KINE 3050 : Torque
1/38
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
39 Terms
Centric forces are those that act
through an objects center of mass
What forces will only result in linear changes in position?
Centric Forces
Eccentric Forces are those that are
not directed through a objects center of mass
What force will cause linear and angular(rotational) changes in position
Eccentric Forces
The turning effect of an eccentric force is called
torque
In order for rotation to occur, what type of force is required ?
Eccentric Force
What is torque?
Vector
The rotational effect of an eccentric force
Units: Nm
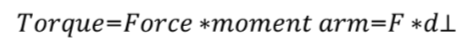
Moment arm is the
perpendicular distance between the axis and the line of force application
Torque is changed throughout the movement because what changes?
the moment arm
What is a lever
Whenever a movement occurs around an axis
can be a set of rigid segments with an axis
Many bones’ primary purpose is to act as one
What are the 3 main components for a lever system?
External force, load or resistance (weight of our bodies)
Internal Force, Effort or Muscle Force (how we move the load)
Fulcrum, Axis, or Pivot Point (often a joint)
What is a class 1 lever?
The internal and external forces are on opposite sides of the fulcrum
ex) external resistance (weight of head) acting on one side of the fulcrum (alanto-occipital joint) and the internal force (all of the neck extension muscles) acting on the other side
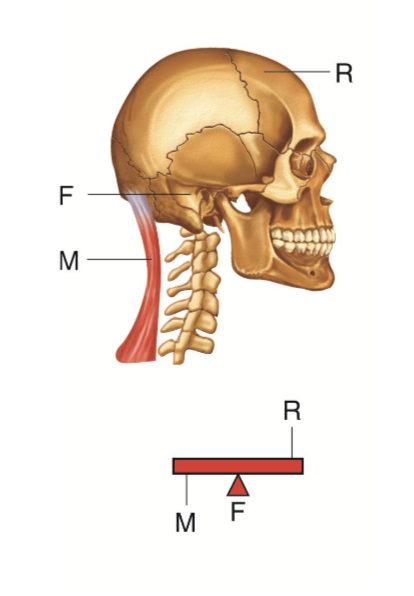
What is a class 2 lever?
have the fulcrum and internal force on opposite sides of the external force
internal and external forces are on the same side of the fulcrum, but the distance from the fulcrum is greater for the internal force
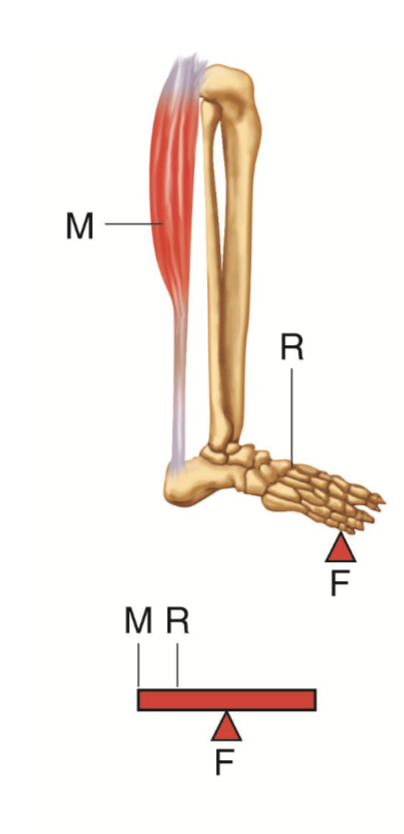
Is it easier to create torque when the distance from the fulcrum is greater for the internal force?
true
Class 3 Lever is
opposite of Class 2
fulcrum and external force is on either sides of the internal force
the distance between external force and fulcrum is greater than internal force (makes it harder to overcome)
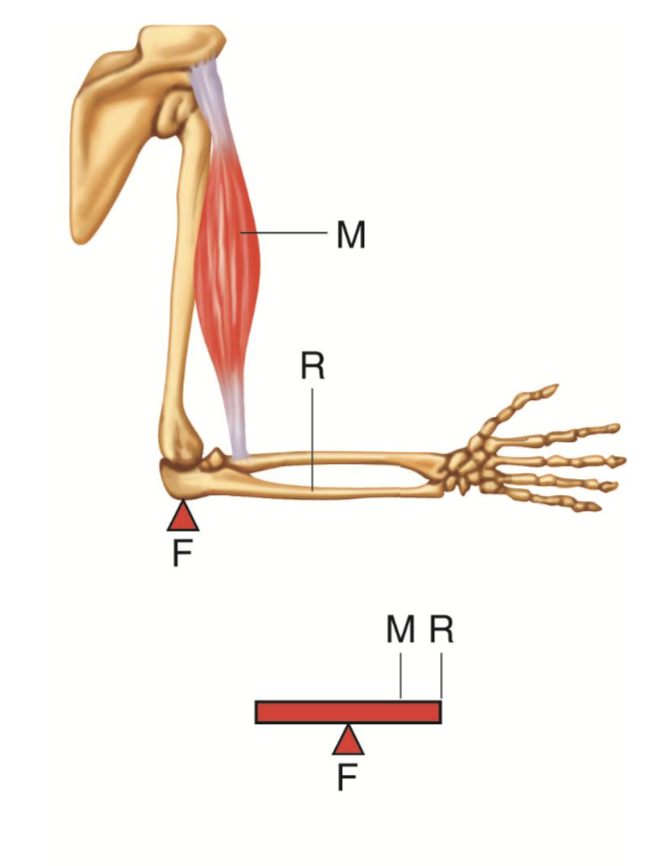
What is the mechanical advantage?
