Transport in plants
1/26
There's no tags or description
Looks like no tags are added yet.
Name | Mastery | Learn | Test | Matching | Spaced |
|---|
No study sessions yet.
27 Terms
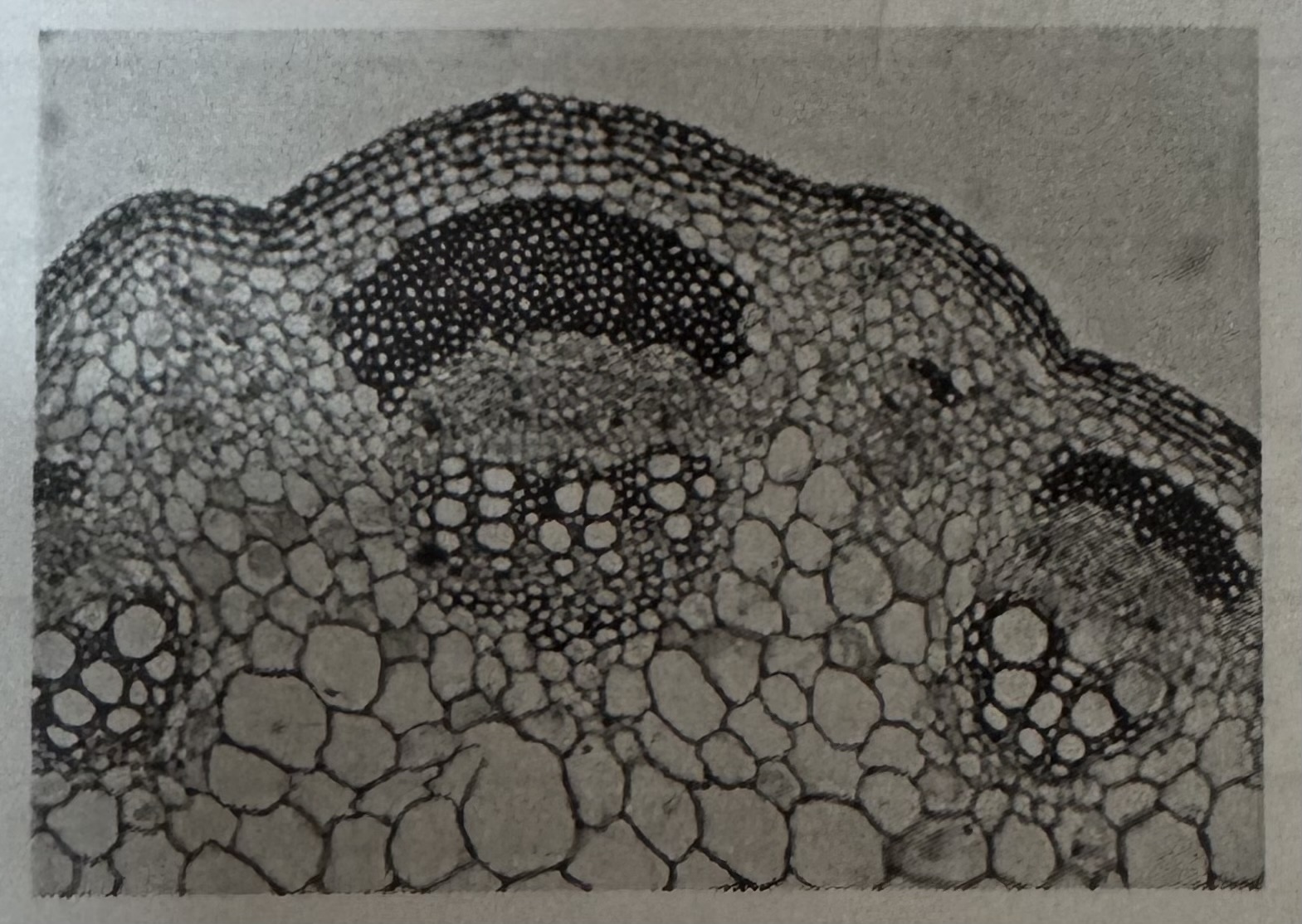
what types of microscope was the image take with ?
Light , 2-D coloured image , low resolution
what is the term that is used to describe xylem and phloem together ?
