Chapter 18: Cell Cycle Control, Mitosis, and Apoptosis in Biology
1/23
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
24 Terms
What are the main phases of the cell cycle?
G1 phase, S phase, G2 phase, and M phase.
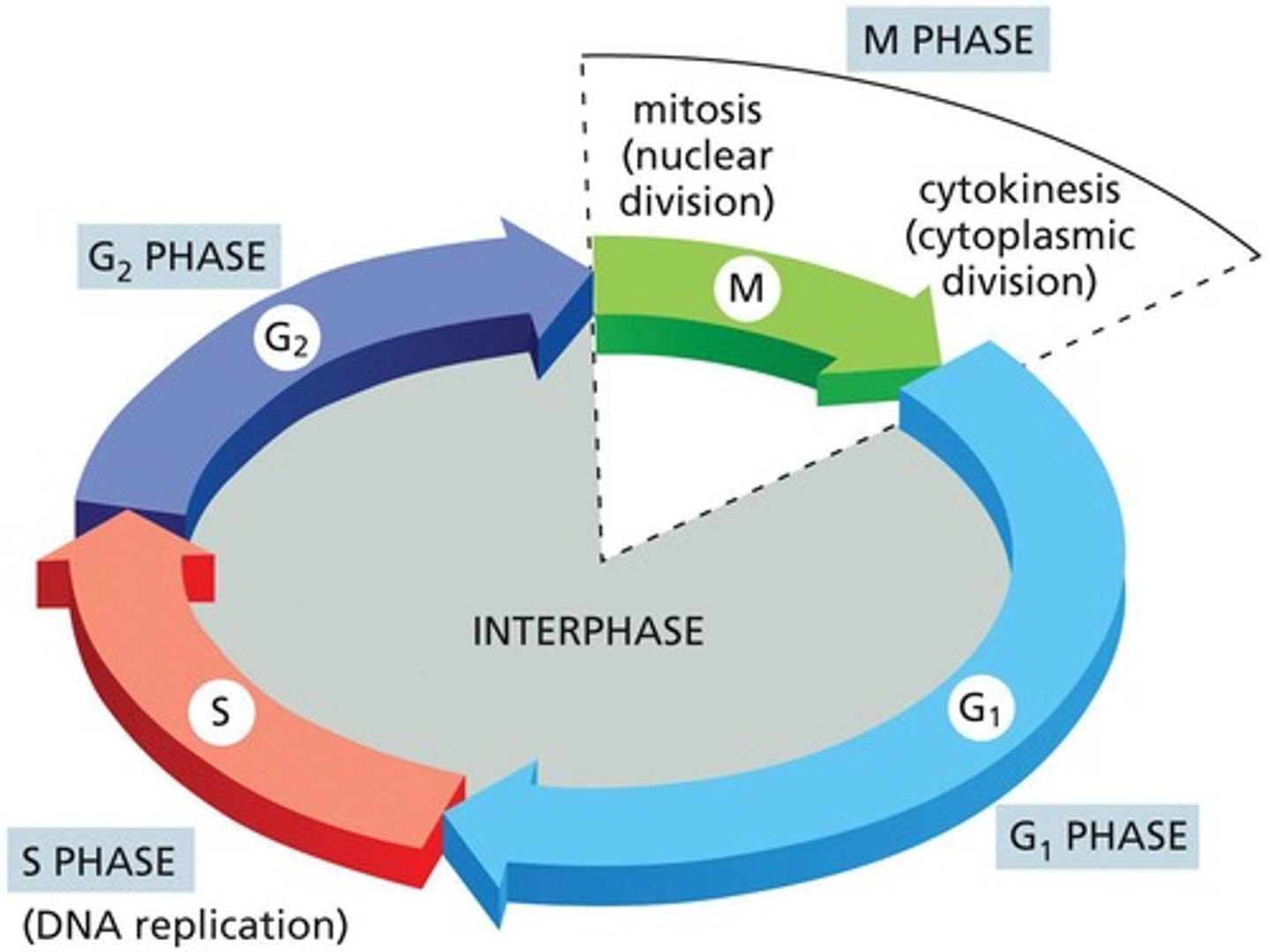
What occurs during the G1 phase of the cell cycle?
