Skeletal II
1/22
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
23 Terms
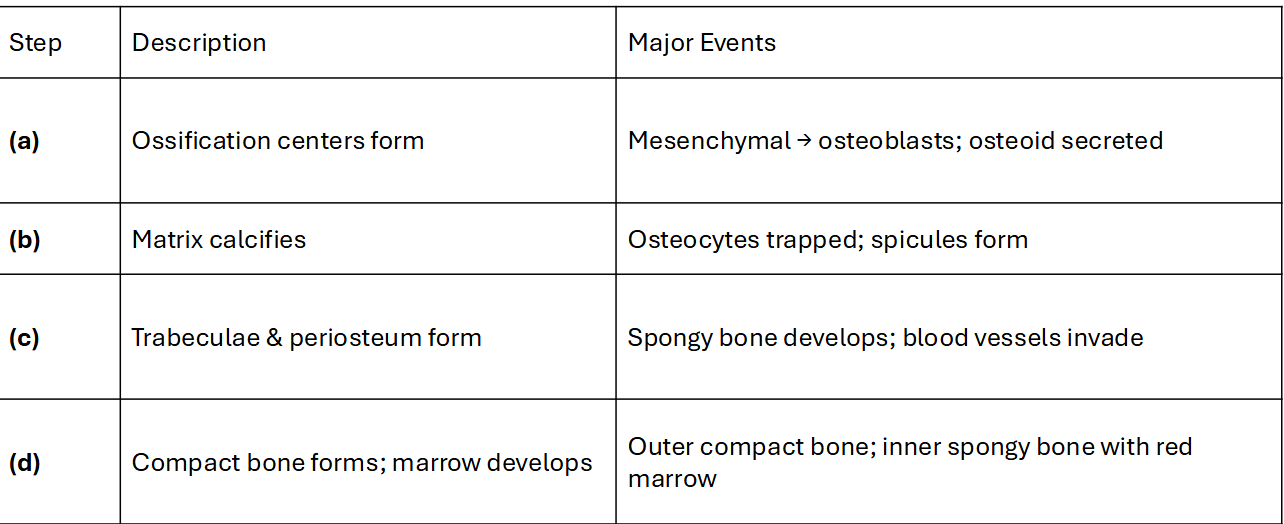
Intramembranous Ossification
Bone formed directly from mesenchyme
Early development: conception → 2 months
Steps: Mesenchymal cells → osteoblasts → spongy bone → compact bone
Ex: flat bones of skull and clavicle
Step A: Development of the Ossificatinon Center
Mesenchymal cells → Osteoprogenitor cells
Osteoprogenitor cells → Osteoblasts
Ossification center
Secrete Osteoid
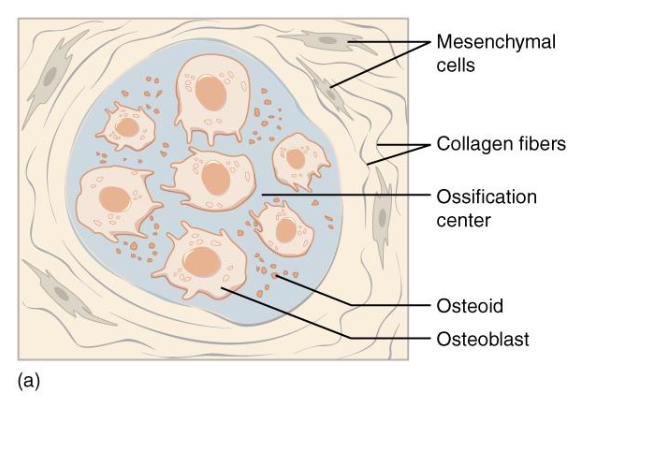
Step B: Calcification and Formation of Early Bone martix
Calcium Salts