Vascular bundle
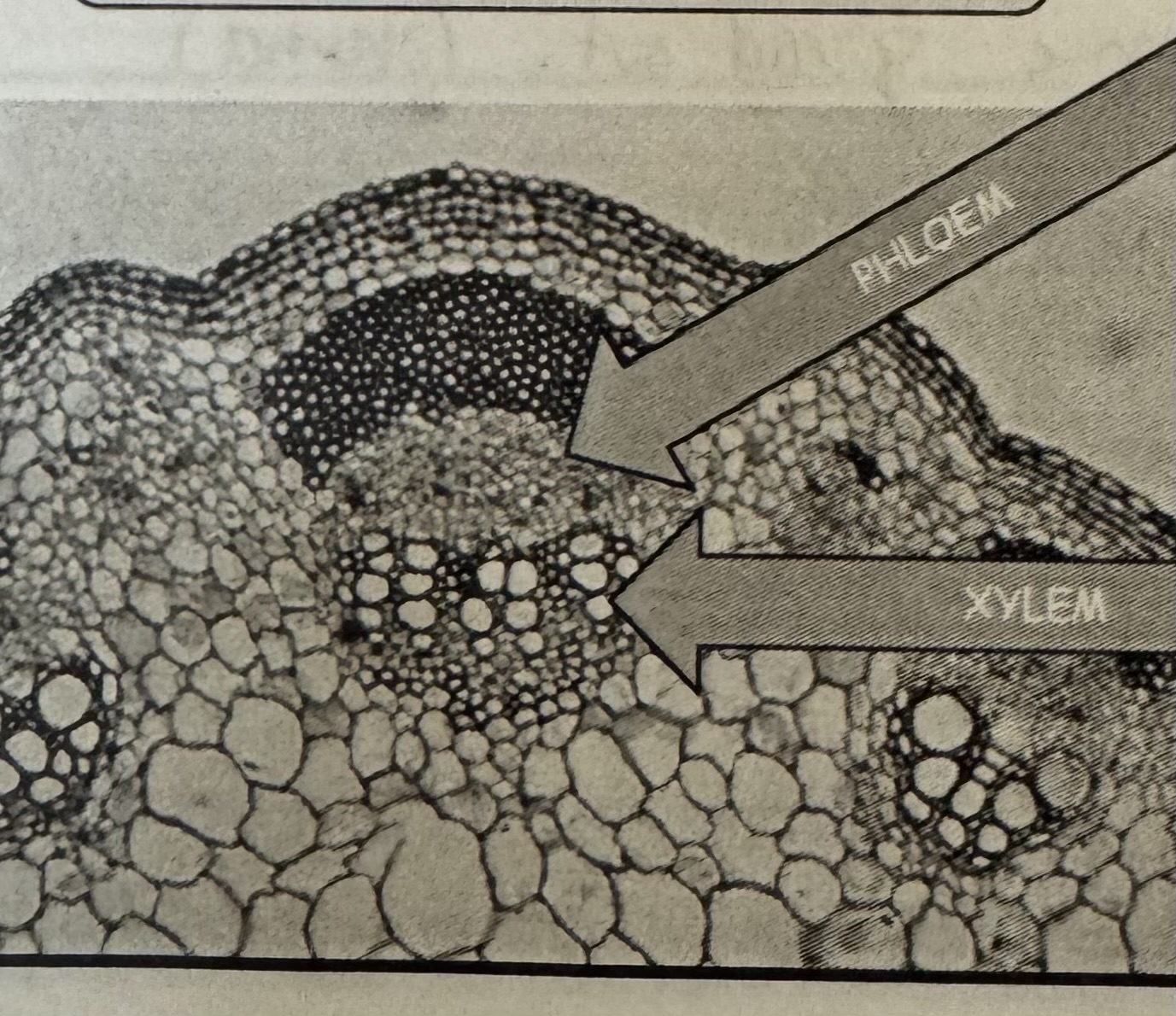
what are the functions of xylem ?
Xylem transports water up from the roots and mineral ions.
Its a dead tissue
what are the functions of phloem ?
Phloem transport sugars from leaves, and carry in both direction.
In chloroplast / leaf
what does xylem tissue look like under a microscopes ?
bigger circle then phloem
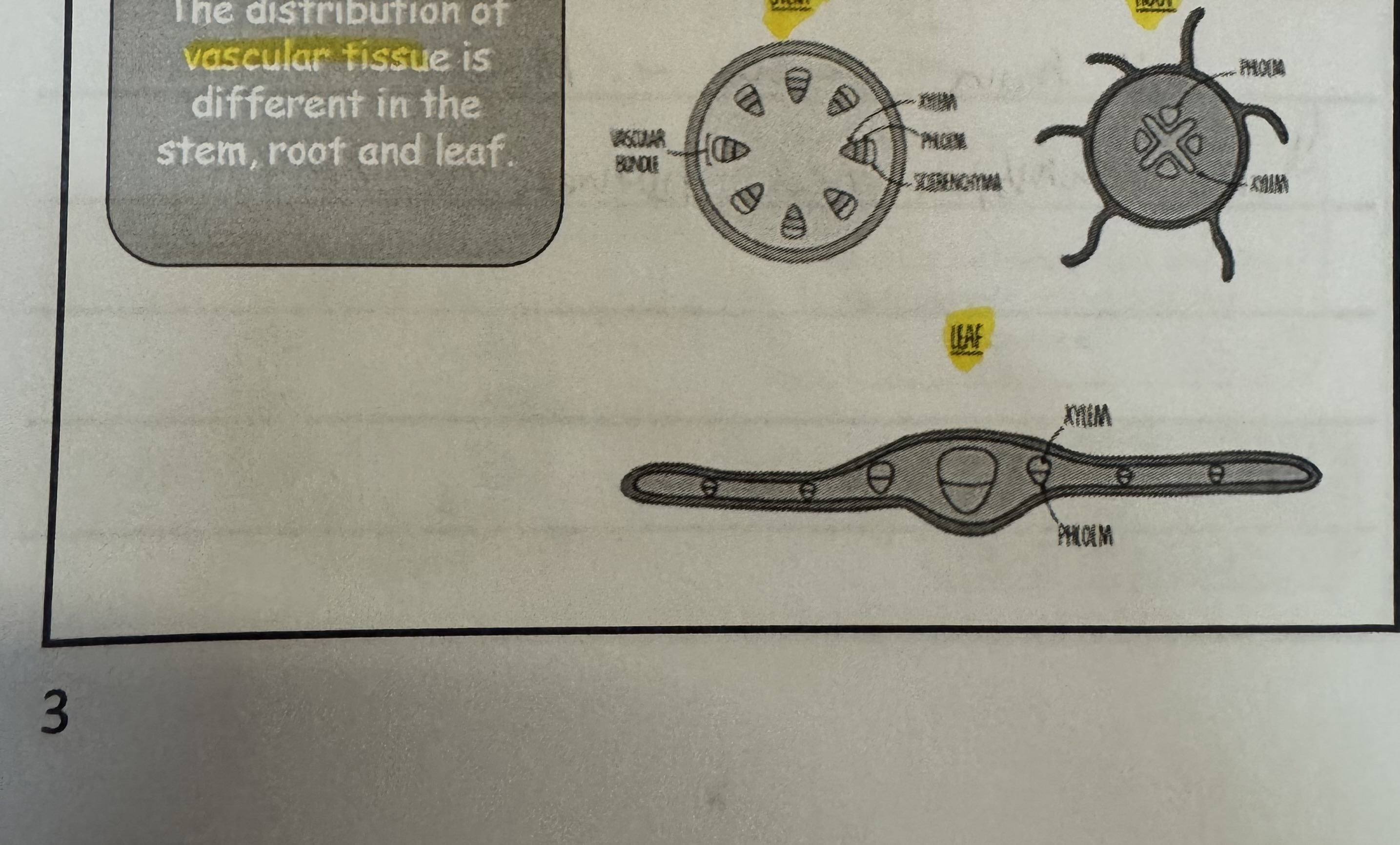
is there a different distribution of vascular tissue for roots, stem and leaf ?
