Comprehensive Guide to Anesthesia Equipment and Monitoring in Veterinary Medicine
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
What is important to maintain for sufficient anesthesia?
A delicate balance of anesthesia depth.
What is the outcome of sufficient depth of anesthesia?
Unconsciousness & insensitivity to pain.
What might happen if a delicate balance of anesthesia depth is not properly maintained?
Compromised cardiovascular & respiratory system function.
How often should patients be monitored during anesthesia?
Every 5 minutes for health patients (ASA 1), but higher risk patients must be monitored more frequently or even continuously in some cases.
What does an anesthetic record document?
Monitoring parameters (which = heart rate, respirations, temperature, iso rate, oxygen rate, oxygen rate, mucus membranes, CRT, SPO2, ETCO2, BP, & fluids), drug administration, & other info.
What are the two critical questions to consider during monitoring?
1. Is the patient safe or in danger? 2. Is the depth of anesthesia appropriate?
Palpebral reflex?
Induced by tapping the skin at the medial or lateral canthus of the eye.
Swallowing reflex?
Response to the presence of food or saliva in the pharynx.
Pedal reflex?
Withdrawal of a limb in response to a painful stimulus, induced when limb is relaxed & a toe is pinched.
Corneal reflex?
Induced by placing a drop of sterile artificial tears on the cornea, resulting in the eye to retract slightly into the orbit & possibly cause a blink response.
Muscle tone?
Assess jaw tone by opening carefully, high muscle tone means inadequate anesthesia.
Eye position & pupil size?
Ventromedial position (toward the chin) during efficient anesthesia, while nystagmus usually indicates light anesthesia.
What can surgical stimulation cause, especially if anesthesia is inadequate?
Sudden & marked increase in heart rate, respirations, & BP.
Esophageal stethoscope?
Amplifies the sound of the heartbeat for monitoring from a distance, by inserting it, lubricated, into the esophagus to the level of the heart (about the 5th rib).
ECG?
Monitors real-time electrical activity of the heart & heart rate.
Is it possible for the heart to stop beating and for the electrical activity to continue for a time after the heart has stopped?
Yes.
Doppler ultrasound?
Detects blood flow through small arteries and converts it into an audible signal; probe must be covered with ultrasound gel before placing.
Where can a Doppler ultrasound probe be placed?
Ventral surface of the paw between the wrist & paw pad, on the ventral surface of the tail base, on the dorsomedial surface of the hock, or on the medial surface of the thigh in patients < 10 pounds.
Sphygomomanometer?
Blood pressure monitor.
Where can a BP cuff be placed?
Foreleg, metatarsus, or tail base with the cuff balloon centered over the artery.
What measurement is represented on a BP when pressure is gradually decreased until the pulse is heard again?
Systolic pressure.
What happens if the BP cuff is too large or too small?
Too large = decreases readings; too small = elevates readings.
How is blood pressure measured?
By inflating a cuff until the artery is occluded and then gradually decreasing pressure until the doppler signal/pulse is heard again.
What are the normal blood pressure values during anesthesia?
Systolic = 100-160, Diastolic = 50-70, Mean = 60-90.
Minimum acceptable mean (mean arterial pressure) BP during anesthesia?
60
Hypertensive BP?
> 160.
What does a pulse oximeter measure?
Changes in the oxygen saturation of hemoglobin & pulse/heart rate.
What oxygen saturation level indicates hypoxemia requiring treatment?
Less than 90%.
Normal oxygen saturation on pulse ox?
> 95%
Emergency oxygen saturation on pulse ox?
< 85% for longer than 30 seconds.
What are the two types of pulse oximeter probes?
Transmission probes = clamp-like with light & sensor on opposite jaws of the clamp.
Reflective probes = placed inside hollow organs, light source & sensor located next to each other.
What is the proper placement for a transmission pulse oximeter probe?
Over nonpigmented tissue that is thin enough to allow light transmission, such as the tongue or ear.
What should be done to reflective pulse oximeter probes before use?
They should be cleaned with alcohol but not immersed or scrubbed.
Capnograph?
End-tidal CO2; measures CO2 levels present in inspired & expired air
What is one of the best indicator of adequate respiration?
Capnograph.
CO2 levels on capnograph?
Inspiration = 0 mm Hg
Awake peak expiration = 35-45
Anesthetized peak expiration = 40-55.
Roughly about how much sq fluids for adult healthy cat?
75-100 mL.
