animal cells and tissues
1/34
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
35 Terms
Muscle tissues produce movement via?
contractions
Muscle cells
Myocytes
Myocytes are filled with what filaments?
Actin
Myosin
What type of force do muscle tissues exert, which causes movement
Mechanical force
3 types of muscle tissues
Skeletal
Smooth
Cardiac
Muscles that are striated and contain more than one nucleus per cell
Skeletal muscles
Multi-nucleated state of muscle cells
Syncytium
Most skeletal muscles are attached to boned via a strong and elastic specialized connective tissue called?
Tendons
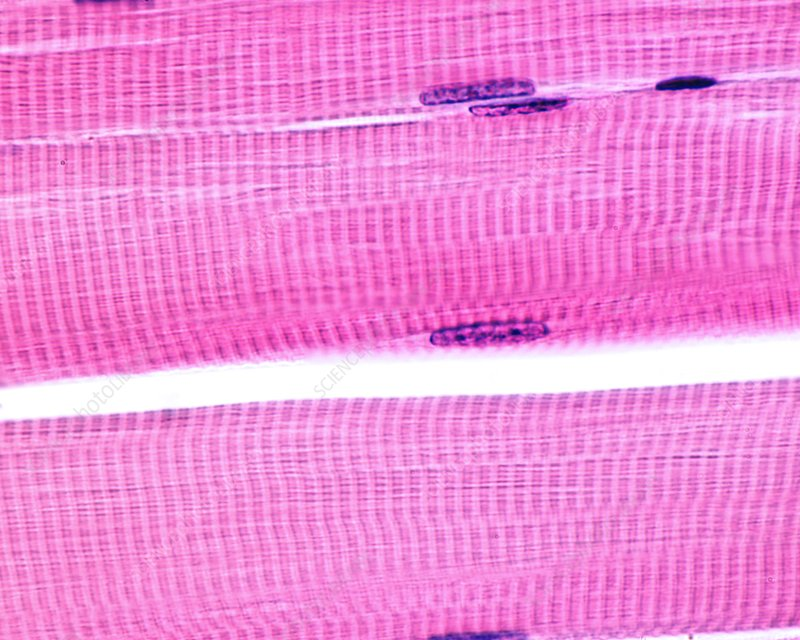
Skeletal muscle
Where are the nucleus located at the striated muscle cells
Periphery
Striations are composed of two bands
I-bands
A-bands
no striations, involuntary
Smooth muscle
How many nucleus per cell in smooth muscles
(1)
most often arranged in sheets in the wall of organs like stomach, intestines, and uterus
smooth muscles
where is the nuclus located at in the smooth muslce
centrally
striated muscles found only in vertebrate hearts
Cardiac muscles
How many nucleus in cardiac muscles
1-2
Branching cardiac muscle cells are are connected via
intercalated discs
Help synchronize the contraction of the muscle cells
Intercalated disc
What regulates the contraction of the heart
Hormones
Automatic nervous system
function in the animal body by facilitating communication, coordination, and control
Nervous tissues
small, string- like structure that carries impulses across the body
Nerve
outer loose connective tissue covering of the nerve
epineurium
Nerve is composed of:
Epineurium
Nerve bundles/ fascicles
Nerve bundles
Fascicles
Fascicle’s dense sheet of connective tissue
perineurium
Fascicle is composed of bundles of:
axons/ nerve fibers
Layer of white insulating material
Schwann sheath/ Myelin sheath
Wraps around each nerve fiber and appears to fill int he rest of the fascicle’s interior
Endoneurium
Functional unit of the nervous system
Neuron
Neuron is composed of?
Cell body/ soma
Protoplasmic extensions
The neuron’s cell body contains?
Nucleus
Protoplasmic extensions of the neuron
Dendrites
Axons
Branch-like protoplasmic extension
Dendrites
Longer, thin protoplasmic extension of the neuron
Axons