yes
what does phloem tissue look like under a microscopes ?
smaller circle than xylem and compact
what is it called when a plants has 2 seeds leaves
Dicotyledonous plant
what does the vascular bundle look at in a dicot ?
The vascular bundle is circulated around the side of the stem.
In dicot, xylem and phloem found in vascular bundles, in a circular distribution in the stem.
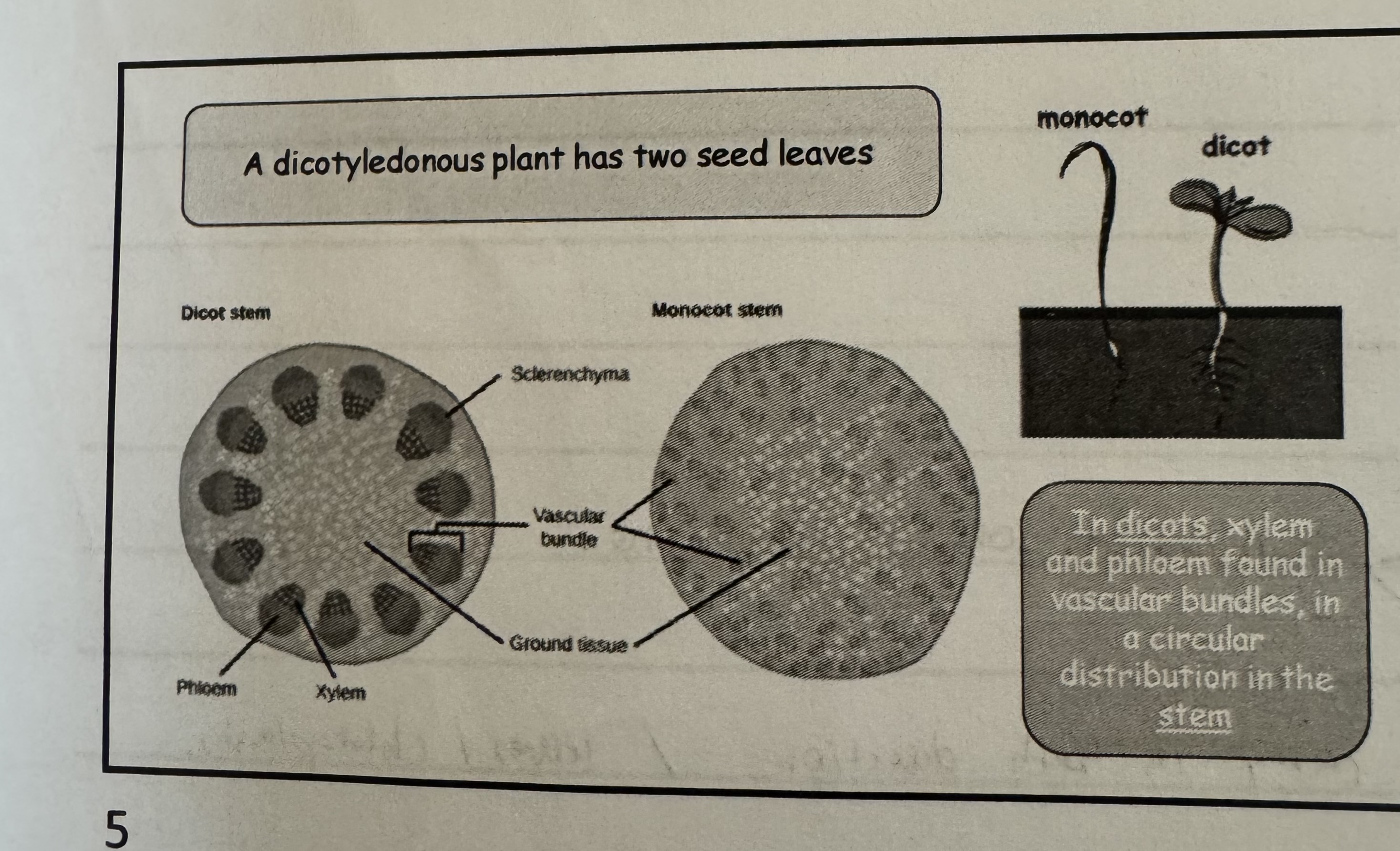
what is it called when a plants has 1 seed leaf ?
Monocot plant
what does the vascular bundle look at in a monocot plant ?
the vascular bundles are more spread in the stem
what is the tissue called in between the xylem and phloem ?
