CHEM0011 - Section E
1/48
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
49 Terms
What is meant by the rate of a reaction?
The rate at which reagents are used up and products are formed.
How do you calculate rate from the reaction R -> P?
Rate = -d[r]/dt = d[P]/dt
How do you calculate rate from the reaction aA -> bB?
Rate = -1/a x (d[A]/dt) = 1/b x (d[B]/dt)
What is the empirical rate law?
Rate ∝ [A]^m x [B]^n
![<p>Rate ∝ [A]^m x [B]^n</p>](https://knowt-user-attachments.s3.amazonaws.com/91bfdcbe-da65-4f28-af66-c362ac6c5bed.jpg)
What does k represent? What does it depend on?
The rate constant for the reaction, solely on temperature.
What are the partial and overall orders of the rate equation Rate =k [A]^m x [B]^n?
Partial orders are m and n, overall order is (m+n).
What values can the order of a reaction take?
zero/integer/fraction
Does stoichiometry affect the order of a reaction?
no
The partial orders of reaction can only be determined experimentally. True or false?
True
What is meant by a zero order reaction? Why may it occur?
Rate of reaction does not depend on concentration so the rate remains constant with time and concentration of reactant decreases linearly with time.
Also known as saturation kinetics; may be limited by surface area (limited number of sites) for example so rate is purely determined by k.
Rate laws show the relationship between rate and concentration. What does a rate equation show and how can this be achieved?
The connection between concentration and time
By doing a mathematical integration of the rate law.
What is the half-life of a first order reaction?
The time required for the concentration to drop to half its original value. t = (ln2)/k
Is half life dependent on concentration in first order reactions?
No, it is constant. t = ln2/k.
For gases, pressure is proportional to __________.
concentration
For a first order rate law, show how a rate equation can be generated.
rate = - d[A]/dt = k[A]
integral([A], [A]₀ --- 1/[A] d[A]) = - integral(t, 0 --- k dt)
ln([A]/[A]₀) = -kt
[A] = [A]₀ x e^-kt
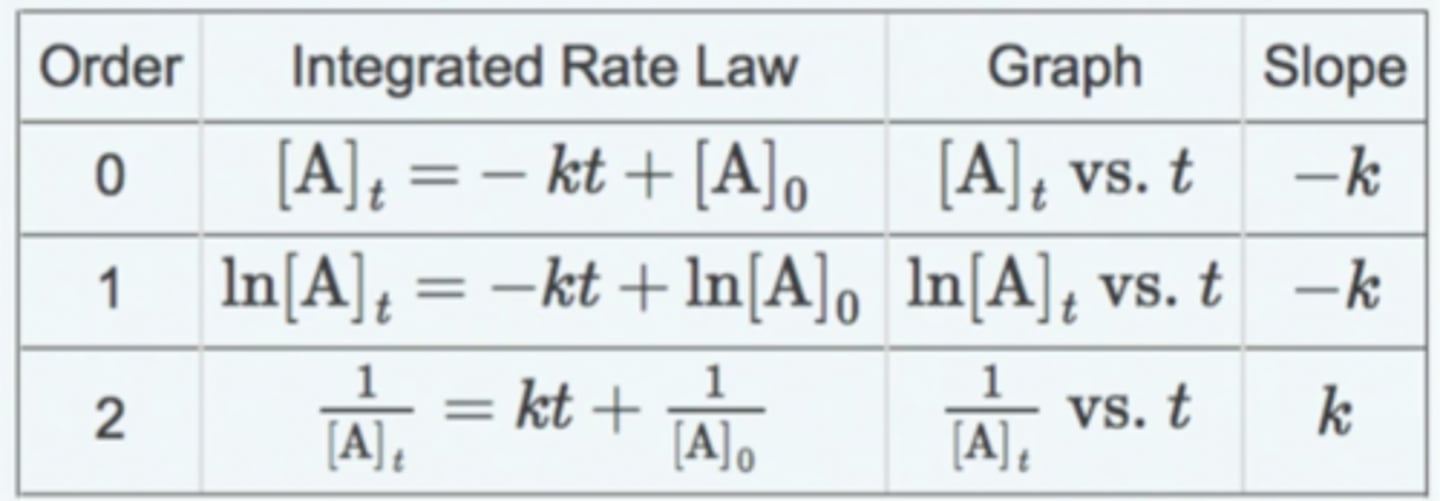
Write the linearised rate equations for zeroth, first and second order, stating what is plot and what the gradient shows.
What is the general procedure for measuring the rate of reaction?
Start the reaction (t=0)
Measure a property as a function of time
Convert property/measurement to concentration
Analyse data
What are some methods of measuring rates of reaction?