Osteoblasts trapped > Osteocyte in lacunae
Osteoid forms spicules around ossification center
Trabeculae
Form delicate trabecular network
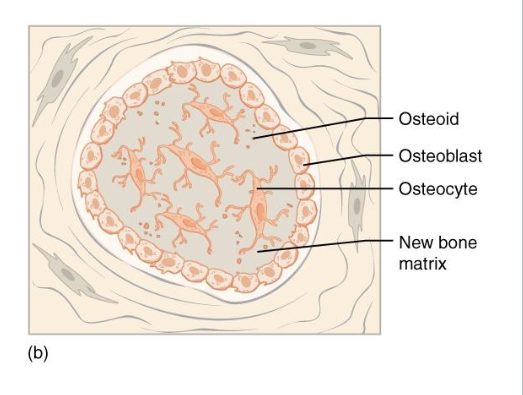
Step C: Formation of Trabeculae and Early Spongy Bone
Spicule Fusion
Full Trabecular Network
Blood Vessels
Mesenchymal Tissue condensation
Forms periosteum
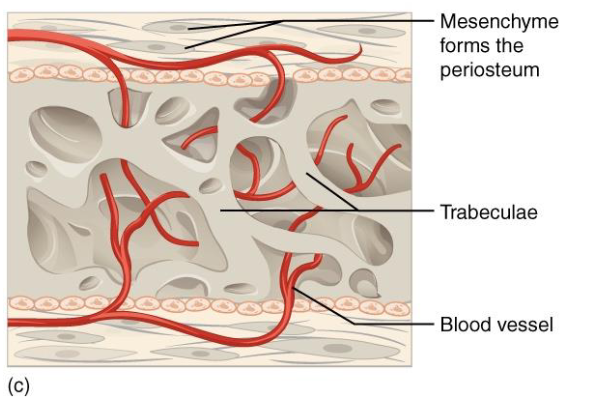
Step D : Formation of Compact Bone and Red Marrow
Remodeling Spongy Bone → Compact bone
At Surface
Inner Spongy bone remains
Houses red marrow
Periosteum remains active
Appositional Growth
The mature structure now contains outer compact bone, inner spongy bone, and red marrow within the trabecular spaces
