The eye and vision
1/20
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
21 Terms
___are involved in the perception of colors.
Cones
The __ allows us to focus on objects that are any distance from us.
lens
__ are the key to seeing well at night.
Rods
Stimulus, receptor, and processed for vision
Stimulus = Light waves
Receptor = Rods and Cones
Processed = Occipital Lobes
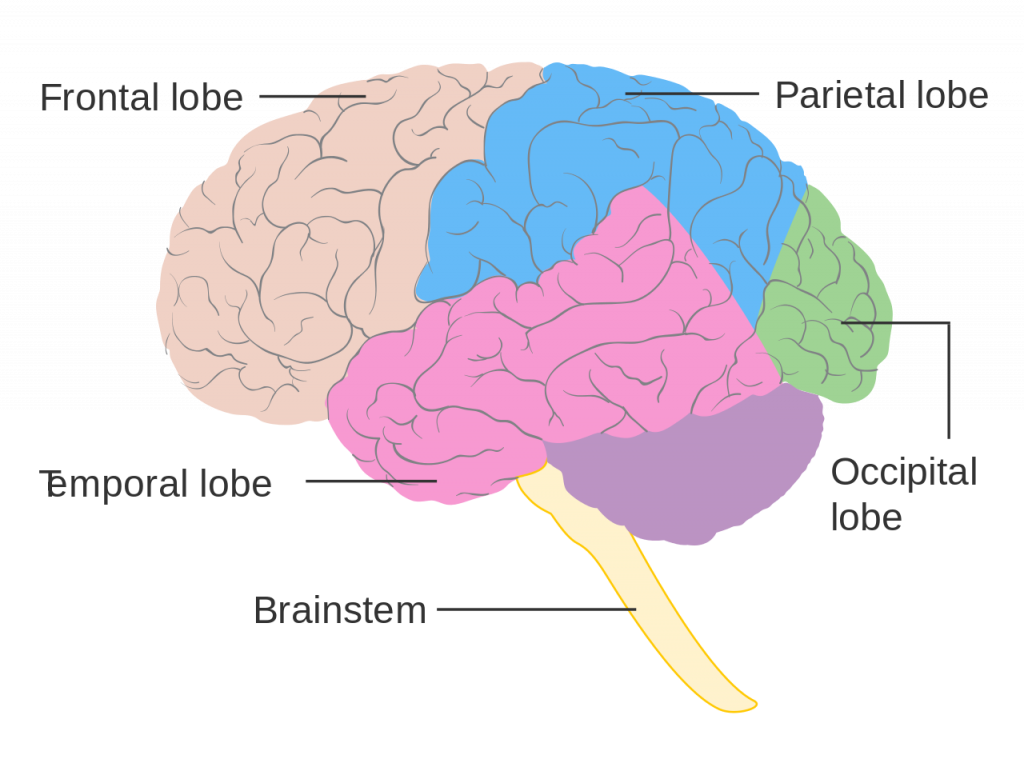
Stimulus, receptor and processed for hearing
Stimulus : sound waves
Receptor: hair cells on basilar membrane in cochlea
Processed: Temporal Lobes
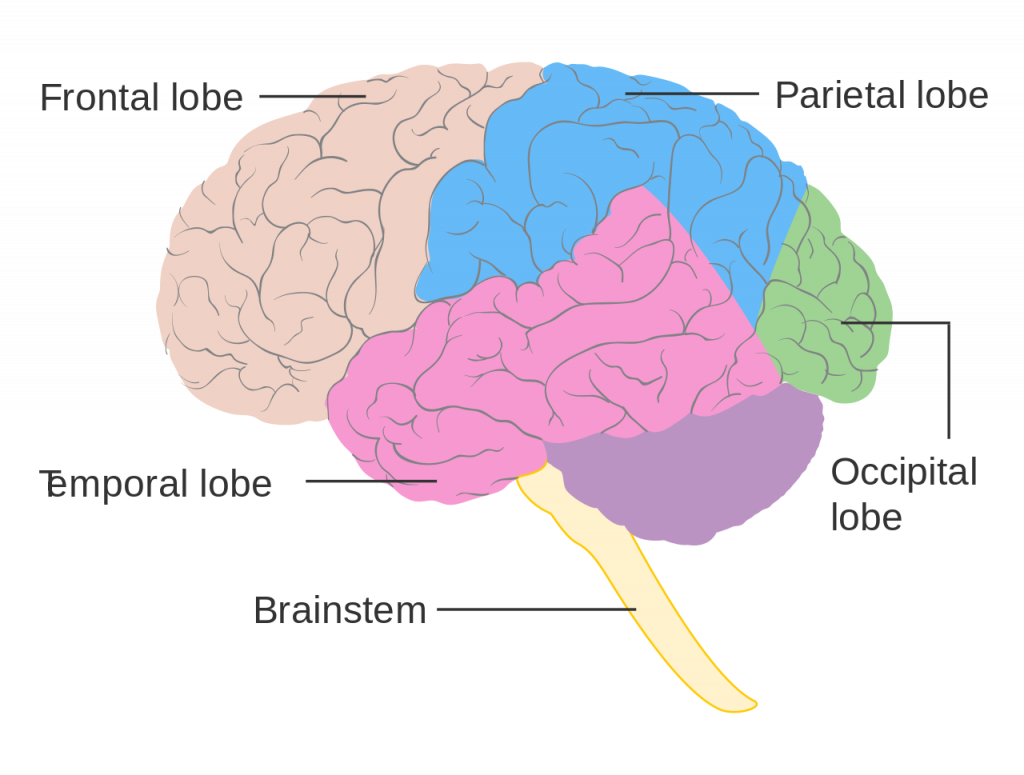
Stimulus, receptor, and processed for taste
stimulus : chemicals
receptor : taste buds
Processed : gustatory cortex ( frontal lobe )
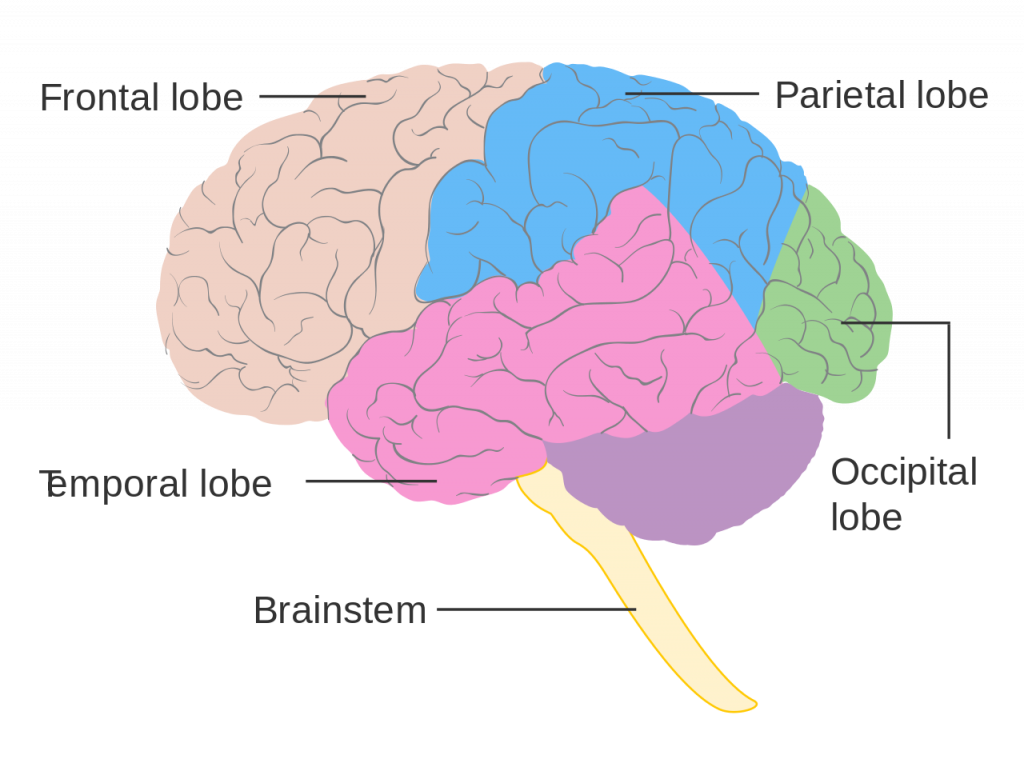
Stimulus, receptor, and processed for smell
stimulus : chemicals
receptor : olfactory hair cells
processed : olfactory bulb

Stimulus, receptor, and processed for skin senses
Stimulus : external contact
Receptor: nerves in skin, joints
Processed : somatosensory cortex
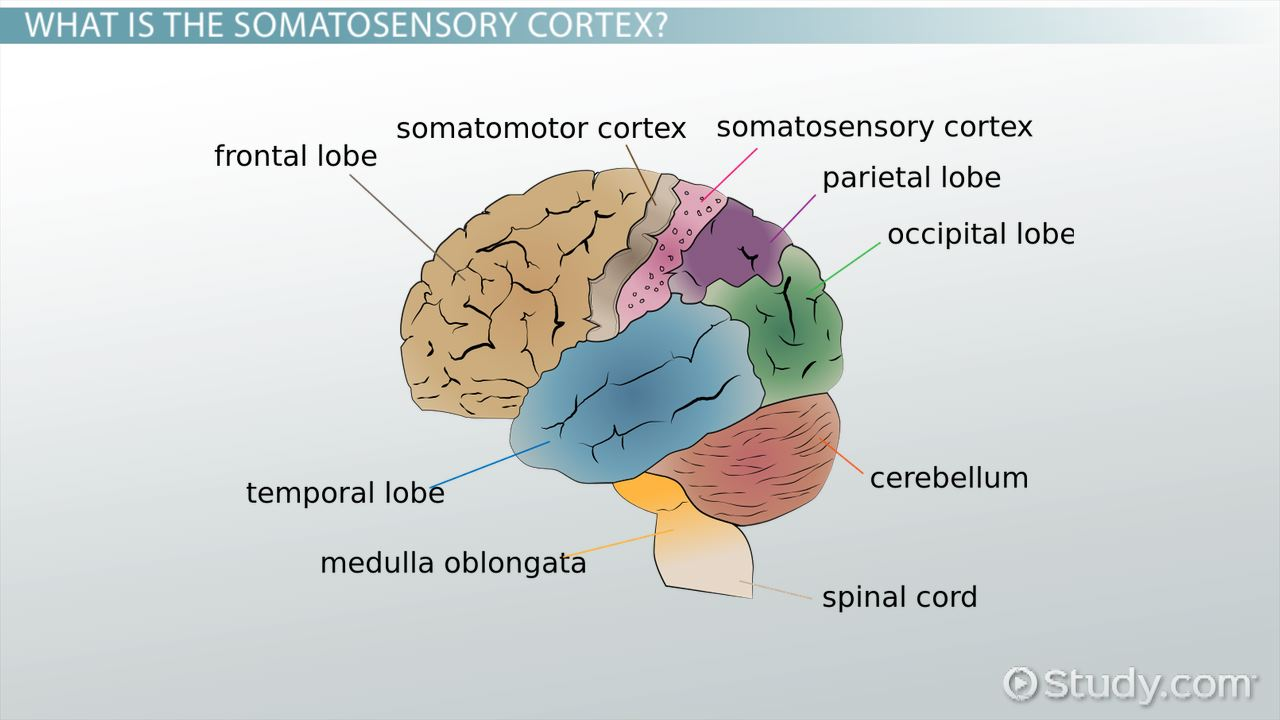
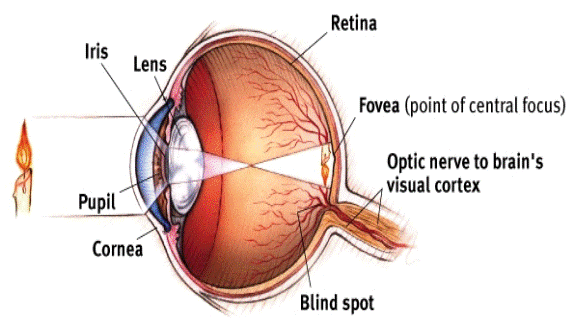
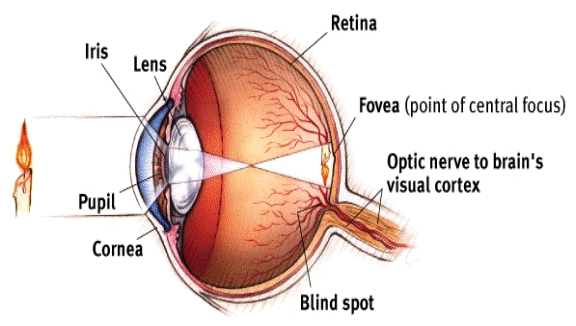
Name all the eyes parts ( 8 ) with descriptions
Cornea = transparent portion of sclera through which light enters
