Investigating photosynthesis: Cell level systems: Biology: GCSE (9:1)
1/18
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
19 Terms
Photosynthesis
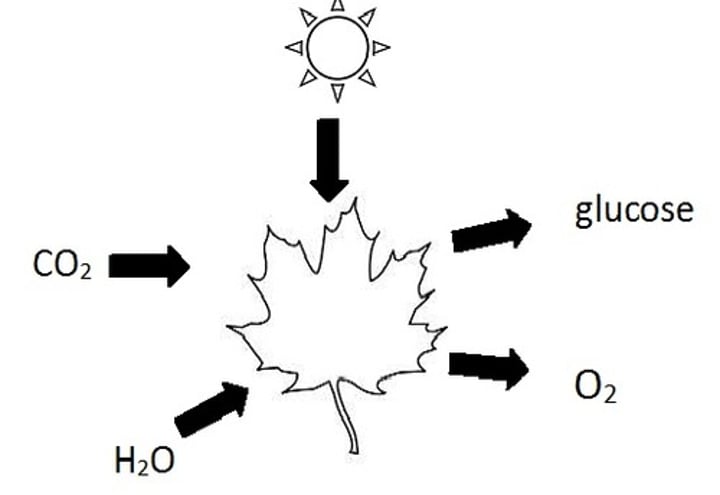
A process where plants and algae synthesise glucose from carbon dioxide and water, using light energy from the sun
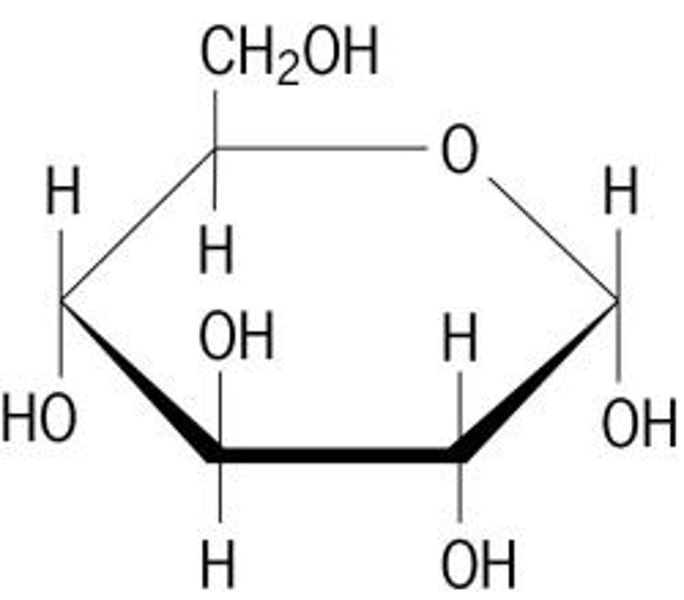
Glucose (C6H12O6)
The main chemical product of photosynthesis that has many different uses in a plant, including respiration
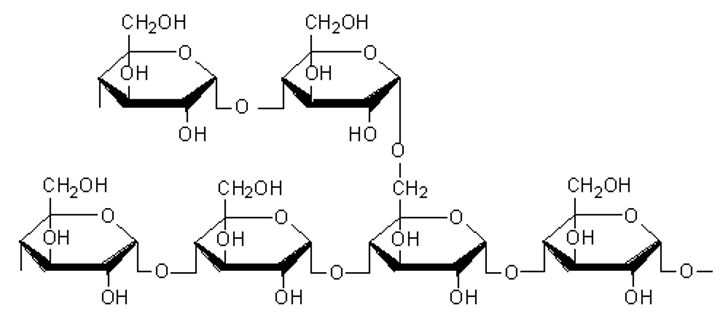
