Introduction to Anatomy: Key Concepts and Structures
1/251
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
252 Terms
Anatomy
The science of the structure and function of the body.
Clinical anatomy
The study of the macroscopic structure and function of the body as it relates to the practice of medicine and other health sciences.
Anatomical Position
Standing erect, upper limbs by the side, and the face and palms of the hands directed anteriorly.
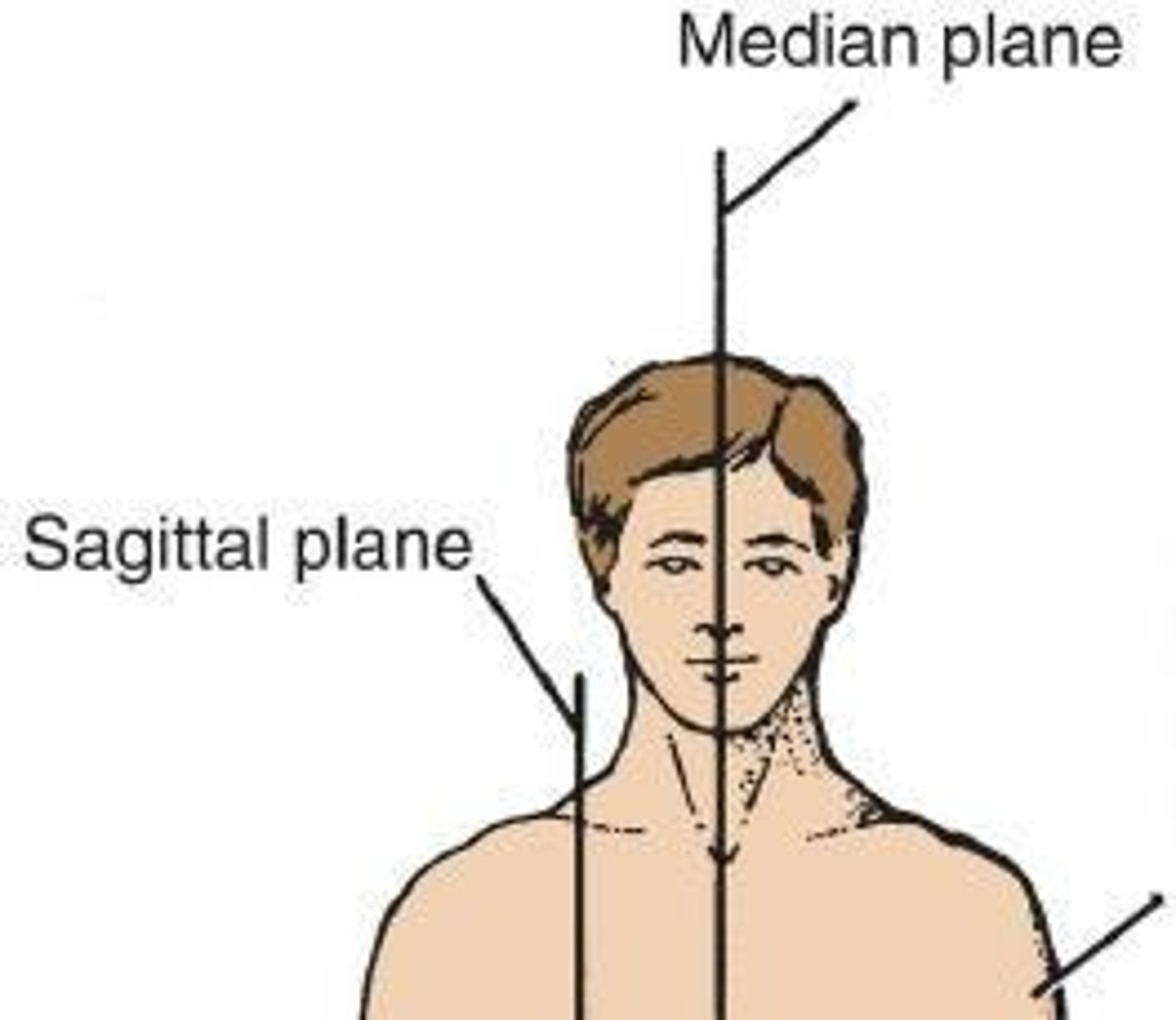
Median Plane
A vertical plane passing through the center dividing into equal right and left halves.
Sagittal Plane
Any plane parallel to the median plane that divides the body into unequal right and left portions.
Coronal (Frontal) Plane
A vertical plane situated at a right angle to the median plane, dividing the body into anterior and posterior portions.
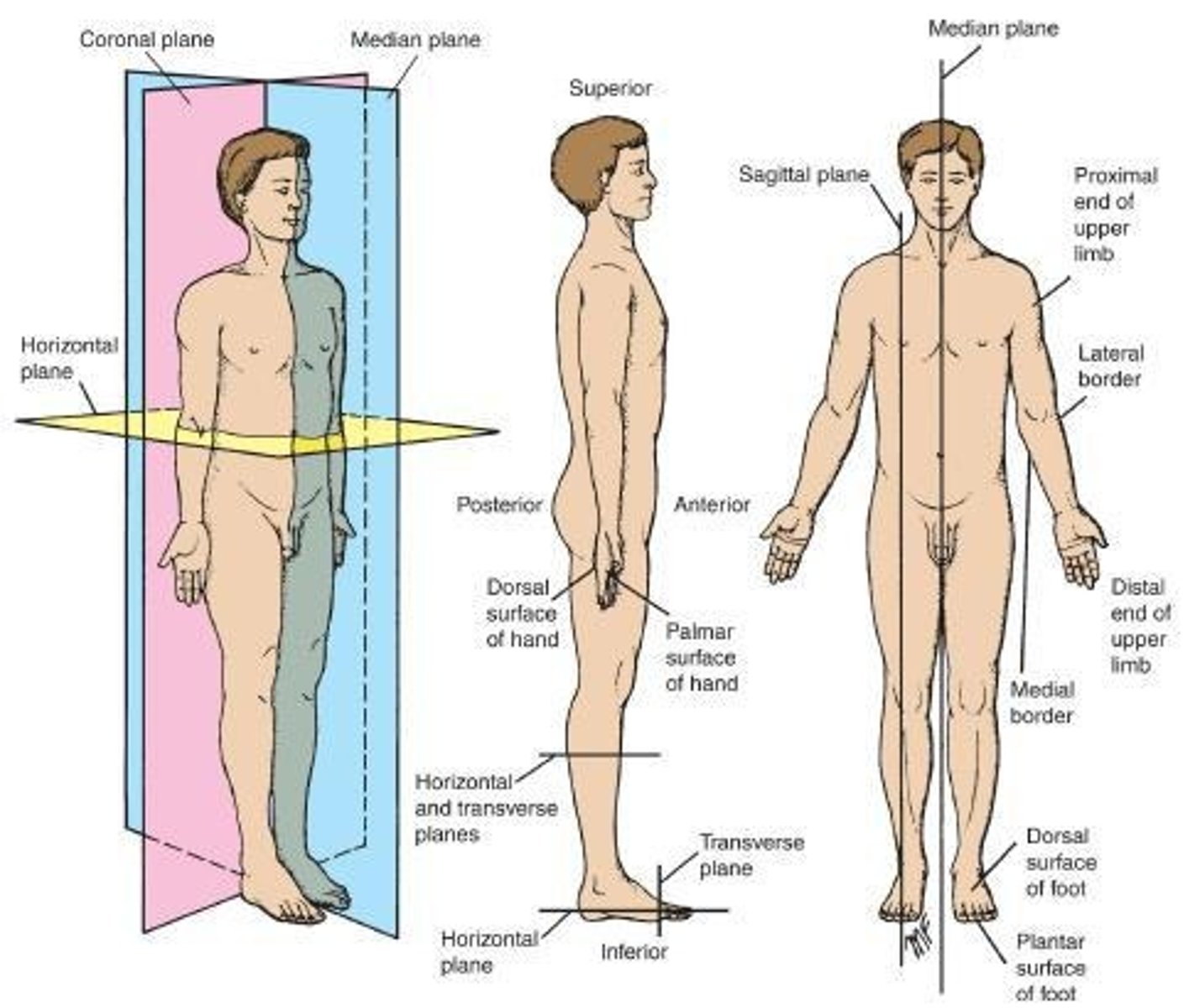
Horizontal Plane
Lies at right angles to both the median and the coronal planes, dividing the body into upper and lower parts.