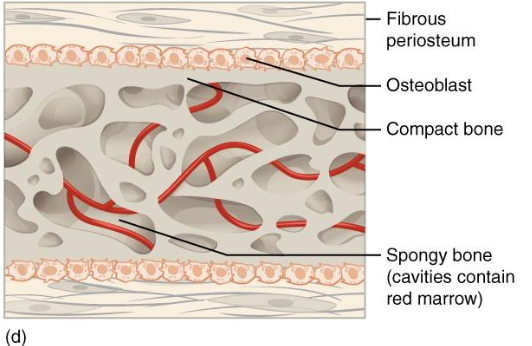
Summary table of Intramembranous Ossification
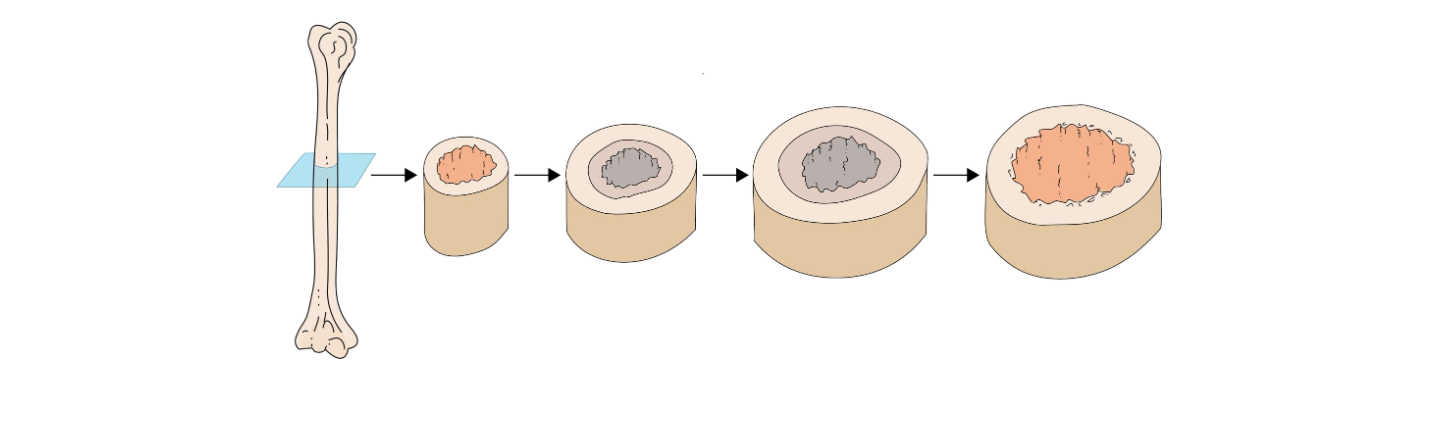
Endochondral Ossification Overview
Vast majority of bone in the body
All bones below skull expect for Clavicle
Primary form of ossification after 2 months gestation
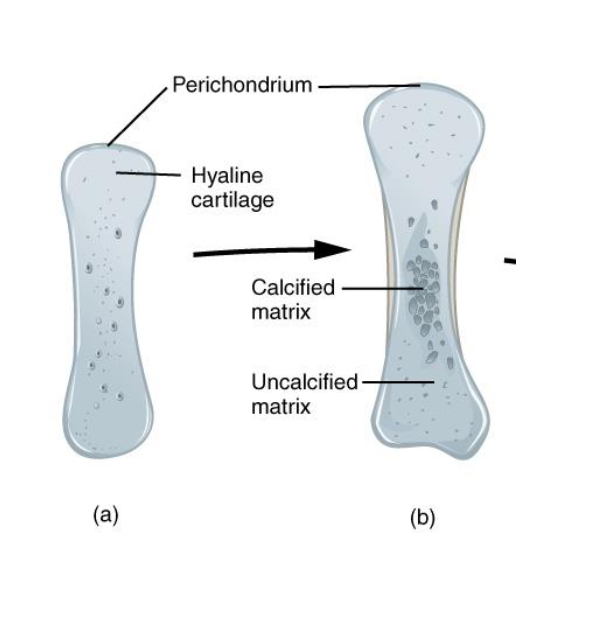
Hyaline Cartialge
The Blueprint
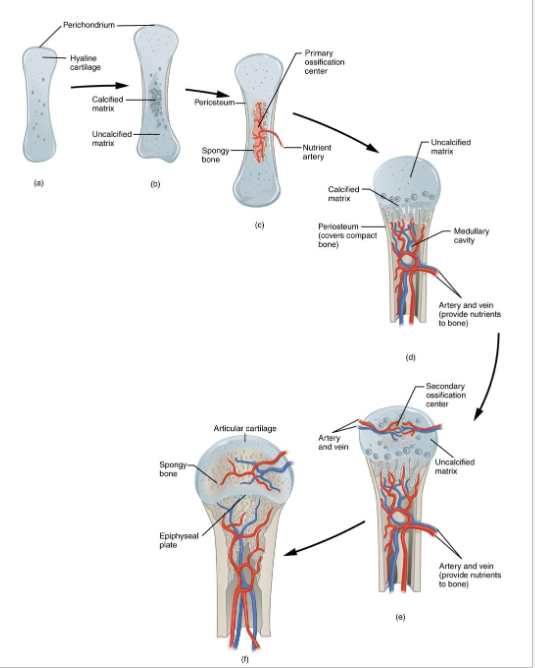
Step A: Formation of the Cartilage Model
Mesenchymal cells → Chondroblasts
Hyaline Cartilage Matrix
Perichondrium
Interstitial Growth - Division of Chondroblasts and chondrosign
