Introduction to Animalia - Trip/dip/loblastic, coelom, metameric segmentation etc.
1/19
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
20 Terms
Characteristics of Kingdom Animalia
motile → in search of food, mate or escape predation
or can only move certain body parts or only in larval stage
multicellular
eukaryotic
no cell wall chloroplasts and permanent central vacuoles
perceive env through receptors connected to nervous system
nervous system and support system evolved tg
sexual reproduction
holozoic heterotrophs
have a blastula
Explain how development of cephalization is linked to being motile
motile organisms had to develop complex sensory organs to perceive and navigate their environment
conc of sensory organs was developed at the front of organism → first body part to encounter hostile situation
concentration of complex sensory organs needed more sensory processing system
lead to nerve swellings - ganglia
lead to cephalization
Blastula Stage
early developmental stage
when zygote divides forming a hollow layer of cells → BLASTULA
—-
entire cell is called a blastula,
the actual fluid filled cavity is the blastocoel,
cells making up blastula are blastomeres
the outer spherical layer of blastomeres is the blastoderm
Define Radial Symmetry
organism can be divide into two equal halves across any plane passing through the axis in the center
Evolution of Radial Symmetry
early animals were sessile/didn’t move much
radial symmetry allowed for all around awareness to capture food and detect potential danger
Define Bilateral Symmetry
organism has similar anatomical parts arranged on opposite sides of a median axis so that only one plane can divide it into essentially two identical halves
Evolution of Bilateral Symmetry
as animals became more motile - concentration of sensory organs to the front (front end perceives danger first)
animals developed anterior, posterior and two laterals → BILATERAL SYMMETRY
cephalization
Advantages/Disadvantages of Radial/Bilateral Symmetry
co-ordinate sides for locomotion
two eyes allows for better vision estimate distances
specialization of body parts
no all around awareness
injury to the head can be fatal
all around awareness
less advanced nervous system due to no cephalization
limited movement efficiency
Distinguish between radial and bilateral symmetry
Radial
sessile organisms like cnidaria
all around awareness
definition - two equal halves on any plane
Bilateral
motile organisms
one plane of symmetry
cephalization
localization of sensory organs
evolution of paired appendages
facilitates stream-lining like arthropoda
Diploblastic organisms
have 2 germ layers
ectoderm - nervous tissue, epidermis and nephridia if present
endoderm - develop into gut and associated glands
have a mesoglea - layer of non cellular gelatinous layer
Triploblastic Organisms
3 germ layers - Gastrula
ecto/endoderm
MESODERM- the 3rd germ layer
muscles
dura mater
bones
cartilage
connective tissue
endothelium of blood vessels and blood cells
dentine of teeth
kidneys
adrenal cortex
Evolutionary Significance of Triploblastic organsisation
3 germ layers: ectoderm, mesoderm, endoderm
Mesoderm allows muscles & internal organs
Enables complex body structures
Supports larger size & active movement
Foundation for coelom and organ systems
Coelom
mesoderm splits into two layer
one lining ectoderm, one endoderm
surrounded by peritoneum
the fluid filled cavity between these layers is called the coelom
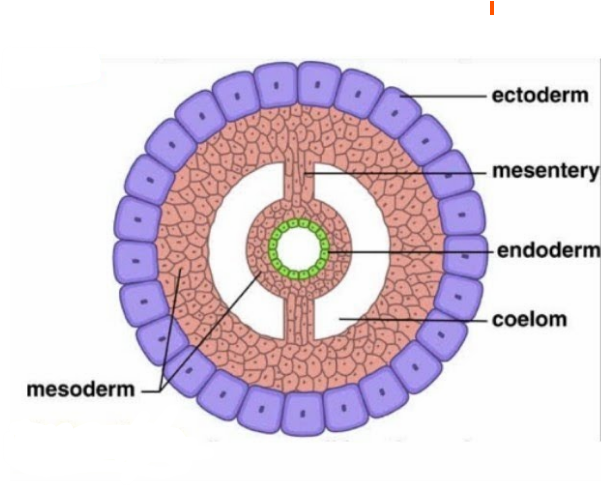
Advantages of a Coelomic Cavity
more space for internal organs → larger and more complex
space where organs can grow and develop
movement no longer hampers digestion
more space for the uterus to expand
hydrostatic skeleton
more space for food or waste
Metameric Segmentation
serial repetition of organs or tissues along the body of an animal dividing body into similar parts or segments (Metamers)
Metameric Segmentation allows for locomotion
repeated segments of annelid are easy to coordinate
Segments contract in a wave (circular then longitudinal muscle).
This creates efficient, coordinated movement,
Metameric Segmentation also allows for the specialization of body parts
different segments can be adapted to do different things
Tagmata
metamers became grouped - further specialization each tagma can develop unique structures
Examples of Metameric Segmentation in Humans
vertebral column
intestinal wall
division of nerve endings
TABLE SUMMARIZING ANIMAL PHYLA PG 15