Lec: Food and Feeding
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
digestive tract review
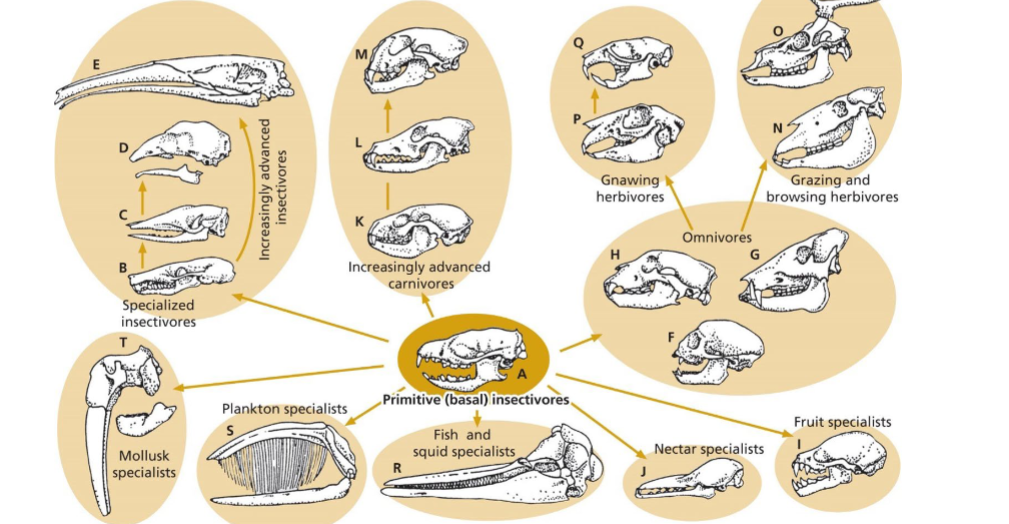
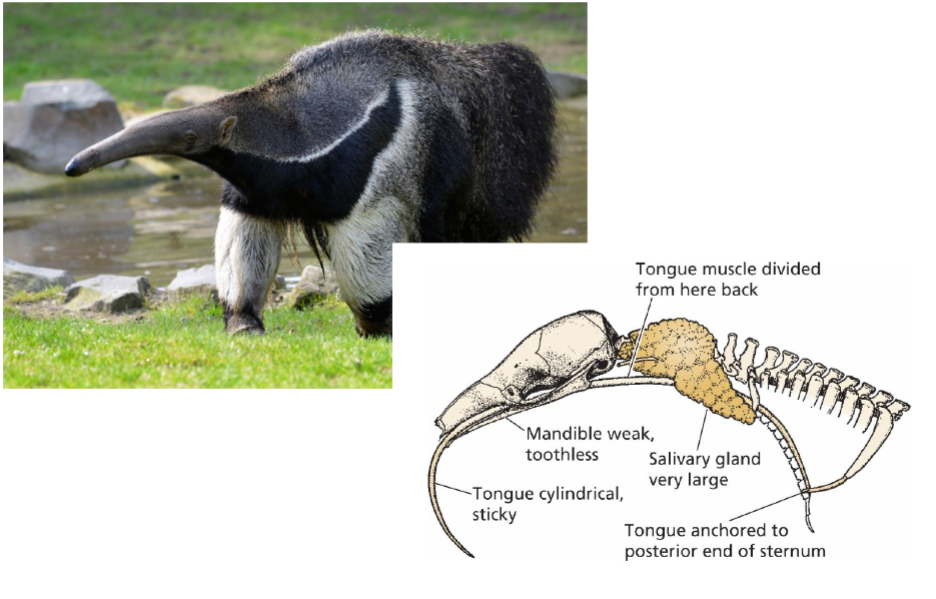
Insectivory
basic/primary mammals (insects were the first major food source), wide range/diversity of mammals, aerial, aquatic, and terrestrial insectivores, incisors procumbent in many, consume minimal amounts of fiber, which affects morphology of digestive tract
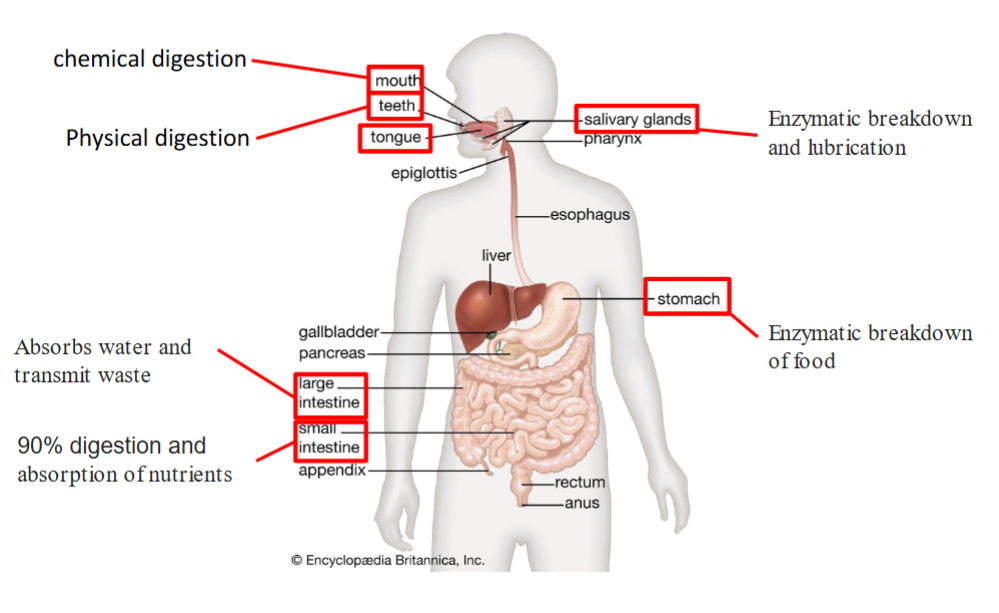
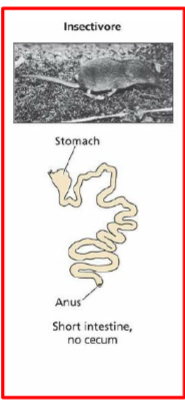
Insectivore digestive tract
stomach is big and muscular, short intestine, no cecum (don’t need to ferment)
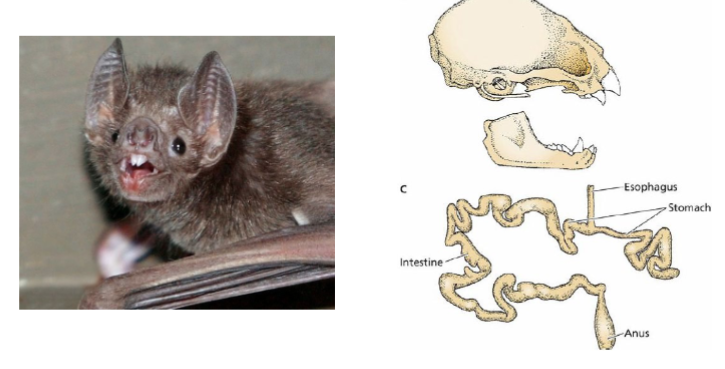
Carnivory
different types (arboreal, terrestrial, marine), sharp cutting teeth w/ some homodont dentition, some specials (sanguinivorous and piscivorous)

Sanguinivorous
blood suckers (vampire bats)
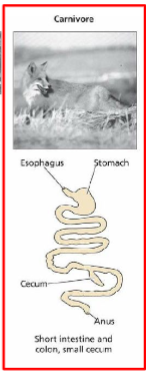
