QCE Chem Flashcards + Questions 2026 syllabus
1/54
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced | Call with Kai |
|---|
No analytics yet
Send a link to your students to track their progress
55 Terms
Linear shape
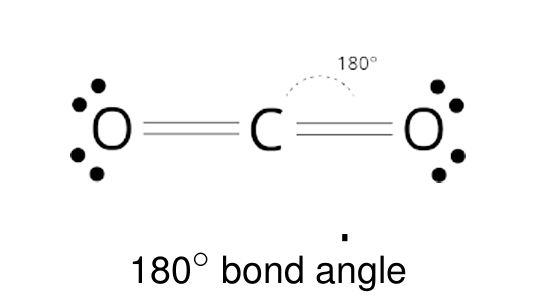
Bent shape
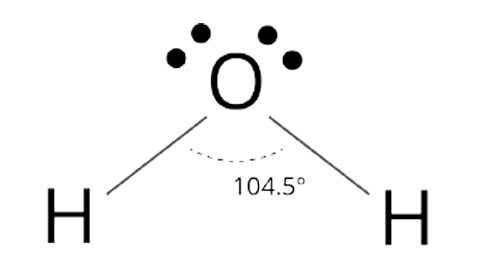
104 degree bond angle
Trigonal planar shape
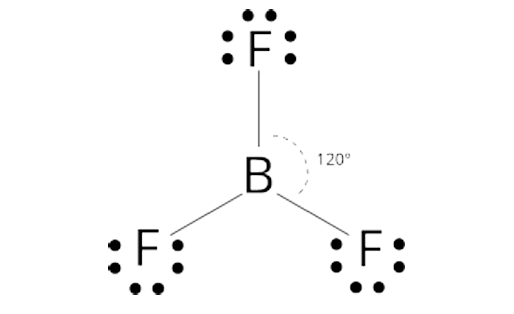
120 degree bond angle
Tetrahedral shape
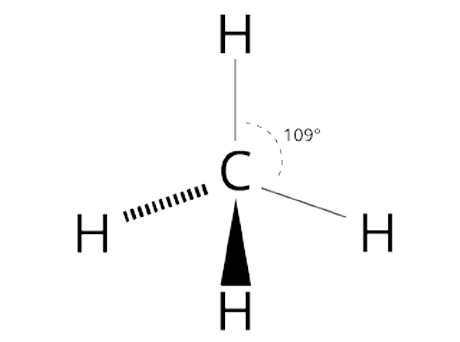
109 degree bond angle
Trigonal pyramidal shape
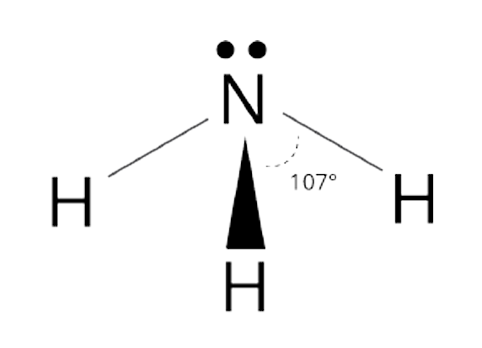
107 degree bond angle
Emission spectrum
Show white lines for emitted light
Absorption spectrum
Rainbow of absorbed light
Electronegativity difference of polar bonds
0.5-1.7 electronegativity difference
Electronegativity difference of non-polar bonds
<0.5 electronegativity difference
2 outer atoms, 1 inner atom
Linear
3 outer atoms, 1 inner atom
Trigonal Planar
4 outer atoms, 1 inner atom
Tetrahedral
3 outer atoms, 1 inner atom, 1 lone pair
Trigonal Pyramidal
2 outer atoms, 1 inner atom with lone pair
Bent
Metals which replace hydrogen in acid and water
Magnesium to potassium
Metals which replace hydrogen in acid only
Lead to aluminium
Metals which don’t replace hydrogen
Platinum to antimony
What is the oxidation number of hydrogen in metal hydrides?
-1
In compounds with nonmetals, what is the oxidation number of hydrogen?