Spectrophotometric methods:
- UV/Vis or IR absorbance, absorbance proportional to conc.
- fluorescence
- stop flow method for fast reactions
- flash photolysis for very fast reactions
NMR integration is proportional to concentration.
Polarimetry:
- reaction of optically active materials with give rise to changes in optical rotation.
- circular dichroism
Conductivity:
- changes in the number of ions gives rise to changes in conductance of a solution.
Electrochemical/pH detection
Pressure changes
Differential scanning calorimetry.
What are pseudo-order conditions (isolation)?
When a large excess of one component is added such that its concentration will remain constant as the reaction proceeds.
[B] >> [A]
When a reaction rate constant is determined under pseudo-first order conditions, it is referred to by what symbol or phrase?
Kobs / K observed
How can the order of the reaction for the species A be determined using pseudo-order conditions in the reaction A + B -> AB?
[B] >> [A]
Run the reaction at several different [A]0.
Plot [A] vs time
Determine initial rate of reaction for each curve by drawing a tangent at t=0.
The ratio of any two rates will be in proportion to the ratio of initial concentrations of A to the power of a.
Or, take logarithms of rate law:
log(rate) = log(Kobs) + alog[A]
Plot log(initial rates) vs log[A], the slope is equal to the order of the reaction.
Kobs includes concentration of [B], which is unchanged, so is not the real rate constant.
What are elementary reactions?
The several steps for a reaction to go to completion (most reactions go via intermediates).
What are the two important types of elementary reactions?
Unimolecular - a single species undergoes a change (e.g. bond cleavage, isomerization).
Bimolecular - two species come together (e.g. bond formation).