Transverse Plane
Lies perpendicular to the long axis of a given structure and divides that structure in a cross-sectional orientation.
Anterior (Ventral)
Indicates the front of the body.
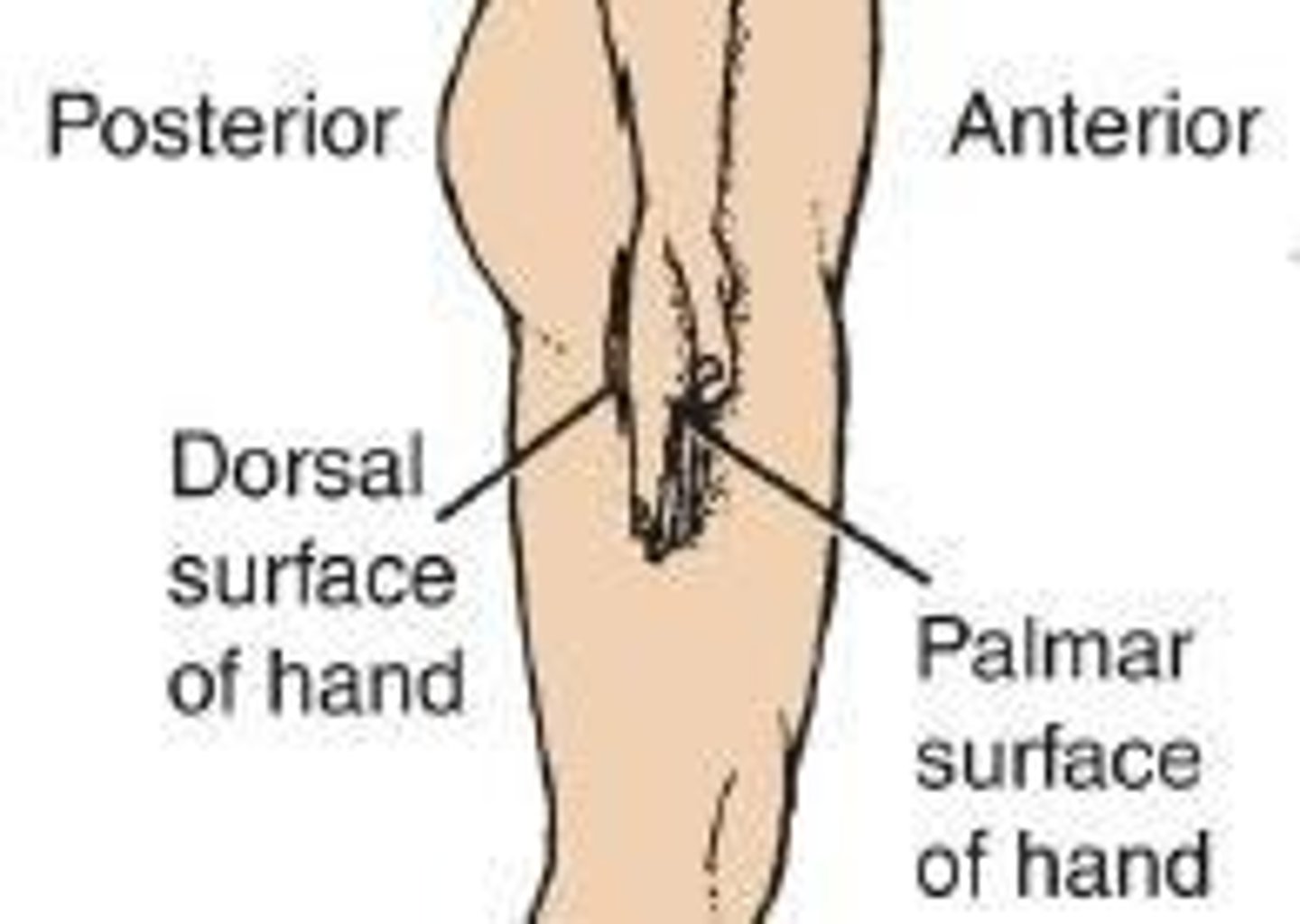
Posterior (Dorsal)
Indicates the back of the body.
Medial
Indicates a structure nearer to the median plane of the body than another.
Lateral
Indicates a structure that lies farther away from the median plane of the body than another.
Superior (cranial; cephalic)
Means toward the head end of the body.
Inferior (caudal)
Means away from the head; lower.
Proximal
Describes a position relative to a reference point.
Distal
Describes positions relative to the reference point.
Superficial
Is closer to the surface.
Deep
Is farther away from the surface.
Ipsilateral
Means it's on the same side from the reference point.
Contralateral
Means it's on the opposite side from the reference point.
Supine position
The position of the body lying on the back.

Prone position
The position of the body lying face down.
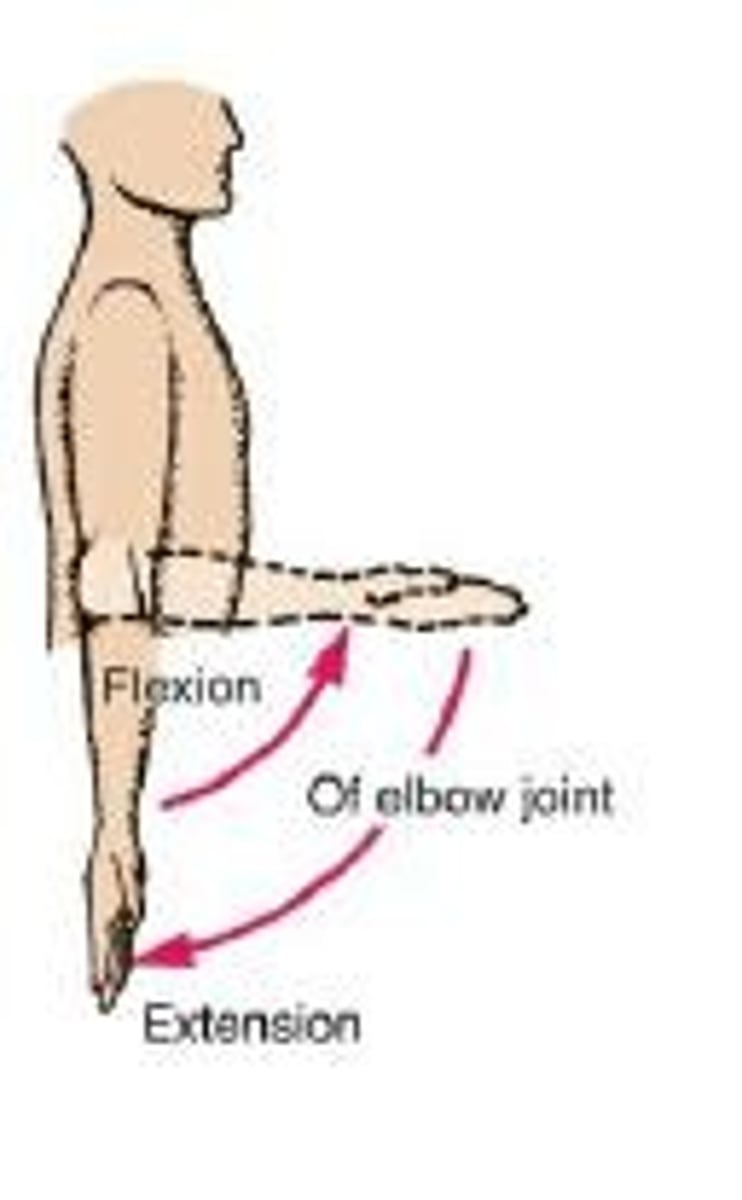
Flexion
The movement in which a joint angle is decreased (closed) during a motion occurring in a sagittal plane.
