Bio 205 exam 1 csulb
1/91
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
92 Terms
What is science?
Knowledge or a system of knowledge covering general truths or the operation of general laws especially as obtained and tested through scientific method
Scientific Method Steps
See a problem ● Make a hypothesis ● Design an experiment / Scientific method: ● Test!!! ○ Again and again and again ● Math :( ● Share results with others ○ Peer review
Laws
describes a natural occurrence without attempting to explain WHY
frequently expressed as simple mathematical
equations
Scientific Theory
explains an occurrence, must be well supported by scientific community
theory=fact
● Must be testable
○ consistent results
○ retesting by other scientists
Theory = fact
Hypothesis
a proposed explanation; tries to solve a problem
● More than an educated guess, idea, or concept
● Must be testable
● You can NEVER prove your hypothesis!!!
● BUT you can FAIL to REJECT it as incorrect
Null Hypothesis
the converse of the expected results. Usually we say there will be "no trend" or any trend we do observe is due to chance.
Alternative/Operational Hypothesis
a falsifiable statement of the predicted results
Scientific Experiment
an orderly procedure carried out with the goal of verifying, refuting, or establishing the validity of a hypothesis
● Designed to be repeatable
● Designed with controls/variables
Variables
characteristic that is being measured(changes)
Controls
static characteristic (remains unchanged)
Properties of Life (1) Order
must be made up of cells & must conform to life's hierarchy of organization

Properties of Life (2) Reproduction
must able to pass genetic information on its own (reproduce)
make babies
Properties of Life (3) Growth & Development
grown in size or numbers
life cycle
Properties of Life (4) Energy Processing
must acquire chemical energy (EAT)
Properties of Life (5) Regulation
must maintain internal environment ● homeostasis
Properties of Life (6) Response to Environment
must respond to external stimuli ● moves if you poke it
Properties of Life (7) Evolutionary Adaptation
must be able to adapt to their environment ● evolvability
Covalent Bond
when atoms share electrons
Ionic Bond
when atoms take/give electrons
Hydrogen Bonds
a weak bond(ish) between polar (+/- charged) molecules
Solvent
the dissolving agent that breaks apart stuff
Solution
a liquid consisting of two or more substances mixed uniformly
Hydrophobic
"water fearing" ● non water soluble
Hydrophilic
"water loving" ● water soluble
Acid
donates hydrogen ions (H+) within a solution typically sour
Base
accepts H+ within a solution (OH-) typically slippery to the touch, tastes bitter
Macromolecules
extra large organic molecules that make up all living things
Organic Compound
carbon based molecules
Dehydration Synthesis
a reaction that removes a molecule of water as it bonds 2 other molecules together
Hydrolysis
a reaction that breaks a chemical bond by adding a water molecule
Polymers
large molecules consisting of many identical/similar building blocks
tissues and cells
Monomers
building blocks of polymers
Carbohydrates
macromolecules that contain C x (H2O)x
Glucose
a monosaccharide
main product of photosynthesis
bodys preffered fuel source
C 6 H 12 O 6
Lipid
macromolecule which does not mix with water ● Important in long-term energy storage ● 2x as much energy as carbs!
Unsaturated Fatty Acid
fatty acid that contains 1+ double bonds ● Fewer than expected H+ ● Unsaturated with H+
liquid at room temp
Saturated Fatty Acid
fatty acid that has no double bonds ● As many H as expected ● That is saturated with H
solid t room temp
Trans Fats
a form of fat that probably is killing us slowly, but deliciously :(
Phospholipids
2 fatty acids +POLAR phosphorous head ● Important part of cell walls!!!
Steroids
formed by four fused rings of carbon ● frequently used as hormones
Amino Acid
Monos that make up proteins
only 20 different amino acids
Polypeptide
a chain of amino acids
Protein
a polymer made up of amino acids
Primary Structure
the amino acids in the specific sequence in which they occur
Secondary Structure
the coiling or folding of the primary structure
Tertiary Structure
the overall 3D shape of the protein
Quaternary Structure
multiple 3rd structured proteins coiled together in a multi subunit complex
Enzyme
highly specific chemical catalysts, Increases rate of reaction without being consumed by the reaction
Prions!!!
infectious proteins!!! A misfolded protein that causes other proteins to also spontaneous misfold. Caused by eating BRAINS!!
Denaturation
when a protein loses its shape, and thus its function
● Usually permanent
● Typically caused by temp, pH, inorganic salts, etc.
Cell Theory
properties of cells ● a scientific theory: 1) Smallest functional unit upon which life is based 2) All living things are made up of cells 3) All cells come from other cells, no spontaneous generation
Eukaryotic
"true cell" (humans, fish, plants, etc.)
prokaryotic cell
a type of cell that does not have a true nucleus or membrane-bound organelles.