What is the rate law for the unimolecular step AB -> A + B?
rate = k[AB]
What is the rate law for the following bimolecular steps? What type of bimolecular steps are they?
A + A -> A2
C + D -> CD
rate = k[A]^2, homonuclear
rate = k[C][D], heteronuclear
The ratio of any two rates will be in proportion to the ratio of initial concentrations of A to the power of a. Write the equation for this.
Rate1/Rate2 = ([A]₀1/[A]₀2)^a
The overall rate of a reaction is determined by the rate of the slowest step. What is this step known as?
The rate determining step.
What is steady state approximation?
The concentration of intermediates in a reaction remains very low and constant throughout, such that in the mechanism A -> B -> c, d[B]/t = 0.
If we construct a hypothetical mechanism for a chemical reaction what do we call each component of the mechanism?
Elementary steps
Imagine that we have a mechanism in solution in which all the steps are fast. What physical process would then limit the rate of the reaction?
diffusion
How does the rate constant depend on temperature? What is this equation called?
k = Ae^(-Ea/RT)
The Arrhenius relation.
How can the Arrhenius relation be linearised?
taking the natural logarithms of both sides
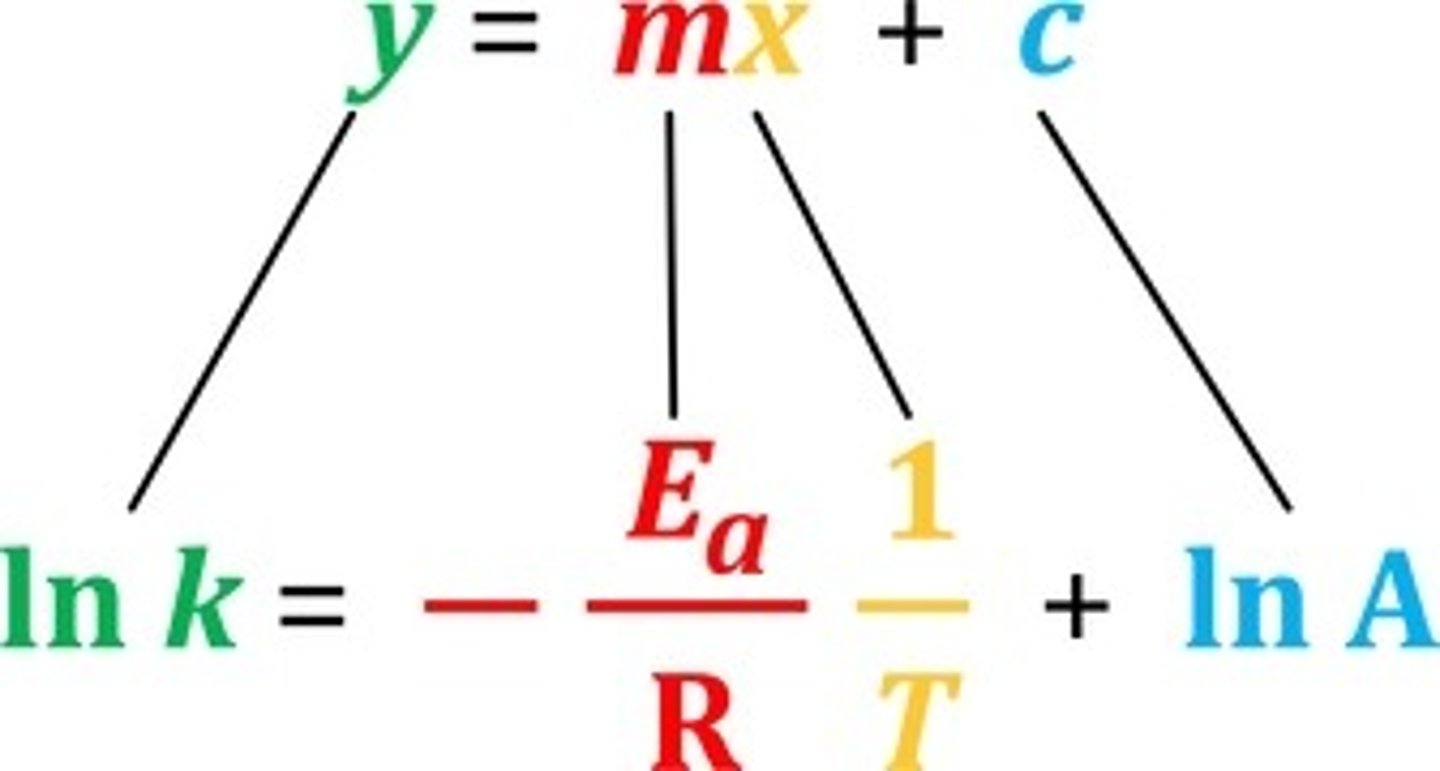
What does A represent in the Arrhenius relation?
In simple cases, the total number of collisions occurring per second.
In more complex cases, factors in the orientation of the molecules in the collision.
What is the Eyring equation?
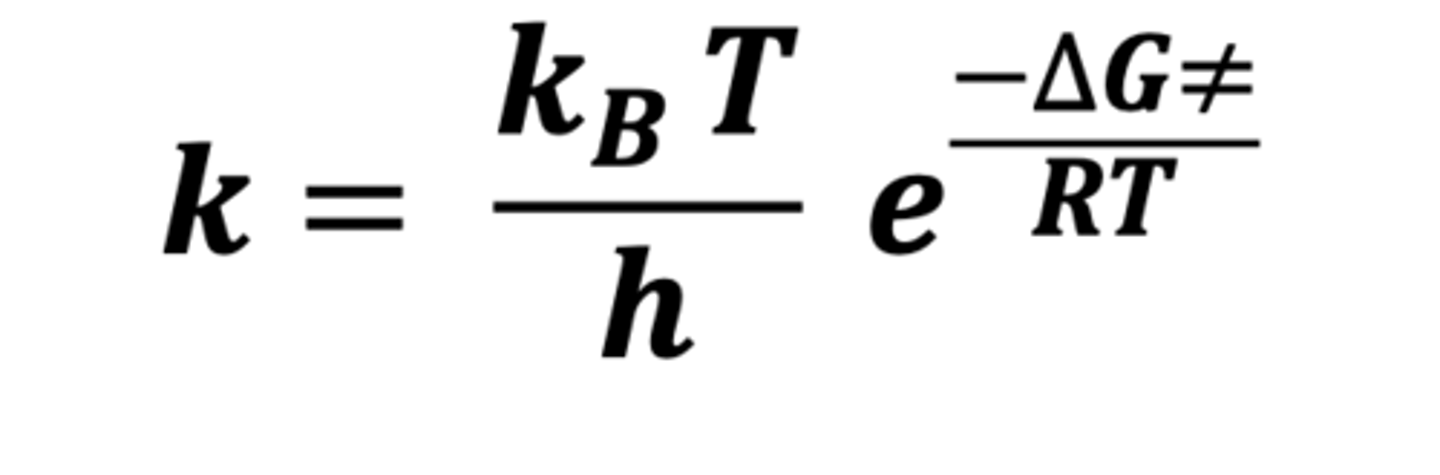
How can the Arrhenius equation be rearranged such that the rate equation can be calculated without the constant A?
ln(K2/K1) = Ea/R x (1/T1 - 1/T2)
What is Graham's Law of Effusion?
The rate of effusion of a gas (rate of leaving a porous container) was inversely proportional to the molecular mass.