Insoluble starch
A complex carbohydrate made from the products of photosynthesis and used for storage
Chloroplast
An organelle found in plant and algae cells where photosynthesis occurs
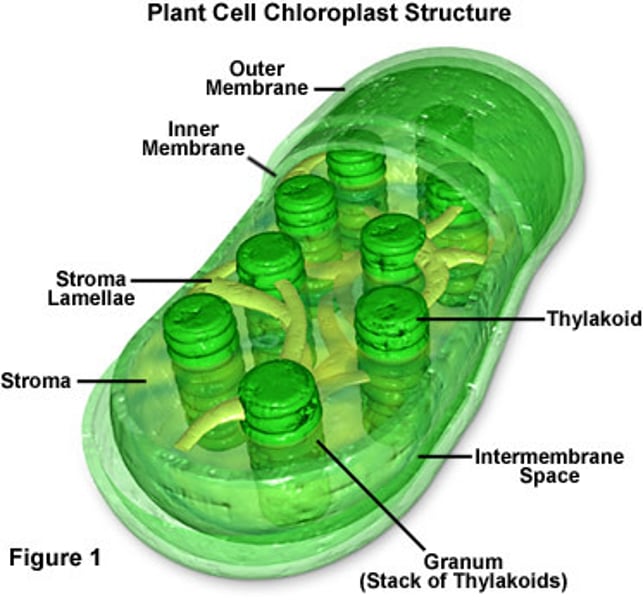
Chlorophyll
A green pigment in plants that absorbs light energy used to carry out photosynthesis
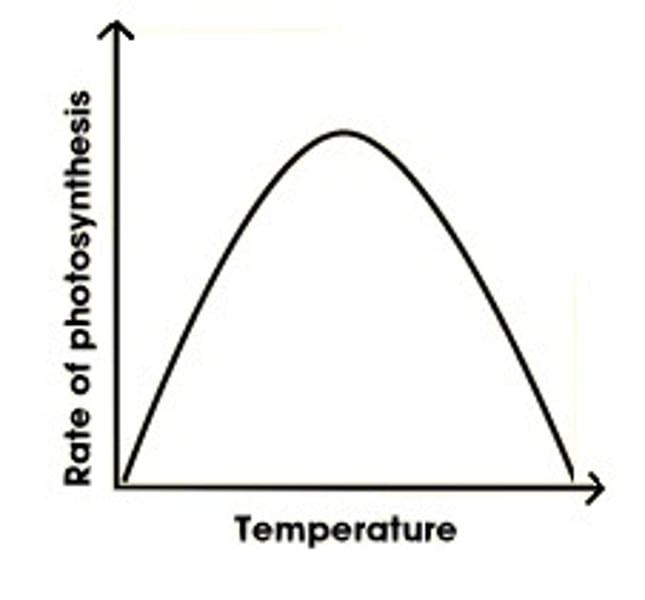
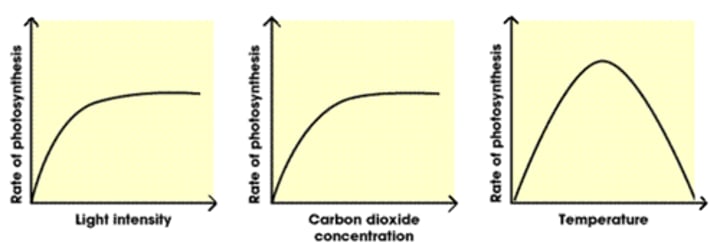
Temperature effect
Photosynthesis rate increases to an optimum and then decreases due to denaturing enzymes