Carnivore digestive tract
big stomach, simple gut, short intestine and colon, have cecum
Kinds of Herbivores
browsers and grazers (hooved mammals and aquatic grazers)
gnawing mammals (rodents and lagomorphs, coprophagy)
don’t get as much energy from vegetation as a carnivore would get from their prey, so they have to constantly graze
Herbivore characteristics and digestive tract
selenodont dentition, canines reduced of absent, broad molars (crushing, shredding, and grinding), fermentation (hindgut and foregut), enlarged cecum
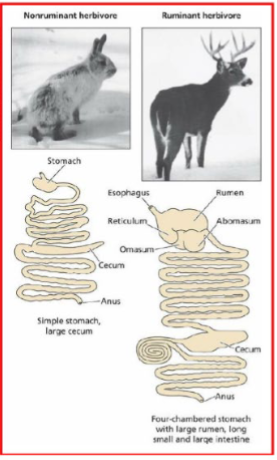
Nonruminant herbivore
large incisors to crop foliage

Ruminant herbivore
lost their upper incisors (callous pad on their upper gum)
Coprophagy
hindgut fermenters, consumption of cecotropes (nutrient dense droppings)

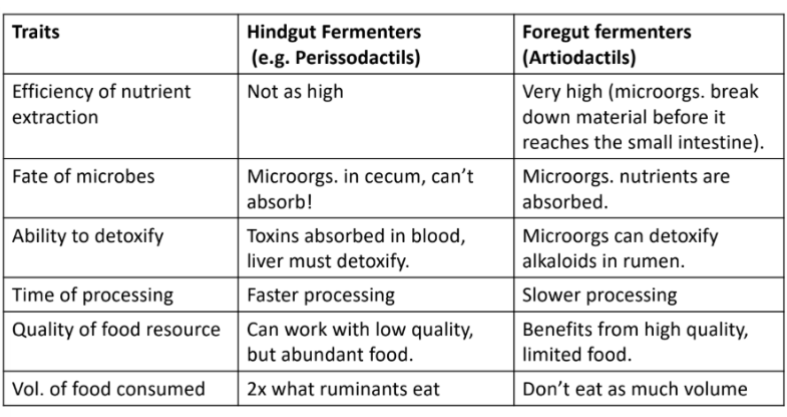
compare and contrast hind and foregut fermenters