Extension
The opposite movement in which the joint angle is increased (opened; straightened) in a sagittal plane.
Dorsiflexion
A special term used to describe the movement of the foot.
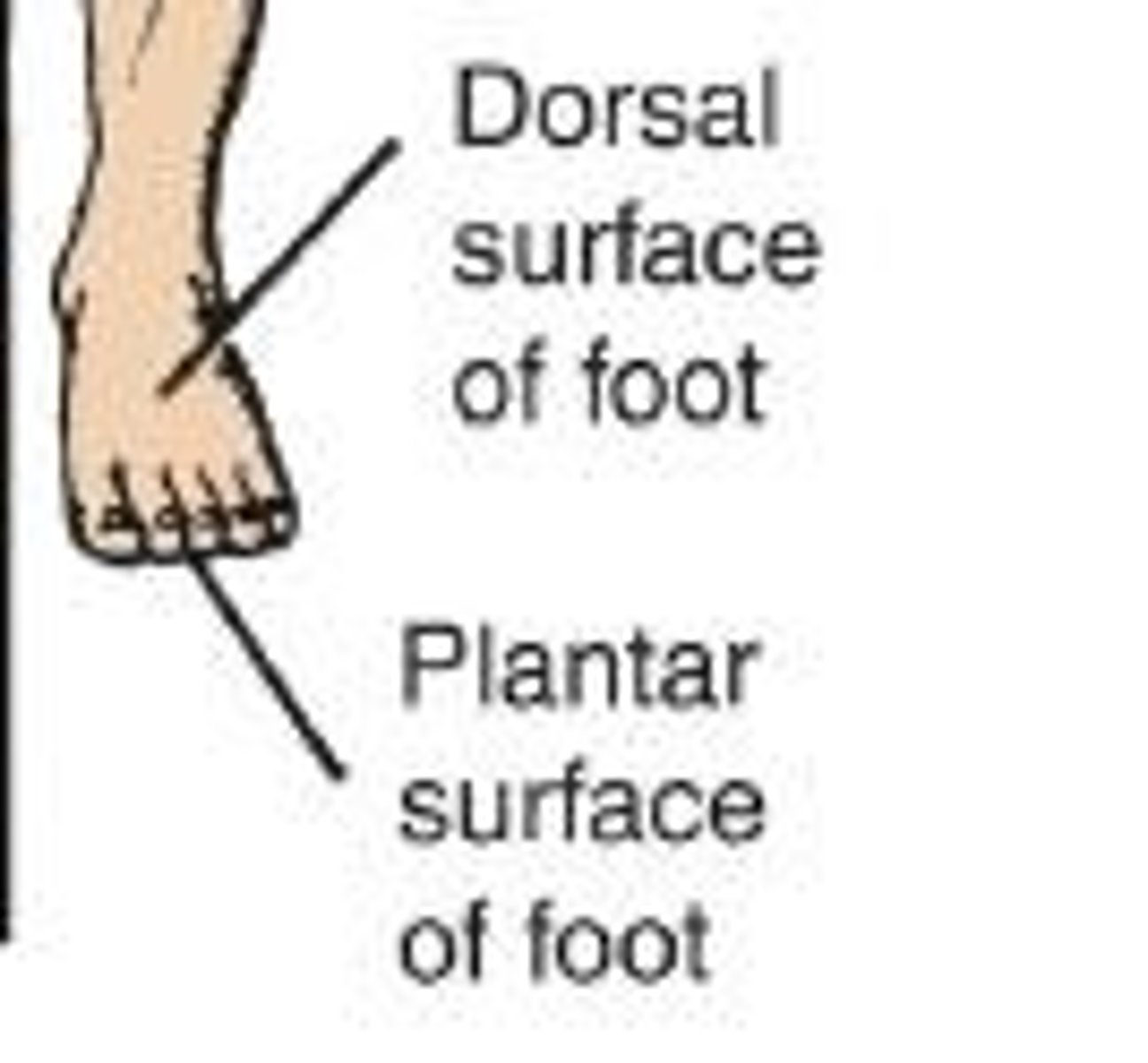
Plantarflexion
A special term used to describe the movement of the foot.
Abduction
Movement away from the midline of the body in the coronal plane.