In between xylem and phloem is a layer of meristem cells called the “ cambium “
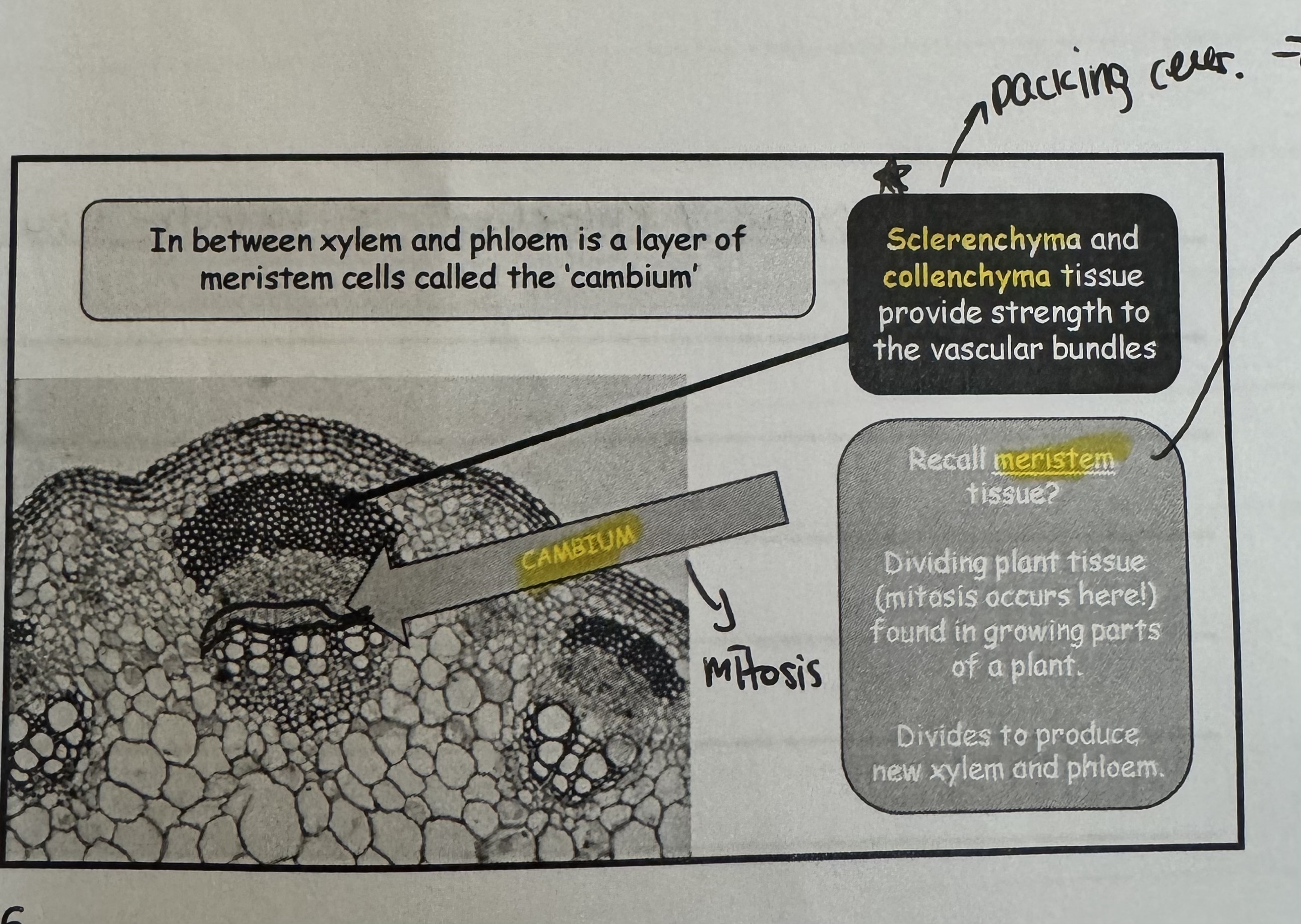
which reproduction is cambium cell under ?
Mitosis
what are the tissues called that provide strength for the vascular bundle ?
Sclerenchyma and Collenchyma tissues
what is the functions of Sclerenchyma and Collenchyma tissues
Provide strength for the vascular bundle.
Packing feels , to be able to let the stem stand.
what is meristem tissue ? Recall*
Dividing plant tissue ( mitosis occurs here ) found in growing parts of a plant
Divides to produce new xylem and phloem.
Can be differentiated to different cell ( stem ), that’s why the cambium / meristem tissue are in between the xylem and phloem.