Protein synthesis, growth, and a decision about cell division.
What is the role of cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdk) in the cell cycle?
Cdk are kinases that regulate progression through the cell cycle and require interaction with cyclins to become active.
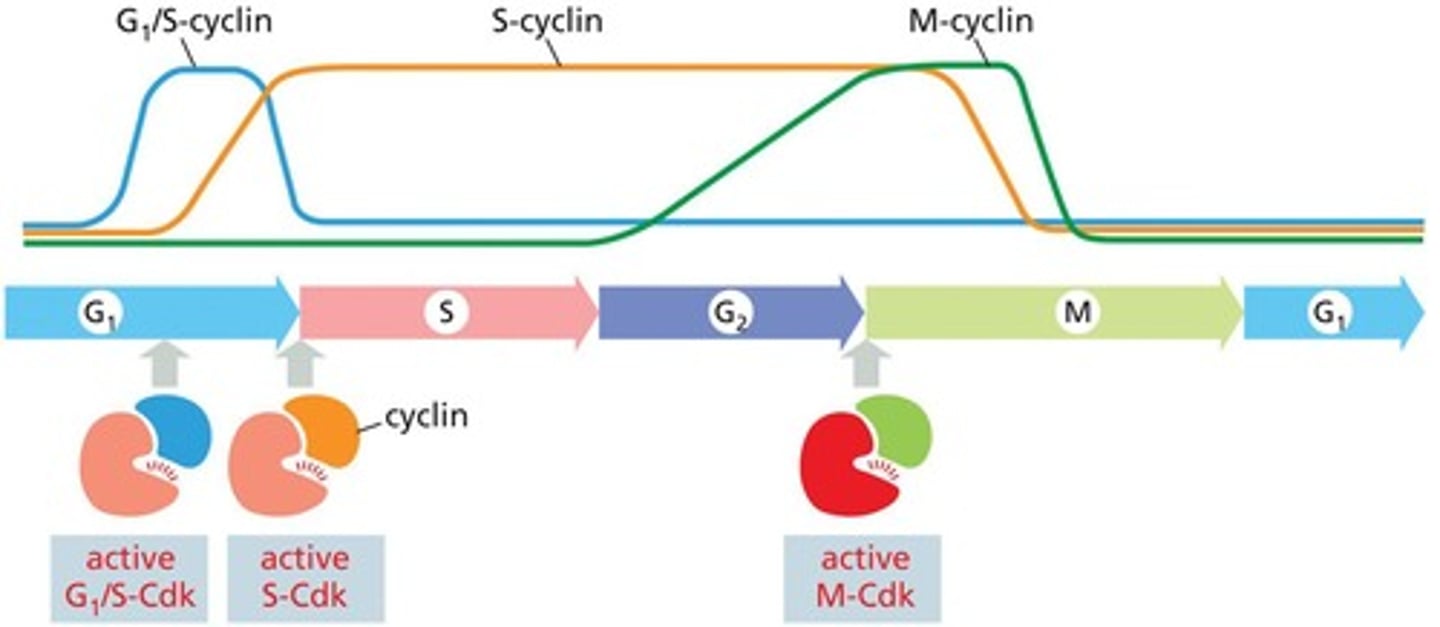
What is the function of M-Cdk (mitotic Cdk)?
M-Cdk triggers events related to mitosis, including chromatin condensation and nuclear envelope breakdown.