ratio of the moment arm distance of internal force to the moment arm distance of external force
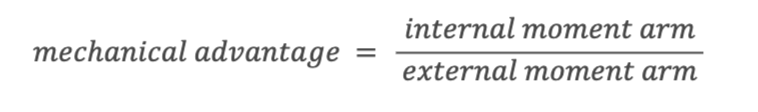
When does mechanical advantage happen?
when internal moment arm size is > the external arm size
When does mechanical disadvantages happen?
when external moment arm size > internal moment arm size
What are some advantages of class 3 levers?
can move lighter loads larger distance
give ability to throw objects
run fast
What is the most common lever class system in the human body?
Class 3
What lever class is the push up exercise?
Class 2
What lever class is a calf raise exercise ?
Class 2
What is the most mechanically advantaged lever system?
Class 2
A small child named Jeff, who is 25kg, sits on a seesaw that has a length of 8m and an axis in the middle. There are 4m on each side of the axis. He sits 3m on the right side of the axis. How much torque is he producing?
τ = F× d
Step 1: Find Force
F = mg
F= 25 × 9.8 = 245N
Step 2: Find Distance from axis
d= 3m
Step 3: Solve
τ = 245N x 3m = 735N
Now Jeff has a friend, Shelly, but her weight is greater than his. She weighs 700N and Shelly is also sitting 3m from axis but on the opposite side. What is the net torque on the seesaw now ?
What we have : τJeff= 735N
Step 1: Find torque produced by Shelly
700 × 3 = 2100N
Step 2: Find the Net Torque
τnet = τJeff − τShelly
735N - 2100N = -1365N
(it is negative because Jeff was positive/clockwise and Shelly was negative because she was counterclockwise )
Based on the Jeff and Shelly problem, how could we create equilibrium (net torque = 0Nm)
Moving Shelly closer to the fulcrum
Muscles generate
torque to cause movement in humans
Muscle actions create?
tension
Since muscles are not located directly on top of joints(axes), they have what?
moment arms
Muscle tension x muscle moment arms = torque at the joint that the muscle crosses
Muscular torque causes our limbs to
rotate about a joint axis
In the weight room, you pick up a 98.1 N dumbbell (10kg x 9.81) so you can hammer out some curls before hitting bench. The dumbbell in your hand is 0.25m from your elbow joint. Your forearm weighs 60 N and its center of gravity if 0.15m from elbow joint. If your bicep attaches 0.03m from the elbow joint, how much force does it need to produce to counteract the forces applied with you elbow flexed at 90 degrees?
What we have :
Dumbbell : Force (98.1N) Distance (0.25m)
Forearm: Force (60N) Distance (0.15m)
Biceps: Force (?) Distance (0.03)
Step 1: Write equation
Fbicep⋅dbicep = Fforearm ⋅ dforearm + Fdumbbell ⋅ ddumbbell
Fbicep⋅0.03 = 60 ⋅ 0.15 + 98.1 ⋅ 0.25
Step 2: Complete Torques
60⋅0.15=9N
98.1 x 0.25 = 24.525N
9+24.525=33.525N
Step 3 : Solve for Fbicep
33.525 / 0.03 = 1117.5N
What may be the bigger factor in humans where we mostly have 3rd class levers?
force
Axis of rotation is the point
around which something rotates
Center of mass is the point where the entire
mass of an object is assumed to be concentrated
Center of gravity is the point where mass is evenly
distributed and where the force of gravity acts
When standing stationary in the anatomical position, the center of gravity is near?
L2-L3 *roughly 55-57% of height)
it will move as we move
From a biomechanics perspective, COG is the
point on the body that follows Newtons Laws of Motion
The location of COG plays a role in
stability, mobility, and balance
What influences torque?
Force and Moment Arm