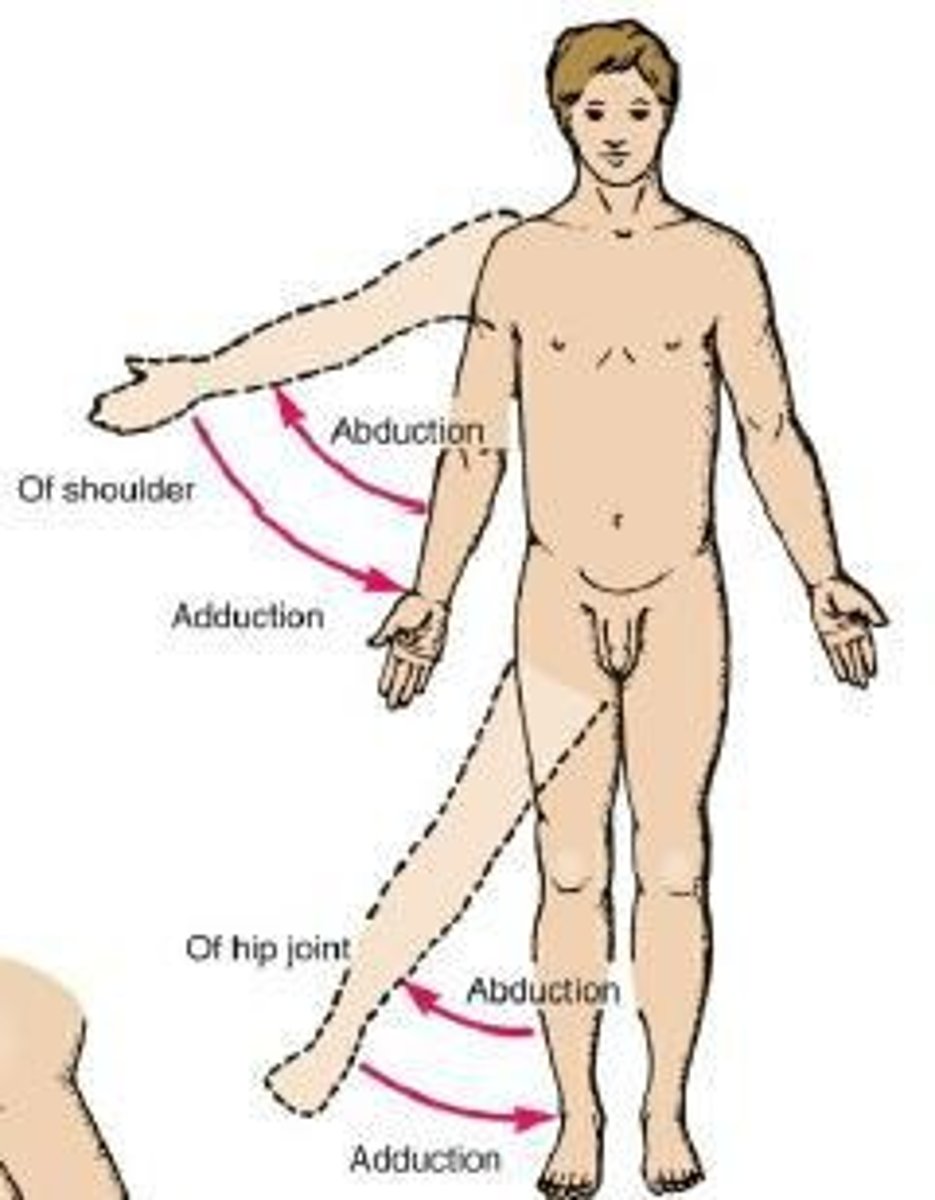
Adduction
Movement toward the midline of the body in the coronal plane.
Inversion
Turning the sole of the foot so the sole faces a medial direction.
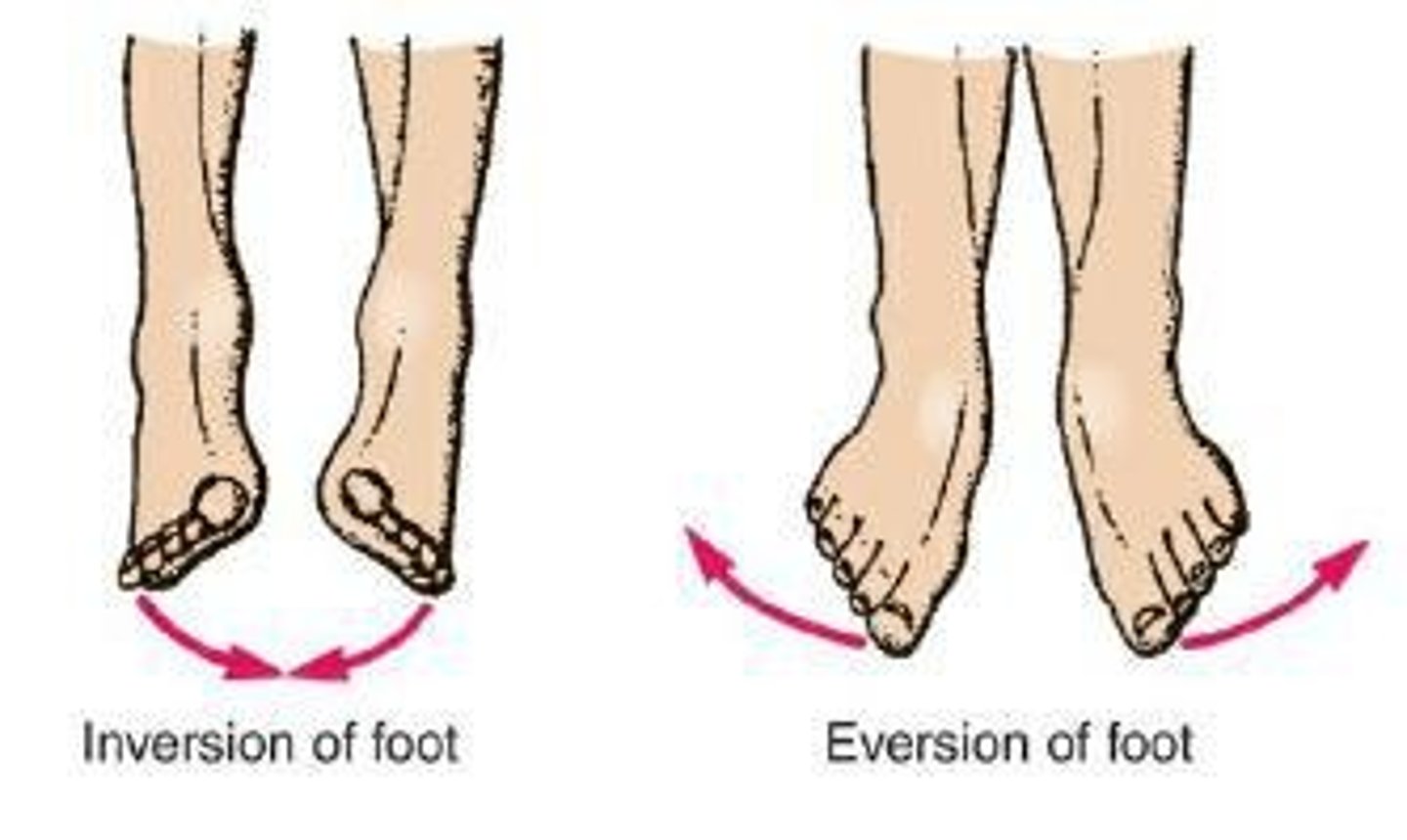
Eversion
Turning the sole of the foot so that the sole faces a lateral direction.
Rotation
The movement of a part of the body around its long axis, with little to no movement through space.
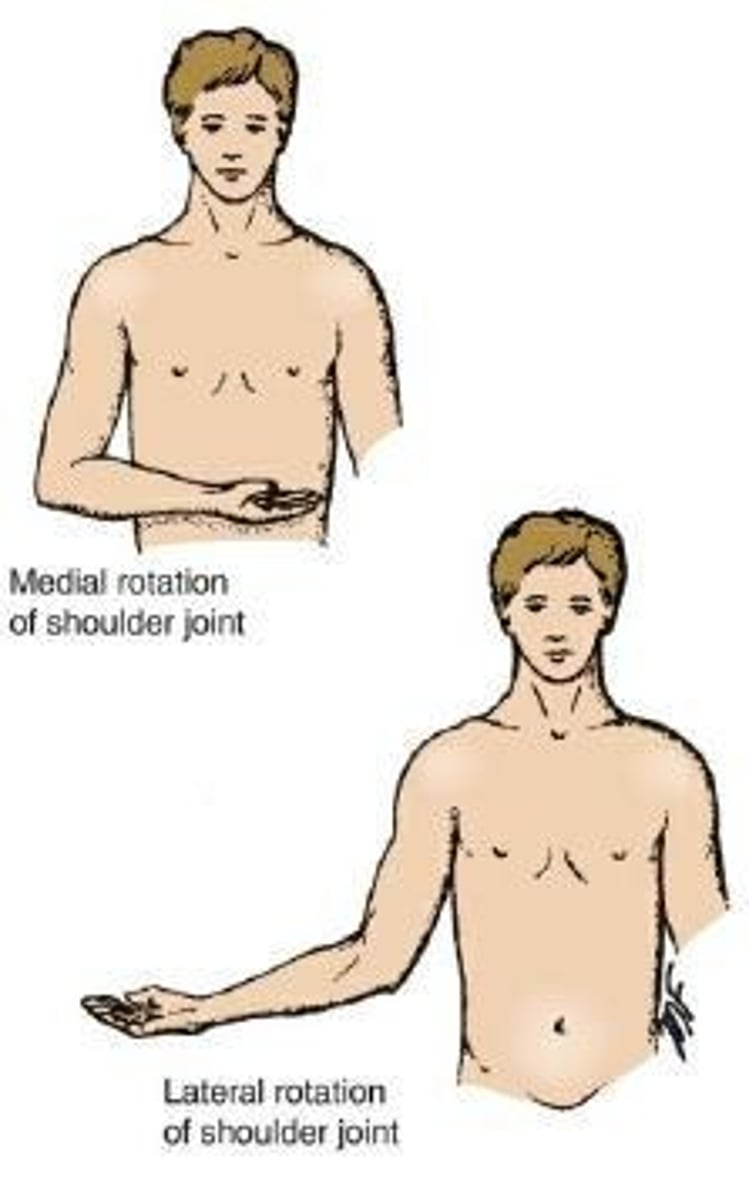
Medial (Internal) Rotation
The movement that results in the anterior surface of the part facing medially.