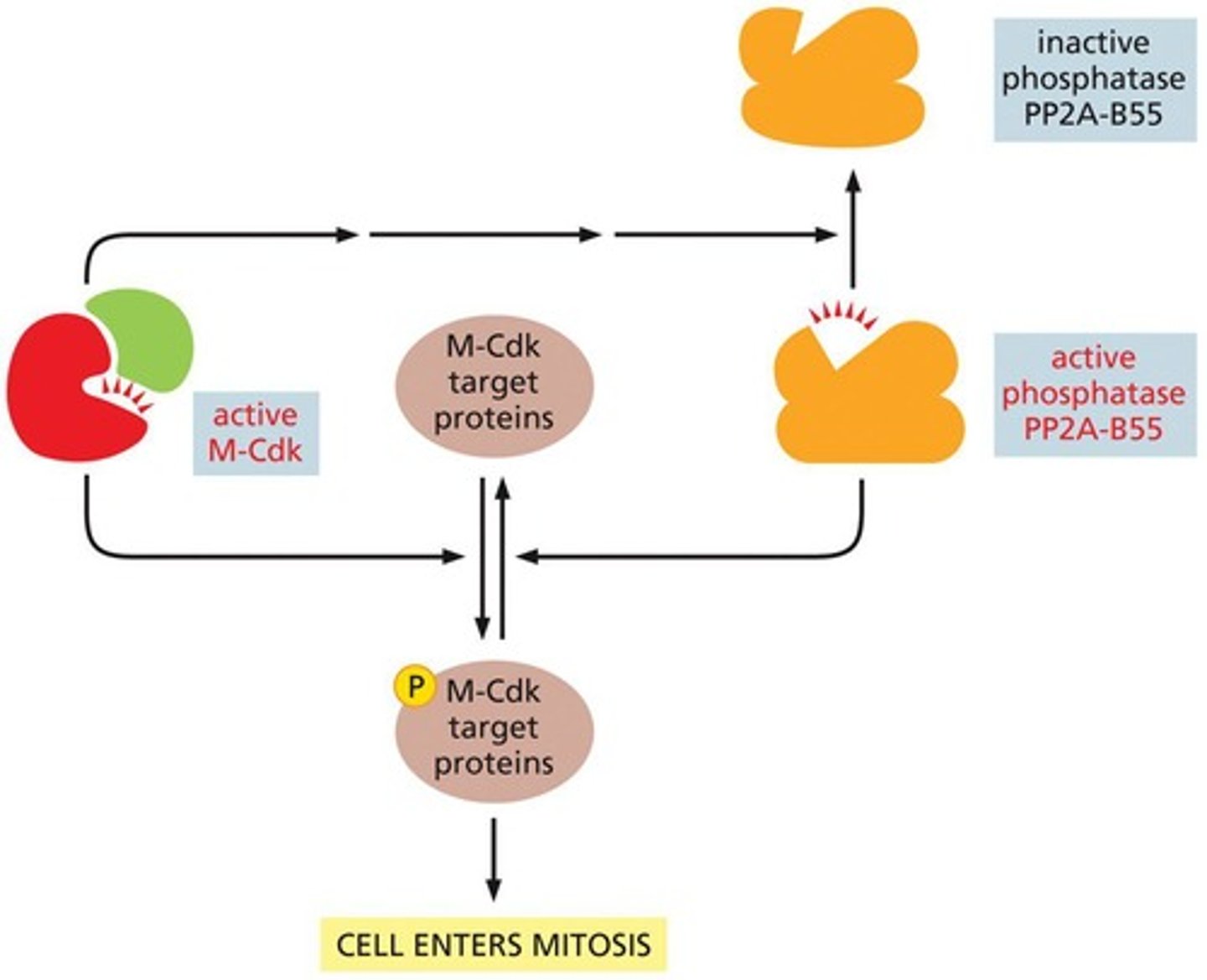
How is M-Cdk activity regulated?
M-Cdk is regulated by phosphorylation; it is inhibited by Wee1 kinase and activated by CAK, with the inhibitory phosphate removed by Cdc25.
What is the purpose of cell cycle checkpoints?
Checkpoints halt the cell cycle if problems are detected, ensuring proper sequence and conditions for cell division.