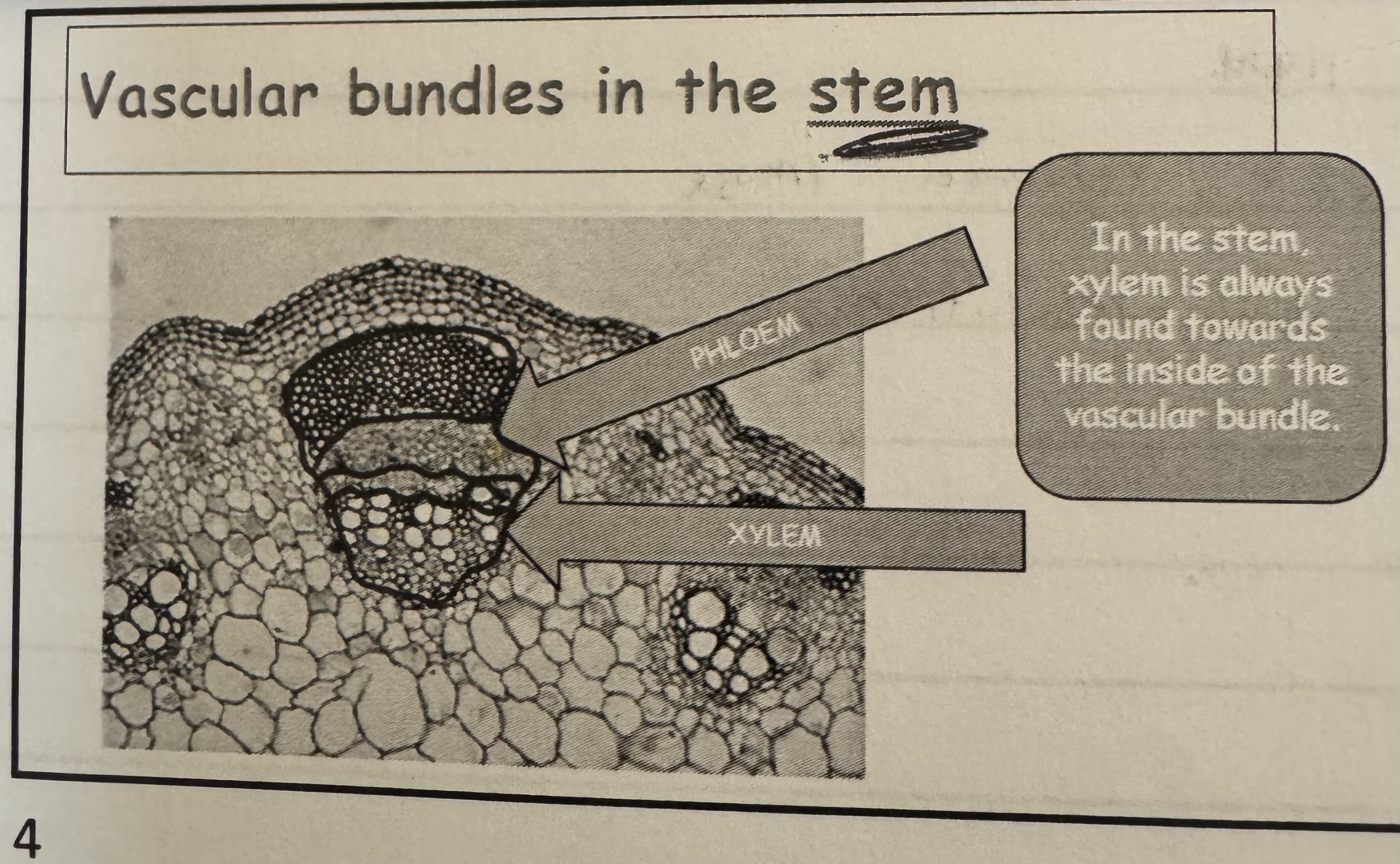
what does the vascular bundles in stem look like ?
In the stem. xylem is always found towards the inside of the vascular bundle.
Xylem are larger tube.
Phloem are smaller smaller tube and found on the outside of the vascular bundle.
what does the vascular bundles in root look like ?