Lateral (External) Rotation
Movement that results in the anterior surface of the part facing laterally.
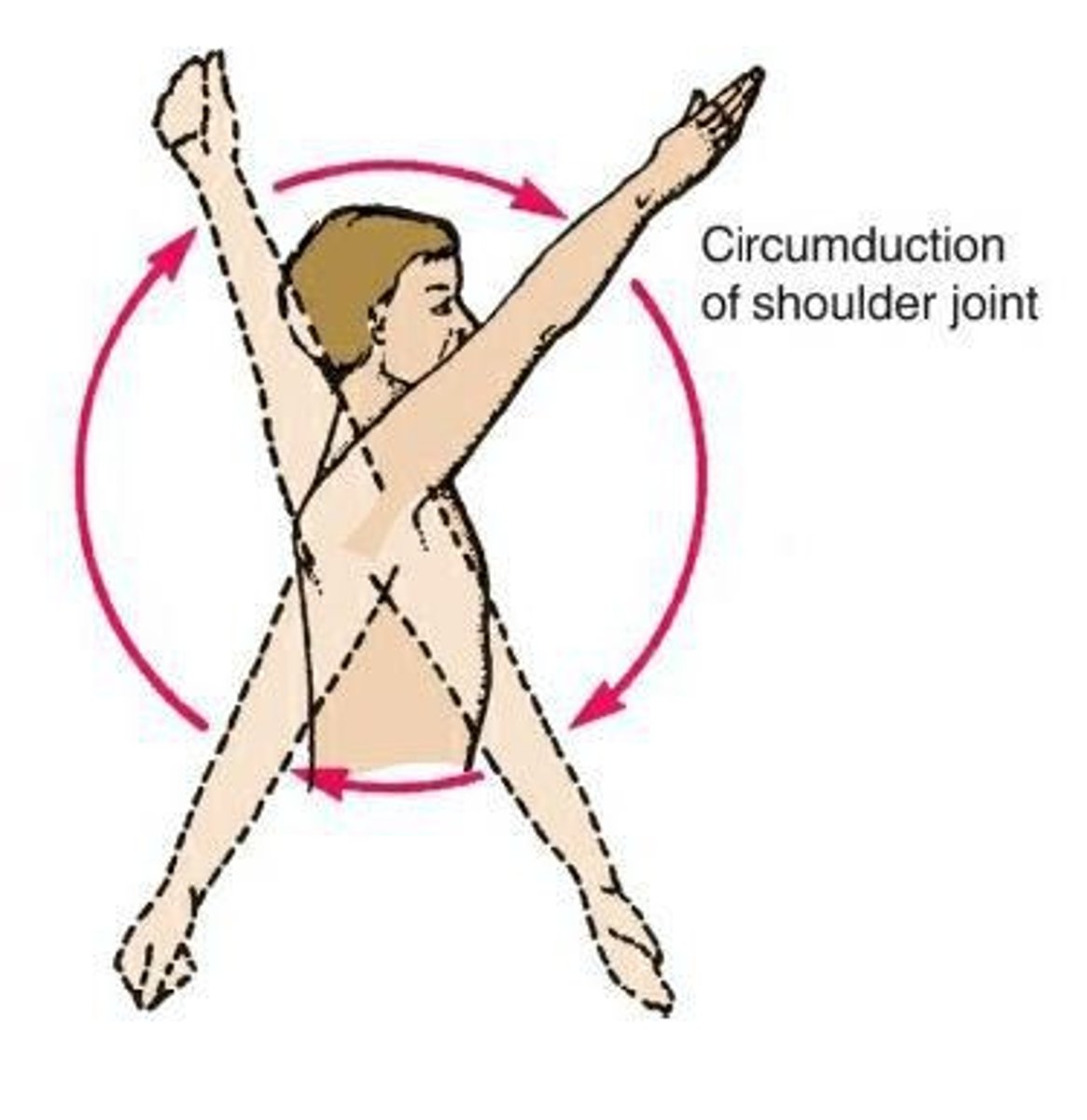
Circumduction
A complex sequence of movements combining flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation.
Pronation
Turning the forearm medially in such a manner that the palm of the hand faces posteriorly.