Appositional Growth - From new layer around hyaline cartialge
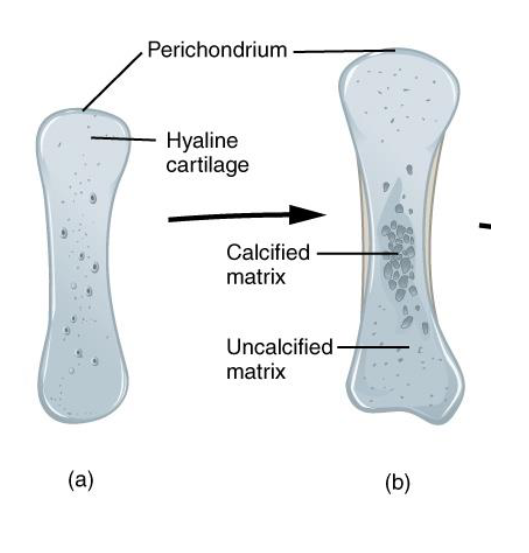
Step B: Growth and calcification of the Cartialge Model
Chondrocyte Hypertrophy
Calcification
Nutrient Impermeability
Chondrocyte Death
Lacuna (cavities left behind)
Perichondrium Response
Forms Periosteum
Osteoblasts Form
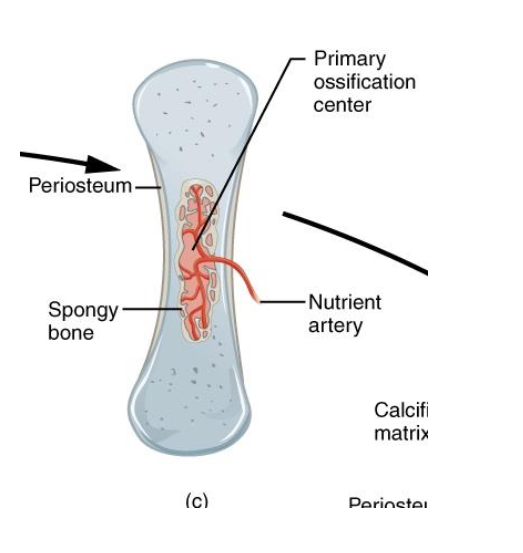
Step C: Invasion by Blood Vessels and Formation of the primary Ossification Center
Nutrient Artery in Diaphysis
Brings in osteoprogenitors and osteoblasts
Primary Ossification Center
Osteoblasts Secrete Osteoid
Form Spongy bone
Periosteum Thickens
Periosteal Bone Collar