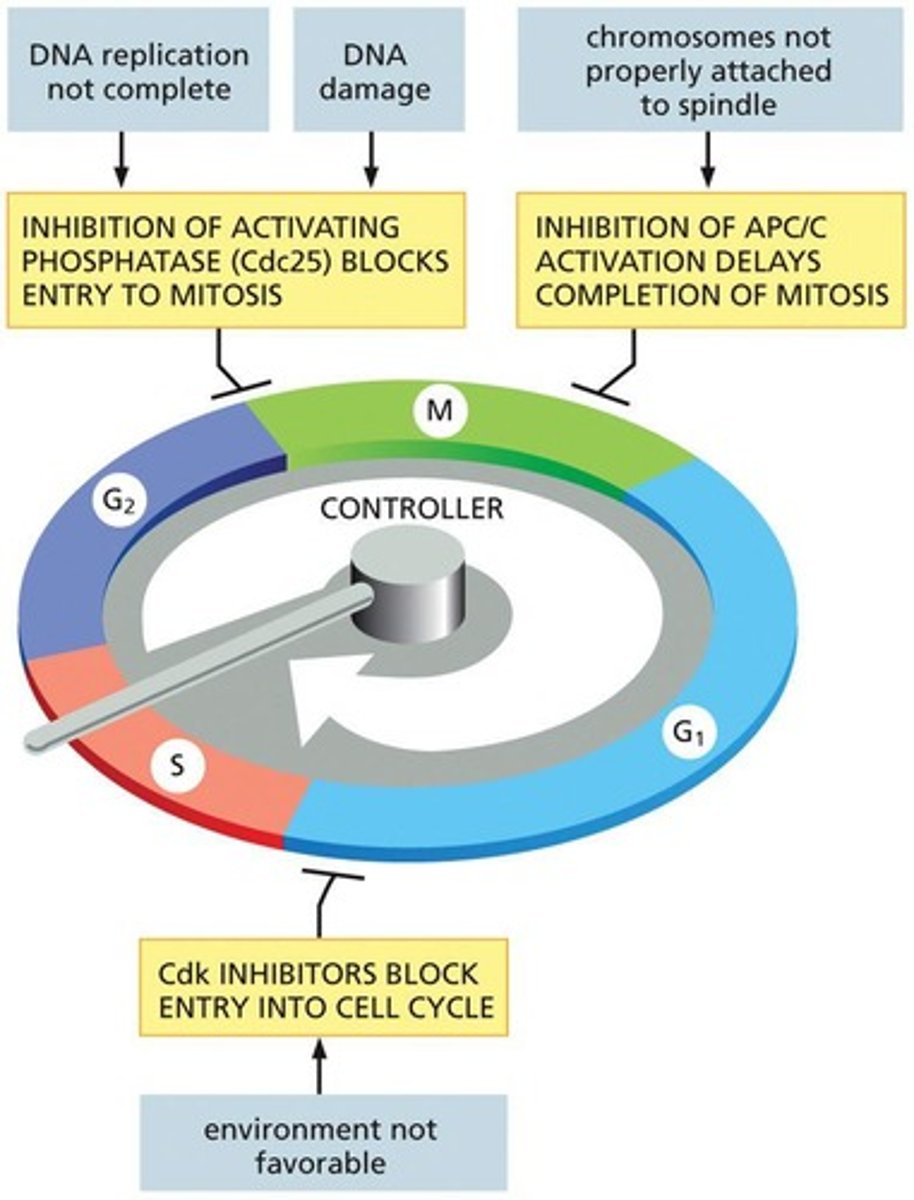
What happens at the G1 checkpoint?
The cell integrates multiple signals to determine its next activity, including activation of G1 and G1/S Cdks.