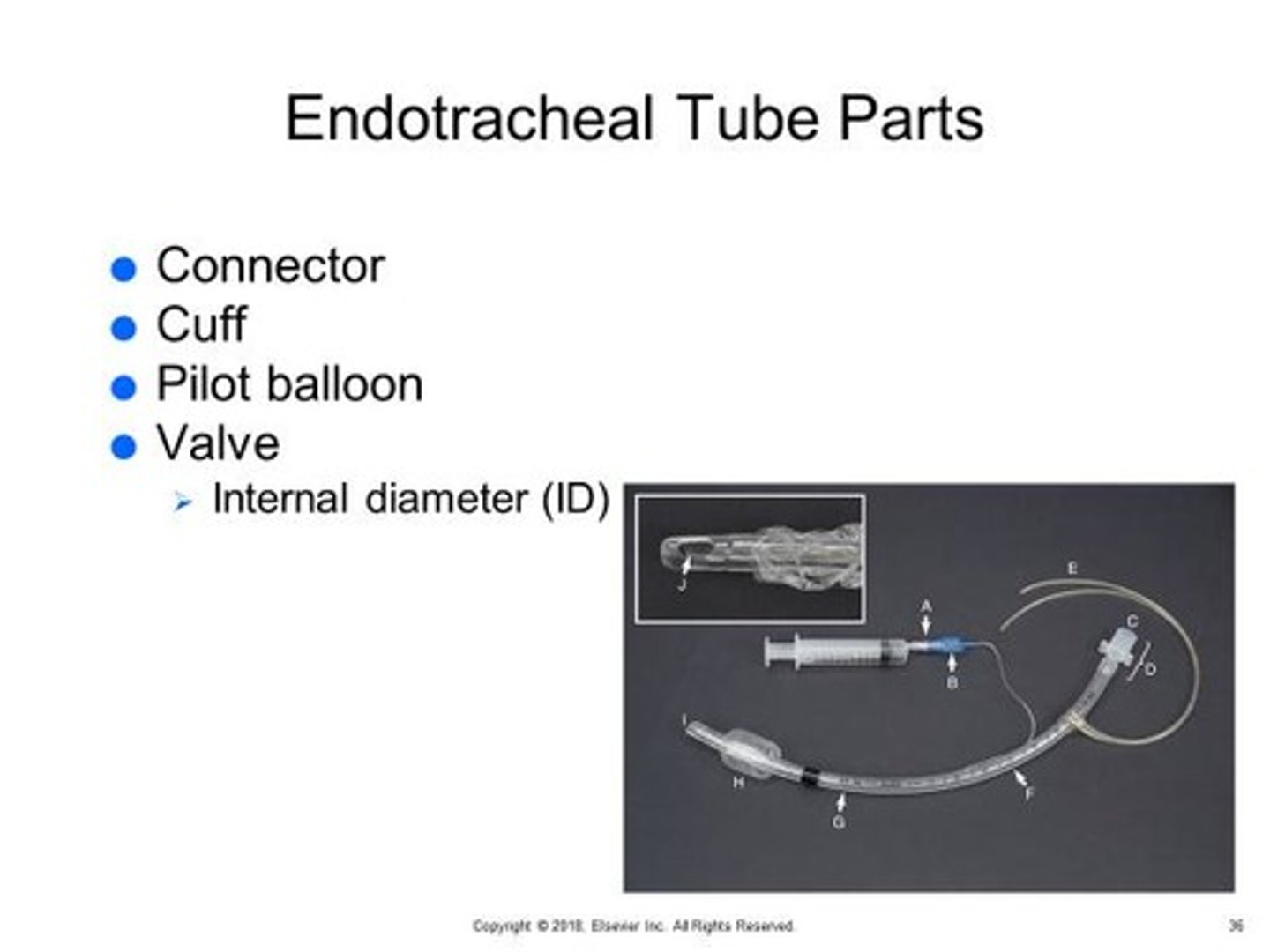
What is the purpose of an ET tube?
Maintain open airway, minimize pulmonary aspiration of blood & stomach contents & etc., facilitating the administration of supplemental oxygen, & allowing ventilation of the patient when necessary.
What is an anesthetic chamber used for?
To induce general anesthesia in patients that are feral, vicious, or intractable.
What is one drawback of anesthetic chambers?
Doesn't allow for close monitoring of patient during induction.
What are some drawbacks of anesthetic masks?
They do not maintain an open airway, protect against aspiration, & doesn't provide ventilation to the patient.
What are the main components of an anesthesia machine?
Carrier gas supply, anesthetic vaporizer, breathing circuit, and scavenging system.
What components are included in the carrier gas supply of an anesthesia machine?
Oxygen supply, flowmeters, oxygen flush valve, pressure-reducing valve, & pressure gauges.
What is the role of the carrier gas supply in anesthesia?
To deliver oxygen and other gases to the patient at a controlled flow rate.
How does the anesthetic vaporizer function?
It vaporizes a precise concentration of liquid inhalant anesthesia and mixes it with carrier gases.
What is the purpose of the scavenging system in an anesthesia machine?
To dispose of waste and excess anesthetic gases.
What is tidal volume (TV) in the context of anesthesia?
The volume of air moved into and out of the lungs during each ventilation cycle.
How do you calculate the reservoir bag size for a patient?
1. TV = 10 to 15 mL x kg
2. TV (range) x 6
3. Convert to liters & round up for bag size range
OR...
1. 60 to 90 mL x kg
2. Convert to liters & round up for bag size range.
What can happen if the reservoir bag is too small for the patient?
Collapse the lungs.
What colors are the precision vaporizers for isoflurane and sevoflurane?
Purple for isoflurane and yellow for sevoflurane.
What should be checked before each anesthetic procedure?
The quantity of carrier gases in compressed gas cylinders and the level of inhalant anesthetic in the vaporizer.
What are the steps in preparing the anesthesia machine?
1. Oxygen (carrier gas) = check levels & replace if needed
2. Isoflurane (inhalant) = check levels & replace if needed
3. Select circuit = rebreathing (> 7kg) or non-rebreathing (< 7kg)
4. If rebreathing, select appropriate size reservoir bag & breathing tubes
5. Assemble & check for leaks
6. Set the pop-off valve
7. Assemble, turn on, & adjust the scavenging system
What tends to be one of the most common leak sources in anesthesia machines?
Reservoir bag.
What are the steps for checking for leaks in an anesthesia machine?
1. Assemble machine & secure connections
2. Close pop-off valve & occlude end of breathing tube
3. Fill reservoir bag until bag pressure is about 30mmHg (or at least 20)
--Rebreathing = Turn on oxygen & oxygen flowmeter to fill reservoir bag
--Non-rebreathing = Turn on oxygen & oxygen flowmeter to fill reservoir bag
4. Turn off oxygen flowmeter & watch bag pressure gauge for pressure drops for at least 10 seconds
5. While still occluding breathing tube, open pop-off valve & deflate reservoir bag to scavenge gas out of the system.
What indicates that there are no leaks in a non-rebreathing system?
The bag remains inflated for at least 10 seconds after the flowmeter is turned off.