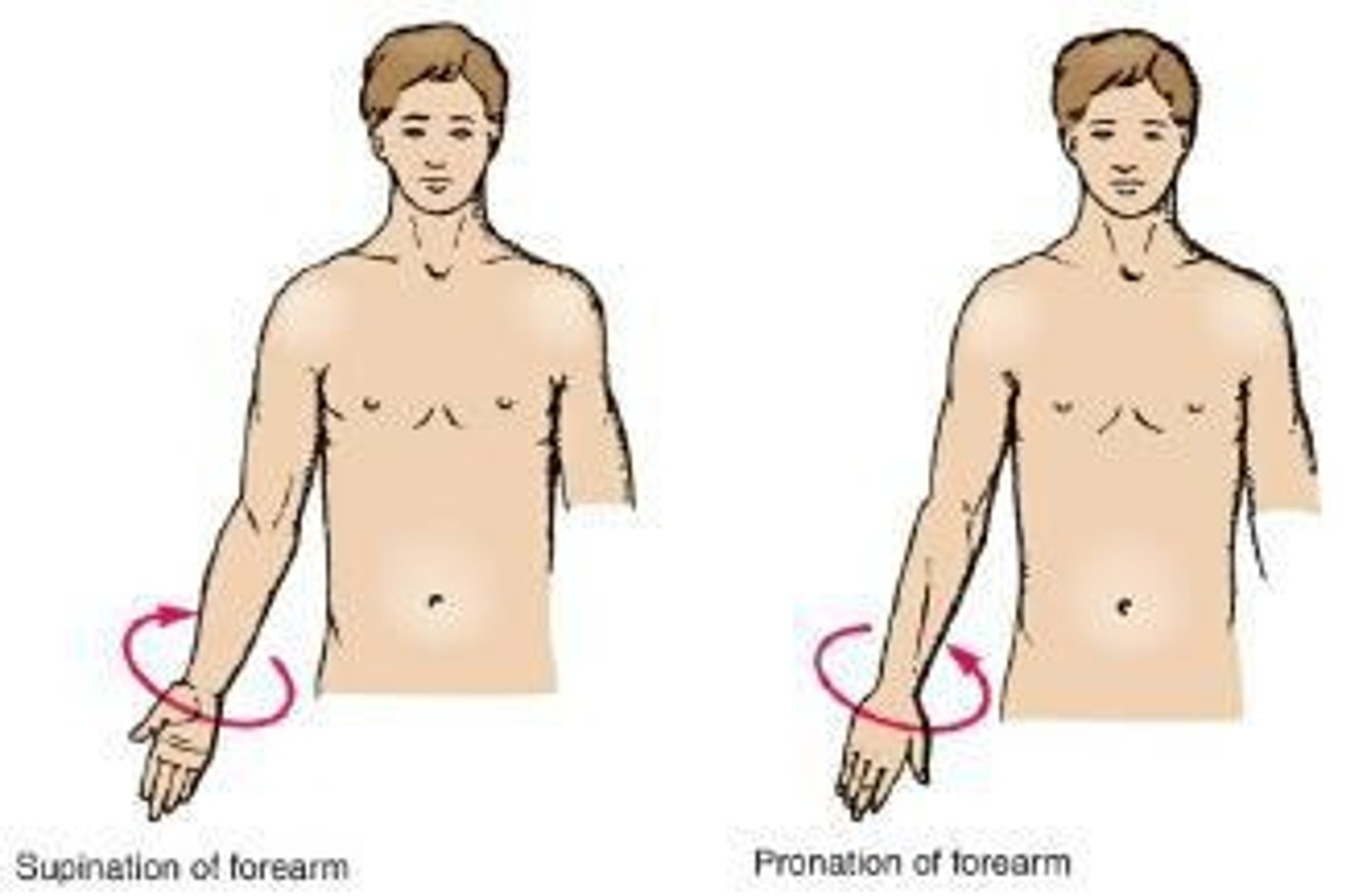
Supination
Turning the forearm laterally from the pronated position so that the palm of the hand comes to face anteriorly.
Protraction
Moving a body part forward.
Retraction
To move a part backward.
Skin
Divided into 2 parts: Epidermis and Dermis.
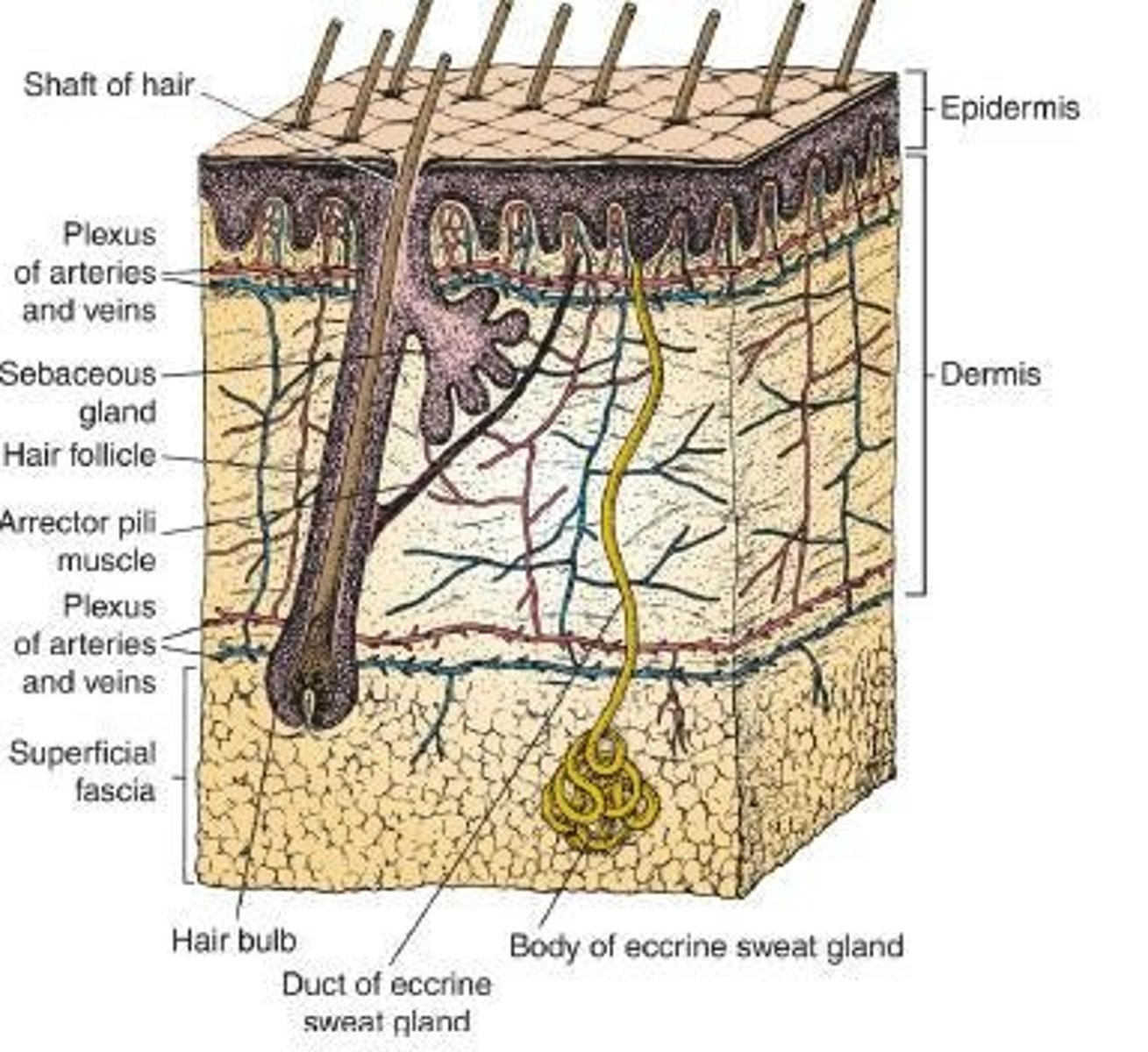
Epidermis
The outer layer of skin.
Dermis
The inner layer of skin connected to the underlying fascia or bones by the superficial fascia or subcutaneous tissue.