Xylem is found in an X or star shape in the centre
Phloem is found between the arms of the xylem
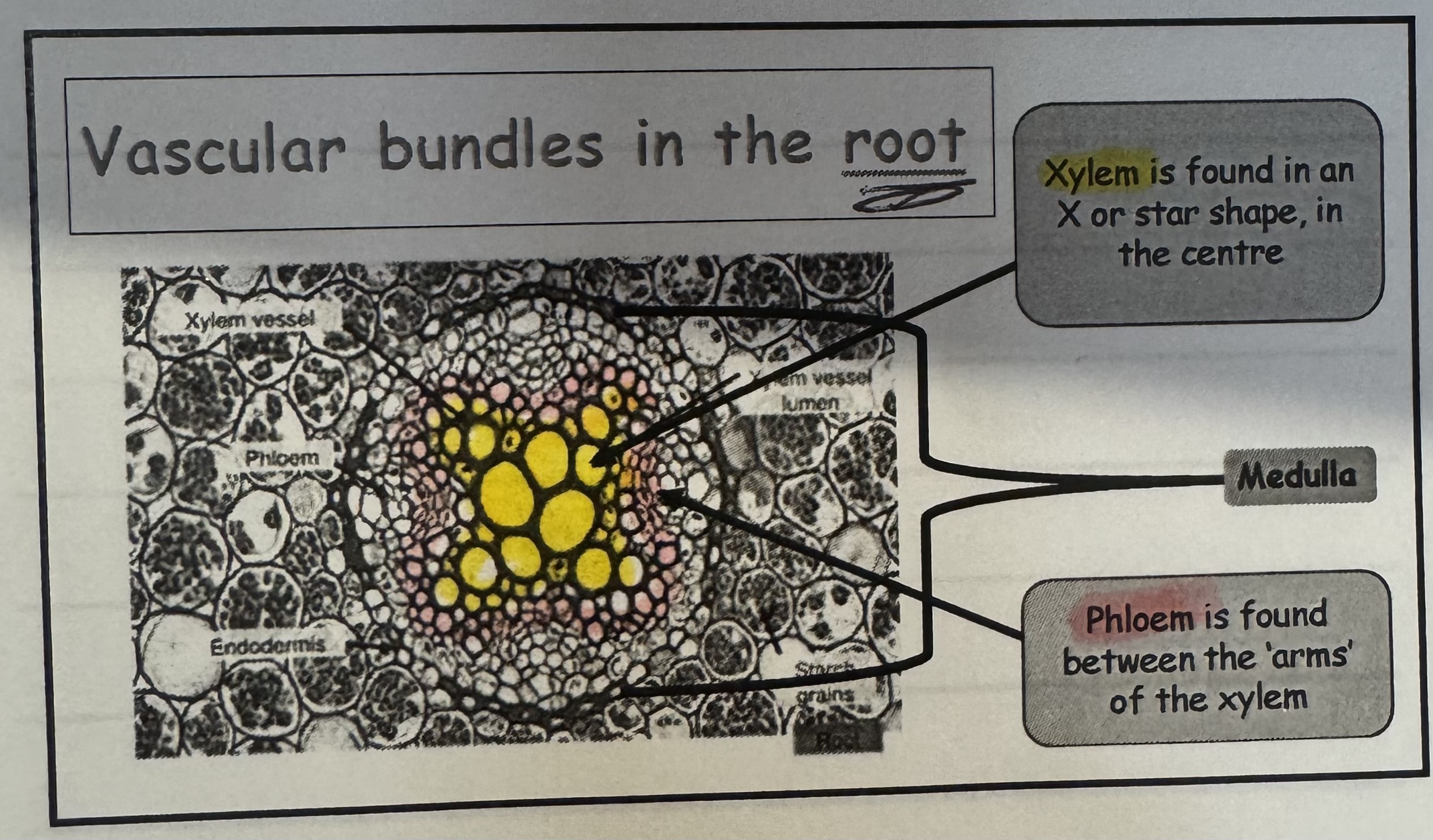
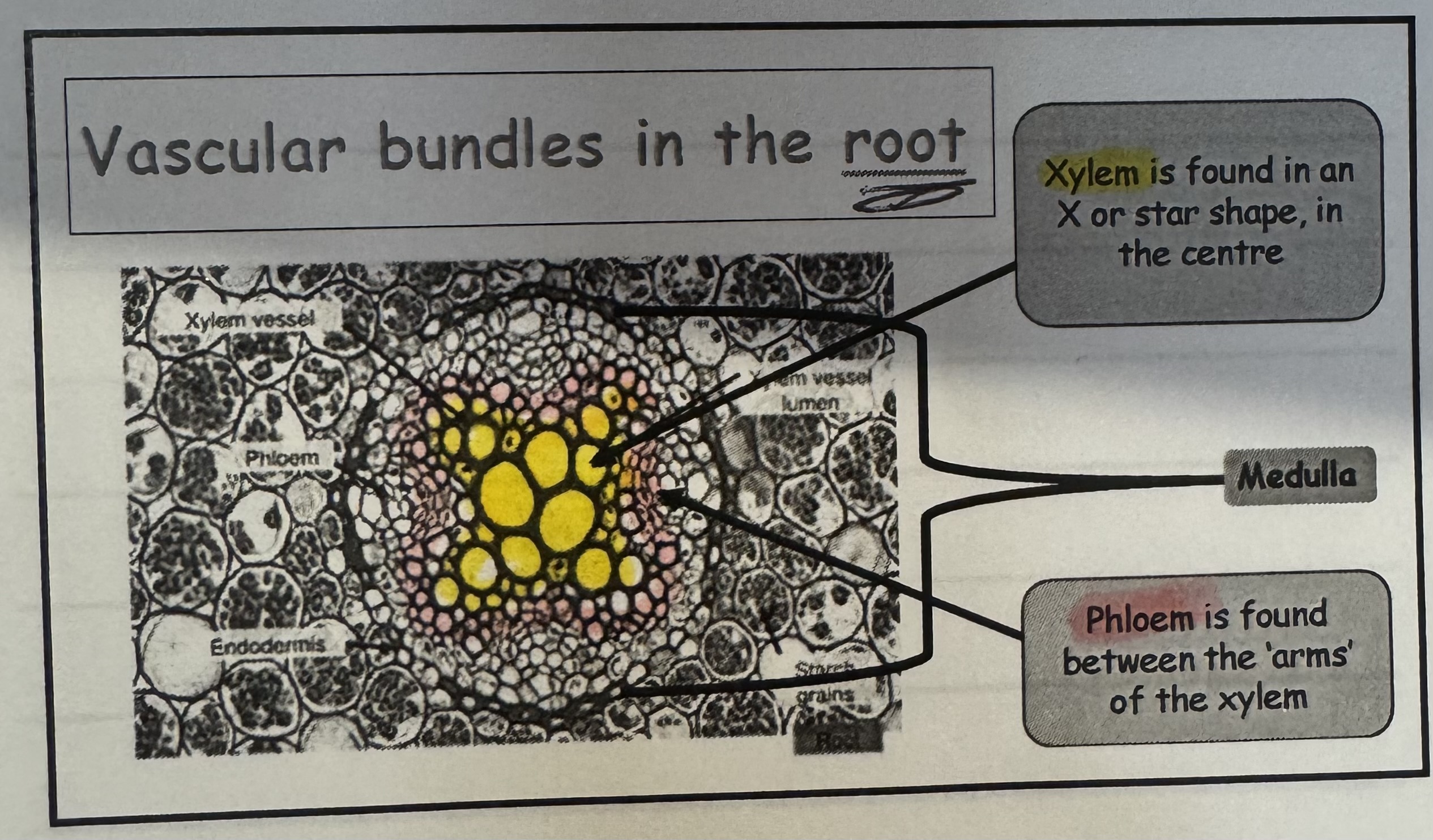
what is “ medulla ‘, where is it found ?
its found on the outside of the phloem tissue, in the middle section \.
Also found in liver, kidney, brain 🧠.