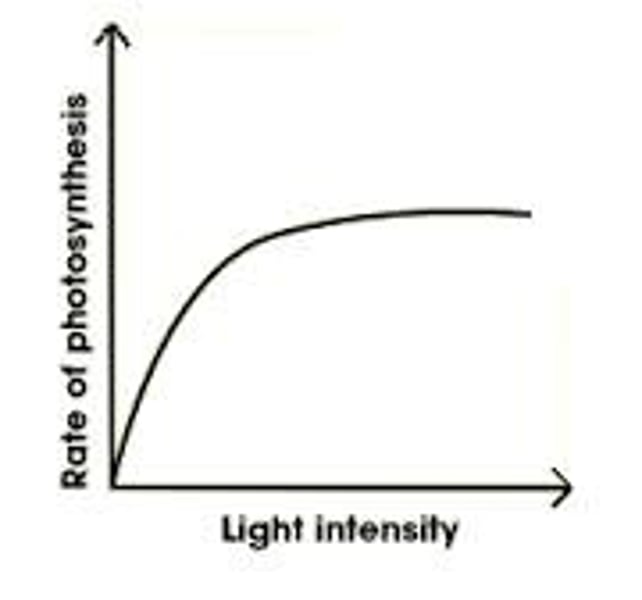
Light intensity effect
Photosynthesis rate increases as more energy is available, up to a certain point
Carbon dioxide concentration effect
Photosynthesis rate increases as more carbon is available to synthesise glucose, up to a certain point
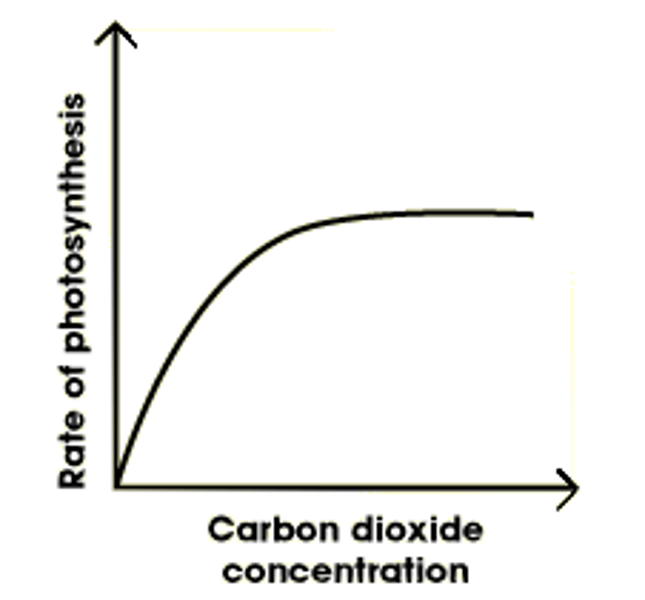
Photosynthetic rate
The rate at which plants take in carbon dioxide, water and the energy from sunlight to produce glucose
Limiting factor
An environmental factor that prevents photosynthetic rate from increasing