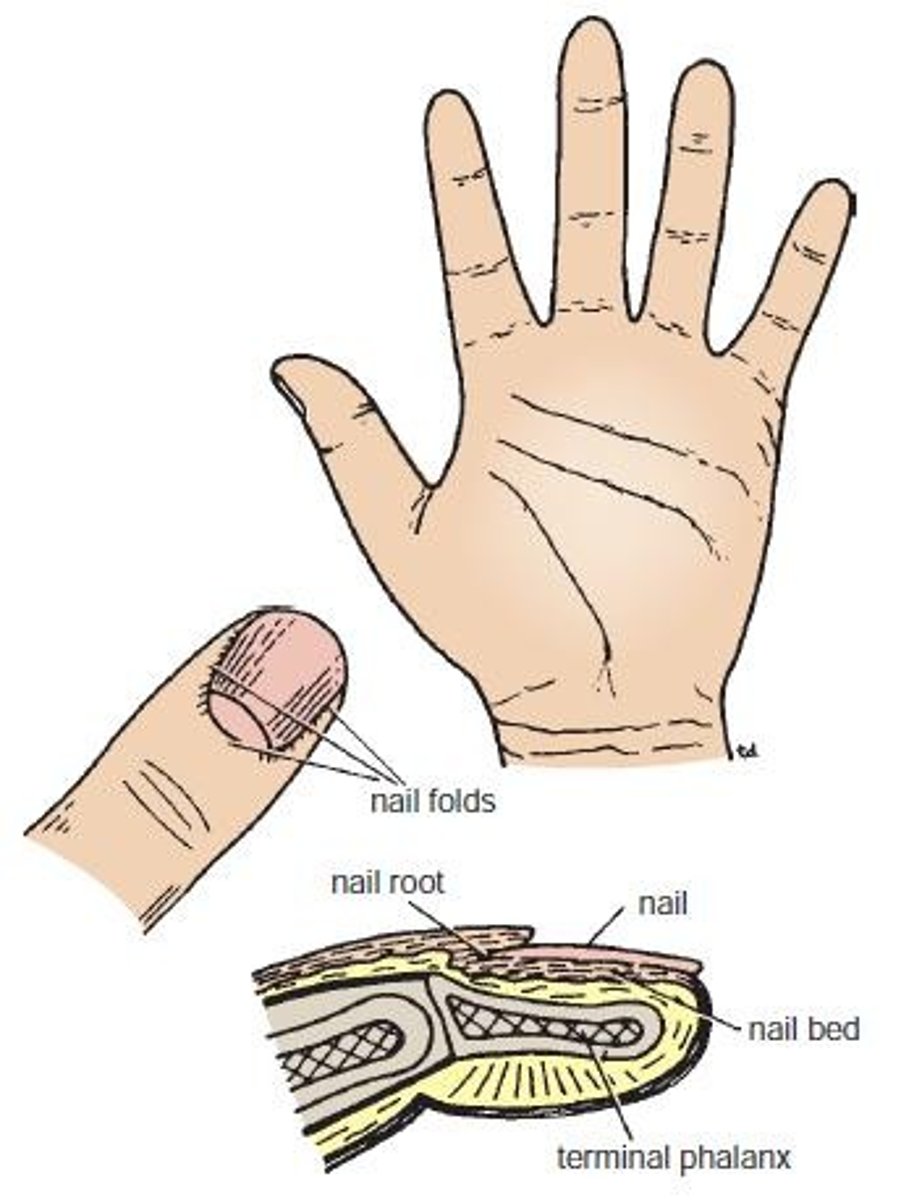
Nails
Keratinized plates on the dorsal surfaces of the tips of the fingers and toes.
Hair Follicles
Structures from which hair grows.
Sebaceous Glands
Glands that secrete sebum.
Sweat Gland
Glands that produce sweat.
Superficial Fascia
Also known as subcutaneous tissue.
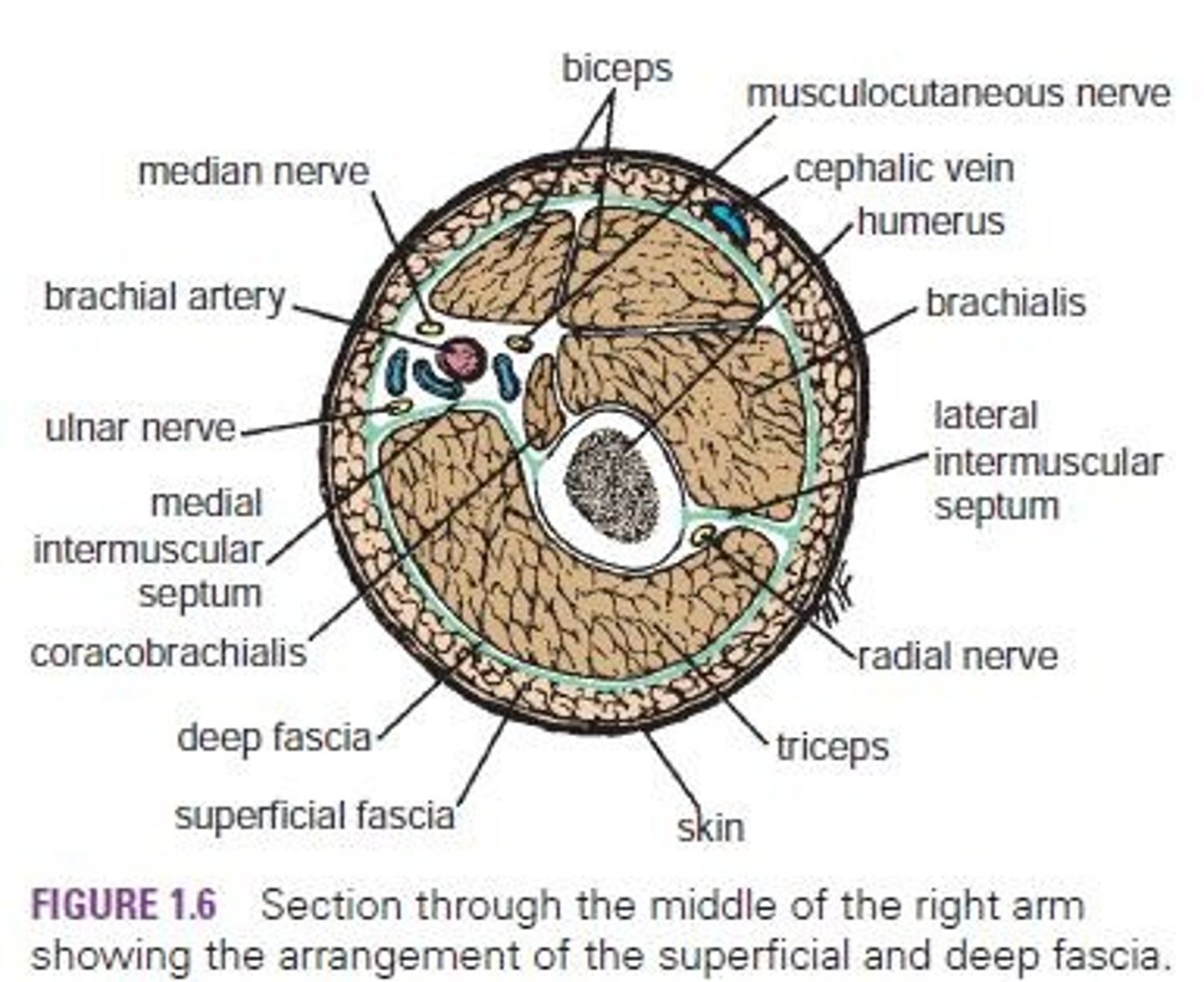
Deep Fascia
A type of fascia that may be considerably thickened to form restraining bands.
Skeletal Muscle
Voluntary muscles that attach to bones.
Prime Mover
The chief muscle or member of a chief group of muscles responsible for a particular movement.
Antagonist
Opposes the action of the prime mover.
Fixator
Contracts isometrically to stabilize the origin of the prime mover so that it can act efficiently.
Synergist
Contracts and stabilizes the intermediate joints.
Smooth Muscle
Lines the walls of organs or blood vessels and is involuntary.
Cardiac Muscle
Striated muscle fibers that form the myocardium and conducting system of the heart.
Joints
Sites where two or more bones come together, whether or not movement occurs between them.
