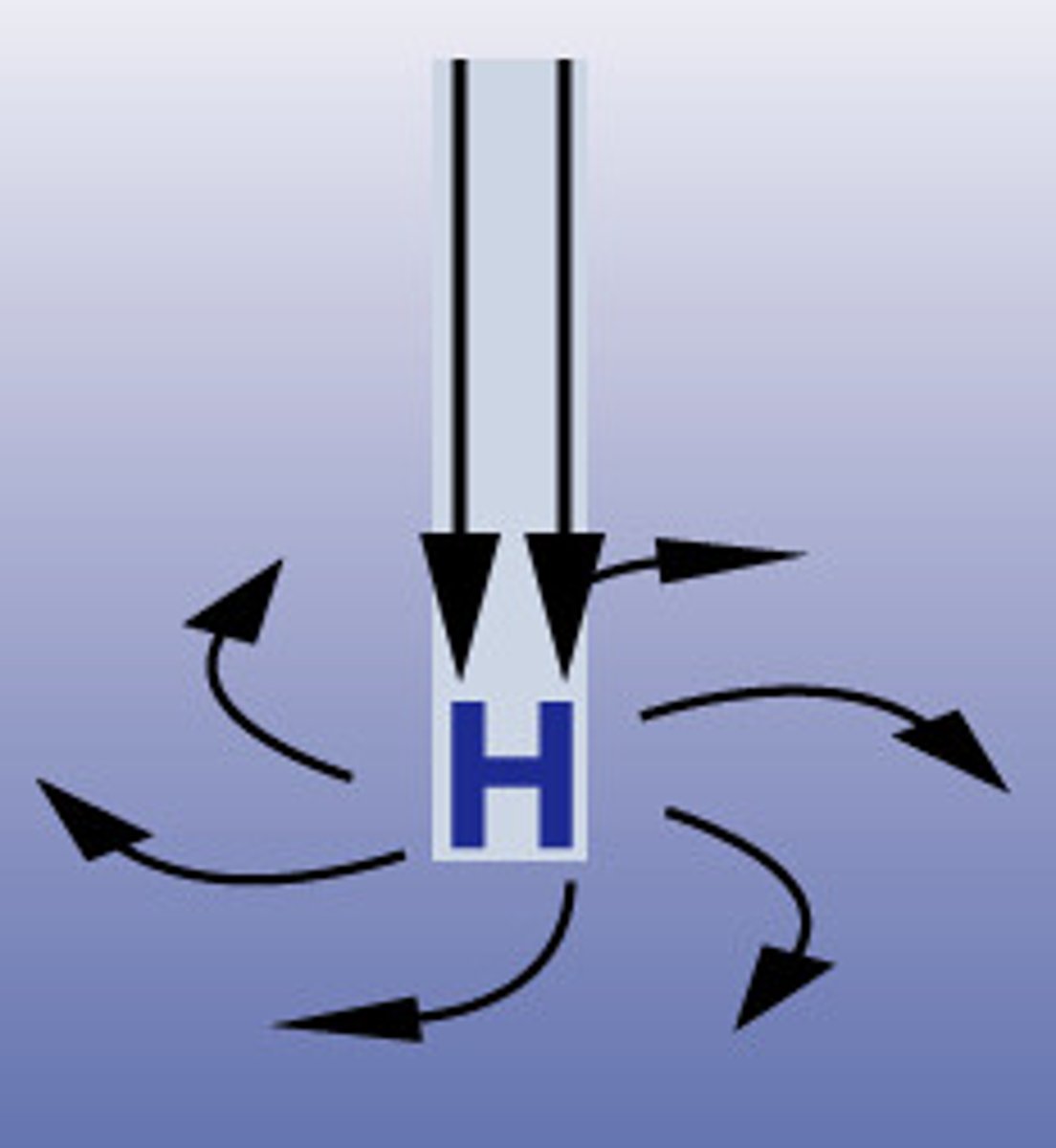
Southern Hemisphere high pressure system
Anticyclone
-non-visible
-counterclockwise
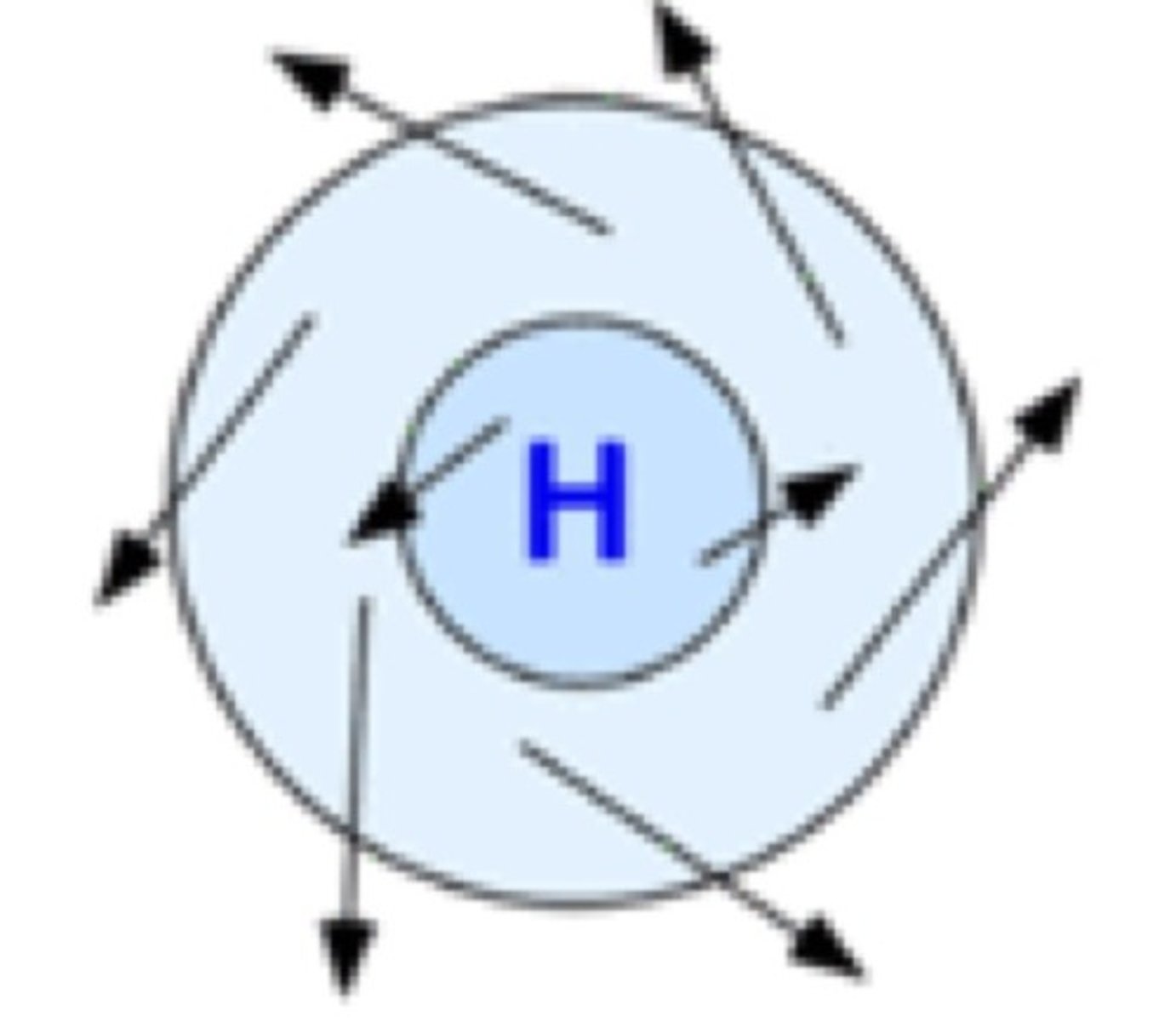
Southern Hemisphere low pressure system
Hurricane/Cyclone
-visible
-clockwise
Driving forces of cyclones
1. Latent Heat
2. Sea Surface Temperature
3. Depth of warm water
Latent heat
heat absorbed or radiated during a change of phase at a constant temperature and pressure
Heat of water
fuel for cyclone
latent heat of evaporation
The amount of heat energy that is needed to evaporate a substance, that is, to change it from a liquid to a gas
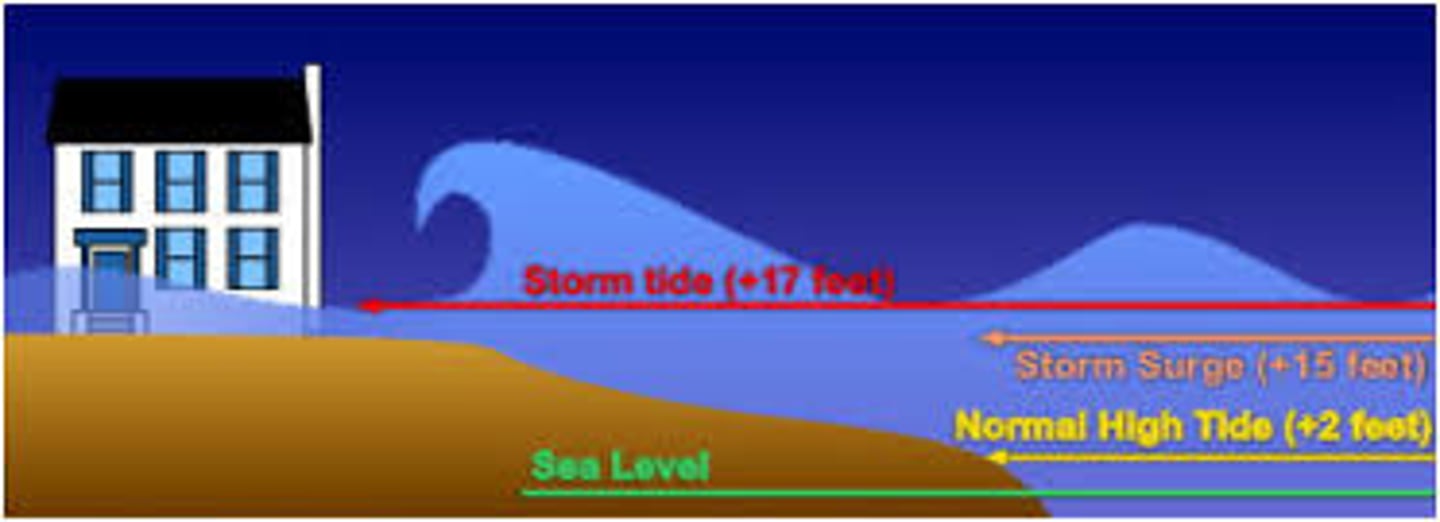
storm surge drivers
1. Winds
2. Low pressure
how do the mantle's convection currents affect the Earth?
They contribute and create movement of tectonic plates
waller creek properties
environmental index (physical looks)
conductivity
total dissolved solids
dissolved oxygen
E Coli and fecal coliform bacteria
streamflow
proxies to determine CO2 levels
-sedimentary rock
-cave formations
-tree rings
-coral
-glacial formations
phanerozoic period
"Visible life"- the most recent eon, began about 540 million years ago
cretaceous period
Period from 144 million to 66 million years ago. Continents move toward their present-day positions as South America splits from Africa. Widespread volcanic activity occurs. First flowering plants appear. Dinosaurs, including Tyrannosaurus rex, dominate. First snakes appear. Mass extinction at the end of the period causes disappearance of many land and marine life forms, including dinosaurs.
carbon cycle drivers:
1. plate tectonics
2. weathering
effects of increases in plate tectonic activity on CO2 levels
increases outgasing of Earth's interior through volcanoes, which adds CO2 to the atmosphere
effects of weathering on CO2 levels
chemical weathering uses CO2 from the atmosphere which lowers CO2 in the atmosphere
anthropocene
Geological epoch defined by atmospheric chemist Paul Crutzen to acknowledge the central role humans play in shaping the Earth's environment - a geological age measured in decades to centuries