+1
How to balance half-equations
Write the skeleton redox half equations
Balance all elements but oxygen and hydrogen
Balance oxygen with H2O, then balance hydrogen with H+
Balance charges with electrons
Multiply each half-equation by a number for an equal amount of electrons
Parts of a galvanic cell
Anode, cathode, electrolyte, external circuit, salt bridge
Electron flow in galvanic cell
Negative anode to positive cathode
Purpose of salt bridge in galvanic cells
Prevents buildup of charges, keeping the electrodes balanced
Parts of an electrolytic cell
Negative cathode, positive anode, porous barrier, electrolyte, voltage
Redox reaction
Transfer of electrons between chemical species
Low on SEP table
Strong oxidising agent, likely to reduce
High on SEP table
Strong reducing agent, likely to oxidise
Why electrode polarity changes in electrolytic cells
Reduction is always at the cathode
Reduction is electron gain, must be at the half-cell gaining electrons
Therefore the cathode always gains electrons
in galvanic cells, electrons spontaneously flow to positive electrode, so cathode is positive in galvanic cells
in electrolytic cells, electrons artificially flow to negative electrode, so cathode is negative in electrolytic cells
Alkanes
No functional group
Alkenes
Double carbon bond, no true functional group
Alkynes
Triple carbon bond, no true functional group
Alcohols
Hydroxyl OH
Aldehydes
Terminal carbonyl (double-bonded oxygen)
Ketones
Non-terminal carbonyl (double-bonded oxygen)
Carboxylic acids
terminal carboxyl group (carbonyl + hydroxyl)
-oic acid
Haloalkanes
Alkane with halogen in place of hydrogen
Rules of branched molecules
longest continuous chain is parent chain
Name: (position of branches)(name of branches)(parent chain)
order of carbons starts from the end the functional group is closest to. double/triple bonds are functional groups, branches are not
Nomenclature rule
hyphenate between letters and numbers, use comma between numbers
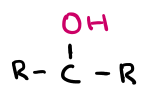
OH
hydroxyl
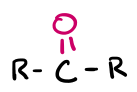
Double-bonded O
carbonyl
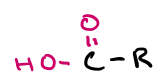
carboxyl group
Ester
Ester functional group (double-bonded O, O in middle)
Product of alcohol and carboxylic acid
Alcohol-yl acid-ate
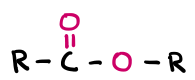
Ester
Amines
Amino functional group (NH2)

Amino group
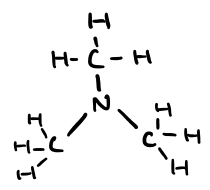
Name this molecule
N,N-dimethylmethanamine (amine)
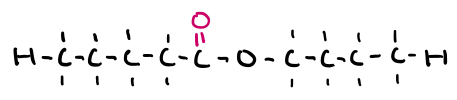
Name this molecule
butyl pentanoate (ester)
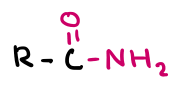
Amide group
Amine
Amide functional group (carbonyl + amino)
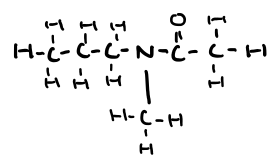
Name this molecule
N-methyl-N-propylethanamide
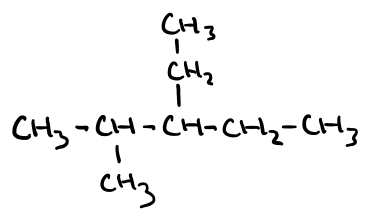
Name this molecule
3-ethyl-2-methylpentane
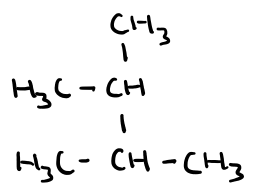
Name this molecule
2,3-dimethylbutane
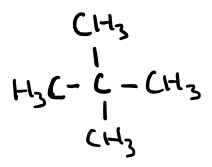
Name this molecule
2,2-dimethylpropane
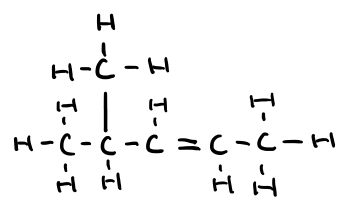
Name this molecule
4-methylpent-2-ene
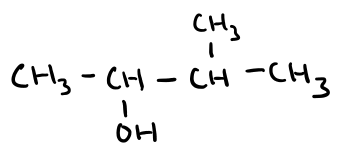
Name this molecule
3-methylbutan-2-ol