Fibrous Joints
Joints where the articulating surfaces of the bones are joined by fibrous tissue, allowing very little movement.
Cartilaginous Joints
Joints united by cartilage, which can be primary or secondary.
Synovial Joints
Joints where the articular surfaces of the bones are covered by a thin layer of hyaline cartilage separated by a joint cavity.
Plane Joints
The opposed articular surfaces are flat or almost flat, and this permits the bones to slide on one another.
Hinge Joints
Resemble the hinge on a door, so that flexion and extension movements are possible.
Pivot Joints
A central bony pivot is surrounded by a bony-ligamentous ring.
Condyloid Joints
Have two distinct convex surfaces that articulate with two concave surfaces, allowing flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction together with a small amount of rotation.
Ellipsoid Joints
An elliptical convex articular surface fits into an elliptical concave articular surface, allowing flexion, extension, abduction, and adduction, but rotation is impossible.
Saddle Joints
The articular surfaces are reciprocally concave convex and resemble a saddle on a horse's back, permitting flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, and rotation.
Ball and Socket Joints
Ball shaped head of one bone fits into a socket like concavity of another, permitting free movements including flexion, extension, abduction, adduction, medial rotation, lateral rotation, and circumduction.
Stability of Joints
Three main factors: shape, size, and arrangement of articular surfaces; ligaments; tone of muscles around the joint.
Hilton's Law
States that often a nerve that innervates a joint also tends to innervate the muscles that move the joint and the skin that covers the attachments of those muscles.
Ligaments
A cord or band of connective tissue uniting two structures, most are dense bundles of collagen, unstretchable.
Bursae
A lubricating device consisting of a closed fibrous sac lined with a delicate smooth membrane.
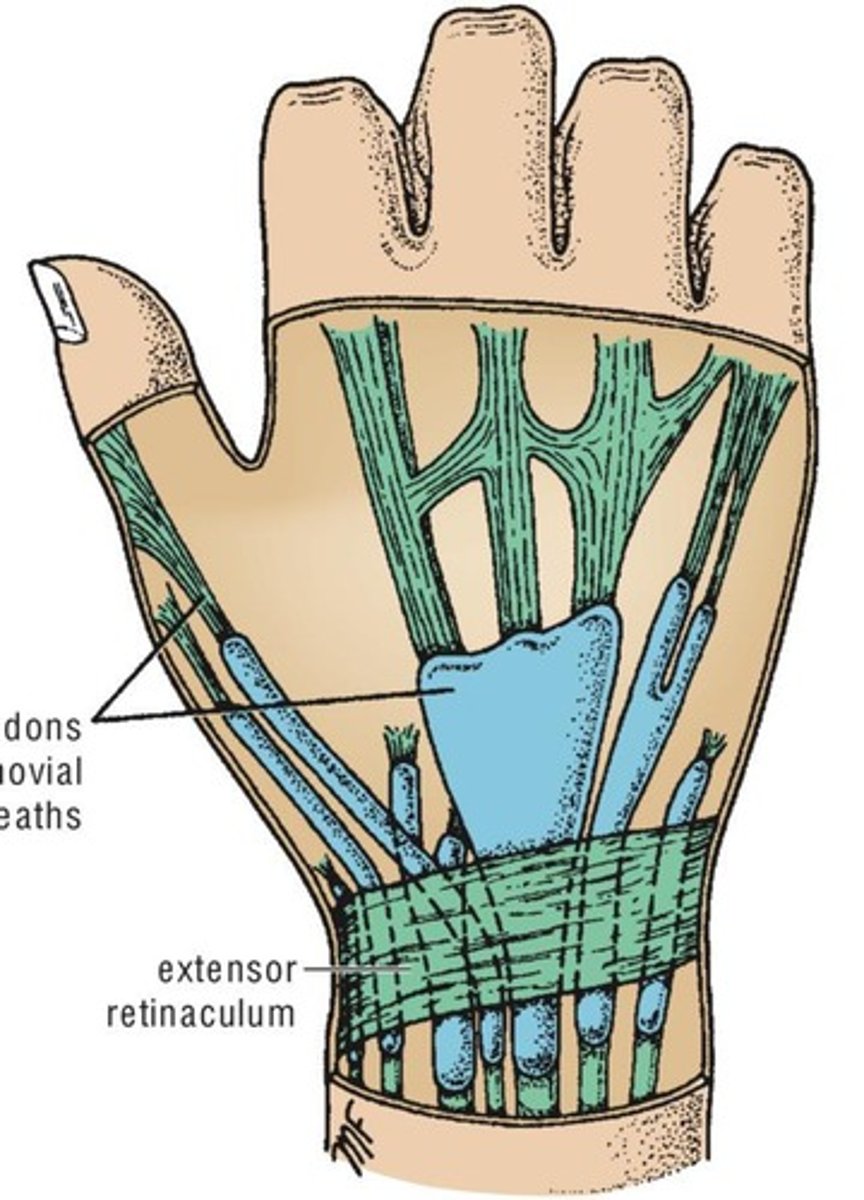
Synovial Sheath
A tubular bursa that surrounds a tendon.
Blood Vessels
Three Types: Arteries, Veins, and capillaries.
Arteries
Transport blood away from the heart and are valve-less.
Veins
Transport blood towards the heart and contain valves.
Capillaries
Microscopic vessels in the form of a network connecting the arterioles to the venules.
Sinusoids
Similar to capillaries but larger and irregular.
Portal System
A system of vessels interposed between two capillary beds.
Anastomosis
The joining of branches of arteries, allowing collateral circulation.
Lymphatic System
Consists of lymphatic tissues and lymphatic vessels.
Lymphatic Tissues
Contains a large number of lymphocytes, including Thymus, Lymph Nodes, Spleen, and Lymphatic Nodules.
Lymph
Fluid in lymphatic vessels.
Lymphatic Capillaries
A network of fine vessels that drain lymph from the tissues.
Afferent Vessels
The lymph vessels that carry lymph to a lymph node.
Efferent Vessels
Transport lymph away from a node.
Right Lymphatic Duct
The lymph reaches the bloodstream at the root of the neck by large lymph vessels.
Central Nervous System
Composed of large numbers of nerve cells and their processes, supported by specialized tissue called neuroglia.
Neuron
The term given to the nerve cell and its processes.
Processes of Neuron
Two types: dendrites and axon.
Dendrites
Short process of the cell body.
Axon
Long process of the cell body.
Gray matter
Consists of nerve cells and cell bodies embedded in neuroglia.
White matter
Consists of nerve fibers (axons) embedded in neuroglia (transmits impulses to farther distance from brain).
Peripheral Nervous System
Cranial nerves and spinal nerves and their associated ganglia.
Cranial Nerves
12 pairs of cranial nerves that leave the brain and pass through foramina in the skull.
Spinal Nerves
A total of 31 pairs of spinal nerves leave the spinal cord through intervertebral foramina in the vertebral column.
Cervical Nerves
8 pairs of spinal nerves associated with the cervical vertebrae.
Thoracic Nerves
12 pairs of spinal nerves associated with the thoracic vertebrae.
Lumbar Nerves
5 pairs of spinal nerves associated with the lumbar vertebrae.
Sacral Nerves
5 pairs of spinal nerves associated with the sacral vertebrae.
Coccygeal Nerve
1 pair of spinal nerves associated with the coccyx.
Cauda Equina
Bundle of nerves that resembles a horse's tail, termination of spinal cord.