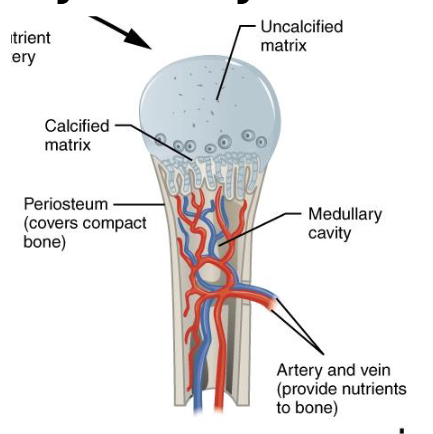
Step D : Formation of the Medullary Cavity
Osteoclasts form Medullary Cavity
Bone Grows in length and diameter
Blood vessels grow throughout
At this stage, the bone has a bony diaphysis surrounding a medullary cavity, while the epiphyses (ends) are still mostly cartilage
Step E: Formation of secondary Ossification Centers
We are now around the time of birth
Secondary ossification centers in bone epiphyses
Blood vessels enter the epiphyses
Bone tissue replaces cartialge
No medullary cavity formation
Articular cartilage remains
Cartilage remains between epiphysis and diaphysis
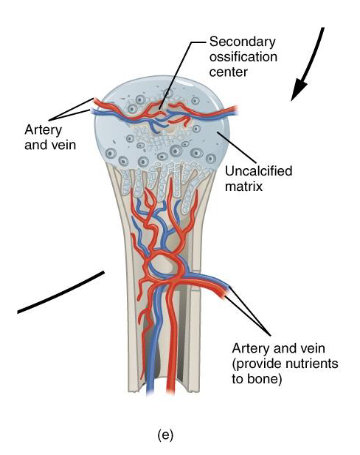
Step F: Formation of Articular Cartilage and Epiphyseal Plate
Articular cartilage still remains
Epiphyseal plate
Growth plate
Contains actively dividing chondrocytes
Longitudinal bone growth
Epiphyseal line
When bone growth stops
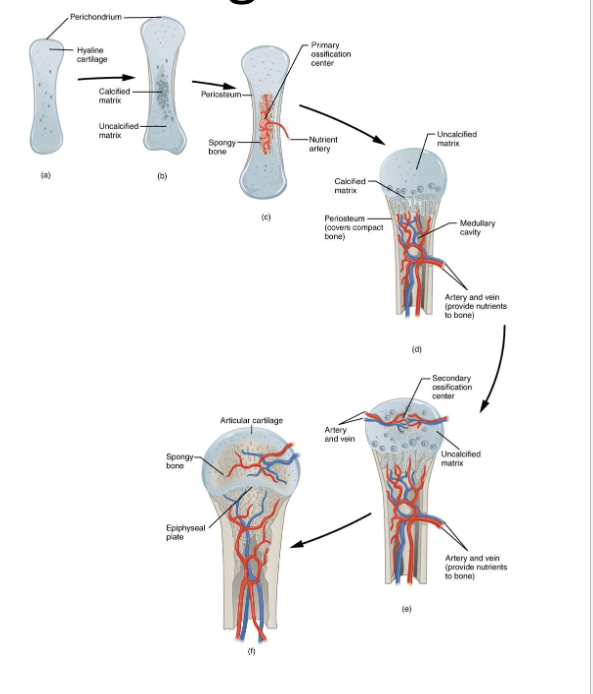
Summary table of Endochondral Ossification
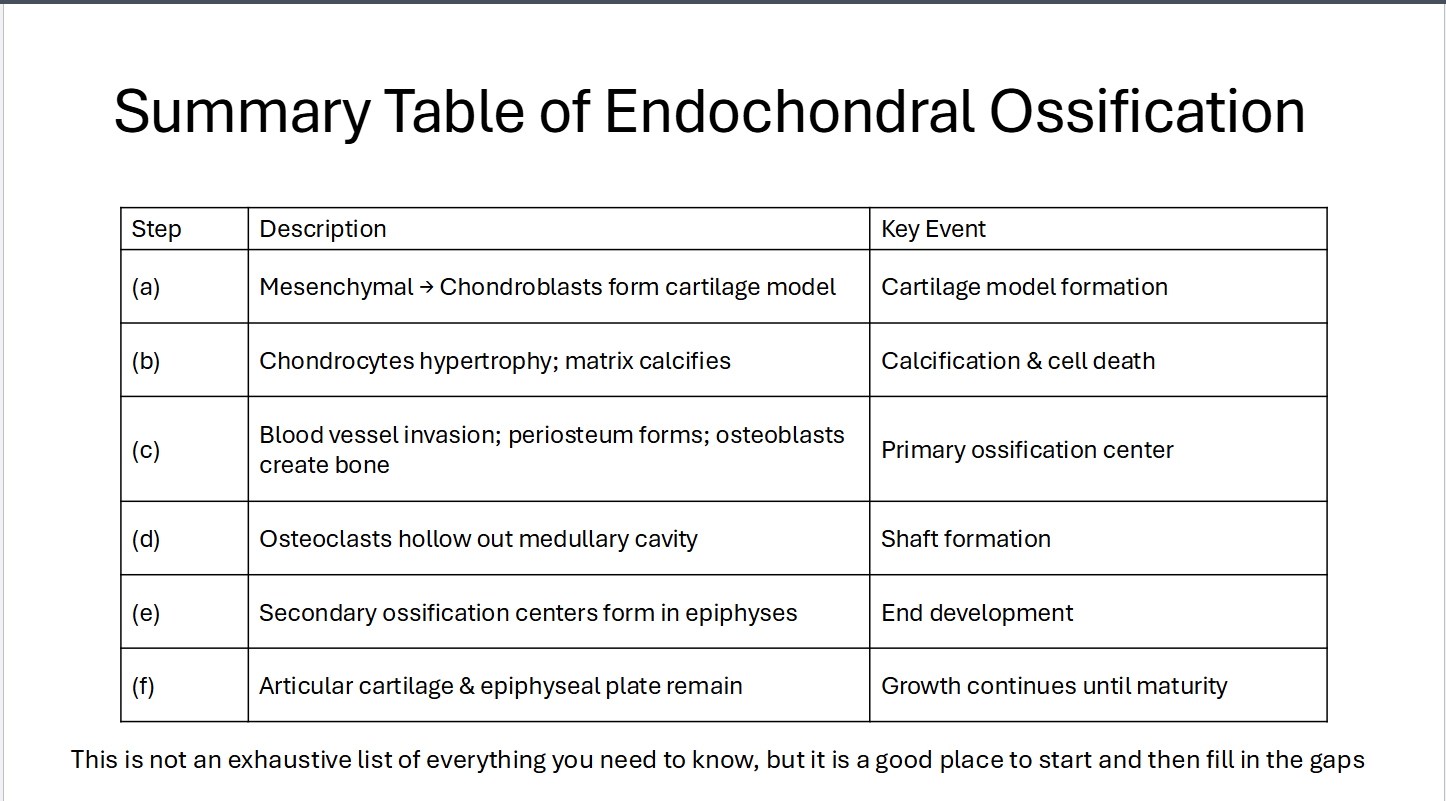
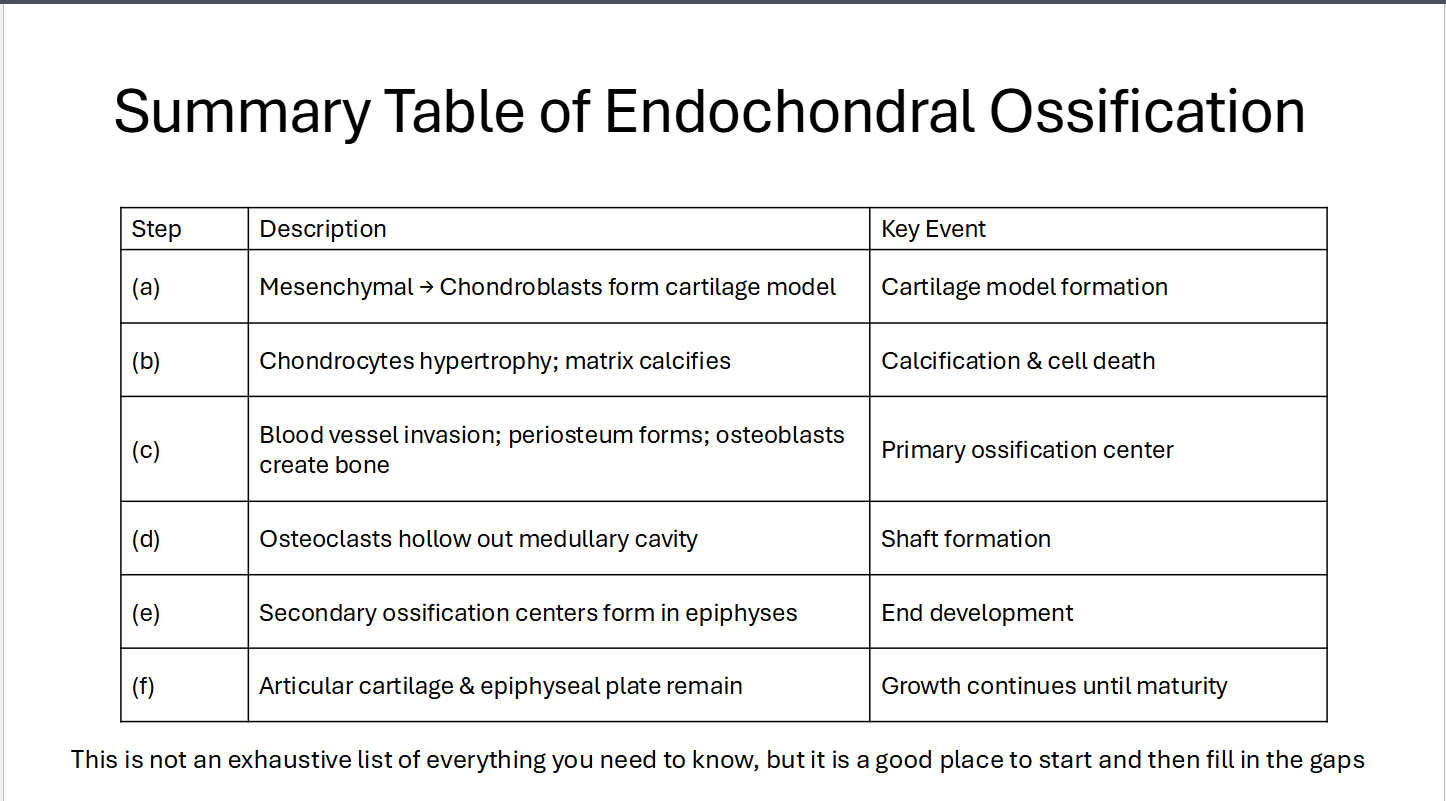
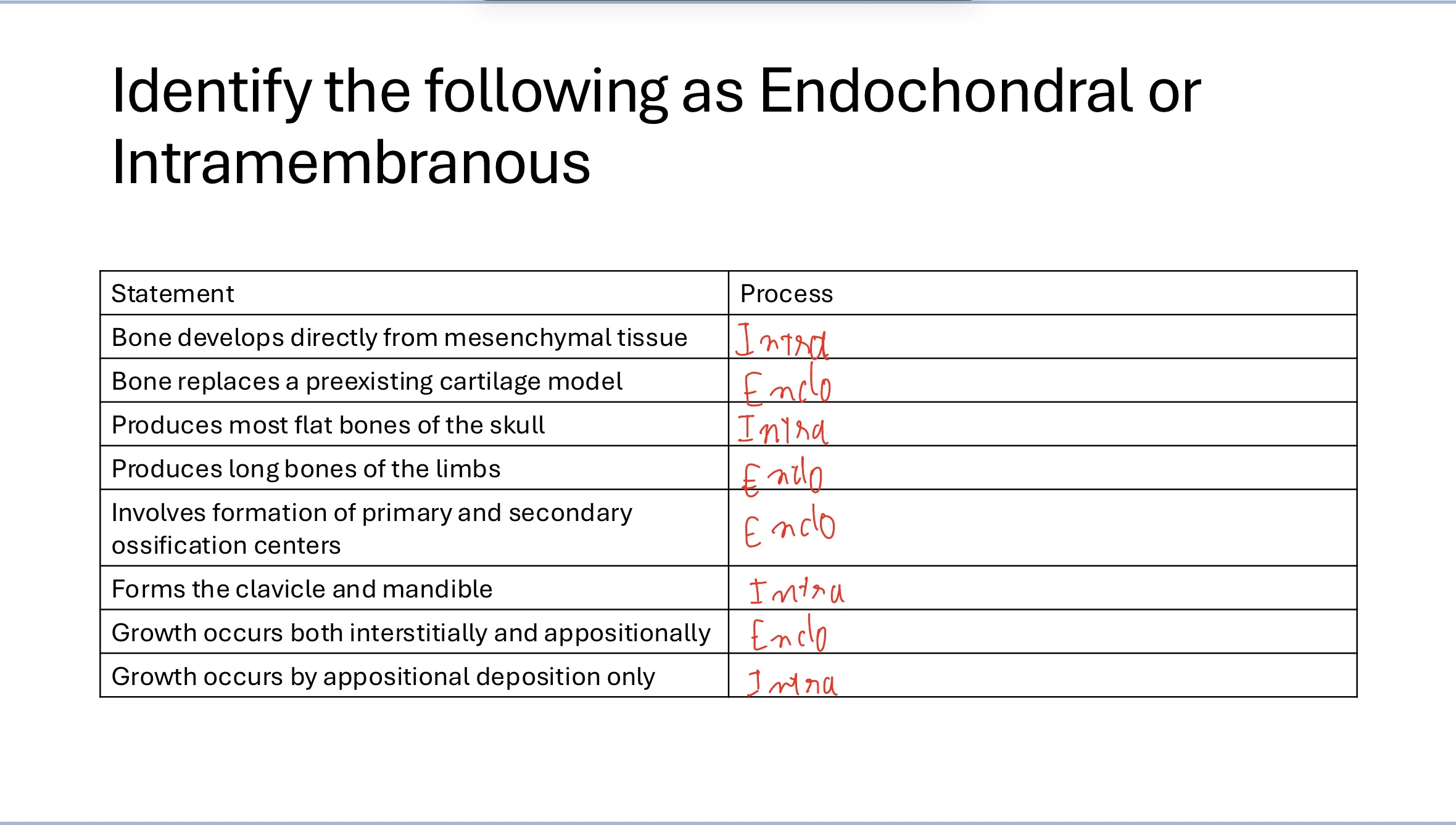
Indentify the following as Endochondral or Intramembranous
Which statement correctly describes the starting material for endochondral ossification?