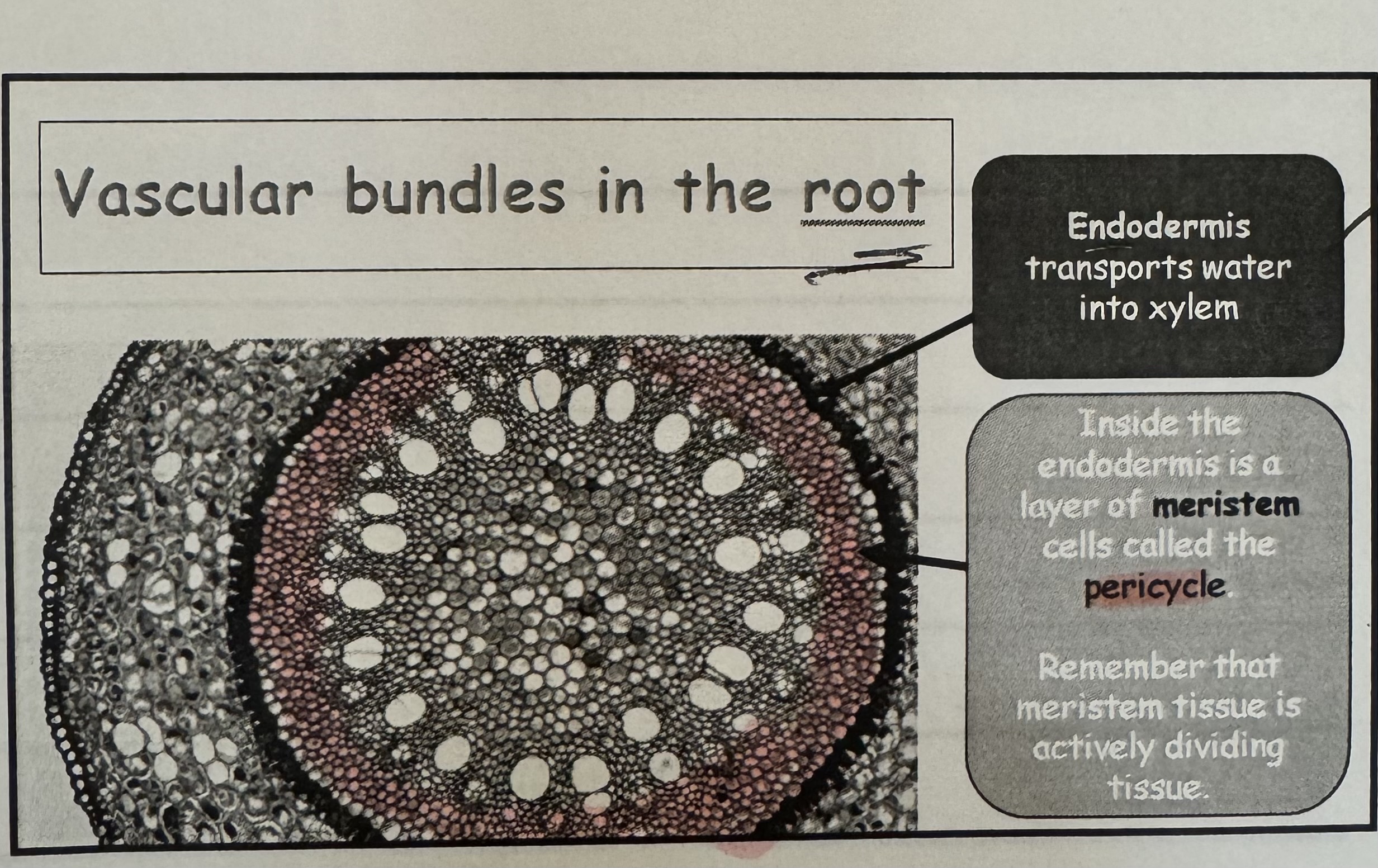
what is the functions of endodermis cell and where is it found ?
Endodermis transport water into xylem, it’s found in the inner layer.
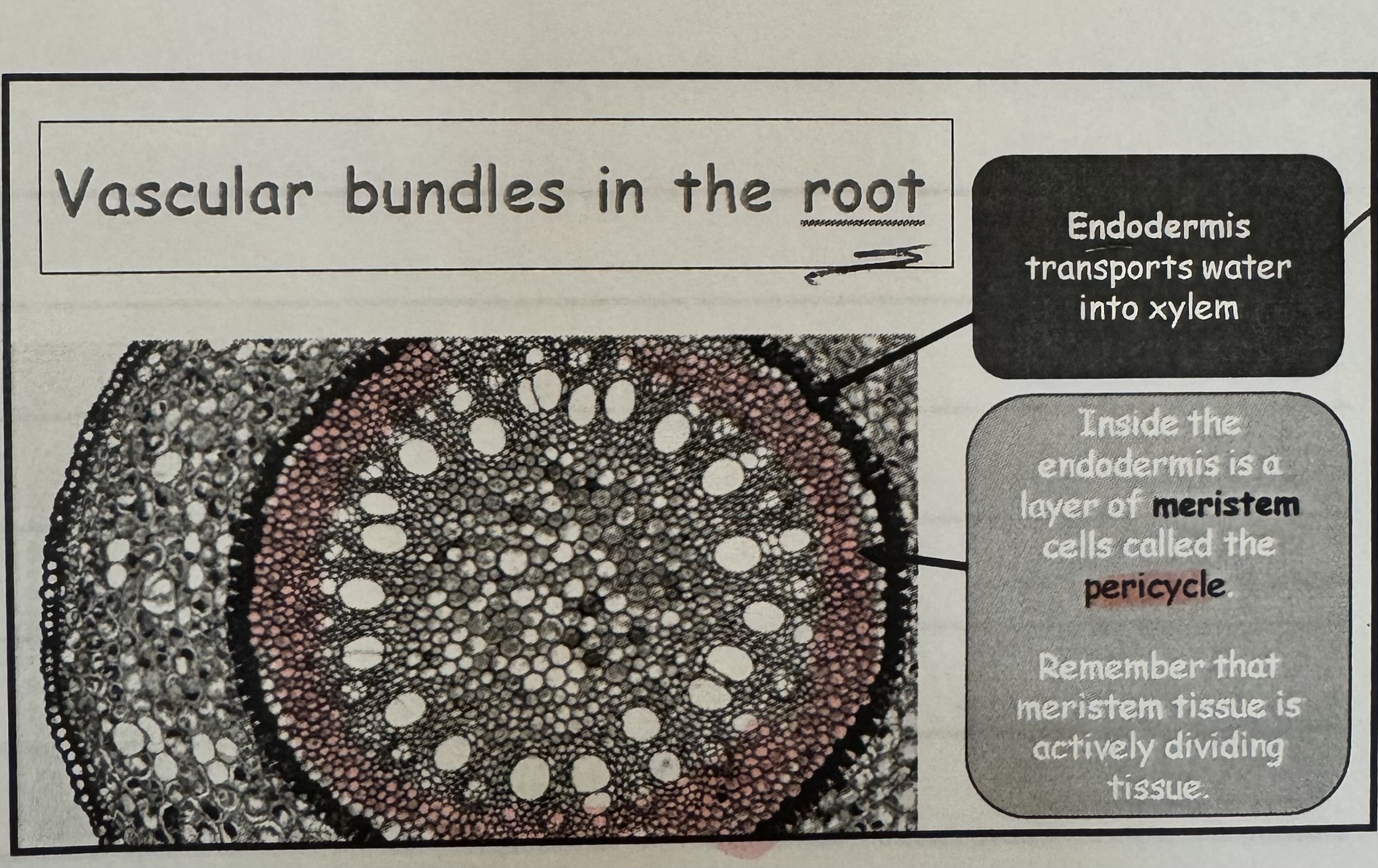
what is cell called that’s is found inside the endodermis ?