Testing leaves for starch
Plant leaves can be tested for the presence of starch using iodine solution, after the leaf has been intensely heated and submerged in ethanol
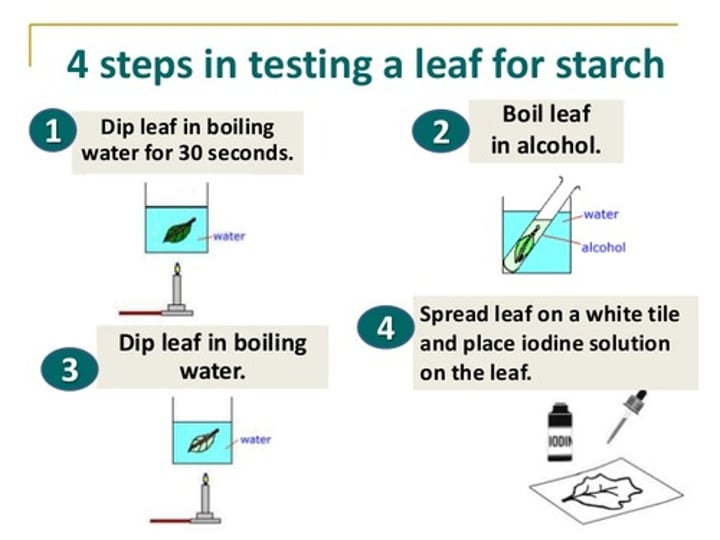
Iodine test for starch
Iodine solution will change colour from orange to blue-black in the presence of starch
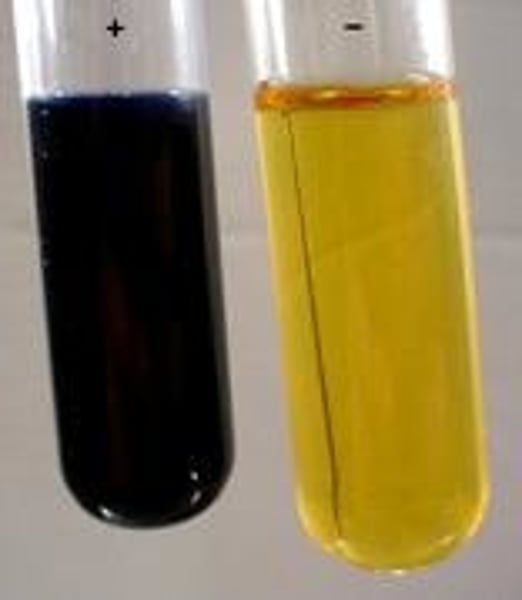

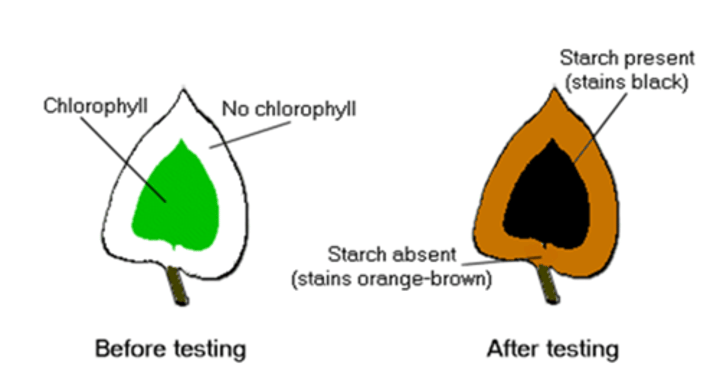
Starch results for plants kept in light conditions
