Optical Isomers
1/8
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
9 Terms
What are stereoisomers?
Molecules which have the same molecular formula, but a different 3D arrangement of atoms in space.
When does optical isomerism occur?
Optical isomerism occurs where two molecules with a chiral centre have the groups arranged in different positions in space.
What is a chiral centre?
A carbon atom with 4 different substituent groups bonded to it.
The 2 molecules are…
Mirror images of each other and are non-superimposable.
This means that they do not overlap.
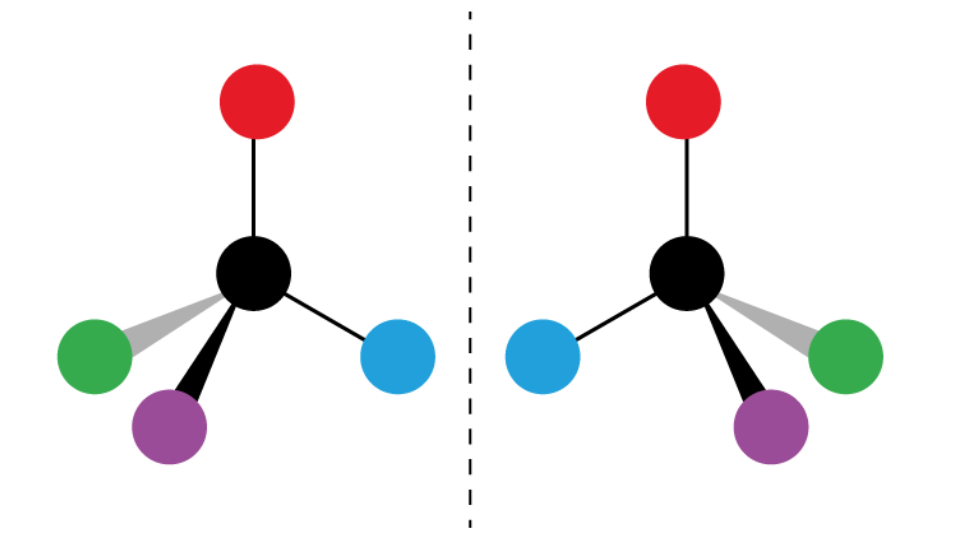
What are enantiomers?
Non-superimposable mirror image isomers.
How can optical isomers be distinguished?
By their effect on plane-polarised light.
The two enantiomers will rotate the plane of vibration of the plane-polarised light in opposite directions. One will rotate the plane clockwise and the other to the same angle anti-clockwise.
What is plane-polarised light?
Plane-polarised light has waves which only vibrate in one direction or plane.
What is a racemic mixture?
A mixture of enantiomers of the same concentration / equal amounts.
What happens if PPL is passed through a racemic mixture?
The rotation in one direction is balanced out by the rotation in another direction.
This is means there is no effect on the plane of polarised light i.e. light continues travelling in a straight line.