Lecture 17 Key Concepts/Terms
0.0(0)
Card Sorting
1/55
Earn XP
Description and Tags
Last updated 12:39 AM on 11/4/22
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
56 Terms
1
New cards
How do fungi fit onto the eukaryotic tree?
have traits that make it seem plant like (unique haploid stages and non motile)
fungi are its own monophyletic clade and actually more closely related to animals than plants
fungi are its own monophyletic clade and actually more closely related to animals than plants
2
New cards
Opisthokonts
organisms from an ancestor with posterior flagellum (includes fungi, animals, and some protists)
3
New cards
what is the sister taxa of opisthokonts
choanoflagellates
4
New cards
what are the "unifying" fungal traits
can have multiple different cell types OR be unicellular
are heterotrophs and absorb nutrients
have cell walls with chitin
some have dikaryon stages (no other organisms do)
many have both sexual and asexual reproduction
three styles of nutrient acquisition
are heterotrophs and absorb nutrients
have cell walls with chitin
some have dikaryon stages (no other organisms do)
many have both sexual and asexual reproduction
three styles of nutrient acquisition
5
New cards
fungal cell types
unicellular (free-living)
multicellular
multicellular
6
New cards
hyphae
The branching, threadlike tubes that make up the bodies of multicellular fungi
7
New cards
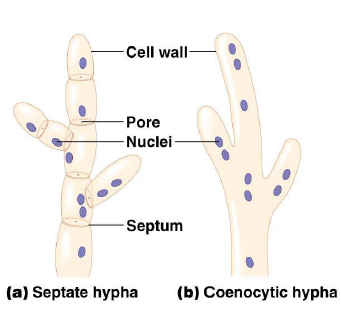
septate fungi
have hyphae divided into cells by septa, with pores allowing cell-to-cell movement of organelles
8
New cards
coenocytic fungi
a fungus that lacks septa and hence whose body is made up of a continuous cytoplasmic mass that may contain hundreds or thousands of nuclei
9
New cards
what does coenocytic fungi mean for evolution?
indicates that cell separation isn't actually that important for fungi
10
New cards
septa
the cells that make up hyphae are divided by these cross sections
11
New cards
Mycelium
densely branched network of the hyphae of a fungus
12
New cards
what is the form of digestion of fungi?
external digestion (absorptive heterotrophy)
13
New cards
absorptive heterotrophs
digest food outside their body and then absorb it
14
New cards
how does the fungal body plan reflect nutrient intake in fungus?
digestive reproductive structures with clusters of hyphae (mycelium)
15
New cards
chitin
Polysaccharide found in arthropod exoskeletons and fungal cell walls.
16
New cards
fungal nuclei
normally haploid, with the exception of transient diploid stages formed during the sexual life cycles
17
New cards
dikaryons
cell containing two haploid nuclei n+n
18
New cards
dikaryon formation
formed from the fusion of two haploid mating strains
19
New cards
can fungi reproduce both sexually and asexually in one life cycle?
yes
20
New cards
Most fungi spend most of their lives in a ______ _______, reproducing ________
haploid state; asexually
21
New cards
spores are reproductive structures
by wind they turn into new individuals; produce new spores by mitosis
22
New cards
plasmogamy
the union of the cytoplasms of two parent mycelia
23
New cards
karyogamy
Fusion of two haploid nuclei to form a diploid nucleus. Occurs in many fungi, and in animals and plants during fertilization of gametes
24
New cards
importance of sexual stages for identification
critical for defining species andphylogenetic placement of fungi
25
New cards
microsporidia
microscopic unicellular parasitic fungi
obligate, intracellular parasites
replicated by host cell
lack mitochondria
obligate, intracellular parasites
replicated by host cell
lack mitochondria
26
New cards
mitosome
an organelle found within certain unicellular eukaryotes which lack mitochondria
27
New cards
chytrids
aquatic
unicellular life stages
flagella present
coenocytic
unicellular life stages
flagella present
coenocytic
28
New cards
chytrids having flagella means what evolutionarily
the first fungi were probably aquatic
29
New cards
what group of fungi is believed to be killing off amphibians?
chyrids
30
New cards
zygomycetes
saprobic or parasitic
coenocytic
sexual reproduction is rare
karyogamy and plasmogamy in life cycle
coenocytic
sexual reproduction is rare
karyogamy and plasmogamy in life cycle
31
New cards
gametangia
in primitive plants, a protective jacket of cells in which gametes and zygotes develop and which prevents drying out.