Plants store glucose as starch in the leaves, plants that are kept in the light will photosynthesise and store starch so their leaves will change colour to blue-black

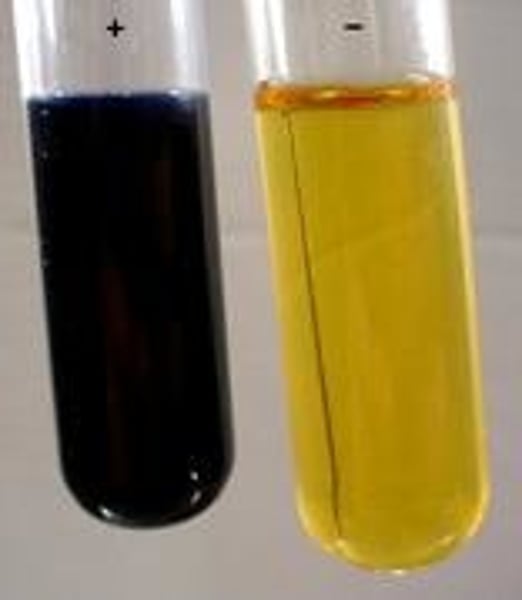
Starch results for plants kept in the dark
Plants in the dark will be unable to photosynthesise meaning glucose will not be made and stored as starch, so iodine will not change colour

Starch results for variegated leaves
Leaves that are variegated have patches absent of chlorophyll, these regions will not cause iodine to change colour as photosynthesis cannot occur here