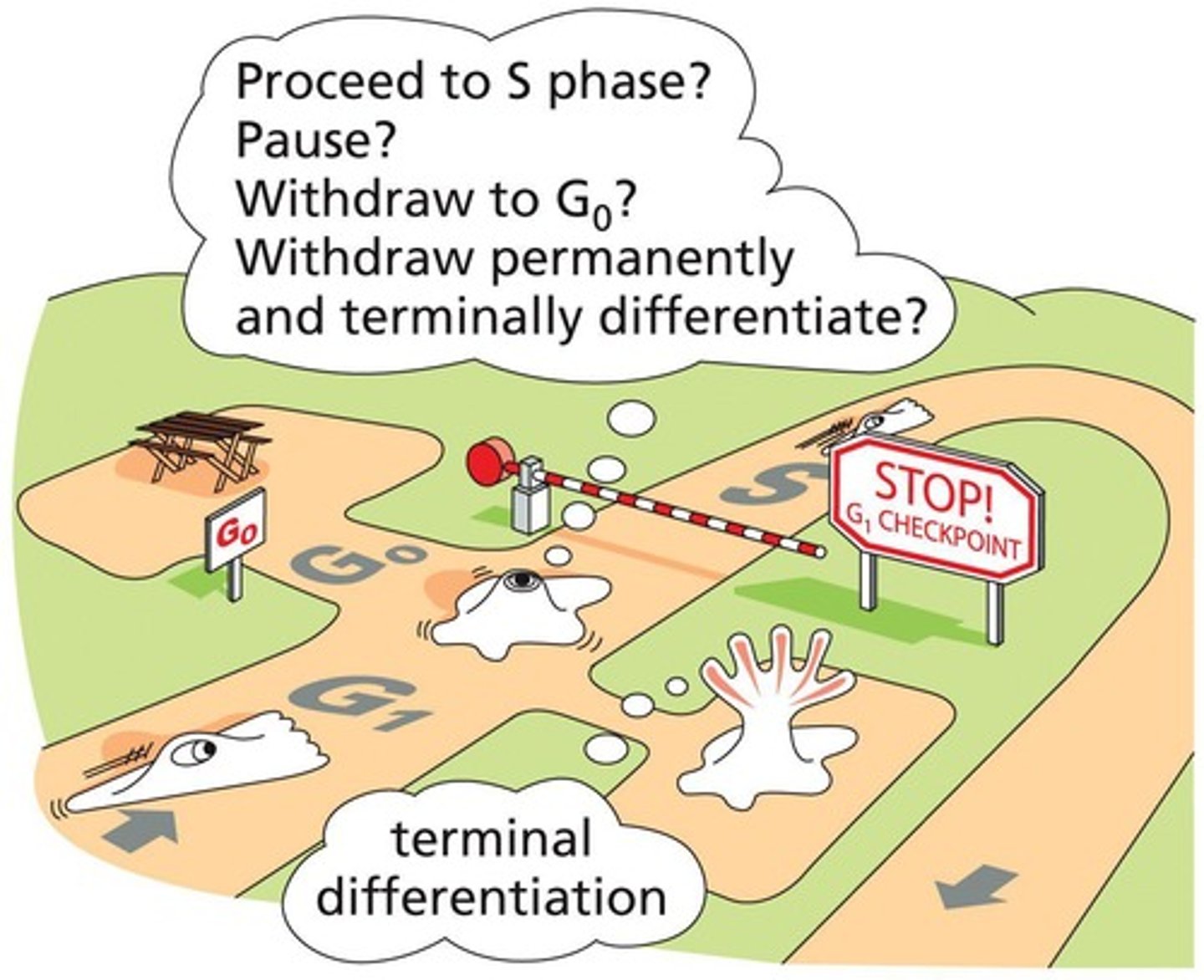
What is the role of p53 in the cell cycle?
p53 triggers the production of p21, a cyclin-dependent kinase inhibitor (CKI) that inhibits Cdks, and can induce apoptosis if active long enough.
What is apoptosis?
Apoptosis is programmed cell death, part of normal development, and can be induced by infection, DNA damage, or lack of signaling.
How does apoptosis differ from necrosis?
Apoptosis is an energy-dependent process involving cell fragmentation and phagocytosis, while necrosis results from acute injury and causes inflammation.
What are caspases?
Caspases are cysteine-aspartic acid proteases that execute apoptosis by cleaving target proteins.
What is the role of Bcl-2 in apoptosis?
Bcl-2 is an antiapoptotic protein that inhibits apoptosis and promotes tumor formation by preventing cell death.
