Causes and Outcomes of the Russian Revolution 1905-1917
1/122
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
123 Terms
Tsar Nicholas II
Autocratic ruler of Russia, resisted reforms.
Russification
Policy enforcing Russian language and Orthodox Christianity.
Social Hierarchy
Peasants dominated, nobility lacked power.
Emancipation of Serfs
1861 policy freeing serfs, limited impact.
Sergei Witte
Statesman advocating foreign loans for development.
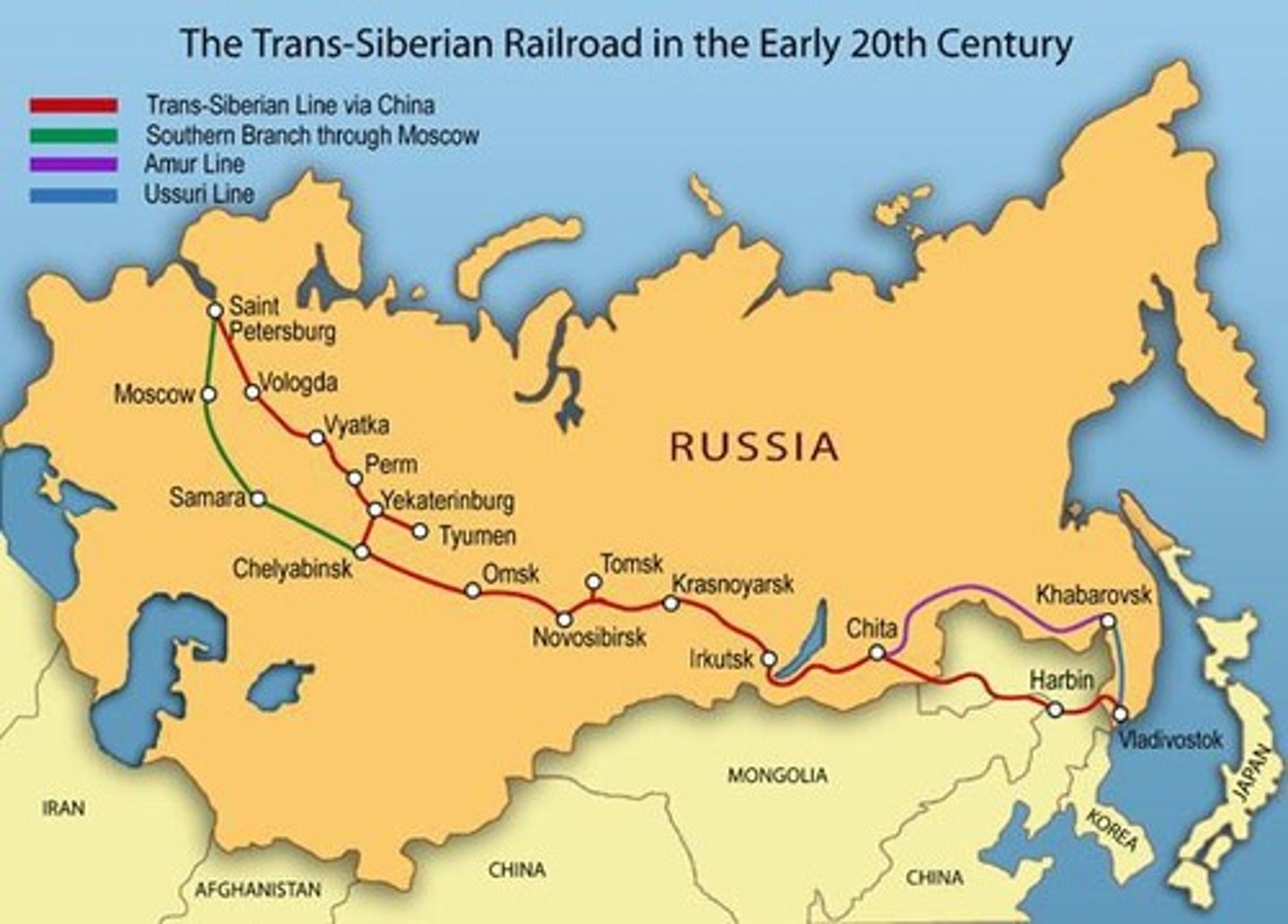
Trans-Siberian Railroad
Major railway project doubling length under Witte.
Socialist Revolutionaries
Radical group seeking wealth redistribution in Russia.
Social Democratic Labor Party
Opposition group inspired by Karl Marx's ideas.
Bolsheviks
Lenin-led faction advocating centralized revolutionary leadership.
Mensheviks
Trotsky-led faction favoring broader revolutionary participation.
Russo-Japanese War
Conflict exposing Russian military weaknesses against Japan.
Battle of Tsushima
Decisive naval defeat for Russia in May 1905.
Bloody Sunday
1905 protest leading to violent repression by army.
1905 Revolution
Political unrest following Bloody Sunday events.
Soviets
Workers' councils organizing strikes during 1905 Revolution.
October Manifesto 1905
Document promising civil liberties and Duma formation.
Duma
Elected assembly with limited powers under Tsar.
Fundamental Laws 1906
Laws asserting Tsar's supreme authority over Duma.
Okhrana
Secret police targeting political dissenters.