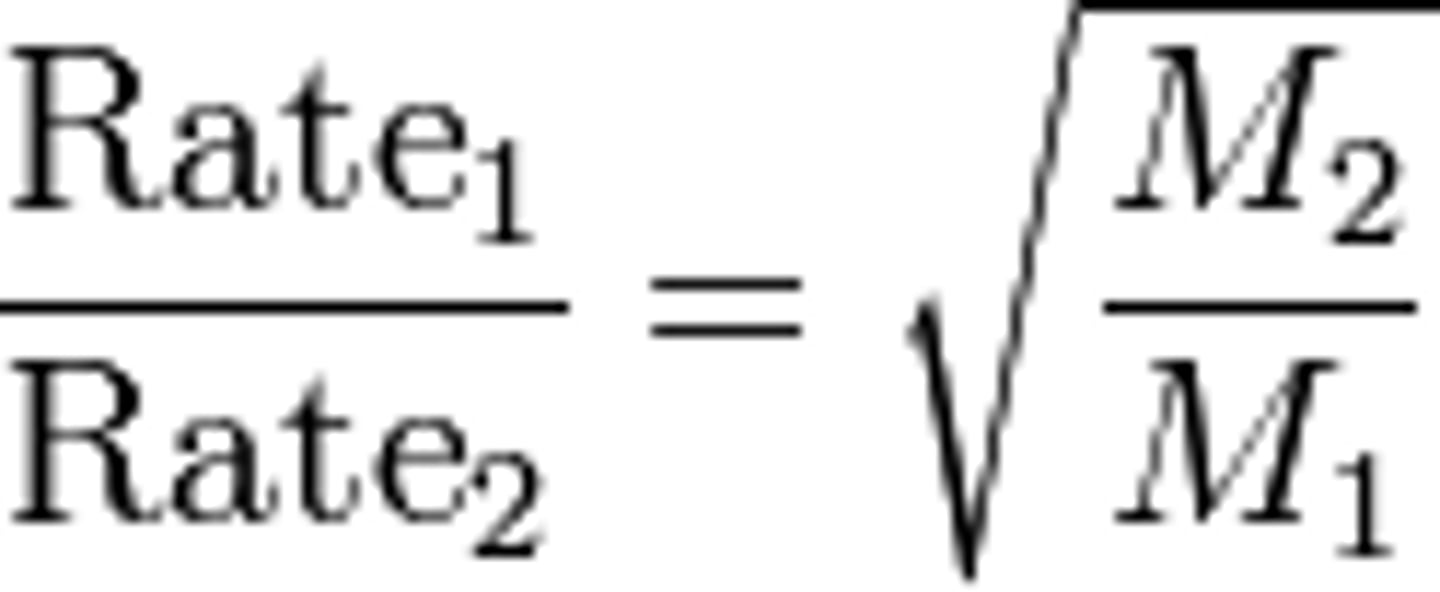
What is Fick's first law of diffusion?
J = -D x dc/dx
Flux (J): net number of molecules moving per unit area per second, depends on diffusion constant for that substance. Minus sign shows flowing from high to low concentration. Change in concentration with a distance x from the starting point depends on the change in the concentration gradient.
What is the equation that shows how far a molecule moves over time during diffusion?
average of x^2 = 2Dt
D is the diffusion constant
What does the diffusion constant depend on?
Stokes law is f = 6πnr (f is like friction).
r is the hydrodynamic radius - an effective radius because when molecules are surrounded by a solvation sphere, they carry the solvent with them, increasing the radius.
n is viscosity of solution
Kb is Boltzmann's constant.
T is temperature

What do we call the A term in the Arrhenius relation?
pre-exponential factor
The word ____ is used to classify a reaction by the number of species that are involved in the transition state.
Molecularity
What is the difference between heterogenous and homogenous catalysts?
Homogeneous - same phase as reactants
Heterogeneous - different phase as reactants
What are catalysts?
A substance which changes the rate of a chemical reaction by providing a separate mechanism (pathway) with a lower activation energy, and can be recovered unchanged at the end of the reaction.
How do you calculate turnover number?
Kcat (turnover) = Vmax / [E]o.
This is the efficiency of the catalyst - how many substrate molecules can be processed per second by one mole of catalyst.
What does Km show?
How strong the enzyme binds to the substrate - lower means stronger.
What does kcat/Km show?
Catalytic efficiency - high value shows a large number of substrate molecules processed per second and enzyme binds easily to catalyst.
What do you plot when you analyse enzyme data by the Lineweaver-Burk method?
1/V vs 1/[S]
[S] is independent variable
What is the difference between an Sn2 and Sn1 reaction in terms of kinetics?
Sₙ2 means rate is dependent on both species (equally), Sₙ1 is only for one species
What are the names of the following plots?
V vs V/[S]
V/[S] vs V
[S]/V vs [S]
1/V vs 1/[S]
Eadie-Hofstee
Scatchard
Hanes
Lineweaver-Burk