What triggers the activation of the apoptosome?
Cytochrome C release from the mitochondria triggers the activation of the apoptosome.
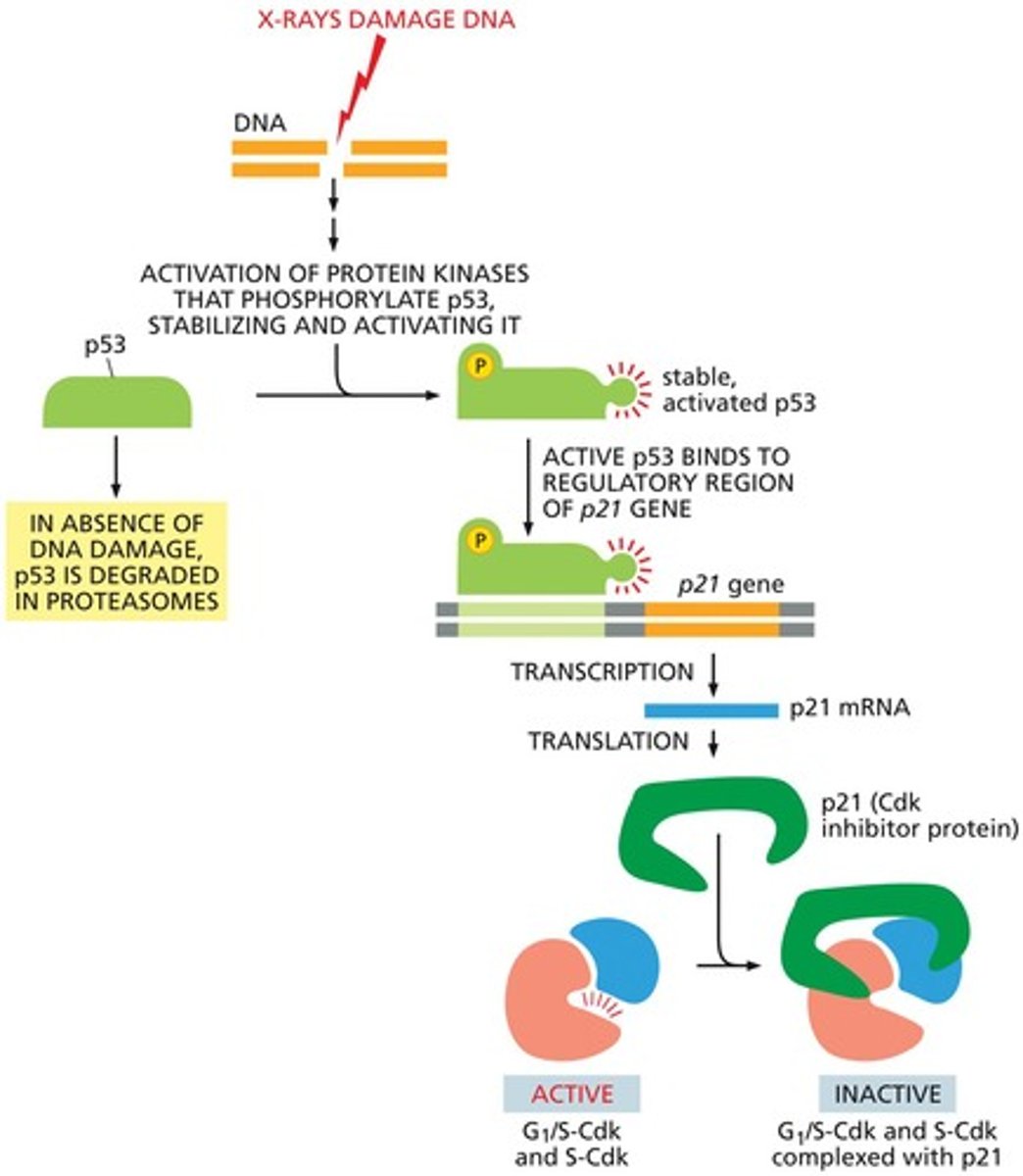
What is the function of the anaphase promoting complex (APC)?