Organelles
membrane bound "little organs" highly specific chemical catalysts
● Increases rate of reaction without being consumed
by the reaction
Cellular metabolism
chemical activities of the cell
● What the organelles are doing
Fluid Mosaic Model
the idea that the plasma membrane is a super complex and awesome thing!!!
Diffusion
the tendency of particles to move from high to low concentrations until an equilibrium is achieved
Concentration Gradient
gradual change in the [solutes] in a solution
Passive Transport
when molecules diffuse across cell membranes
● No work = Passive
● Typically small, nonpolar
& essential stuff
Facilitated Diffusion
a type of PT ● Requires help from a transport protein ○ Typically larger, polar & essential stuff
Osmosis
diffusion of water across a membrane
Osmoregulation
the control of water balance
Tonicity
the ability of a surrounding solution to cause a cell to gain/lose water
Hypotonic
having fewer solutes
Isotonic
having the same amount of solutes
Hypertonic
having more solutes
Active Transport
when a cell must expend energy to move a solute AGAINST its gradient
● Use ATP as fuel
Exocytosis
the process cells use to EXPORT large molecules
(proteins, poly saccs, etc.)
Endocytosis
the process cells use to IMPORT large molecules
(proteins, poly
saccs, etc.)
Cellular Respiration
a set of metabolic reactions which occur in cells
Breaks down organic molecules to produce ATP
(and waste products)
+ waste
ATP
Adenosine Triphosphate!!!
Cell Division
cellular reproduction
4 Reasons Cell Division:
1. Repro of single-celled organisms 2. Multicell organisms grow 3. Repair/replacement of cells 4. Sperm/egg production
Sexual Reproduction
the creation of genetically SIMILAR offspring (think siblings)
Chromatin
DNA + proteins
Prophase
1st part of mitosis, Chromos become visible (with micro)
Metaphase
2nd part of mitosis, Chromos line up on metaphase plate
Anaphase
3rd part of mitosis, Chromos pulled towards poles via centrosome
Telophase
4th part of mitosis
cell elongates
reverse of prophase
Cytokinesis
part of the M
phase
● After mitosis
● Cytoplasm of a cell
divides
Cleavage Furrow
a shallow indentation
in the cell's surfaceorchestrated by cytoskeleton
Cancer is a broad group of diseases
unregulated cell growth
● Escapes checkpoints
● Divides rapidly
● NOT density dependent
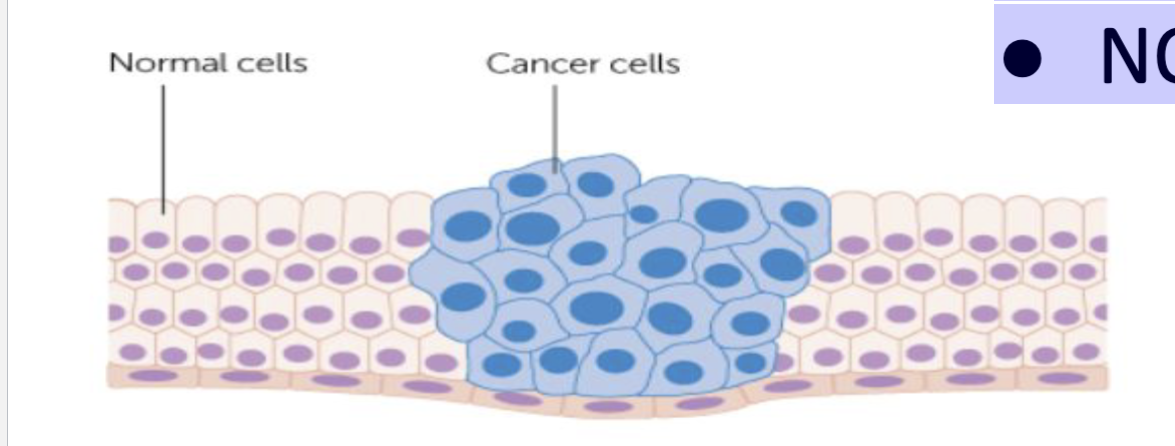
Tumor
is an abnormally growing mass of body cells
Benign Tumors
— remain at the original site
Malignant Tumors
spread to other locations
● “has cancer”
Metastasis
the spread of cancers to other sites
Cancer Staging
— describes the severity of an
individual's cancer
● Universal language
● Stages 0-IV, specific like BC SI or LCS IV
○ some cancers don’t stage
Cancer :(
Breast cancer stage one
Lung cancer stage four
Stage 0
abnormal cells, “precancerous”
Stage I
cancer cells are in one specific part of
the body
● Surgically removed if small enough
Stage 2
cancer advances in that one specific
part of the body
● “Early”
● Can be treated by chemo, radiation, or
surgery
Stage 3
cancer continues to advance in that one
specific part of the body
● Ex: entire left lung or entire right breast
● “Late”
● Can be treated by chemo, radiation, or
surgery
Stage 4
cancer has spread to multiple organs
throughout the body
● Can be treated by chemo, radiation, or
surgery