Iris = pigmented muscle that gives the eye its color and regulates the size of the pupil
Pupil = opening in the iris that light passes through
Lens = transparent shape that changes shape to bring objects into focus
Retina: layer containing photoreceptors, rpds, and cones that transduce light energy to electrochemical energy; operates like film in a camera
Fovea = minute area in the center of retina where vision in shaped, point of central focus
Optic nerve to visual cortex: location on the retina where the optic nerve leaves the eye on its way to the brain
blind spot = nerve that leads out of eye toward the brain carrying information about light
In the retina
rods and cones are receptor cells at the back of the retina
light energy triggers chemical here ( sparking neural signals )
ganglion cells are specialized neurons in the retina
Cones ( location, processes, works in )
Location : fovea
Processes : colar, detail
works in : high light
Rods ( location, processes, works in )
Location : periphery
processes : shapes, movement, light and dark adaptation
works in : low light
Further from center of eye means there are more __ than __
rods than cones ( can see outline of things in dark = rods )
wavelength= __ and amplitude = __, ( both are related to vision )
wavelength = colors, amplitude = brightness
Transduction of light wave steps
light through cornea and pupil
lens focuses on retina
light goes to cones, rods for chemical reaction
neural impulse sent through optic nerve
neural impulse sent to thalamus
neural impulse sent to visual cortex
Accomodation
The process by which the eyes and lens change shape to help focus near or far objects on the retina
Young-Helmholtz Trichromatic Theory
Cones in the retina are specific based on red, green, or blue
work together to allow us to perceive color
each handles a range of wavements
red = lon g
green = medium
blue = short
Opponent Process Theory
Two color opponent process in ganglion cells
red vs green
yellow vs blue
white vs black
afterimages: when you look at the same color long enough, tire out the ganglion cells for that color - when we look at white ( which contains all colors ) , we see the opponent color
Color blindness
Occurs when one type of colo receptor ( cone ) is not functioning
ex: if red cones not functions ( cant see long wavelength colors ) → will have difficulty telling red and green apart
most common: malfunction of green cone system
Colors is a two step process, describe the steps
Retina’s cones respond in varying degrees to different color stimuli
their signals then processed by nervous system’s ganglion cells