First Duma
1906 assembly dismissed by Nicholas II.
Second Duma
1907 assembly faced land reform disagreements.
Economic Structure
Undeveloped agriculture and corrupt tax system.
Political System
Tsar held absolute power without parliamentary limits.
Nationalist Unrest
Discontent among non-Russian ethnic groups due to Russification.
Peasant Revolts
Peasants attacked aristocracy during 1905 unrest.
Political Violence
Opposition often resorted to violence against the Tsar.
Foreign Loans
Witte's strategy to fund industrial growth.
High Interest Rates
Witte's method to attract foreign investment.
Duma
Legislative body in Russia, became an open forum.
Nicholas II
Dismissed Duma, sought alliances with Britain, France.
Pyotr Stolypin
Prime Minister from 1906, focused on agricultural reform.
Stolypin's Reforms
Combined peasant farms to boost productivity.
Peasant Uprisings
Suppressed brutally by Stolypin to maintain order.
Agricultural Output
Increased by 14% under Stolypin's policies.
Third Duma
Operated from 1907 to 1912, included landowners.
Fourth Duma
Lasted from 1912 to 1914, faced political divisions.
World War I
Triggered dismissal of the Fourth Duma in 1914.
Land Reform Policy
Developed during the Third Duma for agricultural improvement.
Military Reorganization
Implemented during Third Duma for military efficiency.
Workers Insurance
Policy created in the Third Duma for worker protection.
Serbia
Nation Russia aimed to protect during WWI.
Archduke Franz Ferdinand
His assassination triggered WWI in 1914.
Austria-Hungary
Declared war on Serbia, starting WWI.
Germany
Austria-Hungary's ally, feared by Russia.
Russo-Japanese War
Russia's defeat led to military improvements.
Russian Army Size
Larger than Germany's in 1914.
Two Fronts
Germany fought on both Western and Eastern fronts.
Cavalry
Inefficient Russian military unit against modern warfare.
Battle of Tannenberg
1914 defeat showing German military superiority.
Military Intelligence
Germany intercepted Russian communications during WWI.
Russian Casualties
70,000 killed and 92,000 captured at Tannenberg.
Railway Prioritization
Military needs disrupted civilian supply transport.
Inflation
Result of Russia printing more money during war.
Duma
Russian legislative body, recalled in July 1915.
Progressive Bloc
Duma group advocating for civil liberties.
Tsar Nicholas II
Took command of military despite lacking skills.
Power Vacuum
Created by Nicholas's absence from court.
Grigori Rasputin
Tsarina's advisor, distrusted by the public.
February Revolution
Workers' strikes led to Nicholas's abdication.
Abdication Date
March 2, 1917, Nicholas stepped down.
Provisional Government
Formed after Nicholas's abdication, led by Duma.
George Lvov
First prime minister of the provisional government.
Alexander Kerensky
Second prime minister, leader of Social Revolutionary Party.
Petrograd Soviet
Claimed to represent workers' and soldiers' rights.
Reforms
Included political amnesty and voting rights.
Dual Authority
Shared power between provisional government and soviet.
Lenin's Regime
Bolshevik government established after provisional government fall.
Council of People's Commissars
Main governing body led by Lenin.
Peace, Land and Bread
Bolshevik slogan representing key policies.
Decree on Land
Law for land transfer to peasants.
Decree on Peace
Withdrawal from war without indemnities.
Decree on Workers
Empowered workers to manage factories.
Bolshevik Censorship
Suppression of opposition press and parties.
The Cheka
Secret police established to combat counter-revolution.
Red Terror
Violent campaign against perceived enemies of Bolsheviks.
Dissolution of the Assembly
Bolsheviks dismissed Constituent Assembly post-elections.
Treaty of Brest-Litvosk
1918 treaty ceding territory to Germany.
Czech Legion
Armed group sparking Russian Civil War.
Reds
Bolsheviks, supporters of Lenin's regime.
Whites
Counter-revolutionaries opposing Bolshevik rule.
Greens
Peasant resistance groups against Bolshevik policies.
Trotsky's Role
Negotiated peace with Germany as foreign minister.
Foreign Intervention
Allied support for White armies against Bolsheviks.
War Communism
Bolshevik policy of nationalizing industry and requisitioning grain.
New Economic Policy (NEP)
Post-war policy allowing limited market economy.
Lenin's Justification
NEP seen as necessary compromise for future progress.
Bolshevik Victory Reasons
Disorganization among Whites and strong Red unity.
Trotsky's Leadership
Led Red Army and recruited former tsarist officers.
Propaganda Use
Bolsheviks utilized media to gain public support.
Railway Control
Key advantage for rapid troop and supply movement.
Industrial Decline
Production fell 82% during War Communism.
Famine Causes
Peasants' subsistence farming led to food shortages.
Lenin's Strategy
Relaxed economy did not imply relaxed political control.
Civil War Outcome
Bolsheviks secured victory by 1920.
Provisional Government
Temporary government established after the tsar's fall.
Land Redistribution
Peasants demanded land from nobility and church.
Peasant Seizures
Peasants took land when government failed to act.
Bolsheviks
Political party led by Lenin, aimed for revolution.
Lenin's Return
Lenin's arrival in Russia weakened the provisional government.
Revolutionary Legality
Bolsheviks recognized land seizures as legitimate.