APC ubiquitinylates proteins, leading to the degradation of Securin and M cyclin, which regulates the progression of mitosis.
What is the significance of myostatin?
Myostatin signals to prevent muscle cell growth; mutations can lead to uncontrolled muscle growth.
What proteins regulate the timing and sequence of cell cycle phases?
Cyclins and cyclin-dependent kinases (Cdks) regulate the timing and sequence of cell cycle phases.
What target proteins are regulated by S-Cdk?
S-Cdk regulates proteins involved in DNA replication, including Cdc6, ORC, and helicases.
What happens to cyclins at the end of M-phase?
Cyclins are selectively degraded, which inactivates the cyclin/Cdk complexes.
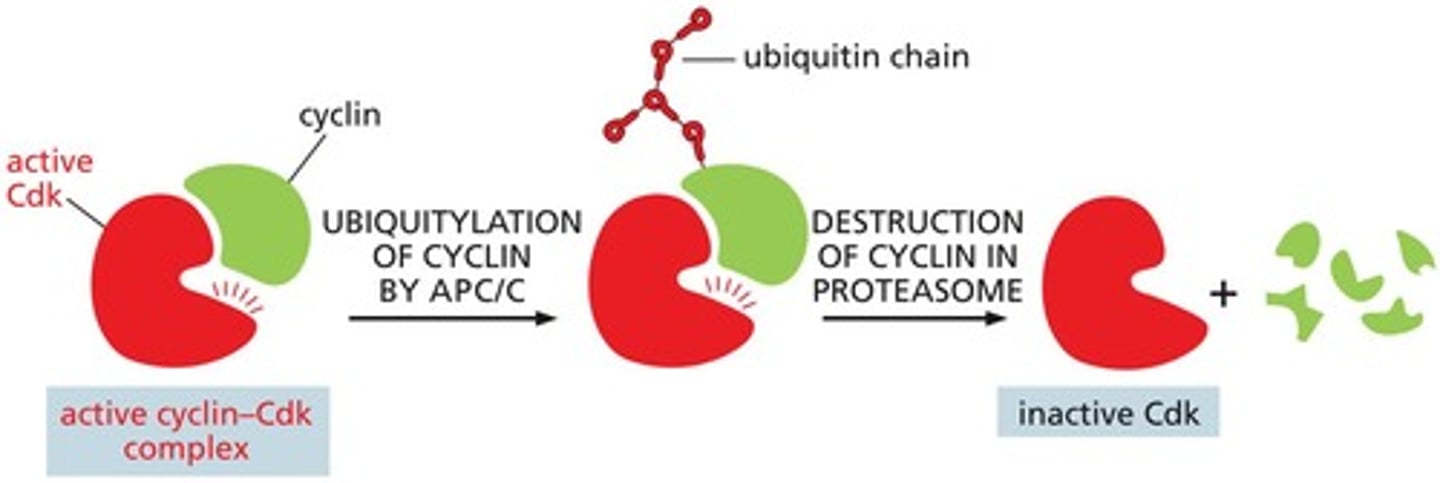
What is the role of the p27 protein in the cell cycle?
p27 regulates G1 cyclin and prevents progression into S phase.
What is the outcome of DNA damage during the cell cycle?
DNA damage triggers a signaling pathway that halts the cell cycle to allow for repair or induce apoptosis.
How does the cell ensure it is ready to proceed through the cell cycle?
The cell checks conditions at checkpoints and integrates signals before progressing to the next phase.
What is the role of transcription factors (TFs) in the G1 phase?
TFs activate genes necessary for entrance into S-phase after the deactivation of Retinoblastoma (Rb) protein.
What is the function of the proapoptotic DNase during apoptosis?
It digests chromosomal DNA, leading to chromatin fragmentation.
What is the role of the initiator and effector caspases in apoptosis?
Initiator caspases activate effector caspases, which amplify the apoptotic signal and carry out proteolytic functions.