Antifungals MedChem
1/64
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
65 Terms
What is the structure of fungi?
Eukaryotic cells with rigid cell walls that have a nuclear membrane, mostly microscopic invisible organisms in single cells/chains
What is the body of the fungus (mycelium) composed of?
Branching network of filaments - hyphae
What is a mycoses?
Fungal infection
What is a superficial mycoses?
Affect the skin, hair and nails
What is a subcutaneous mycoses?
Affect the muscle and connective tissue immediately below the skin
What is a systemic mycoses?
Involve internal organs - needs to get into circulation
What is an allergic mycoses?
Affects lungs or sinuses
Who does allergic mycoses mostly commonly affect?
Patients with chronic respiratory conditions e.g., chronic asthma, sinusitis, cystic fibrosis - those who have difficulty clearing mucus or recurrent respiratory infections
What is the key target in fungal cell walls?
Ergosterol - key steroid
How is fungal cell walls similar to animal cell walls?
Lipid bilayer, uses steroids for rigidity
What is chitin?
Thin layer in the phospholipid bilayer
How can fungi resist treatment using chitin?
Thicken the chitin layer to resist treatments
What are some components of the fungal cell wall that can be targeted?
B-1,3-Glucan, B1-6,glucan, chitin, Ergosterol
What part of the fungal cell wall is a good way to target to allow cell lysis?
B-1,3 glucan and B-1,6 glucan
What are some key classes of antifungals?
Allylamines/steroids, azoles, morpholines, polyenes, 5-flucytosine, echinocandins
What are all steroids derived from?
Squalene
What are some examples of allylamines?
Terbinafine, naftifine
What do allylamines do to the fungal cell?
inhibit squalene 2,3-epoxidase
What are some examples of azoles?
Fluconazole, voriconazole, itraconazole, clotrimazole, ketoconazole
What do azoles do to the fungal cell?
Inhibit lanosterol 14-a demethylase.- another steroid
What is an example of morpholines?
Amorolfine
What do morpholines do to fungal cells?
Inhibit key enzymes for Ergosterol synthesis
What are examples of polyenes?
Nystatin, amphotericin B
What do polyenes do to ergosterol?
Bind to Ergosterol to form pores
What does 5-flucytosine do to the fungal cell DNA?
Inhibits DNA and RNA synthesis
What are examples of echinocandins?
Caspofungin, micafungin
How do echinocandins work on the fungal cell wall?
Inhibit B-1,3 D-glucan synthase
What enzyme does allylamines inhibit in Ergosterol synthesis?
Enzyme ERG1
What enzyme do azoles inhibit in Ergosterol synthesis?
Enzyme ERG11
What are the enzymes that morpholines inhibit?
ERG24 and ERG2
What functional group does naftifine contain?
Napthelene group
What key group do all allylamines contain?
Allyl group - carbon triple bond and N central core atom
What are the properties of azole antifungals?
Synthetic, broad spectrum, fungistatic
What do Azole antifungals selectively inhibit?
Fungal cytochrome enzyme CYP51A1, encoded for by ERG11 gene
What does the use of azole antifungals limit?
Binding of other antifungals e.g., amphotericin as they bind to ergosterol
What atom do azoles antifungals bind to?
Iron atom in Haem residue of CYP
What is a key interaction with azole antifungals and other antifungals?
Inhibits lots of CYPs e.g., fluconazole inhibits human 2C9 and 2C19, Ketoconazole inhibits more CYPs so lots of serious drug-drug interactions
What key functional group do imidazole azoles contain that binds to the iron atom?
Imidazole ring
What is a imidazole ring?
5 membered heterocyclic containing Nitrogen
What are examples of triazole antifungals?
Fluconazole, voriconazole, itraconazole
What key functional group do triazole antifungals contain?
Triazole ring
How many triazole groups does fluconazole contain?
2 residues - 1,2,4 triazoles
What are some different mechanisms of resistance to azole antifungals?
Single point mutation at ERG11 gene, mutations in ERG3 or ERG6, Overexpressing ERG11, increased expression of CDR1 or MDR1
What does a single point mutation at ERG11 gene lead to?
Altered lanosterol 14-a demethylase meaning it cannot be targeted by antifungals
What does the mutation in ERG3/ERG6 genes lead to for azole antifungals?
Produces low affinity sterols
What does the overexpression of ERG11 gene lead to?
Increased production target so higher, potentially dangerous doses would be needed of azole antifungals
What does an increased expression of CDR1 or MDR1 mean for azole antifungals?
Decreased azole accumulation - increases efflux pump
What are some characteristics of amphotericin B structure?
Hydrophilic region to form the pore, hydrophobic region that associates with greasy steroids using Van der Waals forces
What is a downside of nystatin?
Associates with ANY steroid so increases side effect likelihood
How do amphotericin B and nystatin work?
Binds to ergosterol in cell membranes and acts as a steroid sponge - sequesters ergosterol and forms ion channels in membrane BUT also binds to cholesterol
How is amphotericin B administered?
IV - highly protein bound and low half life
What adverse effects can intrathecal injections of amphotericin B lead to?
Neurotoxicity, drug irritates venous endothelia and local thrombophlebitis
What usually accompanies IV administration of amphotericin?
Antipyretics or hydrocortisones/other cortisones
What side effects of Amphotericin can occur due to it being renally toxic?
Interactions with diuretics and other drugs - can lead to hypokalaemia, torsade de pointes, anaemia
What is an example of a formulation of amphotericin B?
Ambisome - liposomal formulation used for deep, systemic mycoses. Mimics cell wall structures and gets embedded into fungal cell wall, liposome emptied and released locally
What is flucytosine usually administered with to treat systemic infections due to a risk of resistance?
Amphotericin
What base is flucytosine based on?
Cytosine
What type of drug is flucytosine?
Pro-drug with limited spectrum
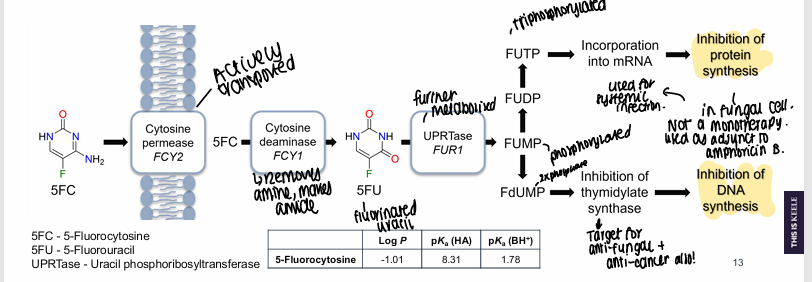
What is the MOA of flucytosine?
Actively transported into membrane by cytosine permease, amine removed and makes an amide, furtherly metabolised - can be triphosphorylated and incorporated into MRNA to inhibit protein synthesis or phosphorylated 2x to inhibit DNA synthesis
What are echinocandins made from?
Amino acids - just not humans amino acids
What side chains are common in echinocandins?
Hydrophobic side chain e.g., alkane in caspofungin, aromatic in micafungin
What echinocandin is a naturally occurring lipopeptides?
Echinocandin B
What infections are echinocandins active against?
Azole-resistant Candida spp
What is the MOA of echinocandins?
Inhibit B-1,3-D-Glucan synthase and bind to Fks1p subunit to inhibit enzyme functions and inhibit steroids
How does resistance to echinocandins occur?
Point mutations in hotspots within FKS1 and FKS2 - leads to mutated B-1-3-D-Glucan synthase