A: Dense fibrous connective tissue membrane
B: Hyaline cartilage model of the future bone
C: Sheets of mesenchymal cells without cartilage
D: Calcified Periosteum surrounding Osteoblasts
B: Hyaline cartilage model for future bone
Put the Following events in the correct order for endochondral ossification:
1: Formation of secondary ossification centers
2: Formation of cartilage model
3: Formation of primary ossification center
4: Perichondrium becomes periosteum
5: Formation of Medullary cavity
2: Formation of cartilage model
4: Perichondrium becomes periosteum
3: Formation of primary ossification center
5: Formation of medullary cavity
1: Formation of secondary ossification center
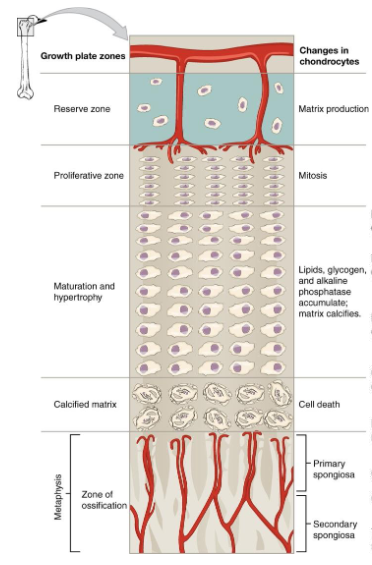
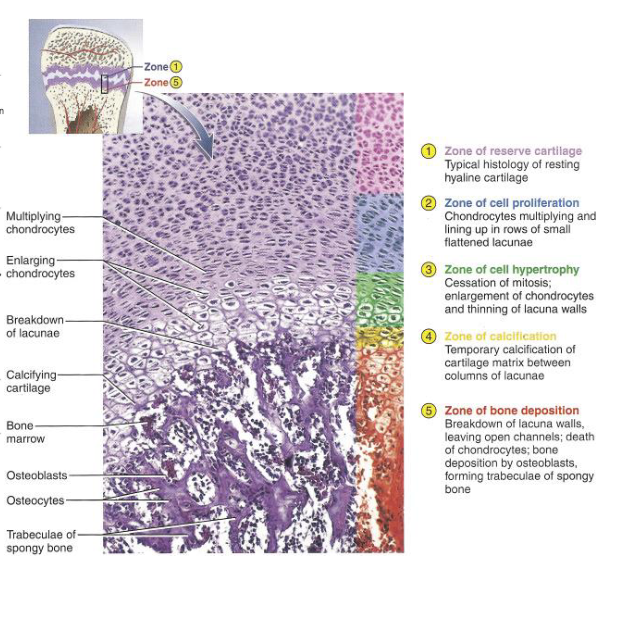
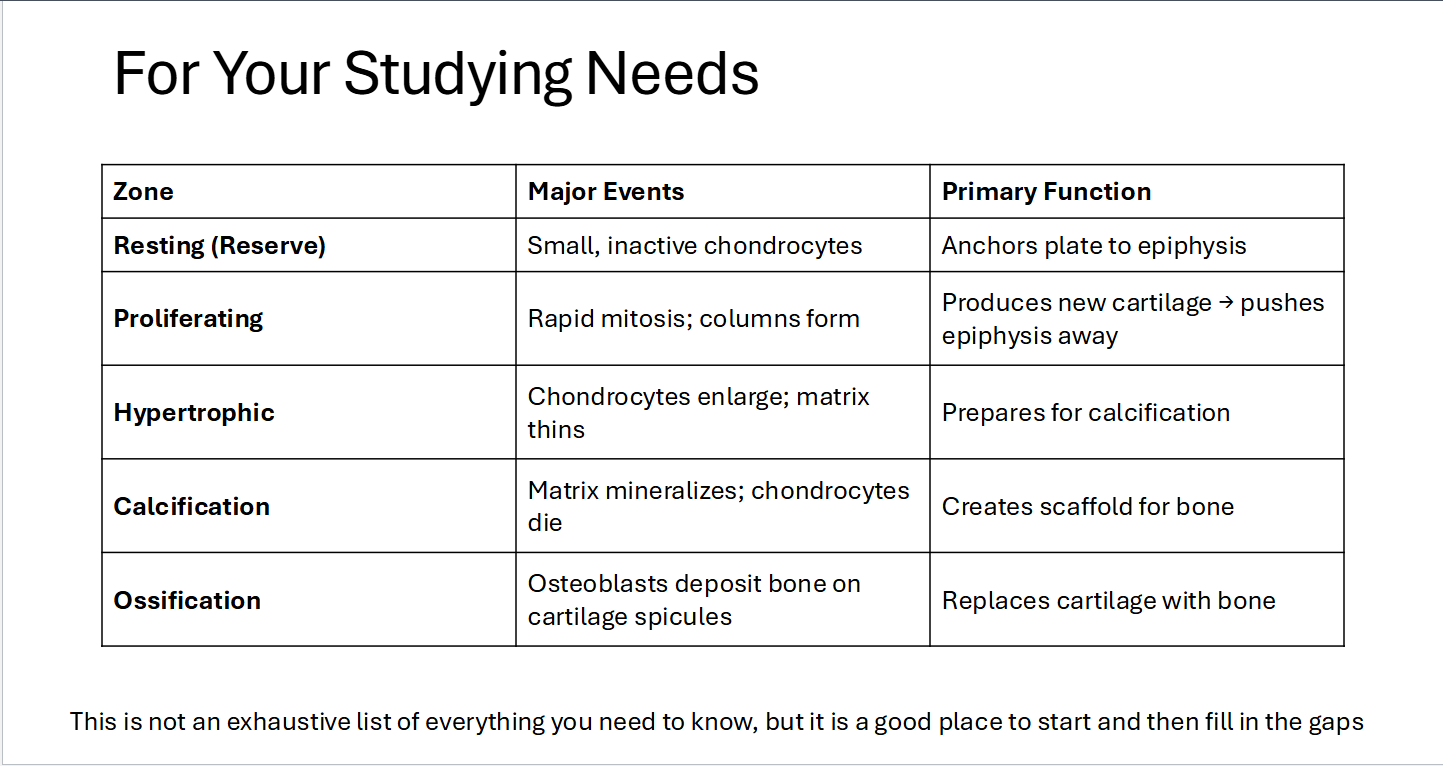