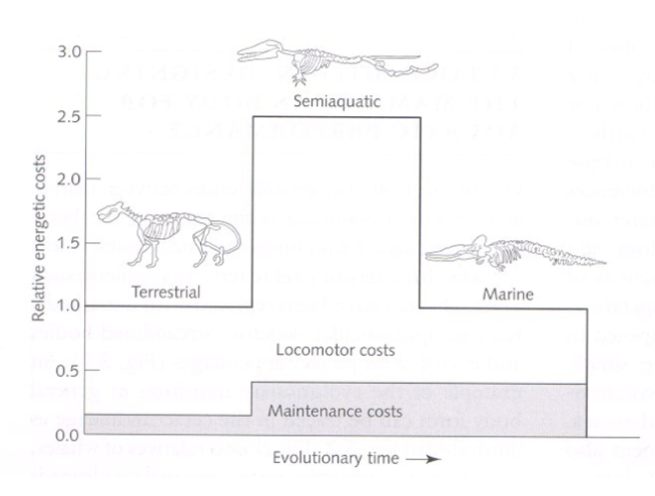
specific dynamic action
the energy expenditure required by the body to digest, absorb, and assimilate food
types of herbivores
folivory (leaf eaters), frugivory (fruit eaters), nectarivory (nectar eaters), gummivory (gum-eating), mycophagy (fungus-eating), granivory (seed eating)
omnivory
everything eater w/ versatile dentition
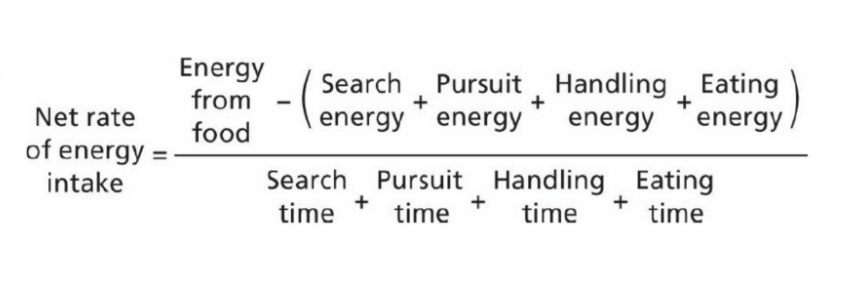
optimal foraging strategies
decisions used by animals to obtain optimal cost-benefit for foraging, have to consider amount of energy to expend and amount of time to spend
marginal value theorem
details of when an animal will decide to leave a food patch, energy spent moving between patches, when is it more productive to move on?
food hoarding and caching
animals that cache (rodents, pikas, carnivores, etc.), store food for later when they are more safe or for when food isn’t as readily available