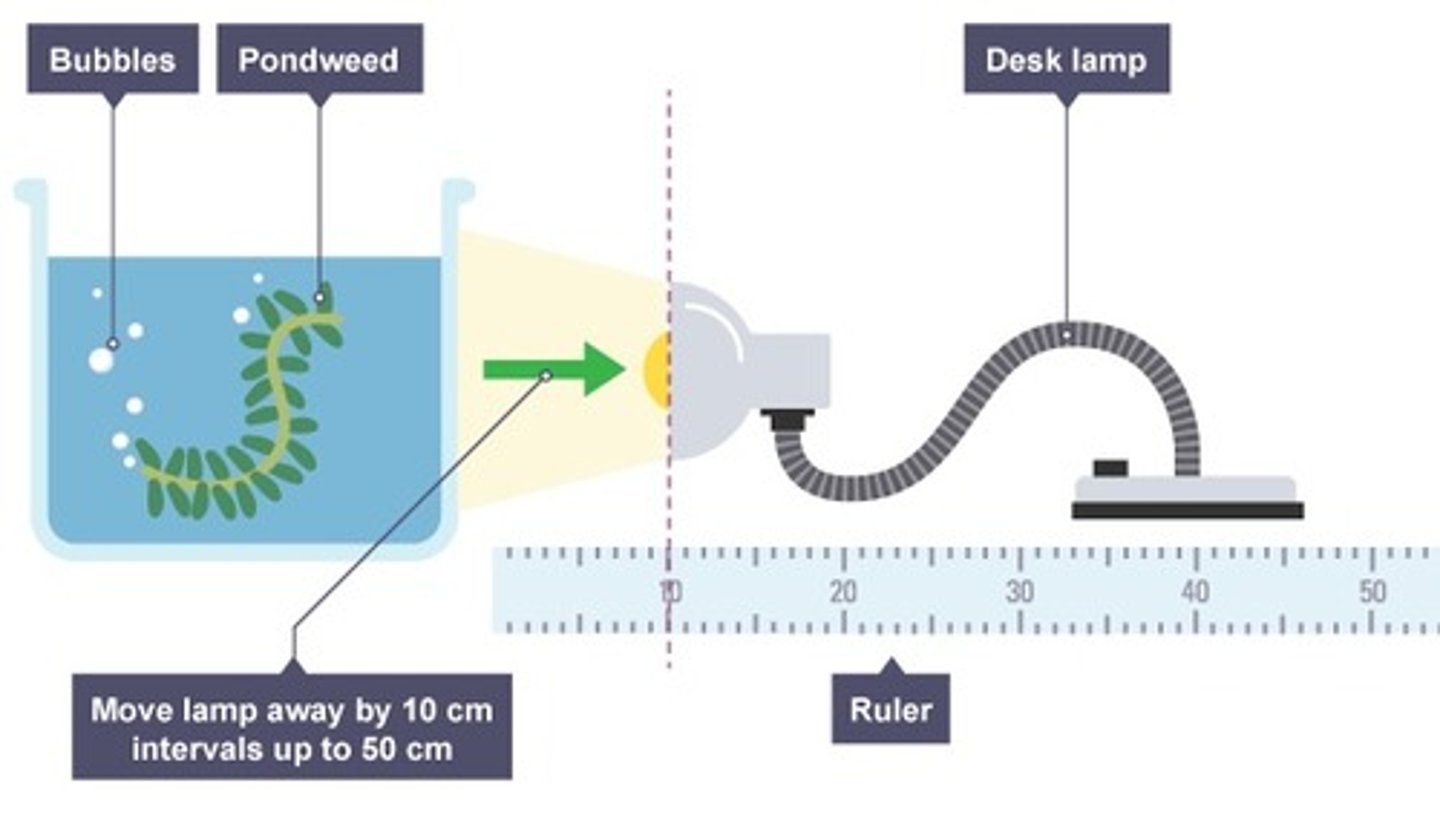
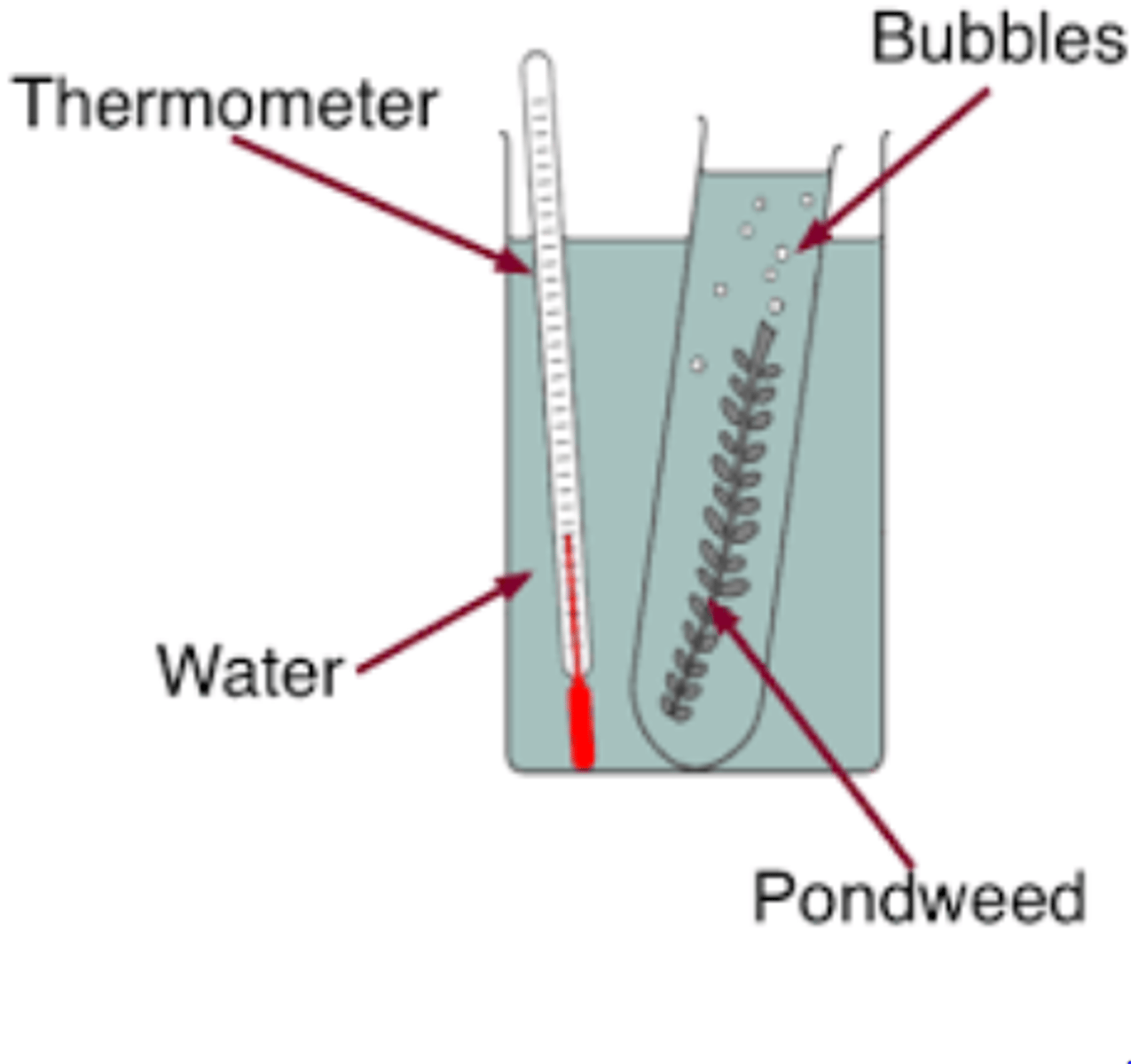
Investigating photosynthesis in pondweed
Aquatic plants produce observable bubbles of oxygen when photosynthesising near light, a possible factor that could be investigated
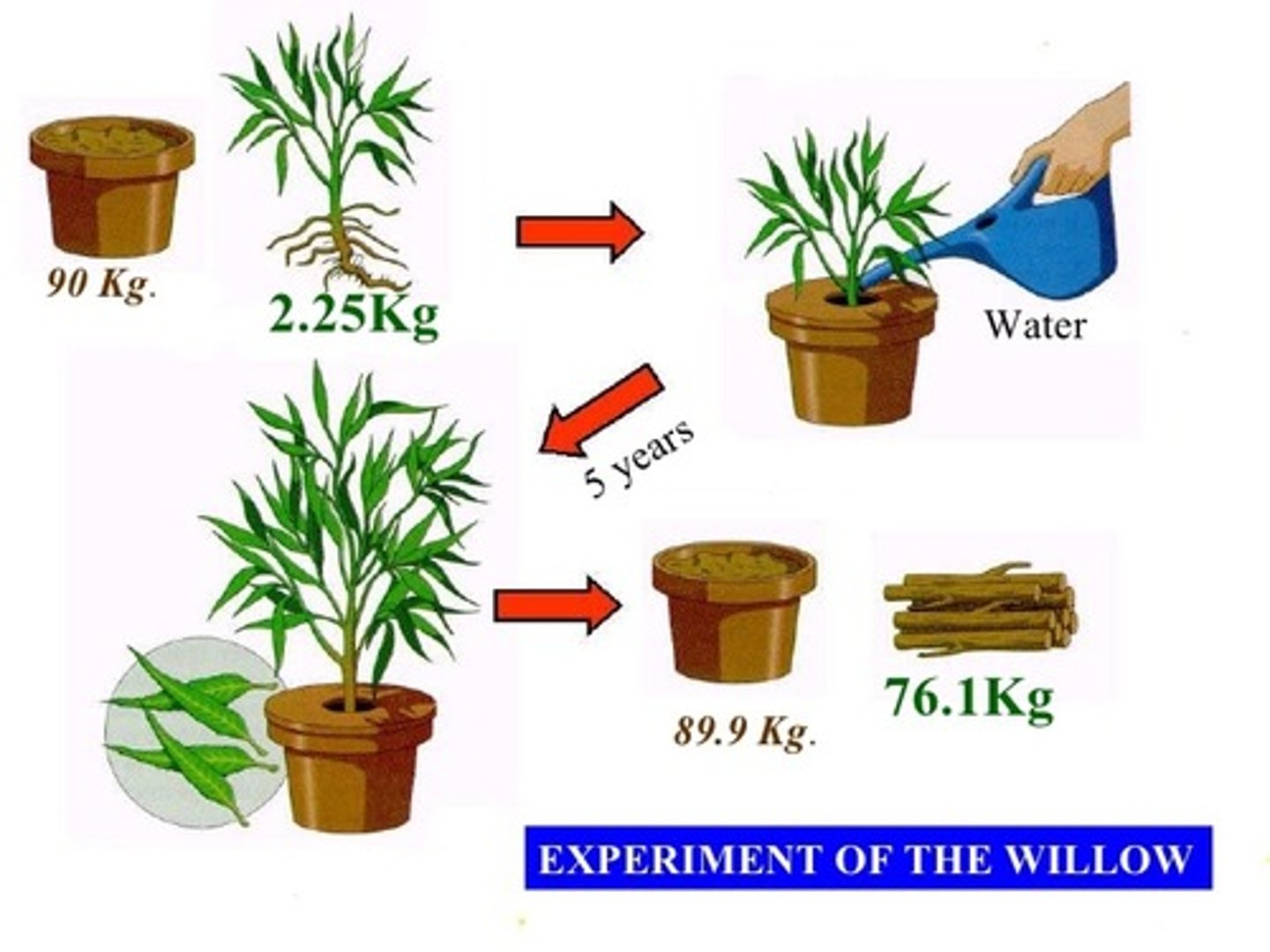
Jan Baptista van Helmont's 16th century experiment
van Helmont weighed a willow tree and a set amount of soil over several years and found that the soil did not decrease in mass as the tree grew, suggesting plants do not get their mass from soil minerals