Epiphyseal Plate Zones
Resting (Reserve): Storage Zone
Proliferative: Chondrocytes rapid division drive elongaton
Hypertrophic: Chondrocytes Elarge
Calcification: Mineralization chondrocyte death
Ossification: Calvilary: Osteogenitor/ Osteoblaste
Longitudinal Growth
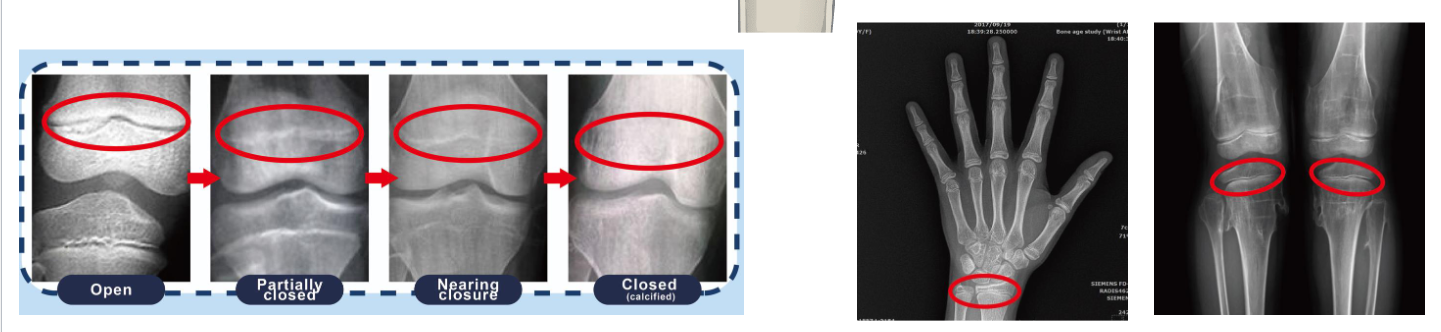
Epiphyseal Plate Closure
During puberty RoCD = RoO
RoO > RoCD
Formation of Epiphyseal line
Longitudinal growth ceases

For studying
Appositional (Width) Growth
Osteoblast activity in periosteum vs Osteoclast activity in Endosteum
Allow bone to grow in diameter and remain lightweight
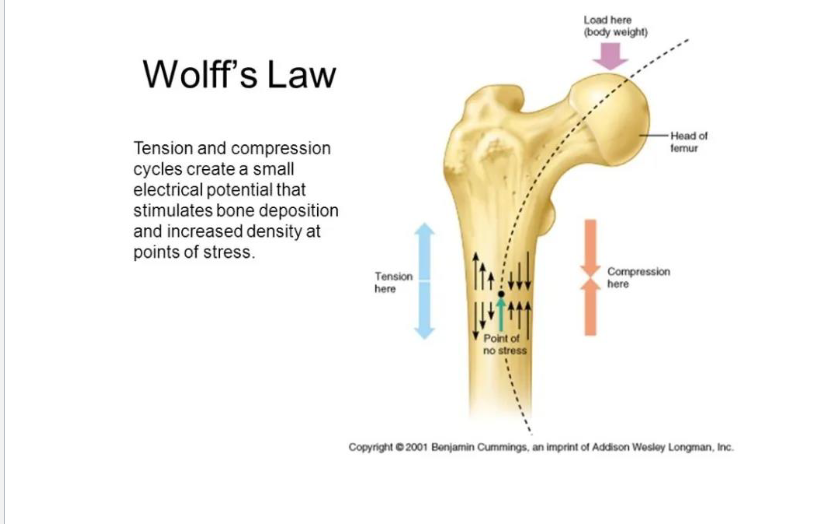
Mechanical Stress Wolff’s Law
Bone adapts to stress (exercise, Weight-bearing)
Hormonal Regulation
Growth Hormone
Thyroid Hormone
Sex Hormone
Testosterone
Estrogen - tell considy stop growth