32
New cards
zygosporangium
In zygomycete fungi, a sturdy multinucleate structure in which karyogamy and meiosis occur.
33
New cards
zygospore
resting spore that contains zygotes formed during the sexual phase of a mold's life cycle
34
New cards
Glomeromycetes
mycorrhizal
coenocytic
do not form mycelia
this group probably made the invasion of plans on land possible
coenocytic
do not form mycelia
this group probably made the invasion of plans on land possible
35
New cards
Mycorrhizae
Ecological relationship between the mycelium of a fungus and the roots of certain plants
36
New cards
ascomycetes
septate
dikaryon forming (short dikaryon stages)
bear spores in cups or sacs
dikaryon forming (short dikaryon stages)
bear spores in cups or sacs
37
New cards
types of ascomycetes
cup fungi
baker's yeast
common molds
cheese molds
plant pathogens
baker's yeast
common molds
cheese molds
plant pathogens
38
New cards
basidiomycota
basidiomata bear spores
septate
dikaryon forming (long dikaryon stages)
septate
dikaryon forming (long dikaryon stages)
39
New cards
basidioma
the multicellular fruiting bodies of the Basidiomycetes often with a protective layer and lined with basidium
40
New cards
basidiocarps
Fruiting bodies where the basidiomycetes produce sexually
41
New cards
mutualist fungi
both organisms benefit; both organisms depend on each other; lichens; mycorrhizal
42
New cards
saprobe fungi
eat dead material; decomposers: clean our world
43
New cards
parasitic fungi
eat living material; i.e.: athlete's foot or ringworm
44
New cards
why are fungal diseases hard to treat?
because unlike bacteria, fungi are eukaryotes. Antibiotics only target prokaryotic cells.
45
New cards
Batrachochytrium dendrobatidis
chytrid been associated with declining harlequin frog populations
46
New cards
cup fungus
In the picture above is a fungus in which the spore-producing layer forms the lining of a shallow cup.

47
New cards
baker's yeast
ascomycete; Fungi used for bread and brewing
48
New cards
penicillin
common mold; ascomycete
49
New cards
truffles and morels
two types of ascomycetes that are commonly used in cooking
50
New cards
chestnut blight
a fungal infection that has nearly eliminated the American chestnut (ascomycete)
51
New cards
dutch elm disease
a fungal disease of elm trees that is spread by elm bark beetles (ascomycete)
52
New cards
cooking mushrooms
basidiomycete
53
New cards
athlete's foot
fungal infection of the foot (parasitic fungi)
54
New cards
ringworm
A highly contagious, fungal infection of the skin or scalp.
55
New cards
Which of the following statements is FALSE about fungi?
A) fungi can be either heterotrophic or autotrophic
B) septa are divisions between fungal cells with small pores that allow cytoplasm to flow between the cells
C) fungal cell walls contain chitin, which is the same material found in insect exoskeletons
D) the fungi and the choanoflagellates are part of a group called the Opisthokonts
E) all fungi are part of a single monophyletic group
A) fungi can be either heterotrophic or autotrophic
B) septa are divisions between fungal cells with small pores that allow cytoplasm to flow between the cells
C) fungal cell walls contain chitin, which is the same material found in insect exoskeletons
D) the fungi and the choanoflagellates are part of a group called the Opisthokonts
E) all fungi are part of a single monophyletic group
A) fungi can be either heterotrophic or autotrophic
56
New cards
E) either A or C would be accurate
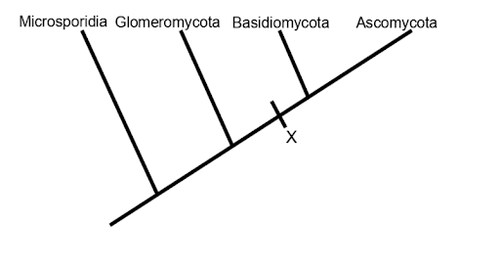
What trait can accurately label the tick mark with the question mark on the tree below?
A) septate
B) coenocytic
C) dikaryotic
D) reproductive parts are basidiomata
E) either A or C would be accurate
A) septate
B) coenocytic
C) dikaryotic
D) reproductive parts are basidiomata
E) either A or C would be accurate