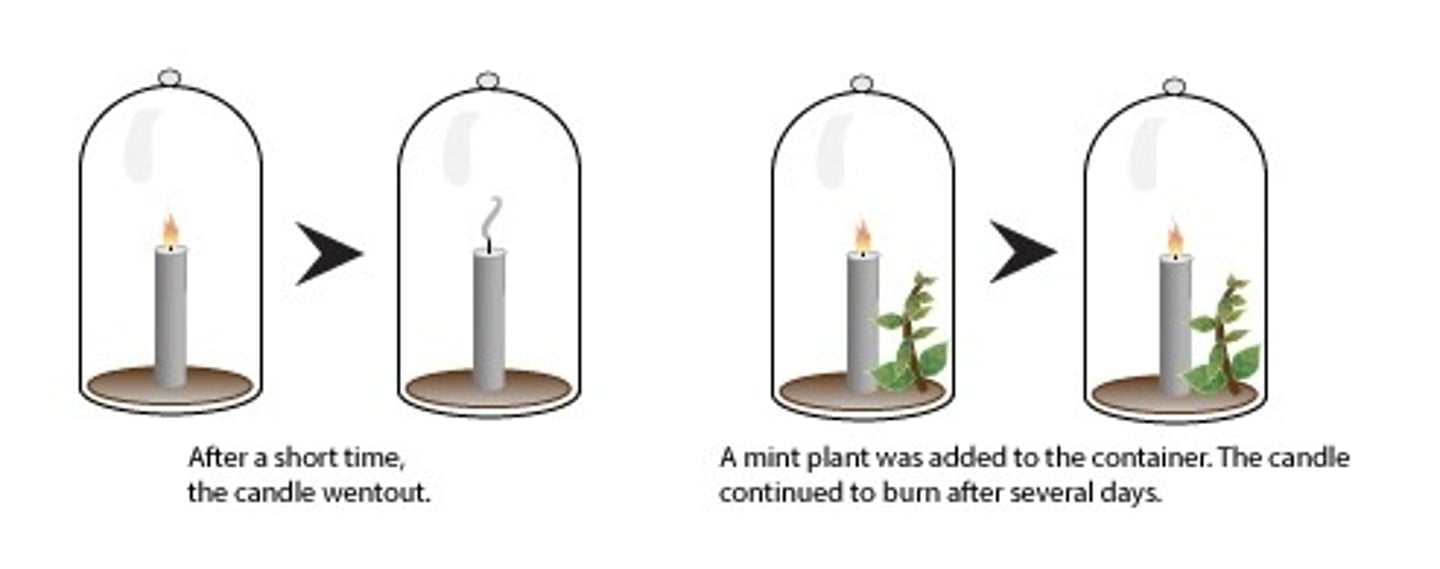
Joseph Priestly's 18th century experiment
Priestly burned a candle in a closed container with a mint plant until the candle went out, many days later the candle could be relit as the mint plant had produced oxygen via photosynthesis
Jan Ingenhousz's 18th century experiment
Ingenhousz investigated the production of oxygen bubbles in plants submerged in water, he noticed that pondweed would not produce bubbles in the dark suggesting light is essential for photosynthesis