Meristem cell called ‘ pericycle “ -
meristem tissue is an actively dividing tissue
what cell is on outer layer of the root ?
The outer layer tissue is called the epidermis.
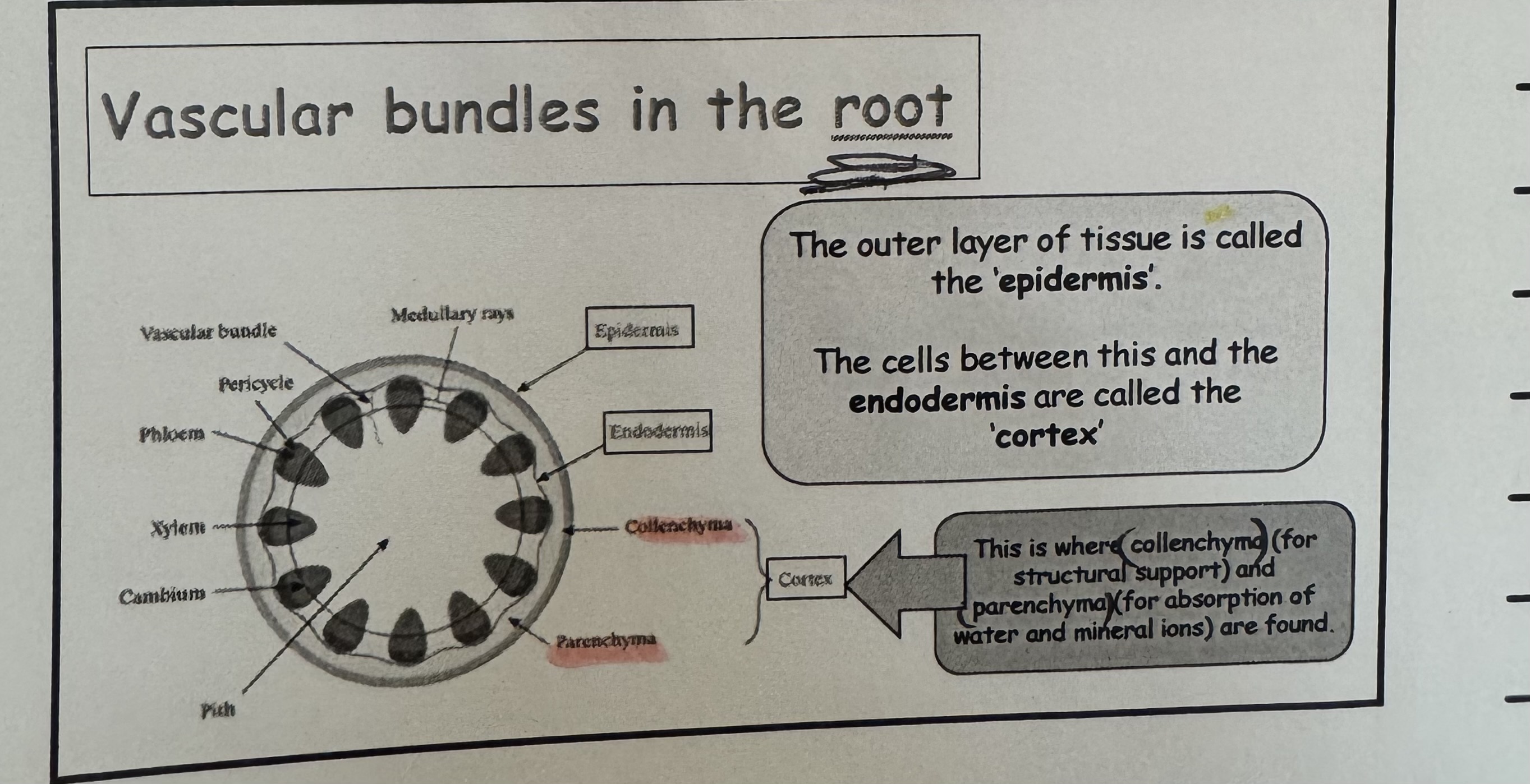
what is the cell called that is between the epidermis and the endodermis cell ?
It’s called the cortex. Its consist of xylem and phloem and endodermis
what are the two cell called that are in the cortex ?
Collenchyma and Parenchyma
what is the function of collenchyma cell ?
For structural support
what is the function of parenchyma cell ?
For absorption of water and mineral ions are found. Vackar
what does the vascular bundle in leaf look like under a microscope ?And where is it form ?
look at a U shape , its form in the midrib and veins of leaf.
